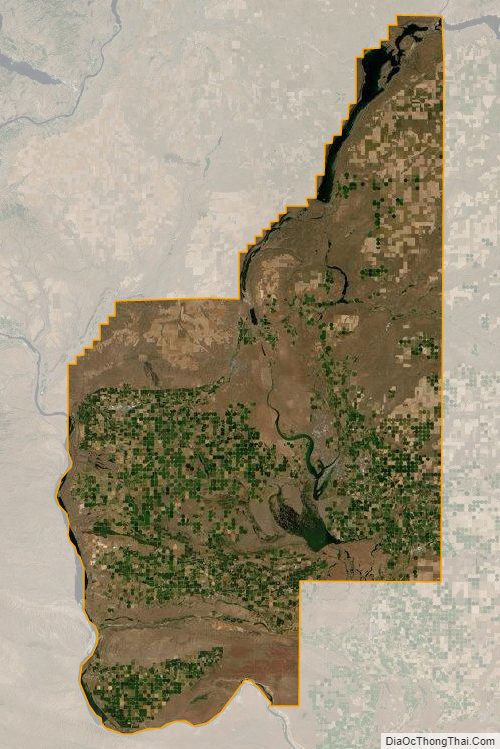
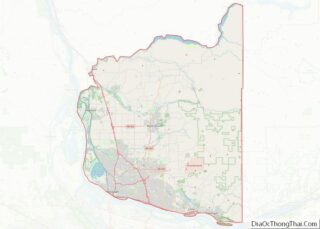
Grant County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 99,123. The county seat is Ephrata, and the largest city is Moses Lake. The county was formed out of Douglas County in February 1909 and is named for U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant.
Grant County comprises the Moses Lake, WA Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also part of the Moses Lake-Othello, WA Combined Statistical Area.
| Name: | Grant County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 53-025 |
| State: | Washington |
| Founded: | February 24, 1909 |
| Named for: | Ulysses S. Grant |
| Seat: | Ephrata |
| Largest city: | Moses Lake |
| Total Area: | 2,791 sq mi (7,230 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2,680 sq mi (6,900 km²) |
| Total Population: | 99,123 |
| Population Density: | 35/sq mi (14/km²) |
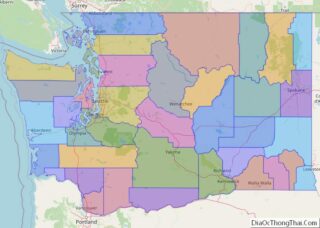
Grant County location map. Where is Grant County?
History
Native American cultures in the area included the Interior Salish, Wenatchi, and Okanagan. The first white settlers began to arrive in the mid-to-late-19th century, primarily with the goal of raising livestock. One government official described the area in 1879 as, “…a desolation where even the most hopeful can find nothing in its future prospects to cheer.”
When railroads arrived they also brought new settlers, and the economy began a shift from ranching to dryland farming. This transition required the people to have ready access to water, and irrigation became a necessity. The first large-scale irrigation attempts began in 1898, but it would be years before real success.
With the influx of dryland farming, the county soon boasted access to three major railway systems; the Great Northern Railway, Northern Pacific Railroad and the Chicago, Milwaukee & St. Paul Railroad. In addition, the Columbia River in this area was navigable. This allowed crops to be transported out of the area easily. Towns like Wilson Creek, Quincy and Ephrata began to thrive.
The Washington State Legislature officially created Grant County on February 24, 1909, naming it in the memory of Ulysses S. Grant, the 18th president of the United States, and a major contributor to the Union victory in the American Civil War. The county seat was located in Ephrata. The area’s population at the time stood at around 8700 people.
The Columbia Basin Project, which ultimately produced the Grand Coulee Dam with its associated irrigation and hydroelectric generating grid, was an outgrowth of the 1902 creation of the United States Bureau of Reclamation. When that agency began studying feasibility of projects in the Northwestern United States, competing groups from Spokane, Wenatchee, Ephrata and elsewhere advanced competing possibilities. One idea was to dam the Columbia River at Grand Coulee. This concept was approved in 1933, and construction continued in the following decades. The project would fundamentally change the region forever.
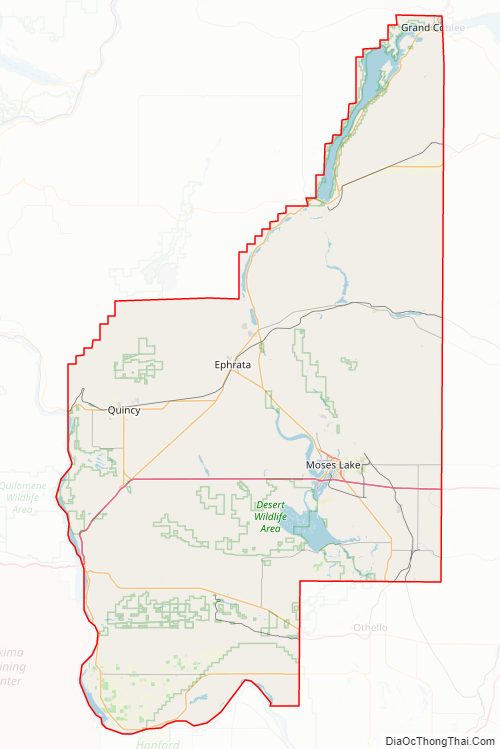
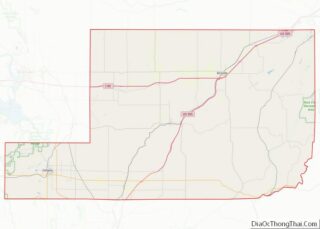
Grant County Road Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 2,791 square miles (7,230 km), of which 2,680 square miles (6,900 km) is land and 112 square miles (290 km) (4.0%) is water. It is the fourth-largest county in Washington by area.
The environmental climate of Grant County is characterized by hot summers and cold winters. Rainshadow caused by the Cascade mountains separates eastern Washington, including Grant County, from western Washington’s more temperate and oceanic climate.
A sign alongside Interstate Highway I-90 where it enters Grant County welcomes travelers to Grant County and says the county is “The nation’s leading potato producing county”.
Geographic features
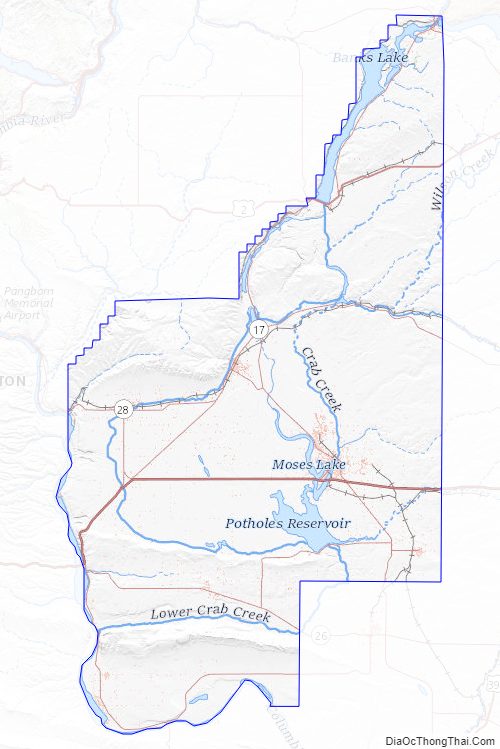
- Columbia River
- Grand Coulee
- Moses Lake
- Potholes Reservoir
- Soap Lake
- Ulysses S. Peak, unofficial name of county high point
Major highways
- I-90
- I-90 BL
- U.S. Route 2
- State Route 17
- State Route 28
Adjacent counties
- Douglas County – north
- Okanogan County – northeast
- Adams County – east
- Lincoln County – east
- Franklin County – southeast
- Benton County – south
- Yakima County – southwest
- Kittitas County – west
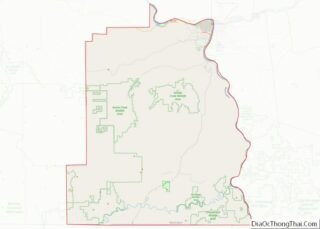
National protected areas
- Columbia National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Hanford Reach National Monument (part)
- Lake Roosevelt National Recreation Area (part)
- Saddle Mountain National Wildlife Refuge (part)