Baltimore County (/ˈbɔːltɪmɔːr/ BAWL-tim-or, locally: /bɔːldəˈmɔːr/ bawl-da-MOR or /ˈbɔːlmər/ BAWL-mər) is the third-most populous county in the U.S. state of Maryland and is part of the Baltimore metropolitan area. Baltimore County (which partially surrounds, though does not include, the independent City of Baltimore) is part of the Northeast megalopolis, which stretches from Northern Virginia northward to Boston. Baltimore County hosts a diversified economy, with particular emphasis on education, government, and health care. As of the 2020 census, the population was 854,535.
The county is home to multiple universities, including Goucher College, Stevenson University, Towson University, and University of Maryland, Baltimore County.
| Name: | Baltimore County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 24-005 |
| State: | Maryland |
| Founded: | June 30, 1659 |
| Named for: | Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore |
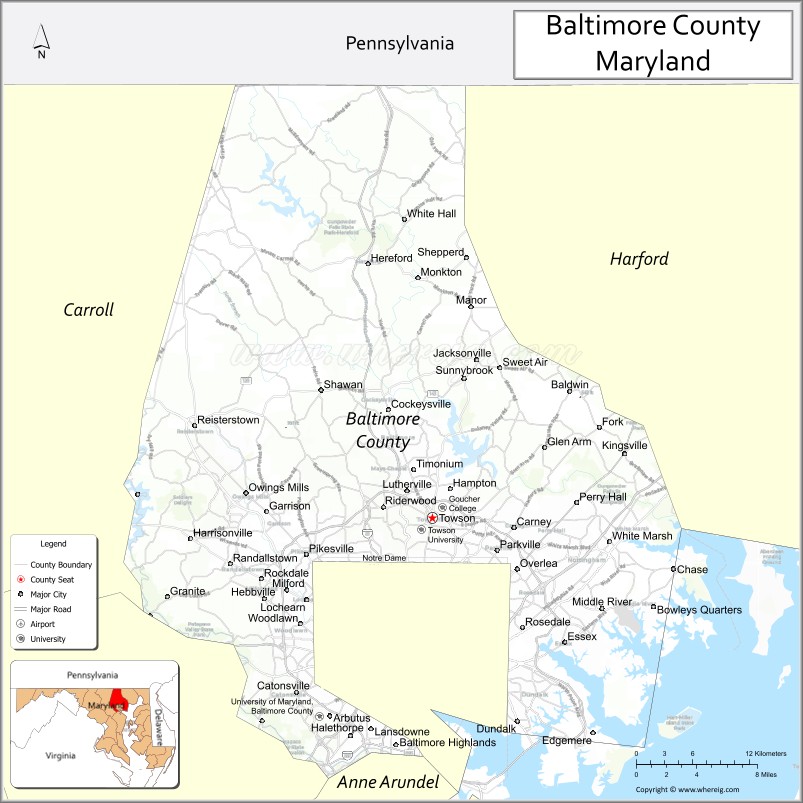
| Seat: | Towson |
| Total Area: | 682 sq mi (1,770 km²) |
| Land Area: | 598 sq mi (1,550 km²) |
| Total Population: | 854,535 |
| Population Density: | 1,300/sq mi (480/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Website: | www.baltimorecountymd.gov |
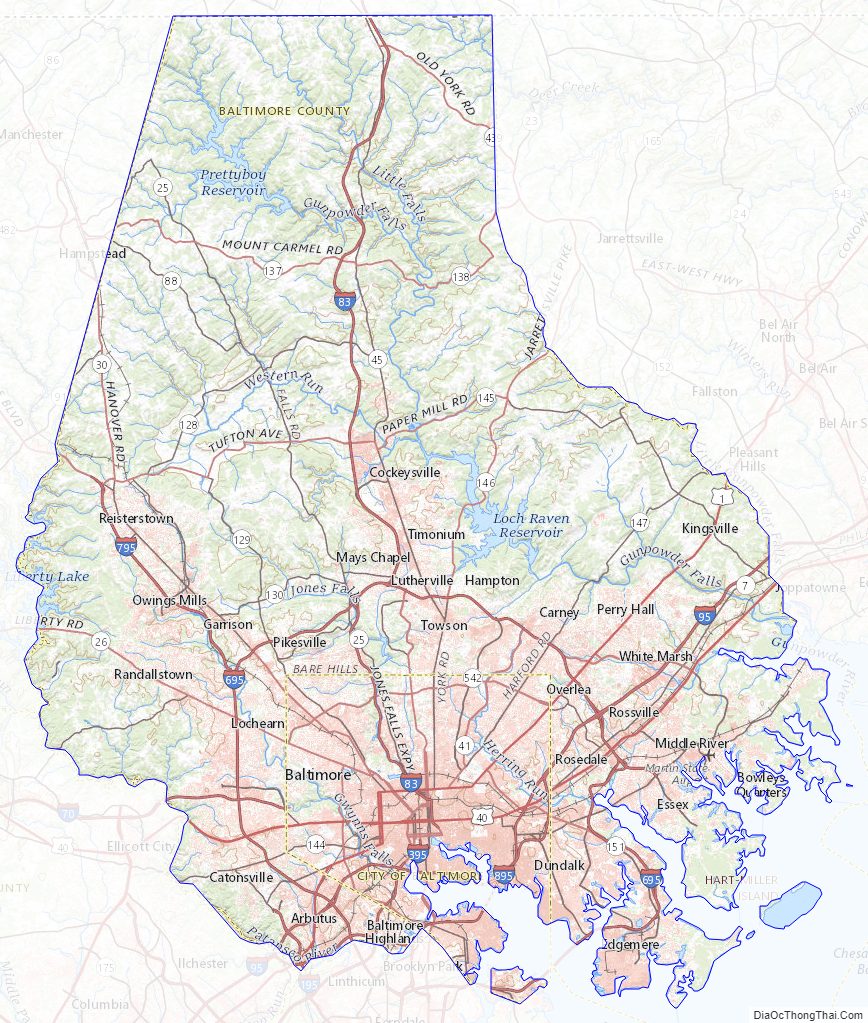
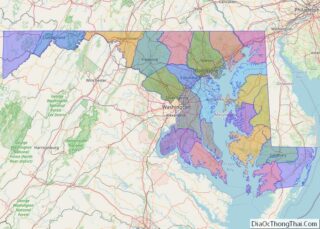
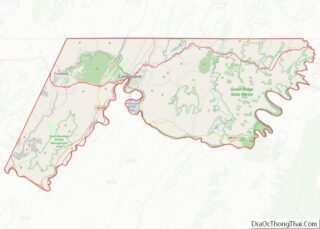
Baltimore County location map. Where is Baltimore County?
History
The name “Baltimore” derives from Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore (1605–1675), the proprietor of the new colony in the Province of Maryland, and the town of Baltimore in County Cork, Ireland. The earliest known documentary record of the county is dated January 12, 1659, when a writ was issued on behalf of the General Assembly of Maryland to its sheriff. The official founding of the county came in 1659, among the now 23 counties of the State of Maryland. This assumes that a certain amount of organization and appointments in the mid-17th century had already occurred. Previously, (old) Baltimore County was known more as a geographical entity than a political one, with its territorial limits including most of northeastern Maryland, which was then the northwestern frontier of the Province and included the present-day jurisdictions of Baltimore City, Cecil and Harford Counties, and parts of Carroll, Anne Arundel, Frederick, Howard, and Kent Counties.
In 1674, a proclamation of the Proprietor established the then-extensive boundary lines for old Baltimore County. Over the next century, various segments of the old county were sliced off as population and settlements increased in fringe regions. A portion of northeastern Baltimore County, as well as a portion of northwestern Kent County, was split off to create Cecil County. In 1748, a portion of western Baltimore County, as well as a portion of Prince George’s County to the south, were split off to create Frederick County. In 1773, Harford County to the east was split off, and in 1837 another part of western Baltimore County was combined with a part of eastern Frederick County to create Carroll County. After the adjustment of Baltimore County’s southern boundary with Anne Arundel County, stated to be the upper Middle and Western Branches of the Patapsco River in 1727, a portion of the county’s northwestern area was designated in 1838 as the “Western District” or “Howard District” of Arundel and in 1851 was officially separated to form Howard County.
Before 1674, Baltimore County court sessions were held in private residences, according to sketchy documentary evidence. In 1674, the General Assembly passed “An Act for erecting a Court-house and Prison in each County within this Province”. The site of the courthouse, jail and county seat for Baltimore County was evidently “Old Baltimore” near the Bush River on land that in 1773 became part of Harford County.
The exact location of Old Baltimore was lost. It was certain that the location was somewhere on the site of the present-day Aberdeen Proving Grounds (APG), a U.S. Army weapons testing facility. APG’s Cultural Resource Management Program attempted to find Old Baltimore, contracting with R. Christopher Goodwin & Associates (Goodwin). Goodwin first performed historical and archival work and coordinated with existing landscape features to locate the site of Old Baltimore. APG’s Explosive Ordnance Disposal of Army personnel defused any unexploded ordnance. In 1997–1998. Goodwin dug 420 test pits, uncovering artifacts including a King Charles II farthing coin, and French and English gun flints. An unearthed brick foundation proved to be the remains of the tavern owned by colonist James Phillips. Another prominent landholder in Old Baltimore was William Osbourne, who operated the ferry across the Bush River.
In his article “Migrations of Baltimore Town”, Reverend George Armistead Leakin related a letter he had received from Dr. George I. Hays. In that letter, Dr. Hays related an account of a raid by the Susquehannocks who took William Osbourne’s oldest son. Osbourne was unsuccessful in an attempt to rescue the boy. The boy was never seen by Osbourne again.
In 1683, the Maryland General Assembly passed “An Act for Advancement of Trade” to “establish towns, ports, and places of trade, within the province.” One of the towns established by the act was “on Bush River, on Town Land, near the Court-House”. The courthouse on the Bush River referenced in the 1683 Act was in all likelihood the one created by the 1674 Act. “Old Baltimore” was in existence as early as 1674, but no documents describe what may have preceded it.
By 1695, the “Old Baltimore” courthouse had evidently been abandoned. County justices put the site up for sale. Apparently a new courthouse at “Simm’s Choice” on the Baltimore County side of Little Gunpowder Falls had been under construction since 1692. In 1700, builder Michael Judd sold it to the county justices. This change of location, away from the Bush River area, reflects the growing economic and political importance of the Gunpowder region. During the next decade, the county seat moved to Joppa.
By 1724, the legislative assembly authorized Thomas Tolley, Capt. John Taylor, Daniel Scott, Lancelot Todd, and John Stokes to purchase 20 acres from “Taylor’s Choice,” a tract named after John Taylor. The assembly’s ordinance directed that the land be divided into 40 lots with streets and alleys to accompany the courthouse and jail erected previously. By 1750, about 50 houses (including a few large two-story brick structures), a church (St. John’s Anglican Parish), a courthouse, three stone warehouses, inns, taverns, stores, a public wharf and a “gallows-tree” with an “Amen Corner” with pillories and whipping posts (now located northeast of the City of Baltimore near present-day suburban “Joppatowne” off Harford Road) existed.
A new port and wharfing site, Elkridge Landing, on the upper Patapsco River’s Western Branch, became prosperous in the 18th century. It was established on the “falls” of the river, below the rapids and rocks, where the river was deep enough for loaded sailing merchantmen. The landing was a designated “port of entry” and was the terminus of several “rolling roads” on which horse or oxen-drawn hogsheads (huge barrels) packed with tobacco were wheeled down to the Landing/port to be loaded on ships sailing for London and Europe. Gradually the site silted-up from soil erosion and poor farming cultivation on the upper Patapsco, and the maritime economy of the Landing faded. In the 19th century, it became an important stop on the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad and the main north-south East Coast highway for wagons and carriages. Still, later it was on Washington Boulevard (designated U.S. Route 1) by 1926.
With a bit of financial pressure, and after paying for the cost of a new courthouse (300 pounds sterling), dominant business, commercial and political residents of the Town of Baltimore were able to have the Maryland General Assembly relocate the county seat to their growing port town. In 1768, following receipt of petitions for and against the relocation, the General Assembly passed an Act that moved the county seat from Joppa to Baltimore. The first courthouse was constructed in 1768 at a new “Courthouse Square” (today on North Calvert Street, between East Lexington and East Fayette Streets).
The Town of Baltimore, Jonestown and Fells Point were incorporated as the City of Baltimore in 1796–1797. The city remained a part of surrounding Baltimore County and continued to serve as its county seat from 1768 to 1851.
The site of the courthouse is now “Battle Monument Square”, constructed 1815–1822 to commemorate the city and county defense in the War of 1812, including the bombardment of Fort McHenry by the British Royal Navy fleet in the Patapsco River, the two-day stand-off in fortifications dug east of the city on Loudenschlager’s Hill (now “Hampstead Hill” in today’s Patterson Park) and the earlier Battle of North Point in “Godly Woods” on the “Patapsco Neck” peninsula in the southeastern portion of the county, during September 12–14, 1814. These events have been commemorated ever since by Defenders Day, an annual city, county, and state official holiday on September 12.
A second city-county courthouse constructed in 1805–1809 was moved to the western side of the Square at North Calvert and East Lexington. A third courthouse including the lower magistrates, commissioners, district and circuit courts, orphans (inheritances/wills) court, small claims court and the old Supreme Bench of Baltimore City was constructed on the entire western block of North Calvert, East Lexington, East Fayette and Saint Paul Streets from 1896 to 1900. In 1985 this building was renamed the Clarence M. Mitchell Jr. City Circuit Courthouse, for the famous Baltimorean and leader of the Civil Rights Movement, Clarence M. Mitchell Jr. (1911–1984), reputed to be the “101st U.S. Senator”.
In 1816, the City of Baltimore annexed from Baltimore County several parcels of land known as the “Precincts” on its west, north, east and southwest sides. The County separated from the city (which it surrounds on the east, north, and west) on July 4, 1851, as a result of the adoption of the 1851 second state constitution. Baltimore became one of the few “independent cities” in the United States, putting it on the same level with the state’s other 23 counties and granting limited “home rule” powers outside the authority of the Maryland General Assembly.
Towsontown was voted in a referendum by the voting citizens as the new “county seat” on February 13, 1854. The City of Baltimore continued annexing land from the county, extending its western and northern boundaries in 1888. The factory and business owners in the eastern industrial communities of Canton and Highlandtown resisted and opposed annexation, but were annexed 30 years later. The last major annexation took place in 1918–1919, which again took territory from the county on all three sides (west, north, and east) as well as to the south for the first time from Anne Arundel County, along the south shores of the Patapsco River.
A new Baltimore County Courthouse was authorized to be built facing Washington Avenue, between Chesapeake and Pennsylvania Avenues to replace the previous courthouse and governmental offices then centered for near 85 years in the city, which had been the official “county seat” since just before the American Revolution. Later surrounded by manicured flower gardens, shrubs and curved walkways, the historical landmark is built of local limestone and marble. It was completed and dedicated in 1855. Wings and annexes were added in 1910, 1923 and 1958. By the 1970s, the county’s legal system and governmental offices had grown so much that a separate modernistic “County Courts Building” was erected to the west behind the old Courthouse with its annexes, separated by a paved plaza which is used for employee/visitors relaxations and official ceremonies.
A constitutional amendment to the 1867 Maryland Constitution was approved by referendum in 1948, prohibiting any future annexations without approval from residents in affected territories.
Extensive city-county hostilities came during the Civil Rights Movement, and by the 1980s the county’s older inner suburbs faced increasing urban social ills. An atmosphere of cooperation emerged with the drawing of cross-border state assembly districts, organizing of regional government agencies, and increasing state assumption of powers.
The county has a number of properties and sites of local, state and national historical interest on the National Register of Historic Places which is maintained by the National Park Service of the U.S. Department of the Interior by the “Historic Sites Act” of August 1935.
Baltimore County Road Map
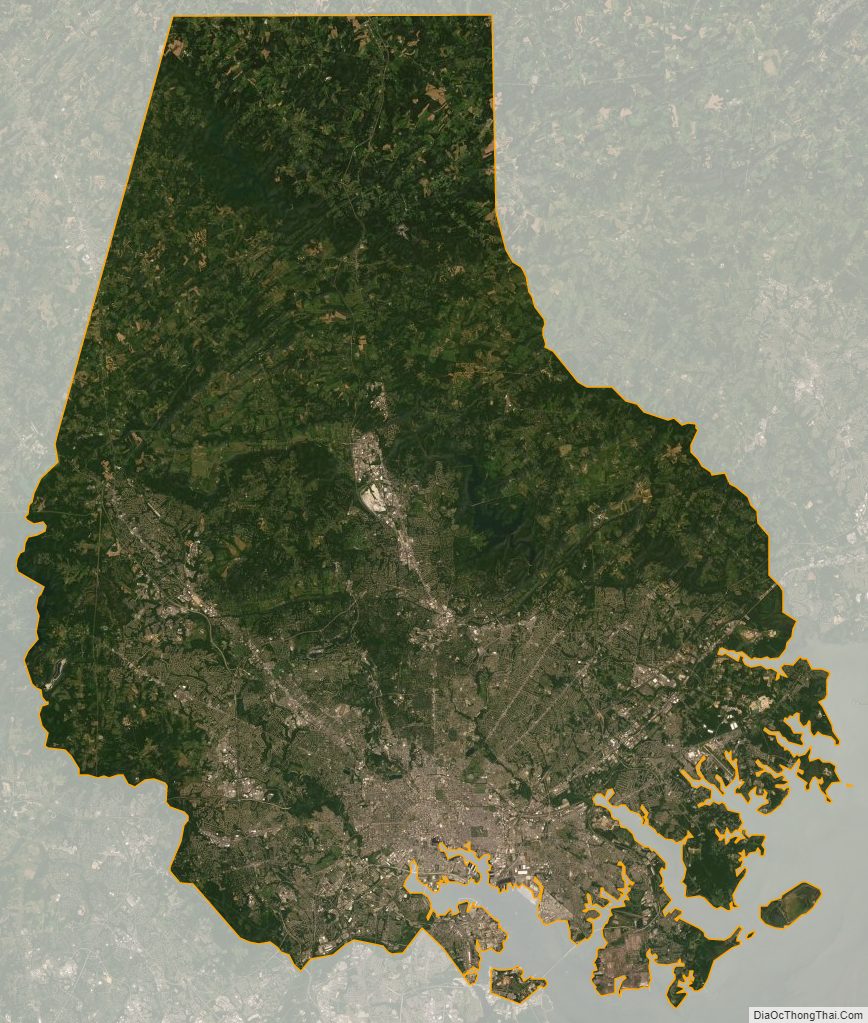
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county covers 682 square miles (1,770 km), of which 598 square miles (1,550 km) are land and 83 square miles (210 km) (12%) are water. It is the third-largest county in Maryland by land area. The larger portion of the terrain is undulating, with bold hills often rising to a height of 800 feet (240 m) above tide water. The highest elevation is approximately 960 feet (290 m) above sea level, along the Pennsylvania state line near Steltz. The lowest elevation is sea level along the shoreline of Chesapeake Bay.
Much of Baltimore County is suburban, straddling the border between the Piedmont plateau to the northwest and in the southern and southeastern regions of the county bordering the Patapsco River and the Chesapeake Bay, the Atlantic coastal plain. Northern Baltimore County is primarily rural, with a landscape of rolling hills and deciduous forests characteristic of the Southeastern mixed forests and shares the geography with its neighbors to the east and west, Carroll County and Harford County, and going north across the historic Mason–Dixon line into Adams County and York County in south-central Pennsylvania.
Climate
The county has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) except in the northern tier where a hot-summer humid continental climate (Dfa) exists. Average monthly temperatures in Towson range from 33.3 °F in January to 76.9 °F in July. [1] The county has three hardiness zones: 6b in some higher northern areas, 7a in most of the county by area, and 7b in areas close enough to the Chesapeake Bay or the City of Baltimore. [2]
Adjacent counties and independent city
- York County, Pennsylvania (north)
- Carroll County (west)
- Harford County (east)
- Anne Arundel County (south)
- Kent County (Southeast)
- Howard County (southwest)
- Baltimore City (south)
National protected area
- Hampton National Historic Site
State protected area
- Soldiers Delight Natural Environment Area