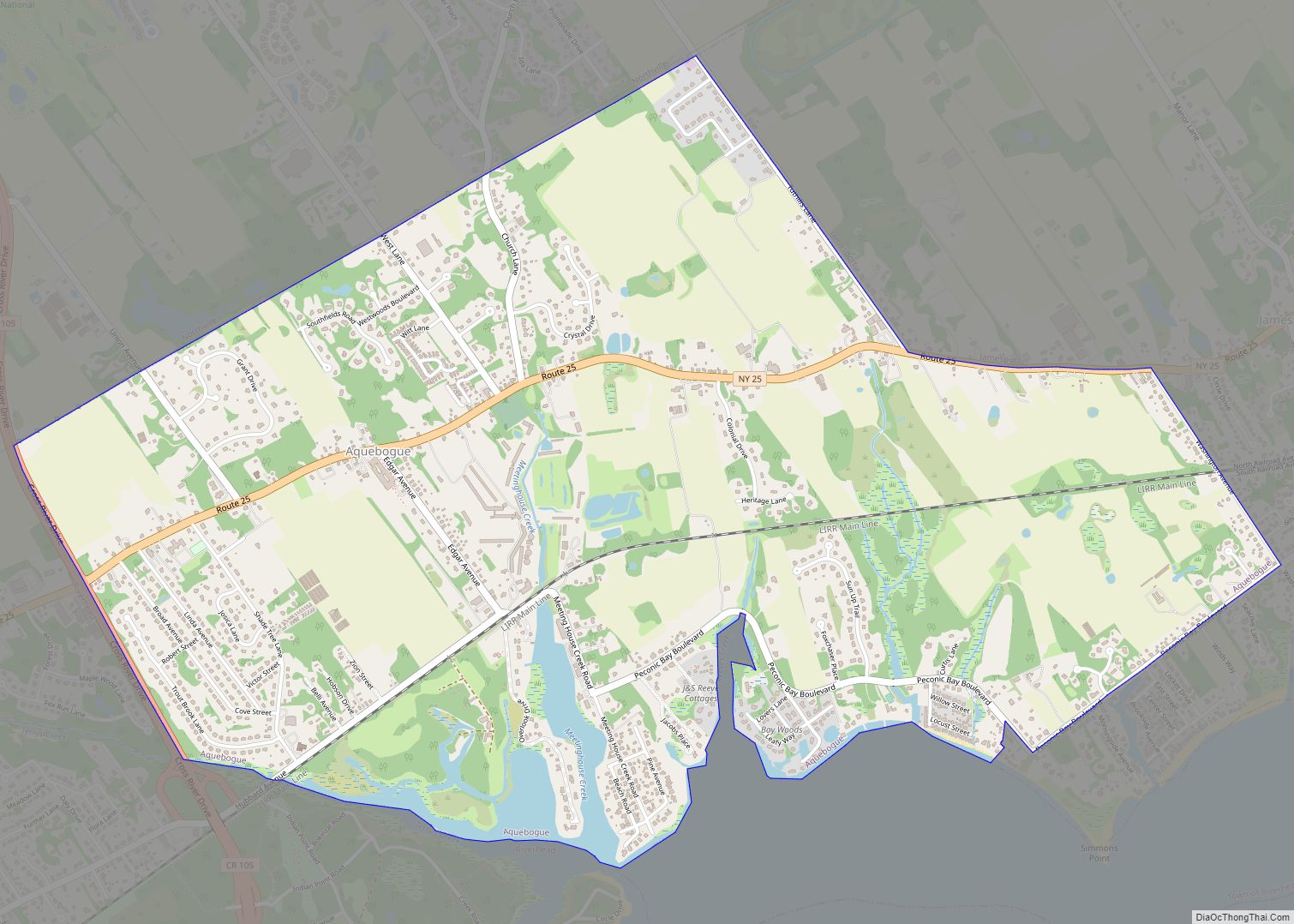
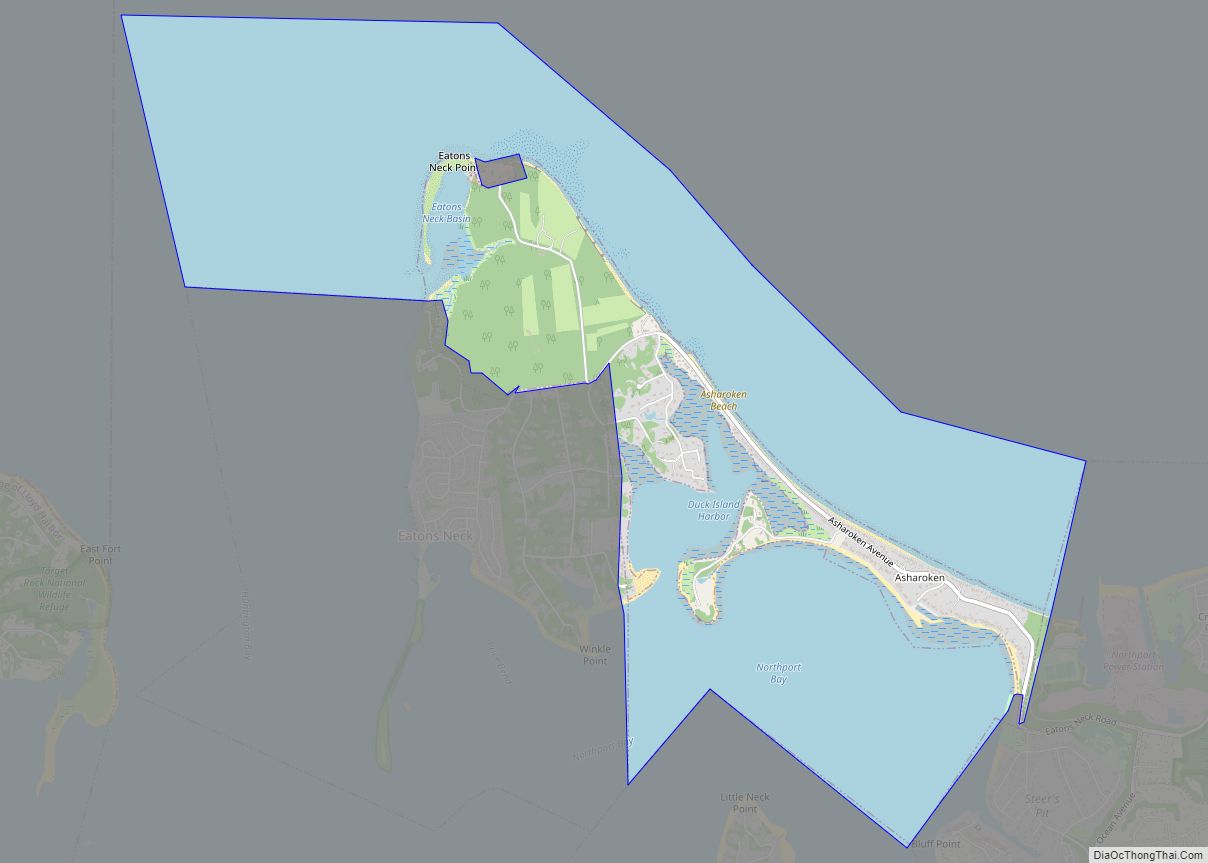
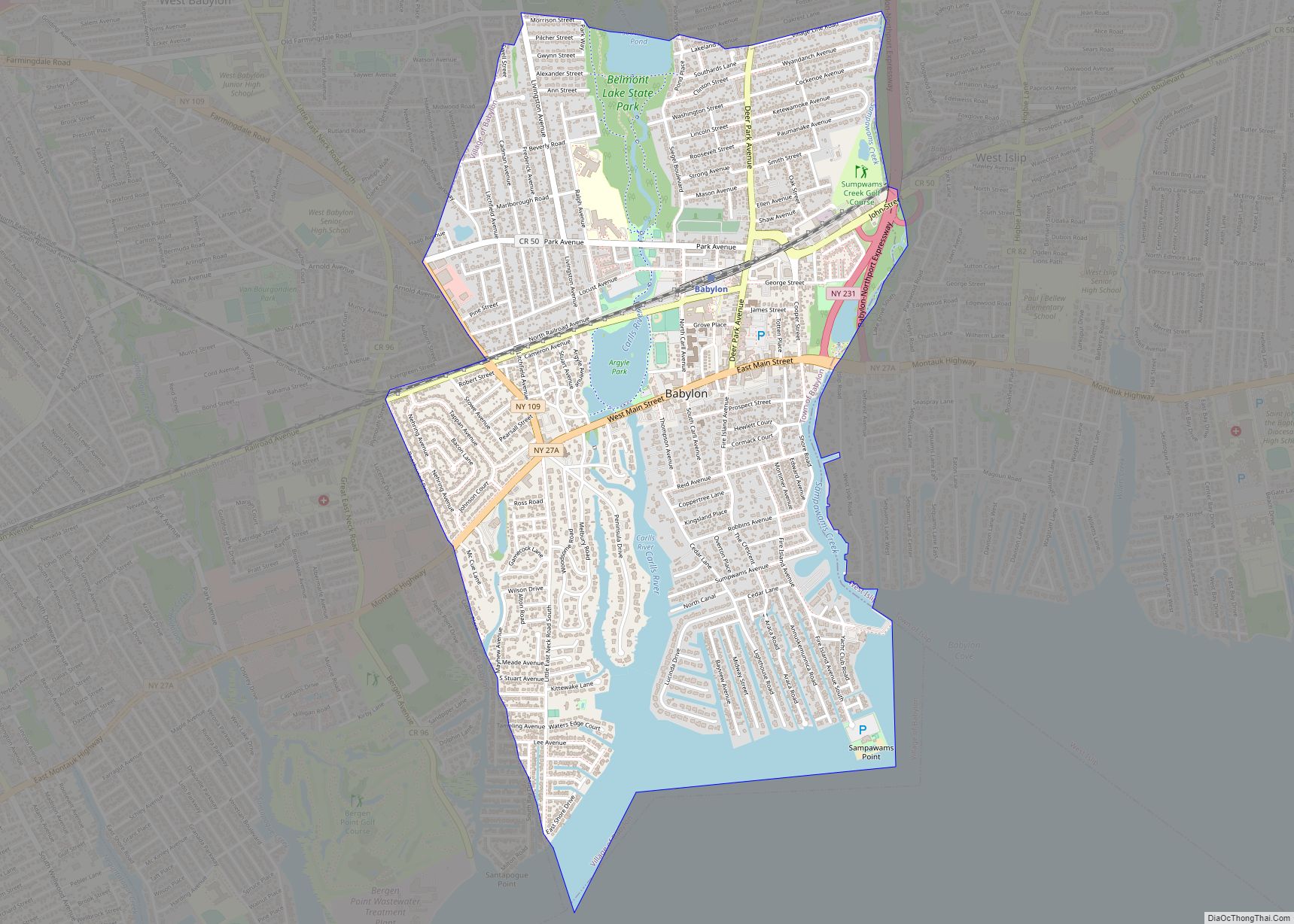
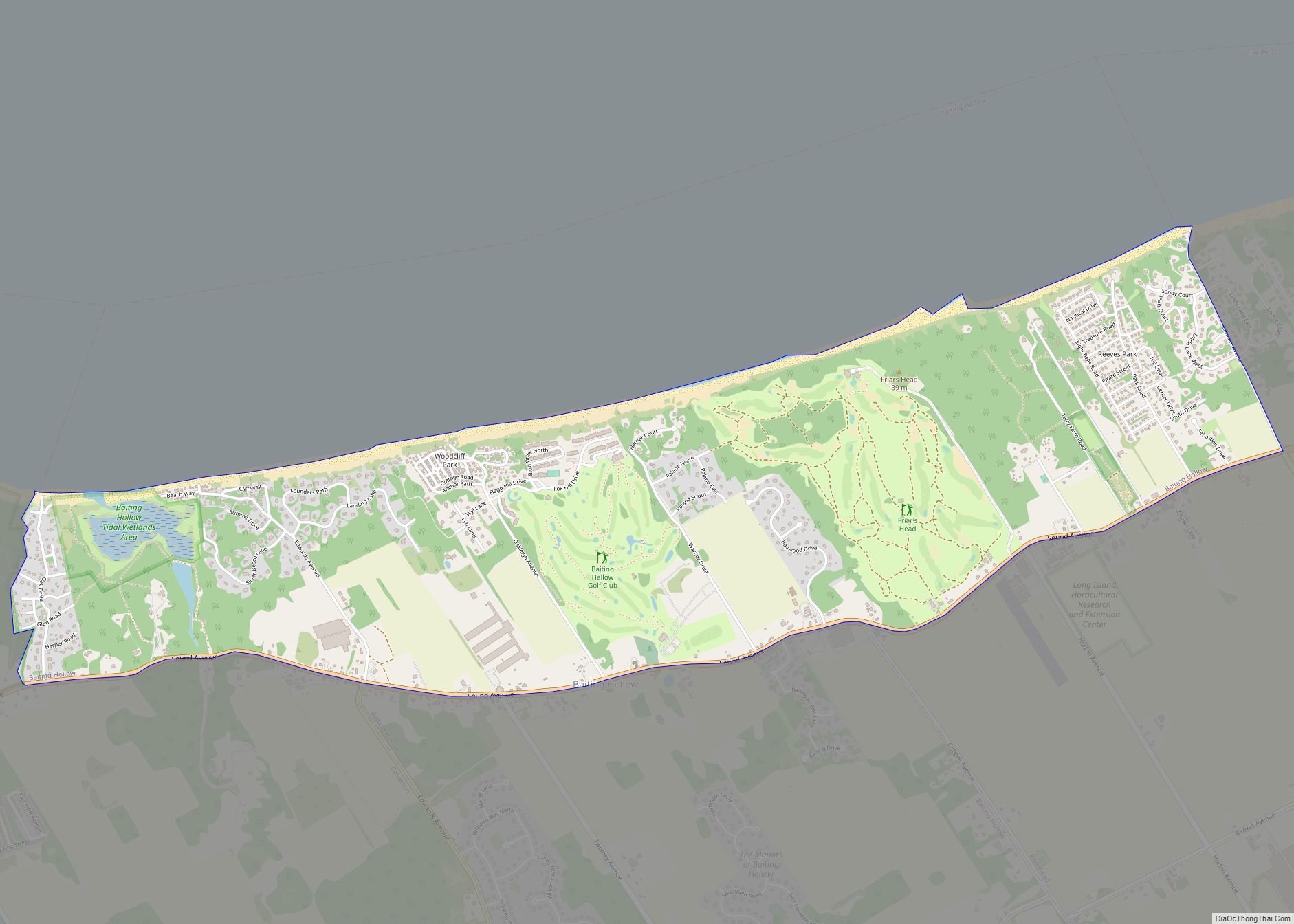
| Name: | Suffolk County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 36-103 |
| State: | New York |
| Founded: | 1683 |
| Named for: | Suffolk, England |
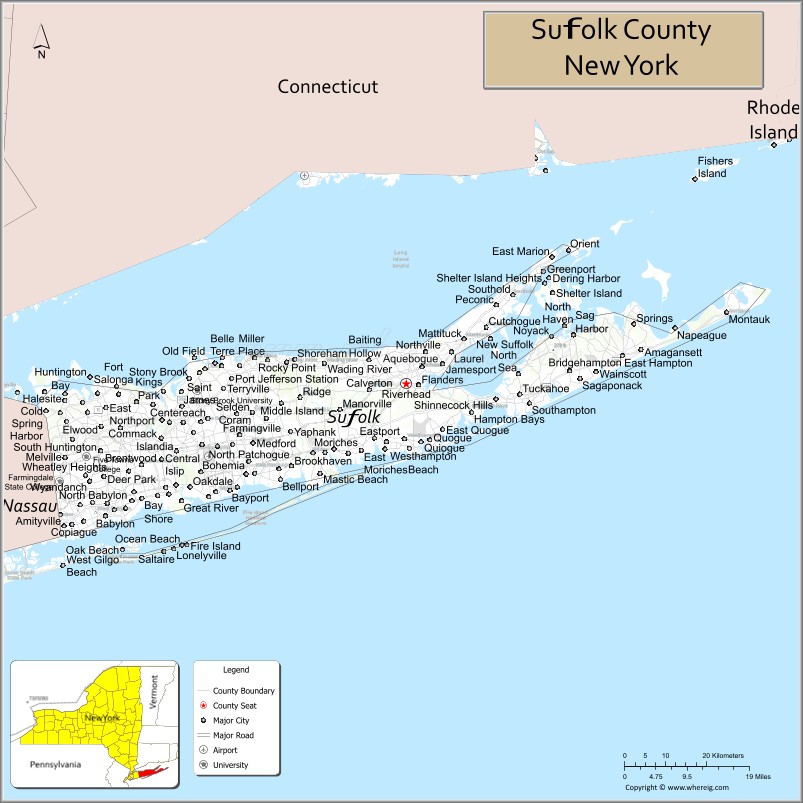
| Seat: | Riverhead |
| Largest town: | Brookhaven |
| Total Area: | 2,373 sq mi (6,150 km²) |
| Land Area: | 912 sq mi (2,360 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,525,920 |
| Population Density: | 1,637.0/sq mi (632.0/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Website: | www.suffolkcountyny.gov |
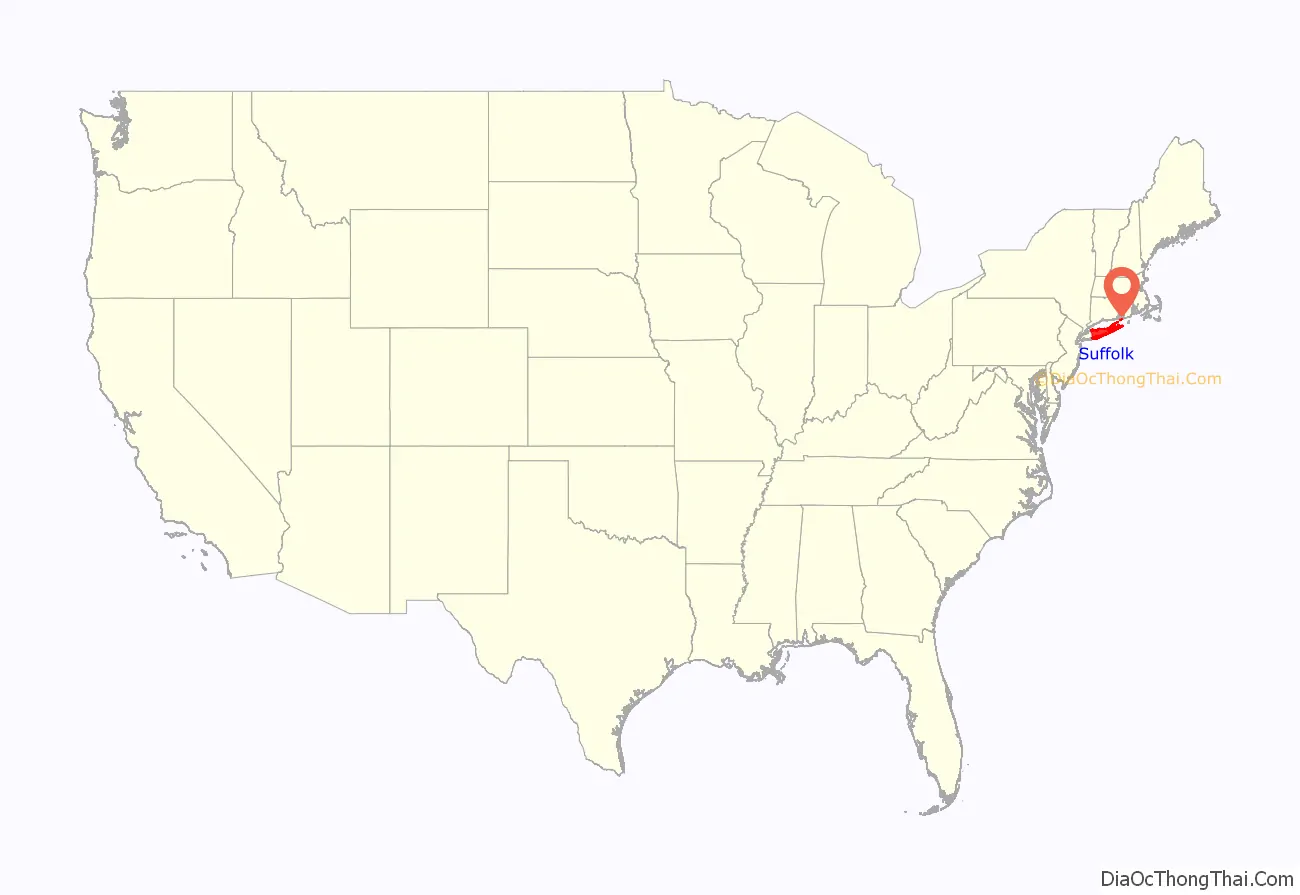
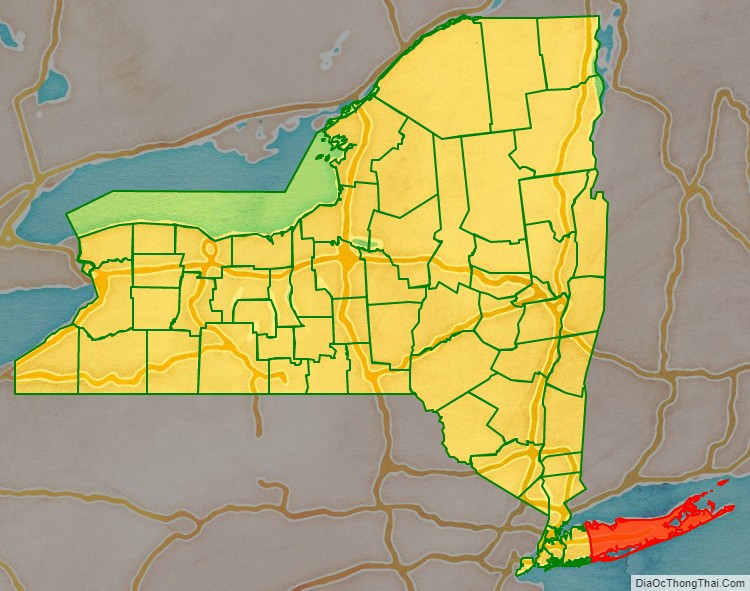
Suffolk County location map. Where is Suffolk County?
History
Suffolk County was part of the Connecticut Colony before becoming an original county of the Province of New York, one of twelve created in 1683. From 1664 until 1683 it had been the East Riding of Yorkshire. Its boundaries were essentially the same as at present, with only minor changes in the boundary with its western neighbor, which was originally Queens County but has been Nassau County since the separation of Nassau from Queens in 1899.
According to the Suffolk County website, the county is the leading agricultural county in the state of New York, saying that: “The weather is temperate, clean water is abundant, and the soil is so good that Suffolk is the leading agricultural county in New York State. That Suffolk is still number one in farming, even with the development that has taken place, is a tribute to thoughtful planning, along with the excellent soil, favorable weather conditions, and the work of the dedicated farmers in this region.”
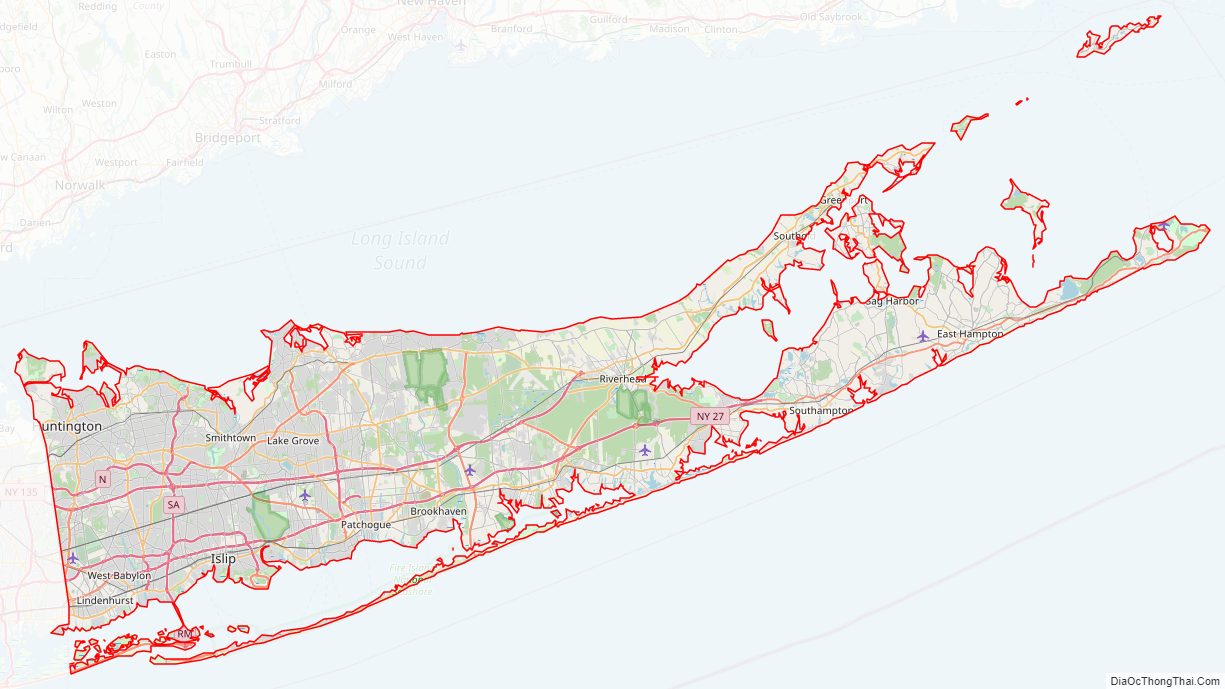
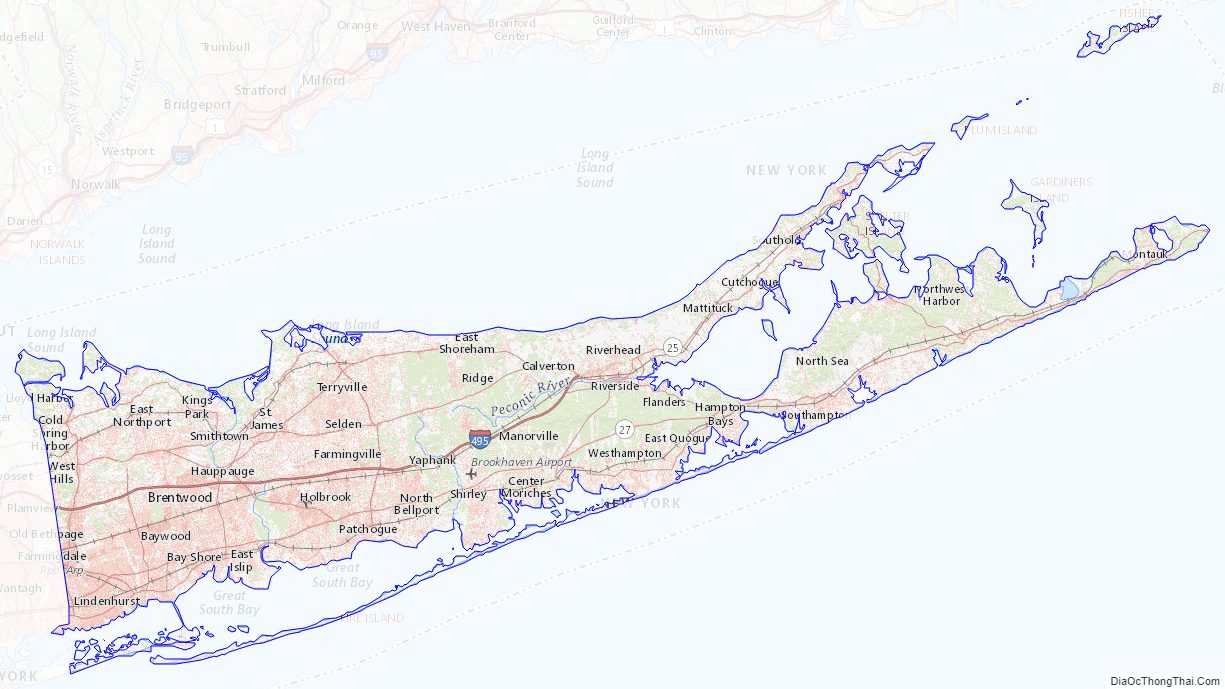
Suffolk County Road Map
Geography
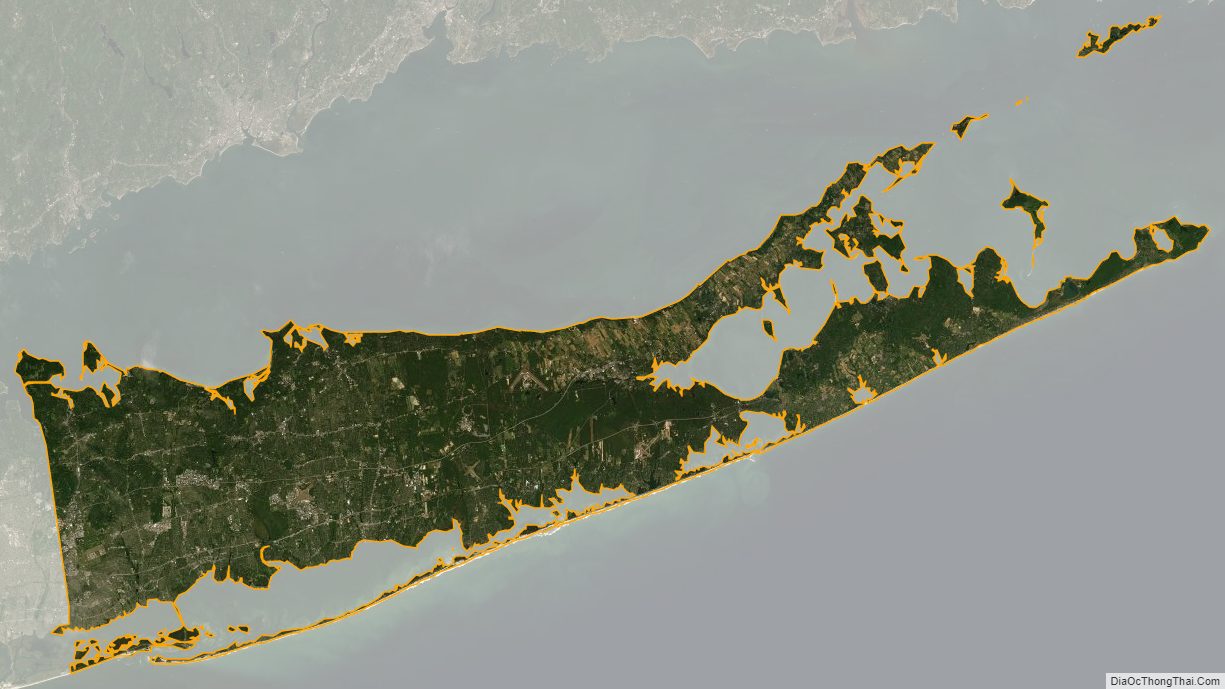
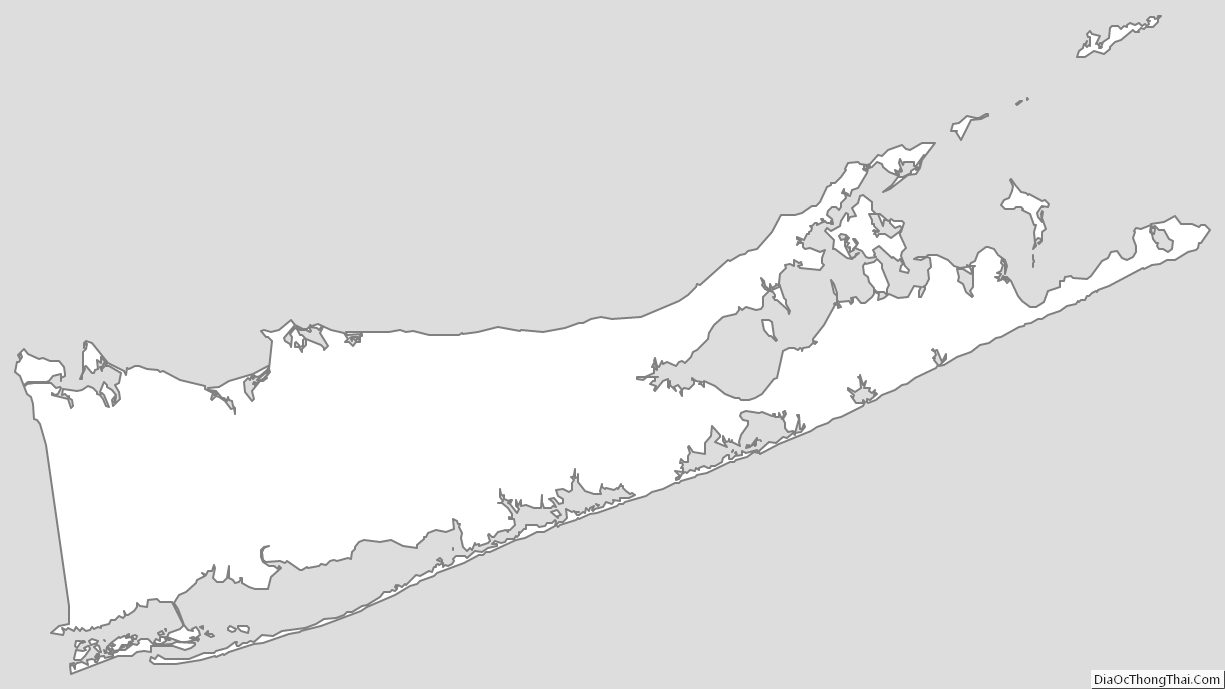
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has an area of 2,373 square miles (6,150 km), of which 912 square miles (2,360 km) is land and 1,461 square miles (3,780 km) (62%) is water. It is the second-largest county in New York by total area and occupies 66% of the land area of Long Island.
Suffolk County occupies the central and eastern part of Long Island, in the extreme east of the State of New York. The eastern end of the county splits into two peninsulas, known as the North Fork and the South Fork. The county is surrounded by water on three sides, including the Atlantic Ocean and Long Island Sound, with 980 miles (1,580 km) of coastline. The eastern end contains large bays.
The highest elevation in the county, and on Long Island as a whole, is Jayne’s Hill in West Hills, at 401 feet (122 m) above sea level. This low lying-geography means that much of the county is vulnerable to sea level rise.
Climate
Suffolk County sits at the convergence of climate zones including the humid continental (Dfa) and humid subtropical (Cfa), bordering closely on an oceanic climate (Cfb). The majority of the county by land area is in the Dfa zone. Summers are cooler at the east end than in the western part of the county. The hardiness zone is 7a, except in Copiague Harbor, Lindenhurst, and Montauk, where it is 7b. Average monthly temperatures in Hauppauge range from 31.0 °F (−0.6 °C) in January to 74.0 °F (23.3 °C) in July, and in the Riverhead town center they range from 30.1 °F (−1.1 °C) in January to 72.8 °F (22.7 °C) in July, which includes both daytime and nighttime temperatures. PRISM Climate Group, Oregon State U On February 9, 2013, Suffolk County was besieged with 30 inches of snow, making it the largest day of snowfall on record in Suffolk.
Adjacent counties
- Nassau County – west
- Fairfield County, Connecticut – northwest
- New Haven County, Connecticut – north
- Middlesex County, Connecticut – north
- New London County, Connecticut – north
- Washington County, Rhode Island – northeast
National protected areas
- Amagansett National Wildlife Refuge
- Conscience Point National Wildlife Refuge
- Elizabeth A. Morton National Wildlife Refuge
- Fire Island National Seashore
- Sayville National Wildlife Refuge
- Seatuck National Wildlife Refuge
- Target Rock National Wildlife Refuge
- Wertheim National Wildlife Refuge