| Name: | Nassau County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 36-059 |
| State: | New York |
| Founded: | 1899 |
| Named for: | House of Nassau |
| Seat: | Mineola |
| Largest town: | Hempstead |
| Total Area: | 453 sq mi (1,170 km²) |
| Land Area: | 285 sq mi (740 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,395,774 |
| Population Density: | 4,897.45/sq mi (1,890.92/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Website: | www.nassaucountyny.gov |
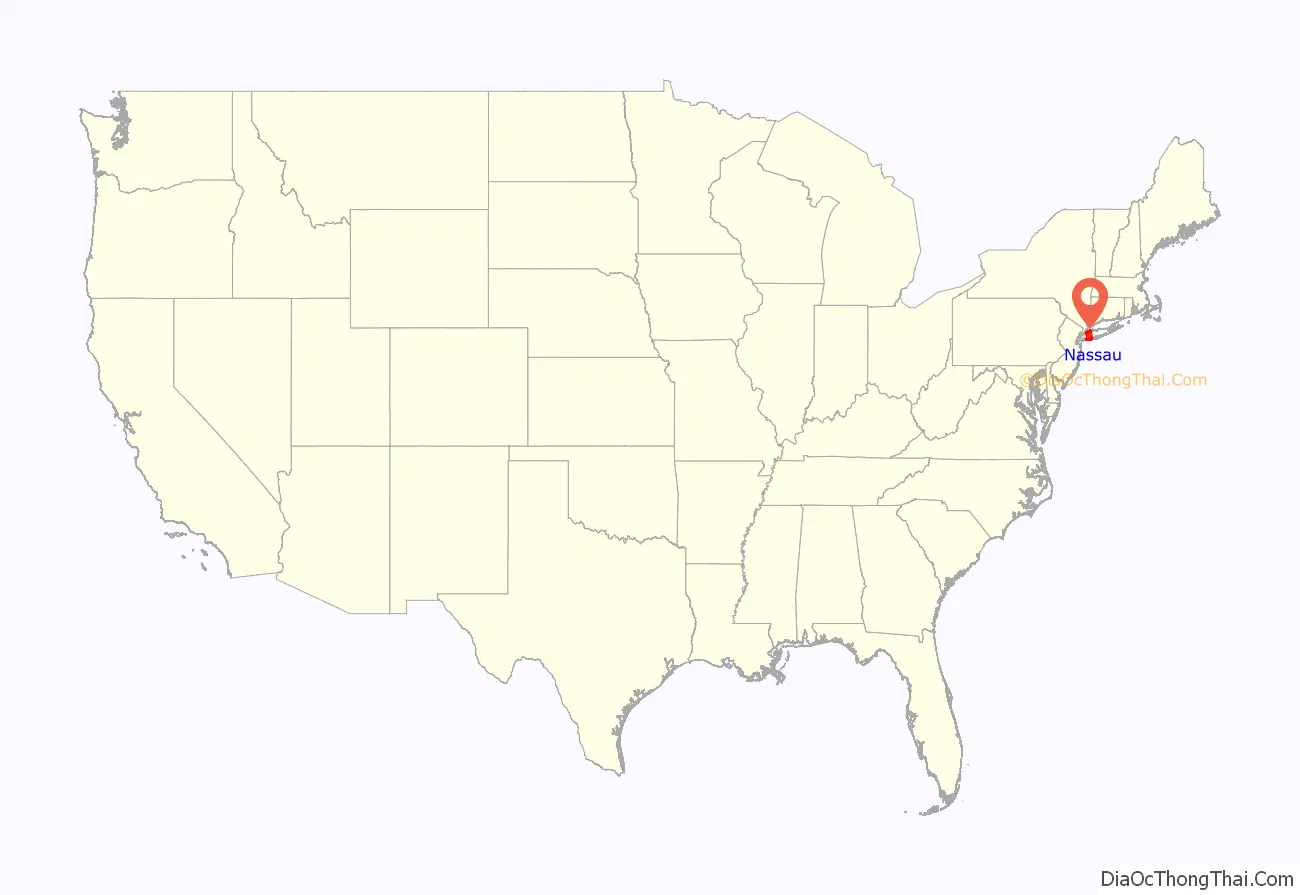
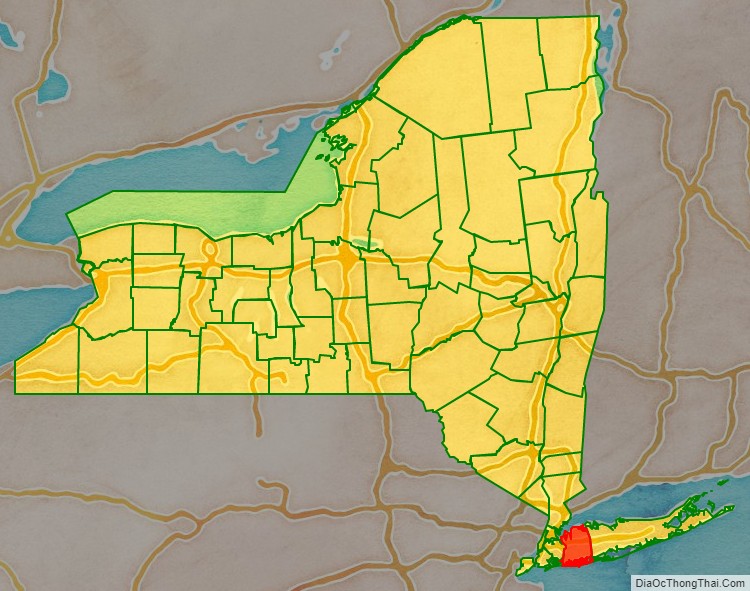
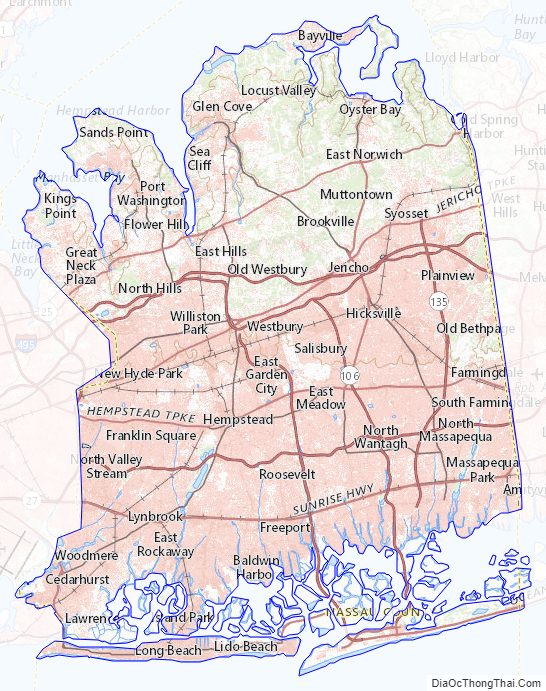
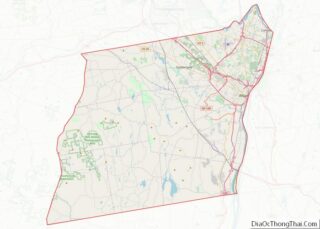
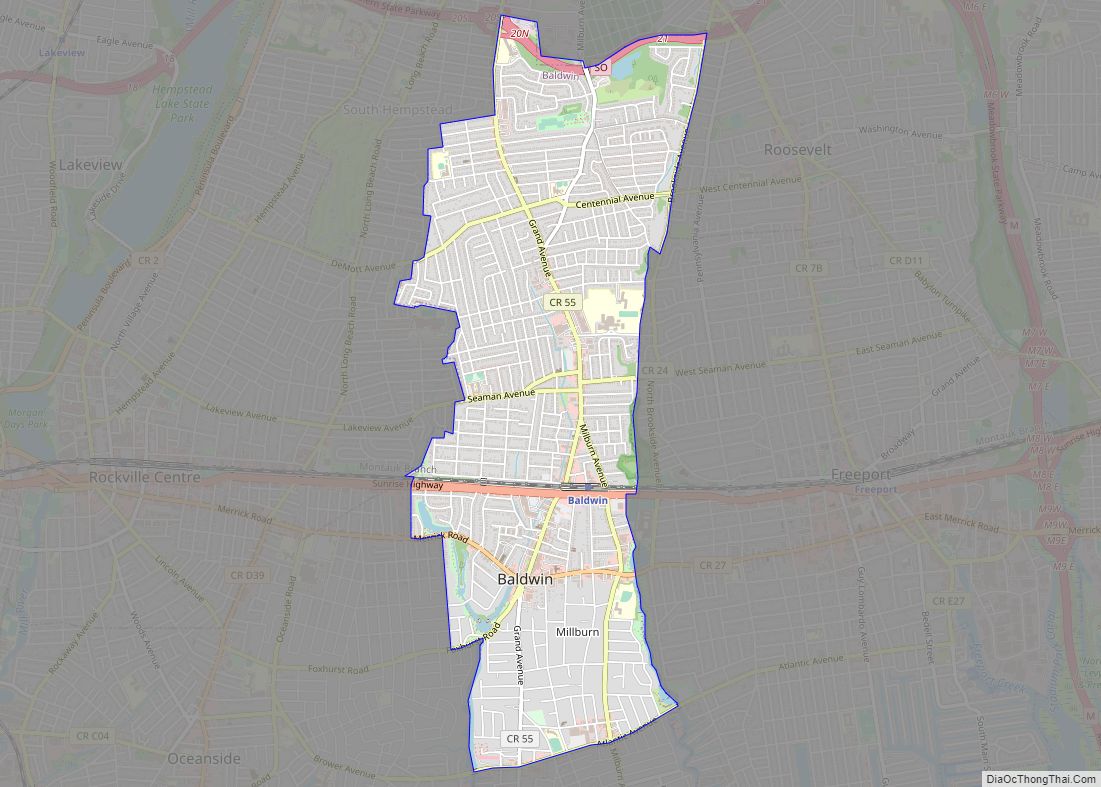
Nassau County location map. Where is Nassau County?
History
The area now designated as Nassau County was originally the eastern 70% of Queens County, one of the original twelve counties formed in 1683, and was then contained within two towns: Hempstead and Oyster Bay. In 1784, the Town of North Hempstead, was formed through secession by the northern portions of the Town of Hempstead. Nassau County was formed in 1899 by the division of Queens County, after the western portion of Queens had become a borough of New York City in 1898, as the three easternmost towns seceded from the county.
When the first European settlers arrived, among the Native Americans to occupy the present area of Nassau County were the Marsapeque, Matinecoc, and Sacatogue. Dutch settlers in New Netherland predominated in the western portion of Long Island, while English settlers from Connecticut occupied the eastern portion. Until 1664, Long Island was split, roughly at the present border between Nassau and Suffolk counties, between the Dutch in the west and Connecticut claiming the east. The Dutch did grant an English settlement in Hempstead (now in western Nassau), but drove settlers from the present-day eastern Nassau hamlet of Oyster Bay as part of a boundary dispute. In 1664, all of Long Island became part of the English Province of New York within the Shire of York. Present-day Queens and Nassau were then just part of a larger North Riding. In 1683, the colonial territory of Yorkshire was dissolved, Suffolk County and Queens County were established, and the local seat of government was moved west from Hempstead to Jamaica (now in New York City).
By 1700, virtually none of Long Island’s area remained unpurchased from the Native Americans by the English colonists, and townships controlled whatever land had not already been distributed. The courthouse in Jamaica was torn down by the British during the American Revolution to use the materials to build barracks.
In 1784, following the American Revolutionary War, the Town of Hempstead was split in two, when Patriots in the northern part formed the new Town of North Hempstead, leaving Loyalist majorities in the Town of Hempstead. About 1787, a new Queens County Courthouse was erected (and later completed) in the new Town of North Hempstead, near present-day Mineola (now in Nassau County), known then as Clowesville.
The Long Island Rail Road reached as far east as Hicksville in 1837, but did not proceed to Farmingdale until 1841 due to the Panic of 1837. The 1850 census was the first in which the population of the three western towns (Flushing, Jamaica, and Newtown) exceeded that of the three eastern towns that are now part of Nassau County. Concerns were raised about the condition of the old courthouse and the inconvenience of travel and accommodations, with the three eastern and three western towns divided on the location for the construction of a new one. Around 1874, the seat of county government was moved to Long Island City from Mineola. As early as 1875, representatives of the three eastern towns began advocating the separation of the three eastern towns from Queens, with some proposals also including the towns of Huntington and Babylon (in Suffolk County).
In 1898, the western portion of Queens County became a borough of the City of Greater New York, leaving the eastern portion a part of Queens County but not part of the Borough of Queens. As part of the city consolidation plan, all town, village, and city (other than NYC) governments within the borough were dissolved, as well as the county government with its seat in Jamaica. The areas excluded from the consolidation included all of the Town of North Hempstead, all of the Town of Oyster Bay, and most of the Town of Hempstead (excluding the Rockaway Peninsula, which was separated from the Town of Hempstead and became part of the city borough). In 1899, following approval from the New York State Legislature, the three towns were separated from Queens County, and the new county of Nassau was constituted.
In preparation for the new county, in November 1898, voters had selected Mineola to become the county seat for the new county (before Mineola incorporated as a village in 1906 and set its boundaries almost entirely within the Town of North Hempstead), winning out over Hicksville and Hempstead. The Garden City Company (founded in 1893 by the heirs of Alexander Turney Stewart) donated four acres of land for the county buildings in the Town of Hempstead, just south of the Mineola train station and the present day village of Mineola. The land and the buildings have a Mineola postal address, but are within the present day Village of Garden City, which did not incorporate, nor set its boundaries, until 1919.
In 1917, the village of Glen Cove was granted a city charter, making it independent from the Town of Oyster Bay. In 1918, the village of Long Beach was incorporated in the Town of Hempstead. In 1922, it became a city, making it independent of the town. These are the only two administrative divisions in Nassau County identified as cities.
From the early 1900s until the Depression and the early 1930s, many hilly farmlands on the North Shore were transformed into luxurious country estates for wealthy New Yorkers, with the area receiving the “Gold Coast” moniker and becoming the setting of F. Scott Fitzgerald’s 1925 novel The Great Gatsby. One summer resident of the Gold Coast was President Theodore Roosevelt, at Sagamore Hill. In 1908, William Kissam Vanderbilt constructed the Long Island Motor Parkway as a toll road through Nassau County. With overpasses and bridges to remove intersections, it was among the first limited access motor highways in the world, and was also used as a racecourse to test the capabilities of the fledgling automobile industry.
Nassau County, with its extensive flat land, was the site of many aviation firsts. Military aviators for both World Wars were trained on the Hempstead Plains at installations such as Mitchel Air Force Base, and a number of successful aircraft companies were established. Charles Lindberg took off for Paris from Roosevelt Field in 1927, completing the first non-stop trans-Atlantic flight from the United States. Grumman (which in 1986 employed 23,000 people on Long Island) built many planes for World War II, and later contributed the Apollo Lunar Module to the Space program.
The United Nations Security Council was temporarily located in Nassau County from 1946 to 1951. Council meetings were held at the Sperry Gyroscope headquarters in the village of Lake Success near the border with Queens County. It was here on June 27, 1950, that the Security Council voted to back U.S. President Harry S Truman and send a coalition of forces to the Korean Peninsula, leading to the Korean War.
Until World War II, most of Nassau County was still farmland, particularly in the eastern portion. Following the war, the county saw an influx of people from the five boroughs of New York City, especially from Brooklyn and Queens, who left their urban dwellings for a more suburban setting. This led to a massive population boom in the county. In 1947, William Levitt built his first planned community in Nassau County, in the Island Trees section (later renamed Levittown; this should not be confused with the county’s first planned community, in general, which is Garden City). While in the 1930s, Robert Moses had engineered curving parkways and parks such as Jones Beach State Park and Bethpage State Park for the enjoyment of city-dwellers, in the 1950s and 1960s the focus turned to alleviating commuter traffic.
In 1994, Federal Judge Arthur Spatt declared the Nassau County Board of Supervisors unconstitutional and directed that a 19-member legislature be formed. Republicans won 13 seats in the election and chose Bruce Blakeman as the first Presiding Officer (Speaker). Among the first class of Legislators were Peter J. Schmitt (R-Massapequa), Judith Jacobs (D-Woodbury), John Ciotti (R-North Valley Stream), Dennis Dunne Sr. (R-Levittown), Francis X. Becker (R-Lynbrook), Vincent T. Muscarella (R-West Hempstead), Ed Mangano (R-Bethpage), Michael Fiechter (C-North Bellmore), Roger Corbin (D-Westbury), Salvatore Pontillo (R-Farmingdale), Bruce Nyman (D-Long Beach), Edward Ward (R-Wantagh), Darlene Harris (R-Uniondale), Ed Oppenheimer (D-Rockville Centre), John Canning (R-Sea Cliff), Bruce Blakeman (R-Woodmere), Lisanne Altmann (D-Great Neck), Richard Nicolello (R-New Hyde Park), Barbara Johnson (D-Port Washington).
According to a Forbes magazine 2012 survey, residents of Nassau County have the 12th highest median household annual income in the country and the highest in the state. In the 1990s, however, Nassau County experienced substantial budget problems, forcing the county to near bankruptcy. Thus, the county government increased taxes to prevent a takeover by the state of New York, leading to the county having high property taxes. Nevertheless, on January 27, 2011, a State of New York oversight board seized control of Nassau County’s finances, saying the wealthy and heavily taxed county had failed to balance its $2.6 billion budgets.
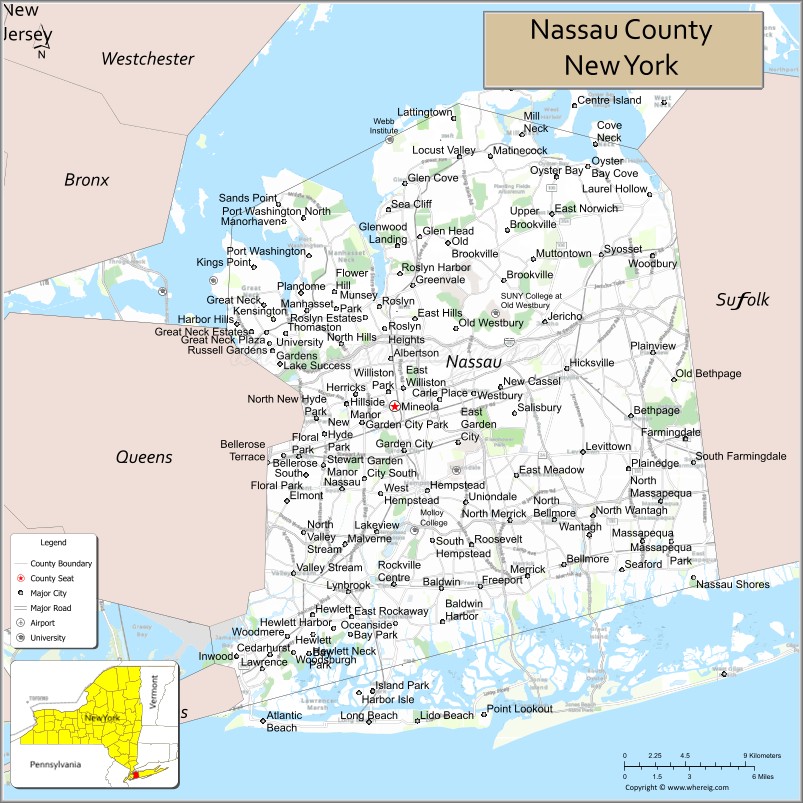
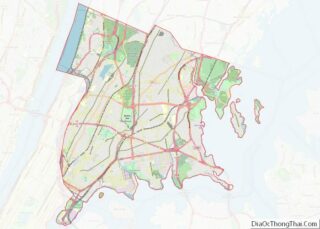
Nassau County Road Map
Geography
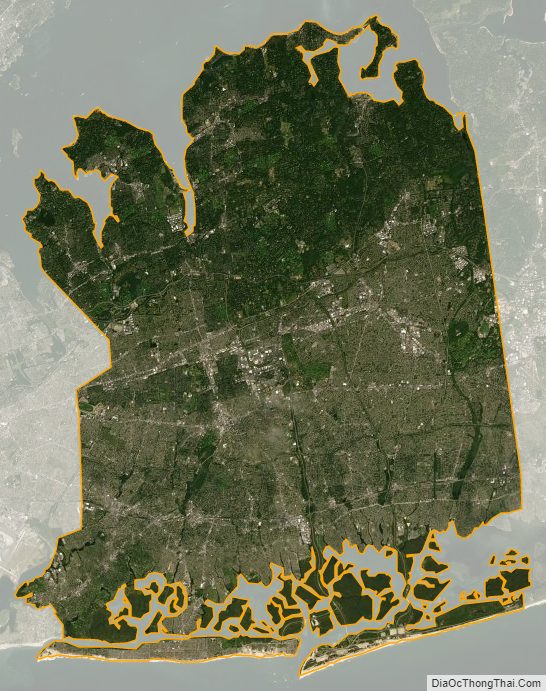
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 453.2 square miles (1,174 km), of which 284.7 square miles (737 km) is land and 168.5 square miles (436 km) (37%) is water.
Nassau County occupies a portion of Long Island immediately east of the New York City borough of Queens. It is divided into two cities and three towns, the latter of which contain 64 villages and numerous hamlets. The county borders Connecticut across the Long Island Sound.
Between the 1990 U.S. census and the 2000 U.S. census, the Nassau County exchanged territory with Suffolk County and lost territory to Queens County. Dozens of CDPs had boundaries changed, and 12 new CDPs were listed.
Countyscape
Climate
Nassau County has a climate similar to other coastal areas of the Northeastern United States; it has warm, humid summers and cool, wet winters. The county is classified as humid subtropical (Cfa) by some definitions, particularly closer to Queens and on the south coast. Other areas of Nassau have a hot-summer humid continental climate (Dfa). A significant portion of the western area of the county is Cfa due to being downwind from the urban heat island effect of New York City.
The winters used to be colder with more snowstorms, but have warmed due to climate change. The Atlantic Ocean helps bring afternoon sea breezes that temper the heat in the warmer months and limit the frequency and severity of thunderstorms. Nassau County has a moderately sunny climate, averaging between 2,400 and 2,800 hours of sunshine annually. Average monthly temperatures in Mineola range from 31.9 °F in January to 74.9 °F in July. PRISM Climate Group, Oregon State U The hardiness zones are 7b and 7a.
Adjacent counties
Nassau County borders the following counties:
- Fairfield County, Connecticut – north (maritime boundary)
- Queens County – west
- Suffolk County – east
- Westchester County – northwest (maritime boundary)
- Bronx County— northwest (maritime boundary)
Transportation
In July 2017, the approval was granted by state legislators to the plan proposed by New York Governor Andrew Cuomo to add a third railroad track to the Long Island Rail Road corridor between the communities of Floral Park and Hicksville in Nassau County. The nearly US$2 billion transportation infrastructure enhancement project was expected to accommodate anticipated growth in rail ridership and facilitate commutes between New York City and Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Island.
The Long Island Expressway, Northern State Parkway, and Southern State Parkway are the primary east–west controlled-access highways in Nassau County. Northern Boulevard (New York State Route 25A), Hillside Avenue (New York State Route 25B), Jericho Turnpike (New York State Route 25), New York State Route 24, and Sunrise Highway (New York State Route 27) are also major east–west commercial thoroughfares across the county. The Meadowbrook State Parkway, Wantagh State Parkway, and Seaford-Oyster Bay Expressway (New York State Route 135) are the major north–south controlled-access highways traversing Nassau County.
Nassau County also has a public bus network known as NICE (Nassau Inter-County Express, formerly MTA Long Island Bus) that operates routes throughout the county into Queens and Suffolk counties. 24 hour service is provided on the n4, n6, and most recently the n40/41 lines.
National protected areas
- Oyster Bay National Wildlife Refuge
- Sagamore Hill National Historic Site
- Lido Beach Wildlife Management Area, a part of the Long Island National Wildlife Refuge Complex