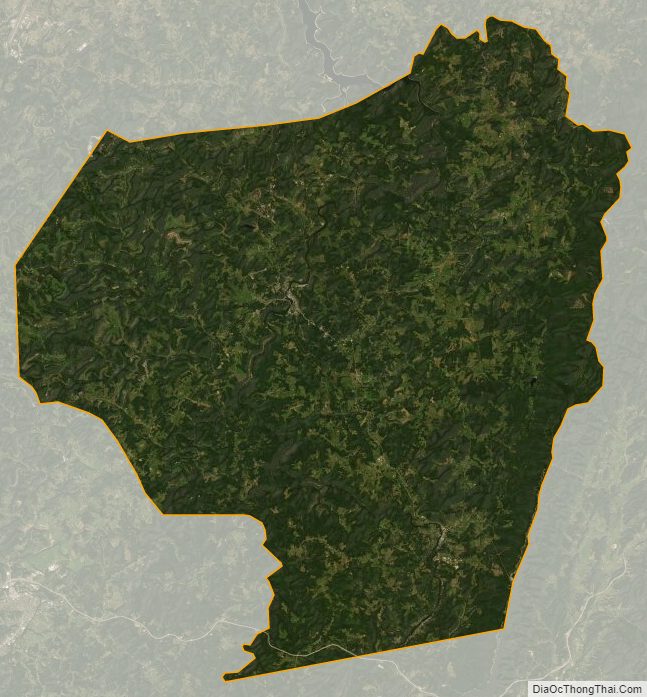
| Name: | Barbour County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 54-001 |
| State: | West Virginia |
| Founded: | March 3, 1843 |
| Named for: | Philip P. Barbour |
| Seat: | Philippi |
| Largest city: | Philippi |
| Total Area: | 342.85 sq mi (888.0 km²) |
| Land Area: | 341.06 sq mi (883.3 km²) |
| Total Population: | 15,465 |
| Population Density: | 45.34/sq mi (17.51/km²) |
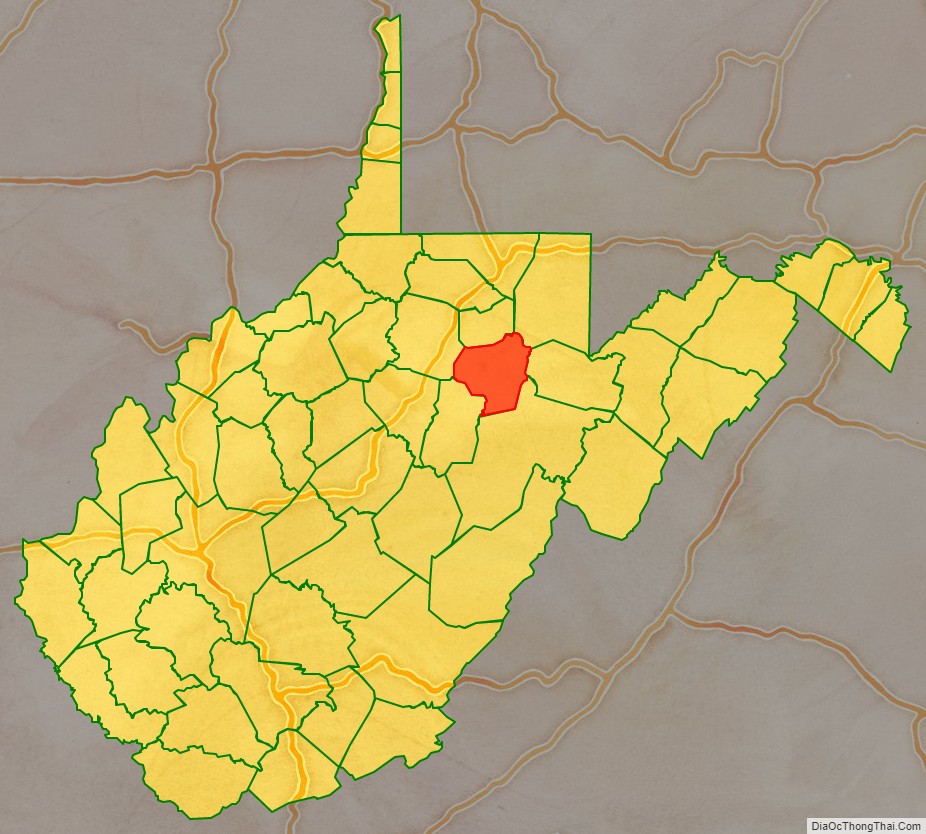
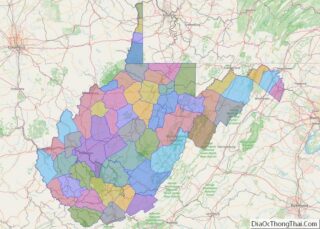
Barbour County location map. Where is Barbour County?
History
Settlement and formation
The first white settlement in present-day Barbour County was established in 1780 by Richard Talbott – along with his brother Cotteral and sister Charity – about three miles (5 km) downriver from the future site of Philippi. At this time the region was still a part of Monongalia County, Virginia. The region had had no permanent Indian settlements and so conflicts with Native Americans were relatively infrequent in the early days. Nevertheless, the Talbotts were obliged to leave their homestead several times for safety and twice found it necessary to retreat back east of the Alleghenies, returning each time. No member of this eventually large family was ever killed by Indian attacks.
Over time, parts of the future Barbour County were included in the newly created Harrison (1784), Randolph (1787), and Lewis (1816) Counties. Barbour County itself was created in 1843 and named for the late Virginia politician and jurist Philip P. Barbour (1783–1841). (Barbour had served as a U.S. Congressman from Virginia, Speaker of the House, and Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court.) The settlement of Philippi – formerly “Anglin’s Ford” and “Booth’s Ferry” – was platted, named, and made the county seat in the same year; it was chartered in 1844. By the 1850s, when a major covered bridge was constructed at Philippi to service travellers on the Beverly-Fairmont Turnpike, the county’s population was approaching 10,000 people.
The first newspaper in the county was the Barbour Jeffersonian, published starting in August 1857 and running only to about June 1861. It was put out by Thompson Surghnor (1820-1864).
Civil War
In April 1861, an Ordinance of Secession from the United States of America was approved throughout the state of Virginia in a referendum. Delegates from 25 western counties, however, assembled at Wheeling on 13 May for the first of a two meetings (see Wheeling Convention) called to repeal the Ordinance. The delegates from Barbour County for the first convention were Spencer Dayton, John H. Shuttleworth, and E.H. Manafee. Barbour County had voted in favor of Virginia’s secession, though, and a palmetto secession flag had been flying above the courthouse since January, 1861.
On 3 June 1861, Philippi was the scene of one of the first battles of the American Civil War. The battle was later lampooned as the “Philippi Races” because of the hurried retreat by the Confederate troops encamped in the town. (The skirmish is reenacted every June during the town’s “Blue and Gray Reunion”.) At daylight on June 3, two columns of Union forces under the command of Col. Benjamin Franklin Kelley and Col. Ebenezer Dumont, with perhaps 3,000 men, arrived from Grafton and attacked about 800 poorly armed Confederate recruits under the command of Col. George A. Porterfield. The Union troops had marched all night through a heavy rain storm to arrive just before daylight. The surprise attack awakened the sleeping Confederates. After firing a few shots at the advancing Union troops, the Southerners broke lines and began running frantically to the south, some still in their bed clothes.
The Union victory in a relatively bloodless battle propelled the young Major General George B. McClellan into the national spotlight, and he would soon be given command of all Union armies. The battle also inspired more vocal protests in the Western part of Virginia against secession. On 11 June, the second Wheeling Convention met in that city and Barbour County was again represented by Dayton and Shuttleworth, who were this time joined by N.H. Taft. The Convention nullified the Virginia Ordinance of Secession and named Francis H. Pierpont governor. These events would eventually result in the separate statehood of West Virginia.
Later history
The economy and infrastructure in Barbour grew steadily, but slowly, through the late 19th century. Although the first railroad had reached nearby Grafton in 1852, a narrow-gauge railroad was not laid through the county until the early 1880s; a standard gauge line followed in the 1890s.
In 1990, private developers offered Barbour County citizens $4M to $6M annually in host fees to accept out-of-state garbage into a County landfill over the following three decades. Up to 200,000 tons of garbage per month would be delivered. (At the time, the county’s annual budget was only about $1M.) County voters rejected the offer.
Registered Historic Places
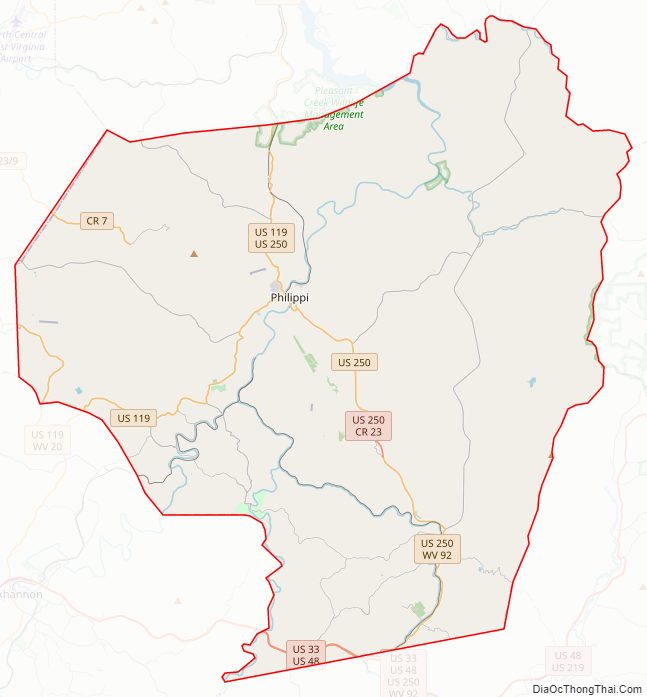
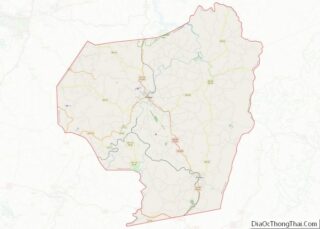
Barbour County Road Map
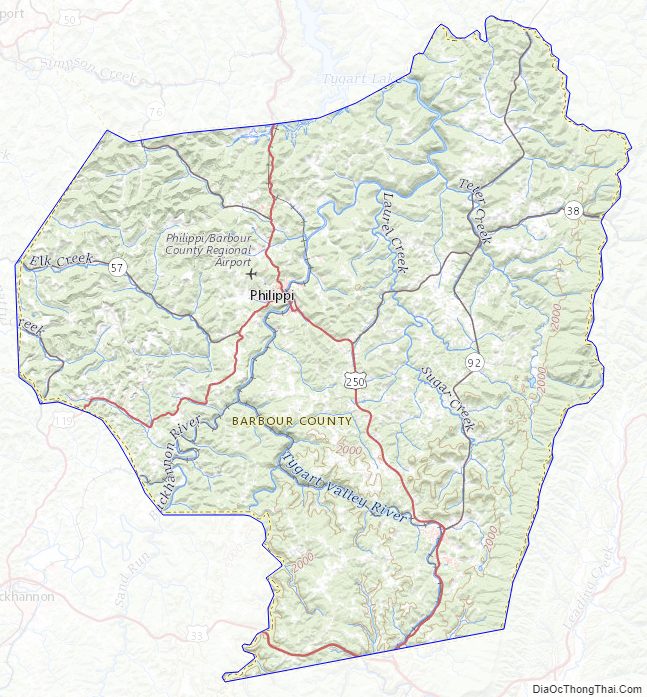
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 343 square miles (890 km), of which 341 square miles (880 km) is land and 1.8 square miles (4.7 km) (0.5%) is water.
Barbour County is situated on the Allegheny Plateau at the western edge of the Allegheny Mountains (represented by Laurel Mountain at the county’s eastern boundary). Most of the county is drained by the Tygart Valley River which traverses it from south to north and on which its three largest settlements – Philippi, Belington, and Junior – are sited. Tributaries of the Tygart in the County include Teter Creek, Laurel Creek, Hacker’s Creek, the Buckhannon River and the West Fork River. A portion of the County in the west drains into the Middle Fork River, principally through Elk Creek. Audra State Park – the county’s only state park – is situated on the Middle Fork in the southwest corner. Teter Creek Lake Wildlife Management Area – the county’s only WMA – is located on that stream and lake in the eastern portion. All of the mentioned streams are part of the greater Monongahela River watershed.