| Name: | West Carroll Parish |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 22-123 |
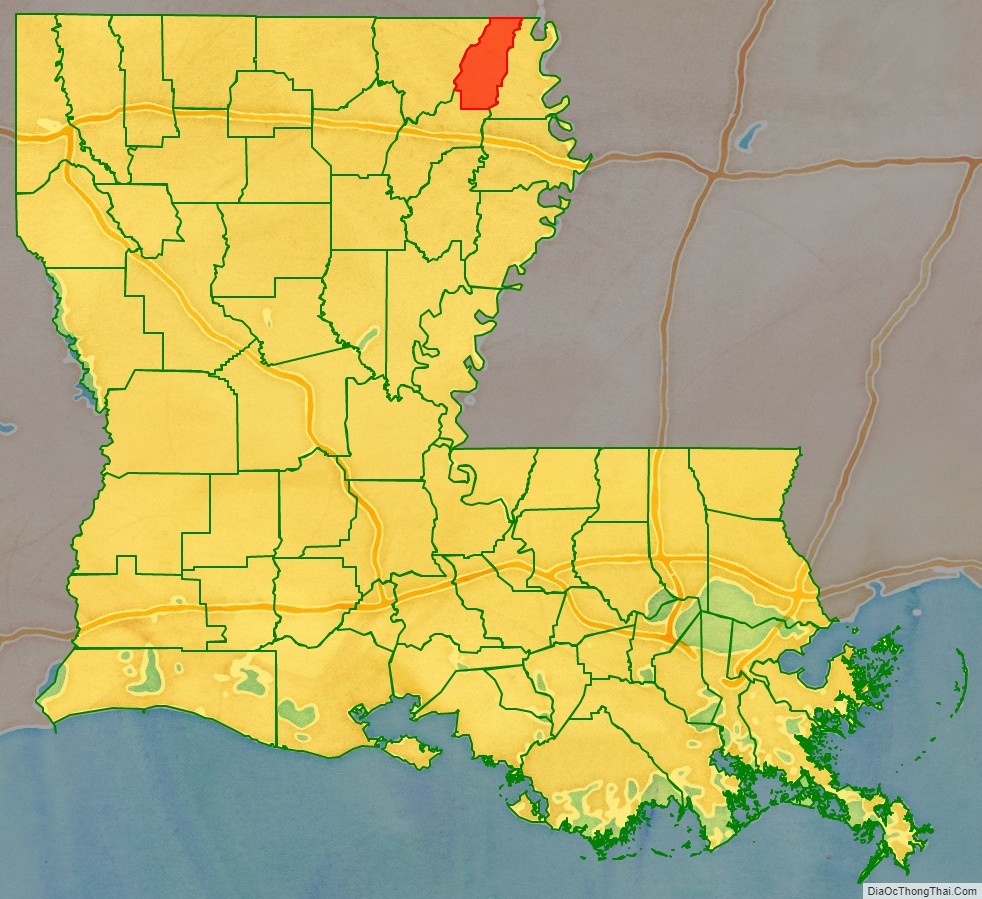
| State: | Louisiana |
| Founded: | March 26, 1877 |
| Named for: | Charles Carroll of Carrollton |
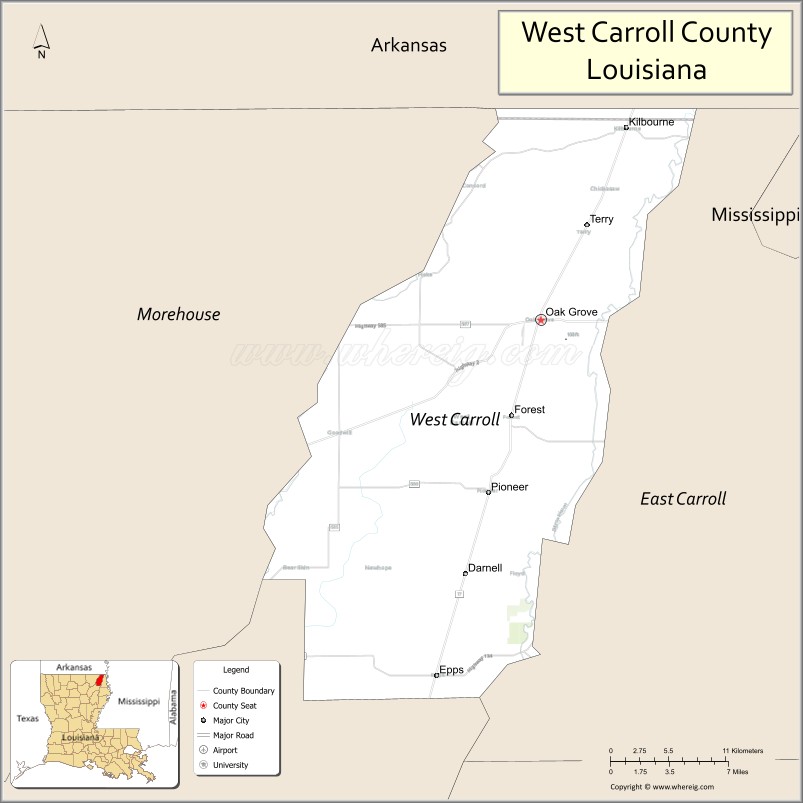
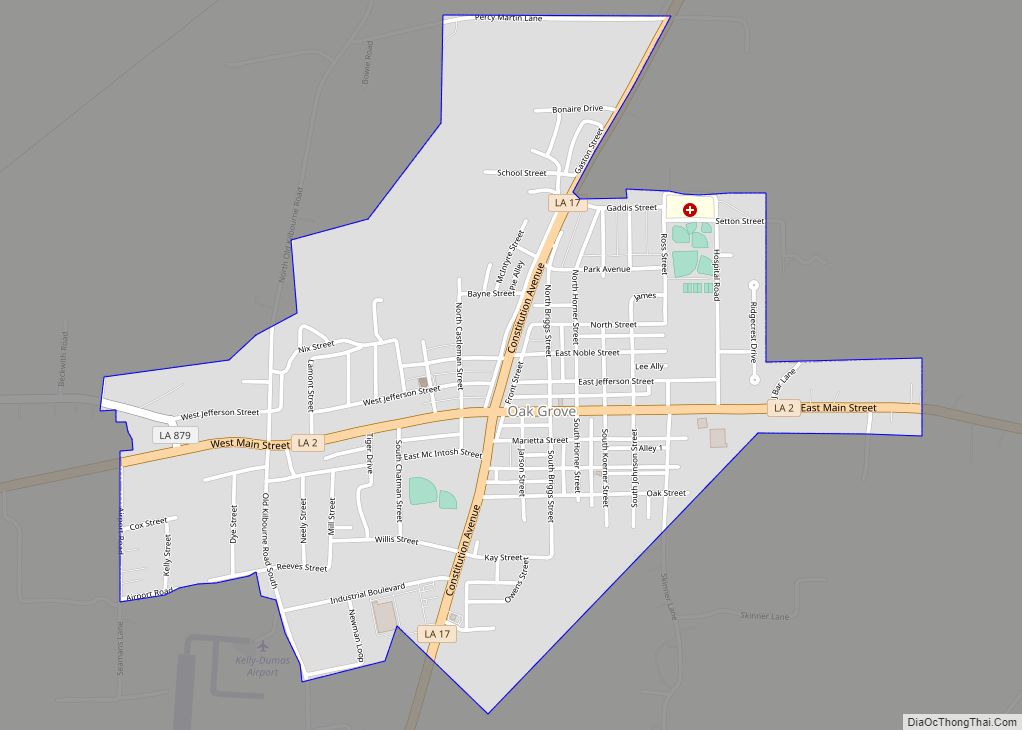
| Seat: | Oak Grove, West Carroll Parish |
| Largest town: | Oak Grove, West Carroll Parish |
| Total Area: | 361 sq mi (930 km²) |
| Land Area: | 360 sq mi (900 km²) |
| Total Population: | 9,751 |
| Population Density: | 27/sq mi (10/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
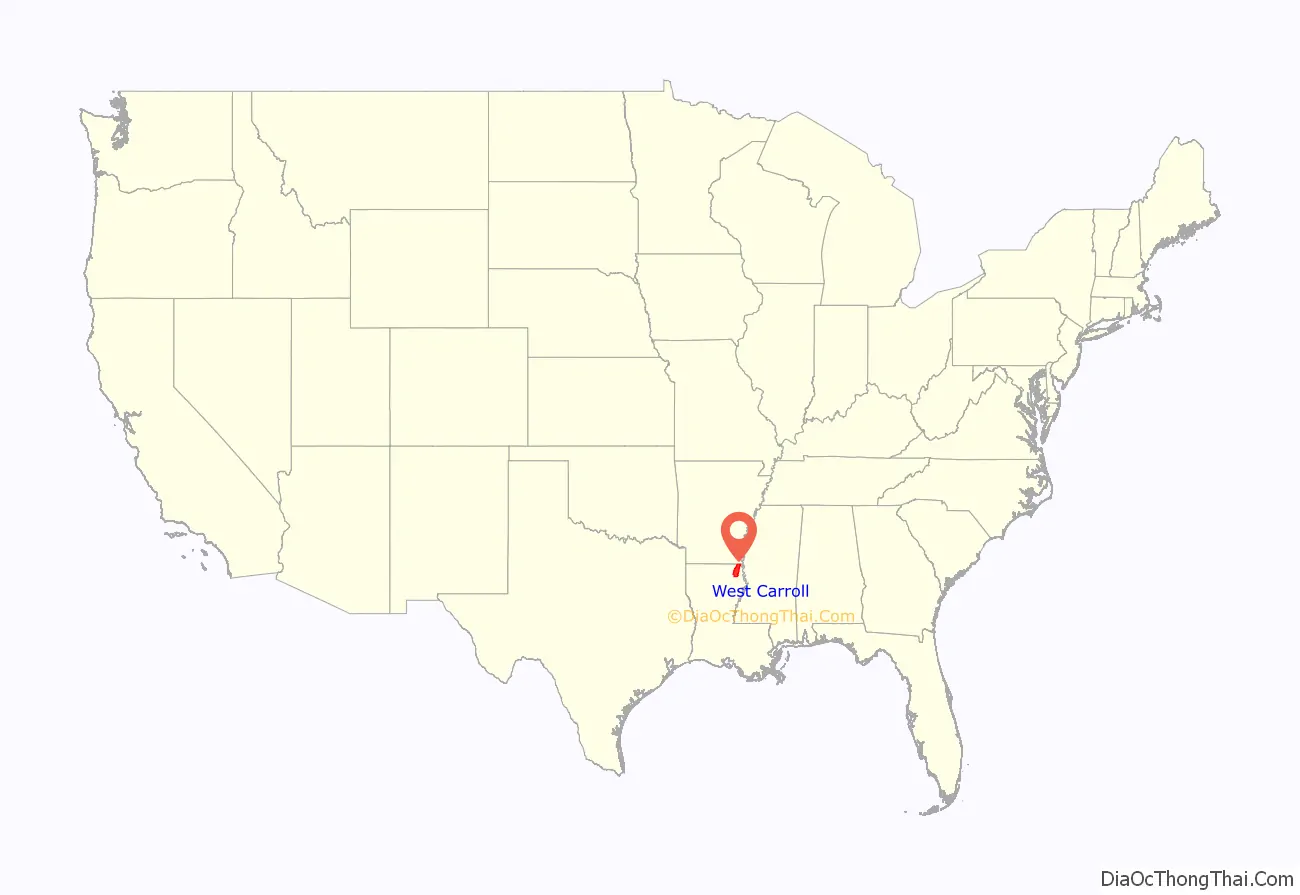
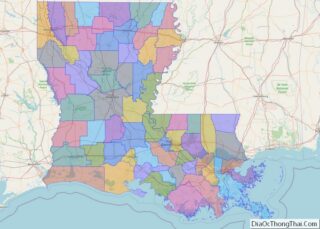
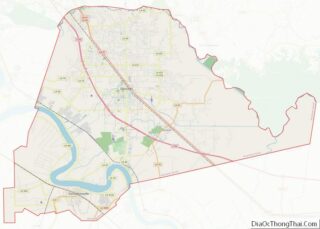
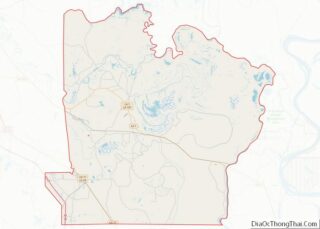
West Carroll Parish location map. Where is West Carroll Parish?
History
Before being divided, Carroll Parish was named for Charles Carroll of Carrollton, Maryland, the only Roman Catholic signer of the Declaration of Independence and the last surviving signer of the document. It was organized by European Americans after the Louisiana Purchase.
West Carroll Parish has a long history of inhabitants who predated the formation of the United States by thousands of years. On the south end of West Carroll Parish is Poverty Point, a nearly square-mile complex of ancient major earthwork semi-circles and radiating lanes, plus additional platform mounds. This is one of the largest Native American earthworks in North America. Archeologists have determined that the site was built in the Late Archaic period beginning about 1500 BCE, and it was the central trading grounds for the Poverty Point culture that occupied the lower Mississippi River Valley. It has been referred to as the New York City of more than two millennia ago. Artifacts show trading reached to present-day Georgia and Great Lakes states such as Wisconsin. Later historic tribes in the area included the Choctaw and Chickasaw.
Though the area was explored by many French and Spanish in the 16th through 18th centuries, they did not establish permanent settlements, favoring areas on rivers with more direct access to the Gulf and major markets.
US annexation and development
After the United States’ Louisiana Purchase of 1803, all of Northeast Louisiana was considered part of Ouachita Parish, including West Carroll. In 1807, a Methodist minister, Moses Floyd, settled on the west bank of the Bayou Macon. Later a trading post known as “Floyd” developed, and the village began to grow. It developed less than a mile from the Poverty Point site.
As the European-American population of Ouachita Parish continued to increase, the area was organized into smaller parishes; in 1832 Carroll Parish was carved out of Ouachita by the state legislature. This was in the period of Indian Removal, when most members of local tribes were moved to Indian Territory (now Oklahoma) to extinguish their land claims in Louisiana.
The parish seat was located in Lake Providence on the banks of the Mississippi River. Throughout the early part of the 19th century, the European-American population of the western portion of Carroll Parish continued to grow; its economy was based mainly on cotton production and timber. By 1855 the population had grown to the point where there were enough votes to move the parish seat west of the Bayou Macon and Floyd was selected. This area had developed into a thriving trading post due to steamboat traffic on the Macon. In 1856 construction began on the new courthouse, which was finished in late 1857.
With the move of the parish seat, more professionals and tradesmen settled in Floyd, and the town grew markedly. It developed as a typical frontier town with a hotel, post office, general store, and saloons.
In January 1861 the Louisiana Legislature voted to secede from the Union and declare itself a free and sovereign state. Less than two months later, Louisiana joined the Confederacy. According to the book, Between the Rivers, the war resulted in a divide that would eventually lead to the creation of West Carroll Parish:
(Note: This oath was required after Union forces occupied Louisiana.)
There was little fighting in this area associated with the Civil War. Union efforts were focused on trying to gain and maintain control of the Mississippi River, especially at Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Some historians believed that insurgent activity, such as the Quantrill Gang, which operated primarily in Missouri, replaced regular forces. This area was isolated and vast lowland swamps surrounded Floyd. Frank James was said to come through with Quantrill in the winter of 1863–1864, on their way to and from Texas. In the early 1870s during Reconstruction, Frank and his brother Jesse James continued their outlaw activities, robbing banks for personal gain from Missouri to Texas.
During the Reconstruction era, local leaders opposed those appointed by the federally appointed state government. Some people worked against the provision of rights to freedmen. In the 1870s, chapters of the White League developed throughout Louisiana, paramilitary groups that intimidated Republicans, suppressed voting by freedmen, and supported white Democrats returning to power in the state legislature.
Post-Reconstruction to present
Federal troops were withdrawn from the state in March 1877 as part of a federal compromise. Soon after white Democrats regained power in the state legislature, they approved the creation of West Carroll Parish, which had a majority-white population. Initially it had a population of 800 people and 200 families, both white and black. East Carroll Parish was majority black, as it had been the center of cotton plantation agriculture, dependent on the labor of numerous enslaved African Americans. After emancipation, they voted in support of the Republican Party.
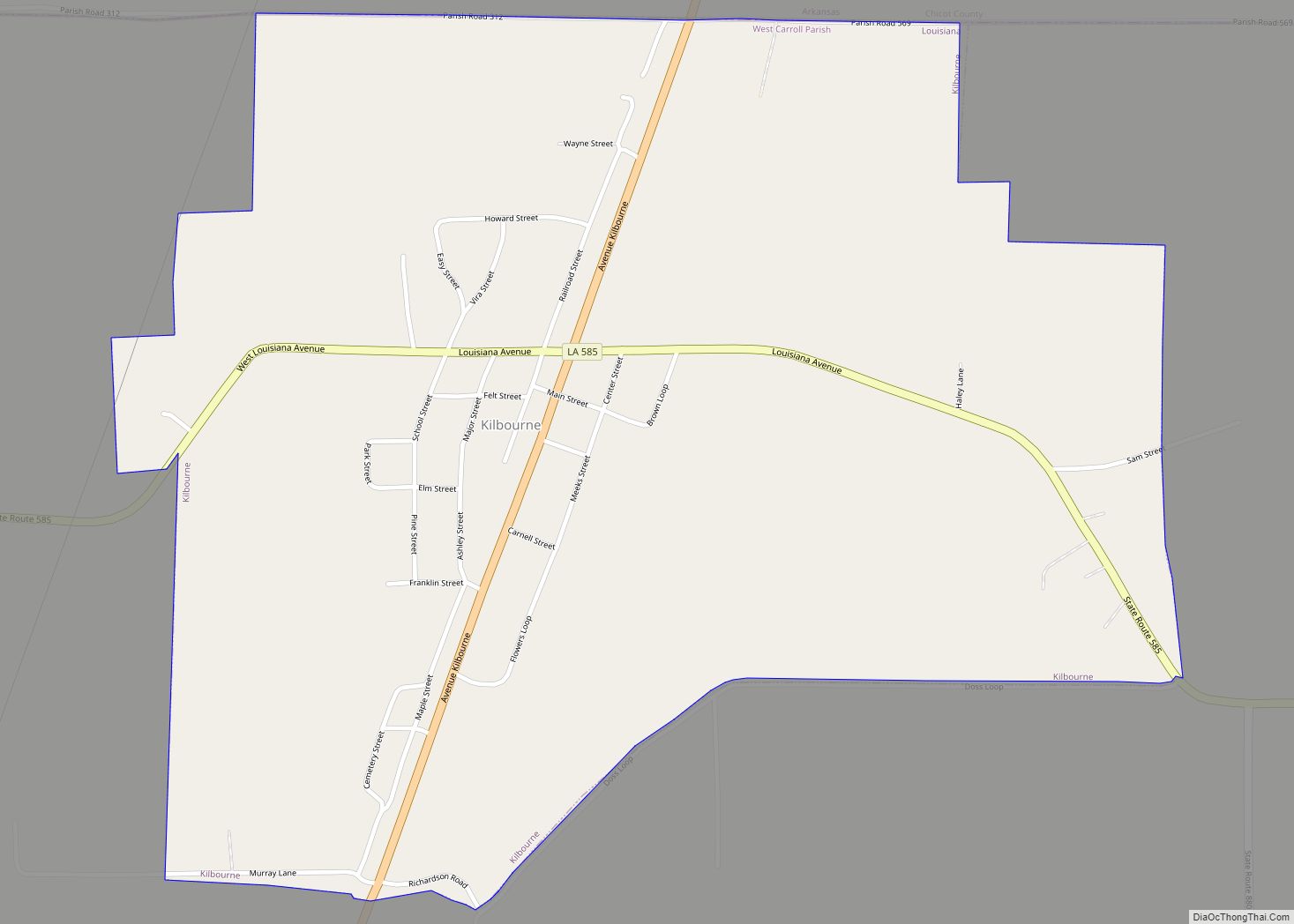
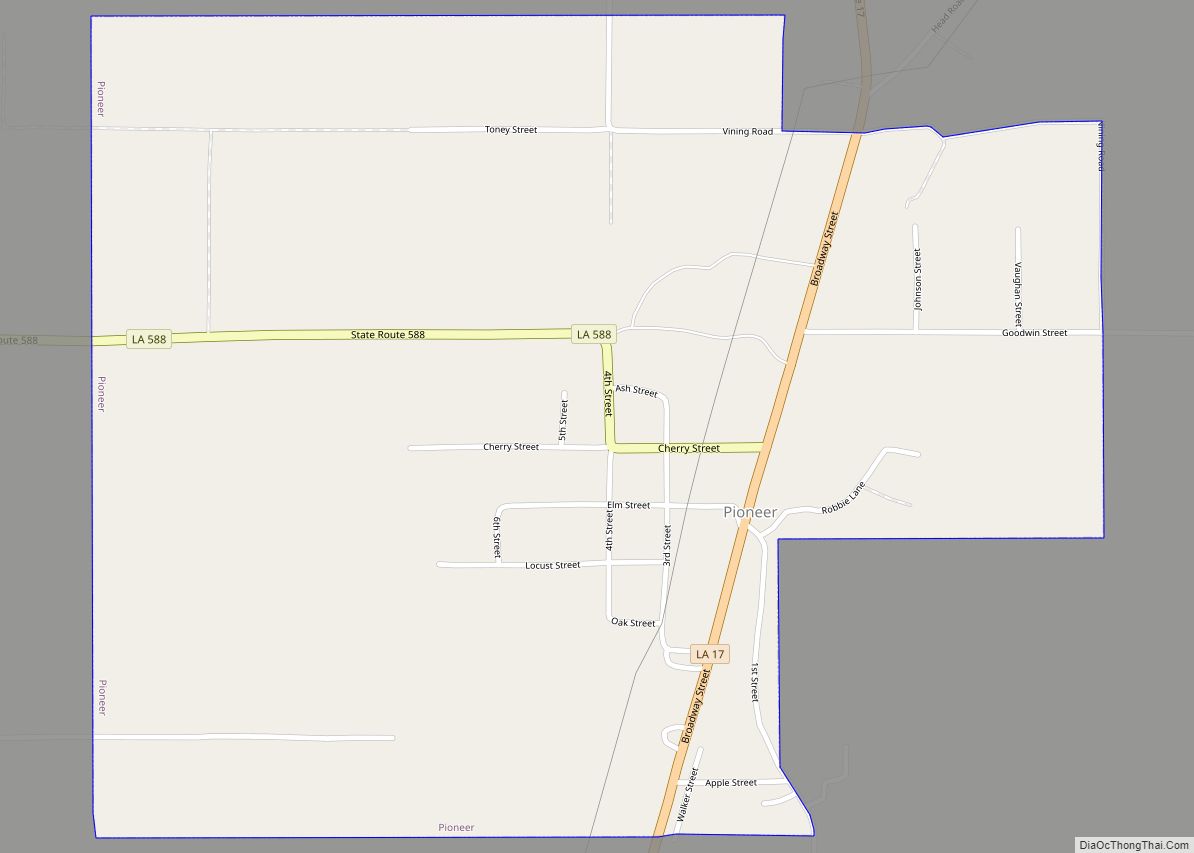
Cotton and timber continued to be the life-blood of the new parish, although areas dependent on agriculture in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century had economic difficulties. The parish had ten cotton gins and three sawmills, and steamboats continued to run Bayou Macon as the main hub of transportation. Steamboat traffic on the Boeuf and Macon rivers dwindled due to the competition of railways constructed through the South. With the railroad, parish towns began to develop along the north-south road (La. 17). Among these were Pioneer, Forest, Oak Grove and Kilbourne. Closest to the parish seat and with a major sawmill, Pioneer grew rapidly.
In January 1909, Oak Grove was incorporated. Many of the parish’s prominent citizens, such as Leopold Lipp, considered it as the intersection of the North-South and East-West (La. 2) roads. It was to become the economic center of the parish in the near future.
In 1915, an election was held to move the parish seat from Floyd to a town located on the railroad. The two towns competing for the honor were Oak Grove and Pioneer. With the largest population living in the south end of the parish, the people of Pioneer felt confident they would get the seat; but, the people of the north end of the parish gained the selection of Oak Grove by a small margin. With the parish seat moved, Pioneer began to decline.
In 1916, construction began on the new courthouse at Oak Grove. Before it was completed, a hail storm and tornado devastated the town late that year. It destroyed the first theater, a large majority of the new courthouse, and many other buildings in town. In January 1917 the new courthouse was opened, and so began of the modern era of Oak Grove. Its Main Street had businesses varying from general stores, drug stores, a modern theater, cafes, two banks and more.
The economy of the parish continued to be dominated by the timber and cotton industry. In the early part of the 20th century, Donald B. Fiske opened a state-of the art cotton gin and compress to complement his sawmill. It became one of the largest employers of the parish.
After World War II, the town and parish continued to prosper with new industry and business. In 1950, the most modern movie theatre in the South was opened by Fiske, and it is still in operation today. In this area, farmers began to cultivate sweet potatoes rather than cotton. The textile industry gradually moved out of southern mills to offshore locations out of the United States. A cannery was built along the railroad, and operated until near the end of the 20th century.
In the 1960s and 1970s, city growth continued, with the construction of a modern hospital and nursing home, and the Wells Lamont garment factory. In 1969 the entrepreneur Shelton Ruffin built a pre-manufactured pole barn for personal use. Its style and construction quickly gained in popularity around the region, thus spurring the formation of Ruffin Building Systems. It is now one of the largest manufacturers of metal buildings in the South and ships buildings internationally.
With the coming of the 1980s and the rise of the large department stores in malls, business on Main Street began to decline. But this historic district continues to remain vibrant with over 50 percent of its buildings occupied.
By the early 21st century, entertainment and retail shopping have become major parts of the economy in West Carroll. In 2004 the Thomas Jason Lingo Community Center opened with a 1,000-seat auditorium; it has many live events each year. The Fiske Theatre has been renovated and returned to regular operation as a first-run movie theatre. Both of these venues attract families from all over Northeast Louisiana and Southeast Arkansas to the parish for entertainment.
Today agriculture is still king in West Carroll; the main crops are corn, rice, cotton, and sweet potatoes. But the largest employers are West Carroll Health Systems, West Carroll School Board, Ruffin Building Systems, and Wal-Mart. West Carroll has five banking institutions to serve people’s financial needs.
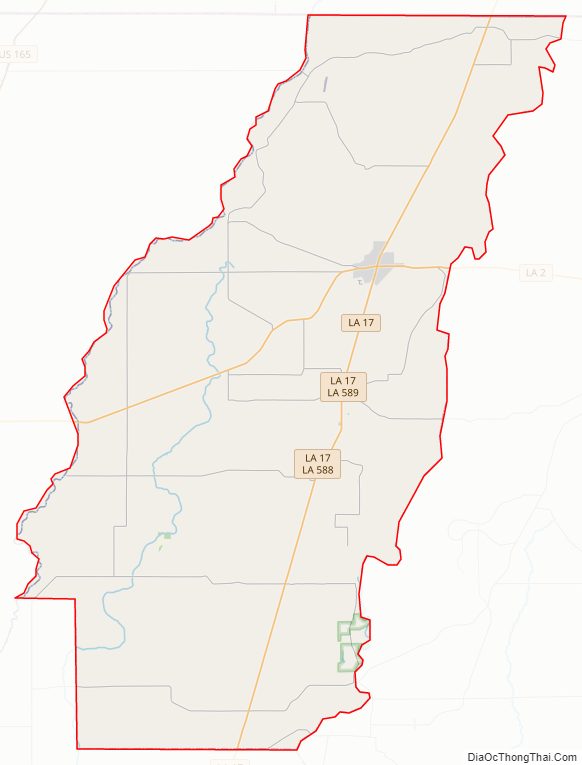
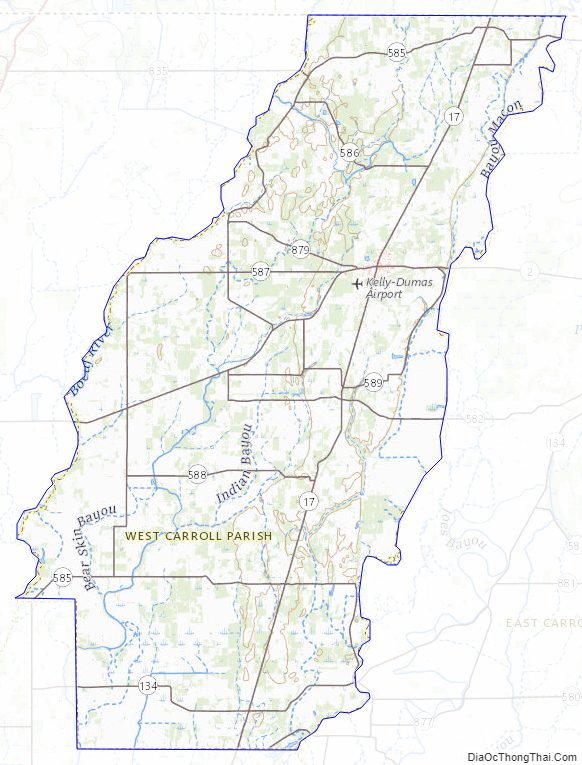
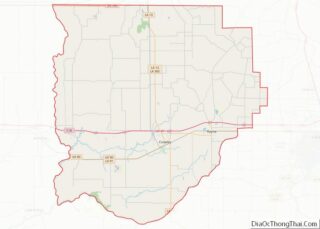
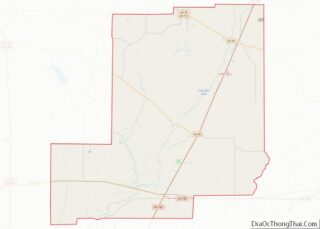
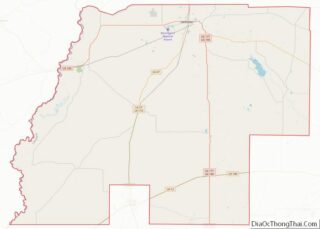
West Carroll Parish Road Map
Geography
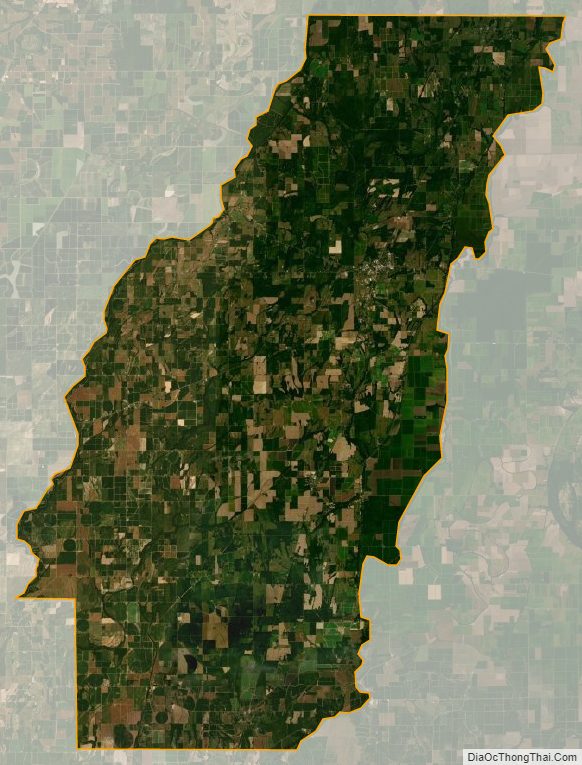
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the parish has a total area of 361 square miles (930 km), of which 360 square miles (930 km) is land and 0.9 square miles (2.3 km) (0.3%) is water.
Major highways
- Louisiana Highway 2
- Louisiana Highway 17
Adjacent counties and parishes
- Chicot County, Arkansas (north)
- East Carroll Parish (east)
- Richland Parish (south)
- Morehouse Parish (west)
National protected area
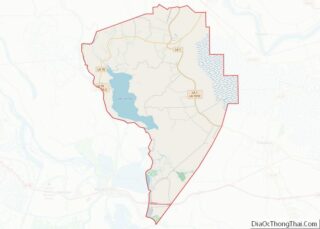
- Poverty Point National Monument