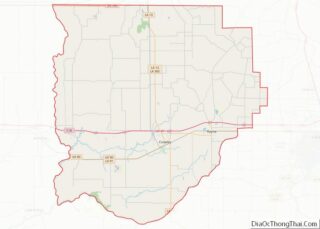
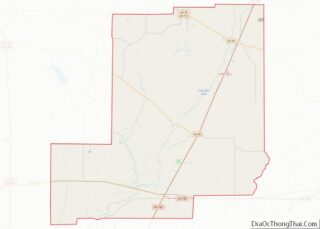
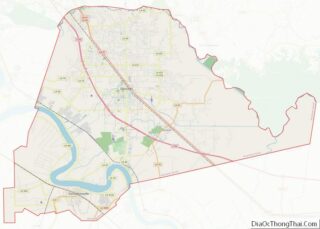
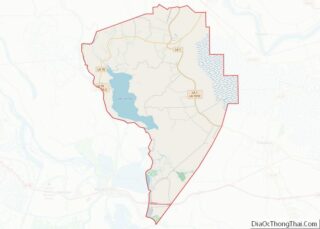
Avoyelles (French: Paroisse des Avoyelles) is a parish located in central eastern Louisiana on the Red River where it effectively becomes the Atchafalaya River and meets the Mississippi River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 39,693. The parish seat is Marksville. The parish was created in 1807, with the name deriving from the French name for the historic Avoyel people, one of the local Indian tribes at the time of European encounter.
Today the parish is the base of the federally recognized Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe, who have a reservation there. The tribe has a land-based gambling casino on their reservation. It is located in Marksville, the parish seat, which is partly within reservation land.
| Name: | Avoyelles Parish |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 22-009 |
| State: | Louisiana |
| Founded: | March 31, 1807 |
| Named for: | Avoyel Native Americans |
| Seat: | Marksville |
| Largest city: | Marksville |
| Total Area: | 866 sq mi (2,240 km²) |
| Land Area: | 832 sq mi (2,150 km²) |
| Total Population: | 39,693 |
| Population Density: | 46/sq mi (18/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | www.avoypj.org |
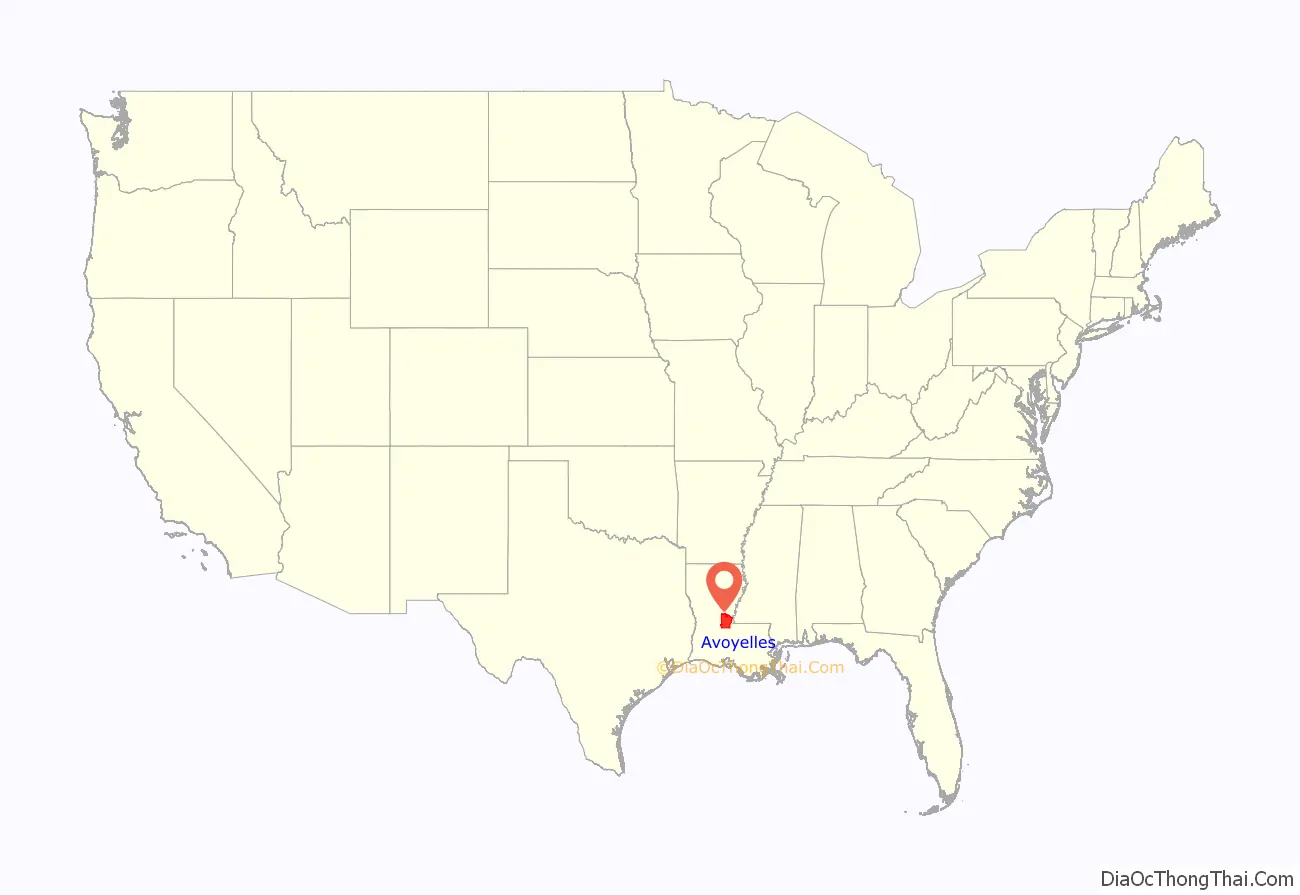
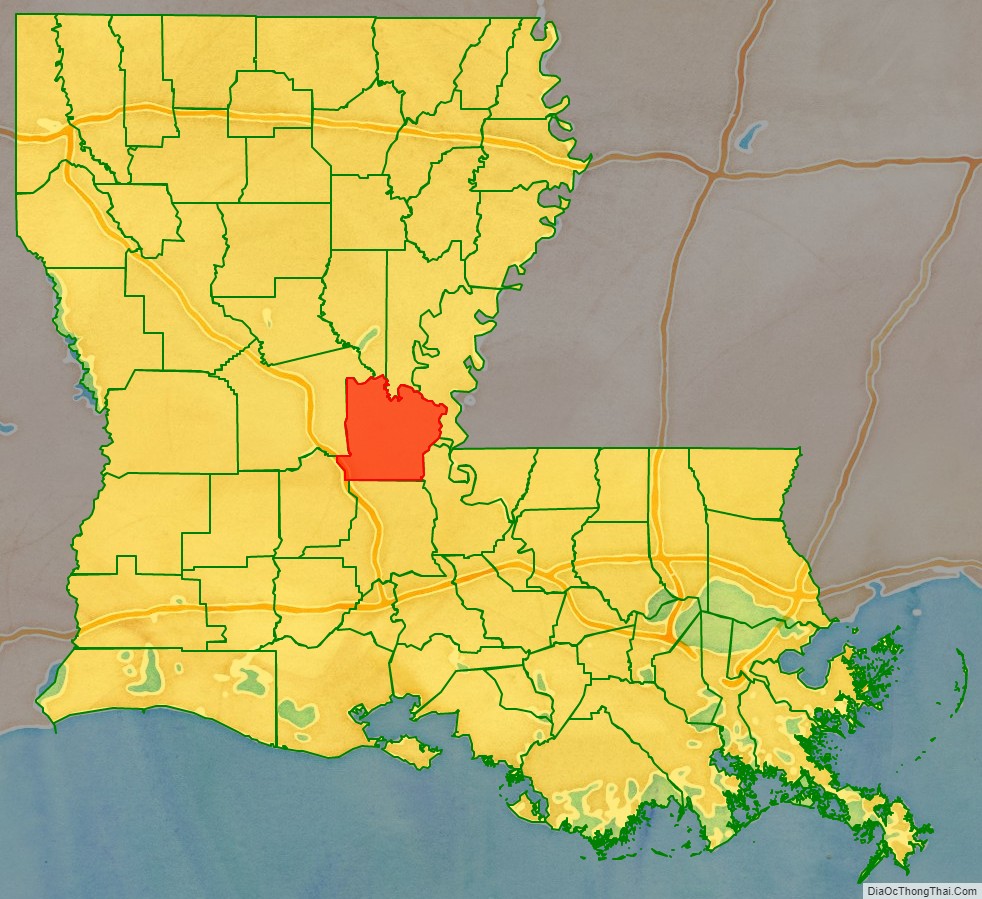
Avoyelles Parish location map. Where is Avoyelles Parish?
History
Native Americans occupied this area beginning around 300 BC. Varying indigenous cultures flourished there in the following centuries. Today on the banks of the old Mississippi River channel in Marksville, three large burial mounds have been preserved from the Mississippian culture, which flourished especially along the upper Mississippi, the Ohio River and other tributaries, from about 900 AD to 1500 AD. Mounds of its major city, Cahokia, are preserved in western Illinois across the Mississippi from St. Louis, Missouri. The trading network reached from the Gulf Coast to the Great Lakes. A museum and a National Park commemorate this early culture.
The Tunica people had bands whose territory extended into the central Mississippi Valley. They absorbed the smaller remnant of Avoyel people nearly two centuries ago. Through the years, they also intermarried with the more numerous Biloxi people. The peoples organized politically in the 20th century and were federally recognized in 1981 as the Tunica-Biloxi Indian Tribe. They are the largest Native American tribe in Avoyelles Parish and have a reservation that extends into Marksville. Descendants of other smaller tribes are also enrolled in this tribe.
Avoyelles Parish is known for its French colonial history and tradition of French language use. The contemporary Creole traditions, in both music and food, reflect European, African and Native American influences. While Avoyelles has a distinctive history of European immigrants, dominated by the French in its early history, it is considered the most northern of the 22 “Acadiana” parishes. These have a tradition of settlement by French-speaking refugees from Acadia (now eastern Canada) in the late 18th century. They contributed strongly to the development of culture in this area, as did Africans and the indigenous Native Americans. The parish is noted for its brand of Cajun/Creole style music and its gumbo, a popular soup with roots in the three major ethnicities noted above.
The central part of Avoyelles Parish is sited on a large plateau, slightly above the floodplain of the waterways. Travel by water was long the primary way to move around this area. The Indians used canoes, and the early French settlers developed their own boats, known as pirogues.
Records from the Catholic churches in Mansura and Marksville document the founding of a trading post and a Catholic school by French colonists. The merchants wanted to conduct fur trading with the Tunica Tribe and the missionaries hoped to convert the natives to Christianity. The trading post was built near the Avoyel/Tunica settlement; it was preserved until the mid-1960s. Historic roadside markers on LA 1 identify the site of the historic Catholic mission school.
Franco-European settlers first called this area Hydropolis, meaning water city, referring to the marshes and bayous. The major mode of transportation was by Indian canoe and pirogue (a French-style dug-out canoe). Church records identify settlers with all their family members listed, as well as some property; in some cases they listed slaves by name. Church records and documentation were recorded in French during the years of initial settlement, then in Spanish during their brief rule in the late 18th century, with a return to French after France reacquired the area under Napoleon Bonaparte in the early 19th century.
After his troops failed to regain control over Saint-Domingue (now Haiti), Napoleon withdrew from North America. He sold the large Louisiana Purchase territory in 1803 to the United States under President Thomas Jefferson. As the US expanded its rule, local documents began to be recorded in the English of the new government. The United States arranged for the Lewis and Clark Expedition and others to survey the Louisiana Territory. It hired local French soldiers, surveyors and doctors, many of whom eventually settled in the area.
Many of the French people who settled Avoyelles Parish immigrated from France in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Many of the French words commonly used today in the parish date to terms used during the Napoleon period in France, indicating that this was the period of immigration. They have not been used in France for many generations.
The Spanish influence in Louisiana was more dominant in New Iberia — this was named after colonists from the Iberian Peninsula, commonly known as Spain and Portugal. There are no Spanish surnames in Avoyelles. A few families from French Canada (Quebec) settled in Avoyelles. They were from a different geographic area of Canada than the Acadians of present-day Nova Scotia, who were expelled by the British from their homeland (Acadie) beginning in 1755 during the Seven Years’ War with France. Many deported Acadians eventually made it to Louisiana from 1764 – 1788, after several years of living in exile along the eastern Atlantic seaboard, Canada, St. Pierre and France.
In the later 19th century, immigrants from Scotland, Belgium, Italy, and Germany also settled here, following the French Creoles. Together they established today’s towns and villages. Their direct ties to Europe set them apart from the Acadians (Cajuns) of southern Louisiana, who came from a culture established for generations in Canada. At the turn of the 19th century, free people of color of African-French descent also settled in Avoyelles. Many came from New Orleans, which had a large community of free people of color. Others were refugees from Saint-Domingue, where slaves had rebelled to gain independence as the nation of Haiti. Others came from other colonies in the French West Indies.
The blending of these three cultures: Native American, European and African, created a distinct Louisiana Creole culture noted in the local language, food, Catholic religion, and family ties.
In the 21st century, the Avoyelles Parish culture has been classified as “Cajun” because of the perceived similarities in speech, food, and various folk traditions with the more southern Acadian parishes. But, few families in Avoyelles are of Acadian descent. From the 1800s until the mid 1900s, local Confederate units and local newspaper reports in The Villager always referred to the Avoyelles French families as Creoles, the term for native-born people of direct descent from early French colonists and born in the colony.
In 1906, V.L. Roy served as education superintendent in both Avoyelles and Lafayette parishes. In 1908, he helped with the founding of the Corn Club, later known as the Louisiana 4-H Club.
Following the disastrous Great Flood of 1927, the US Army Corps of Engineers built a system of levees along the Mississippi River. It reduced immediate flooding in Marksville and other towns, but has caused indirect damage to the wetlands. This has ultimately caused more serious flooding as the speed of the river has increased.
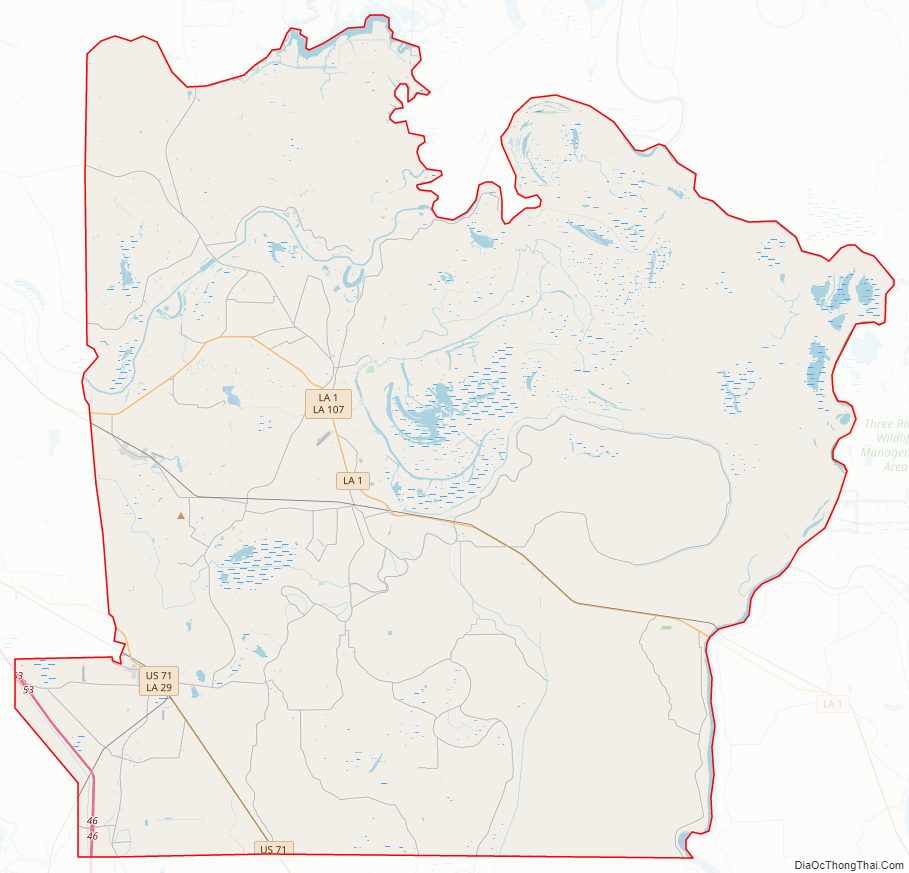
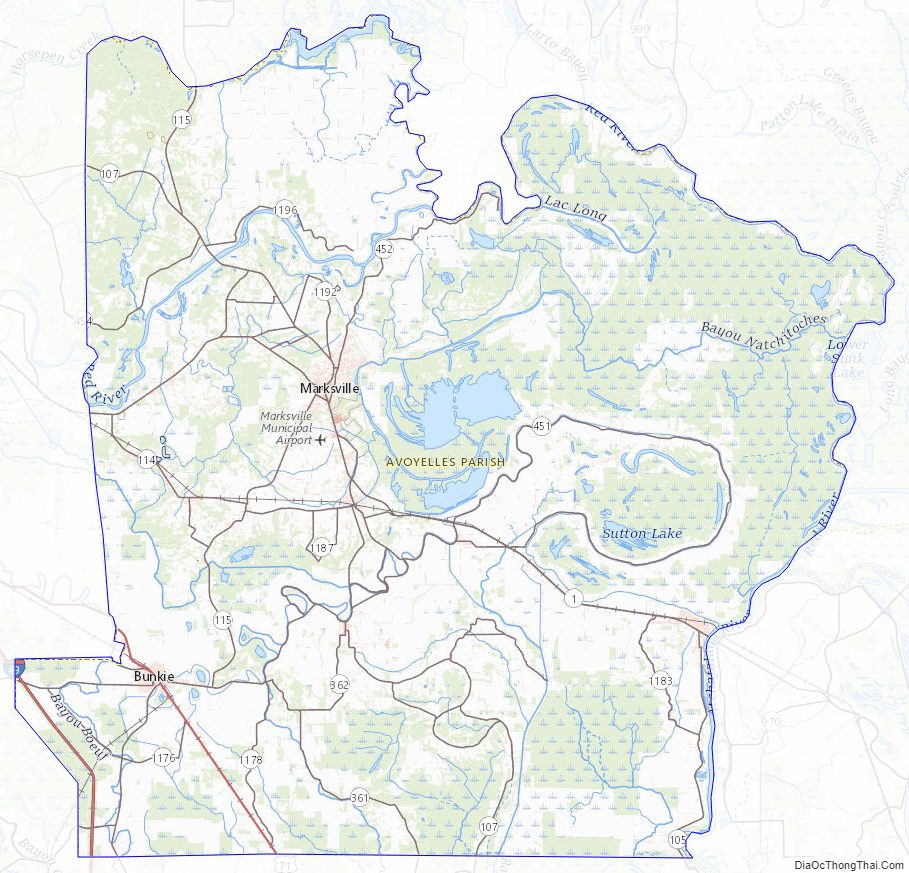
Avoyelles Parish Road Map
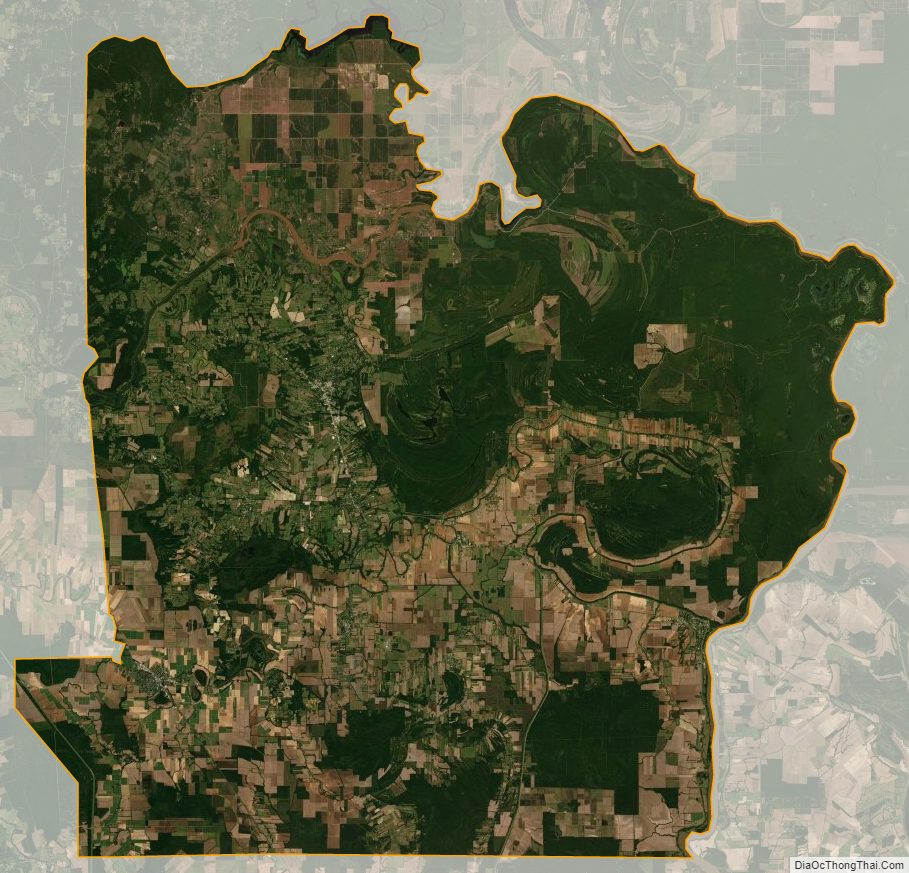
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the parish has a total area of 866 square miles (2,240 km), of which 832 square miles (2,150 km) is land and 33 square miles (85 km) (3.8%) is water. The parish is bounded on the east by what was just the Red River in the first millennium CE, and is now the Red River and Atchafalaya River. The formation of the Atchafalaya River happened when the Mississippi River changed course, breaking up the Red River. In the 20th century the Old River Control Structure was built at this area to control the flow of the three rivers.
Major highways
- Interstate 49
- U.S. Highway 71
- Louisiana Highway 1
- Louisiana Highway 29
- Louisiana Highway 107
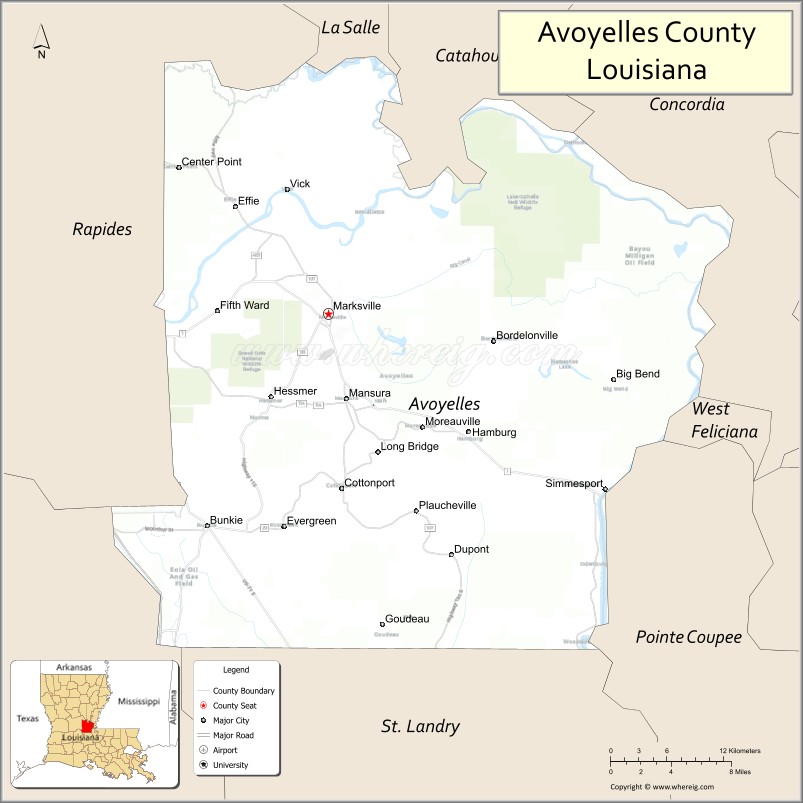
Adjacent parishes
- La Salle Parish (north)
- Catahoula Parish (north)
- Concordia Parish (northeast)
- West Feliciana Parish (east)
- Pointe Coupee Parish (southeast)
- St. Landry Parish (south)
- Evangeline Parish (southwest)
- Rapides Parish (west)
National protected areas
- Grand Cote National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Lake Ophelia National Wildlife Refuge