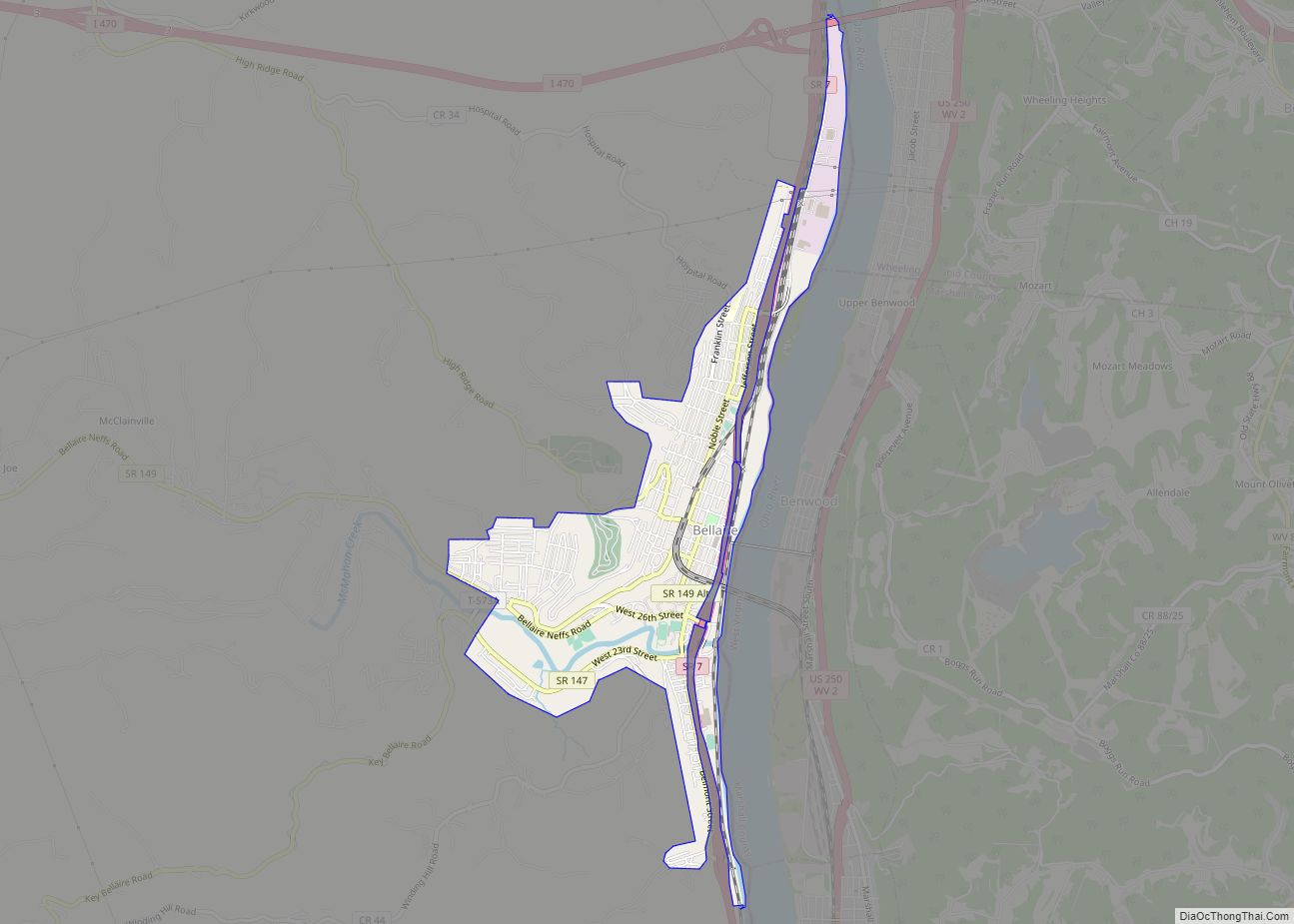
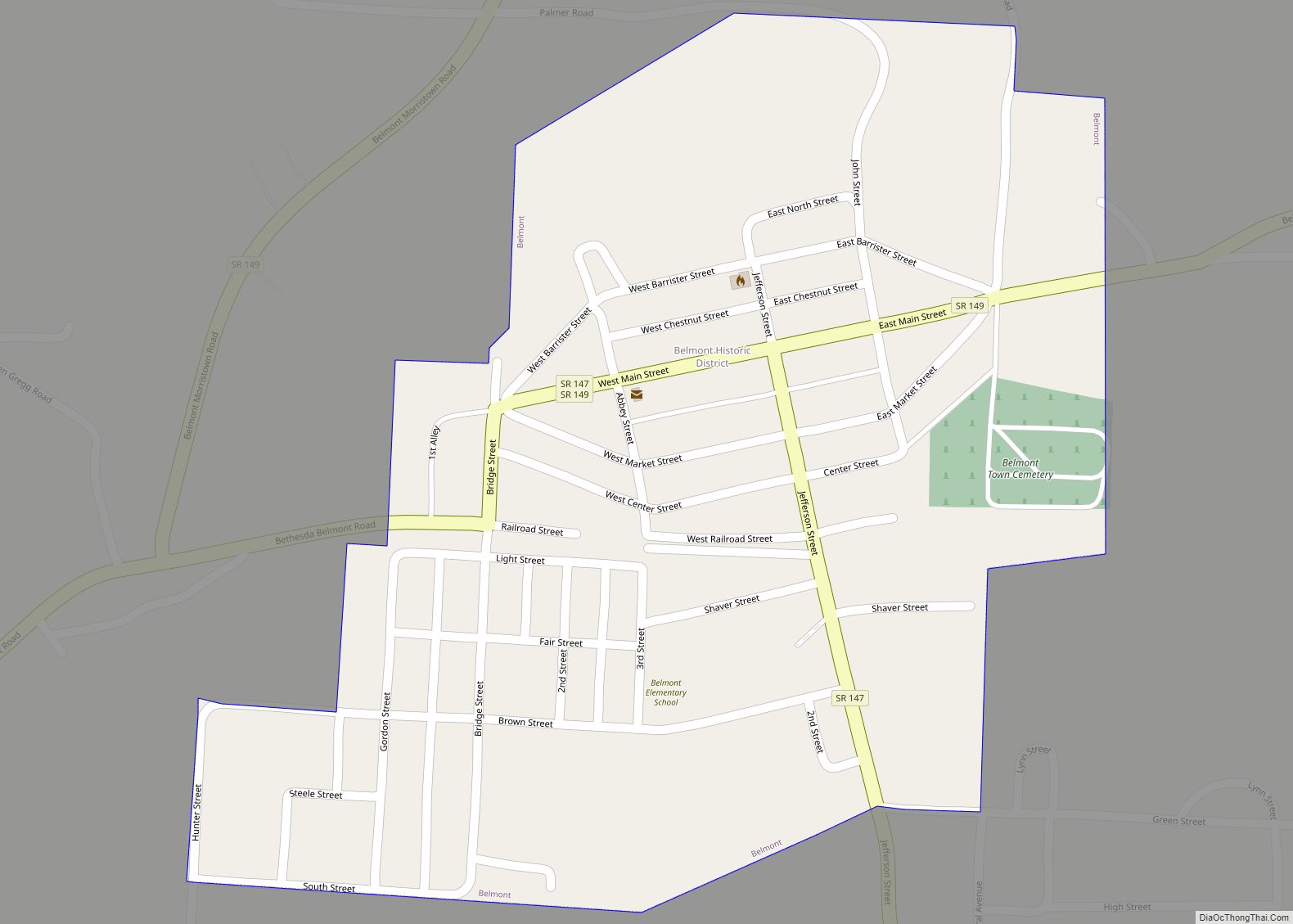
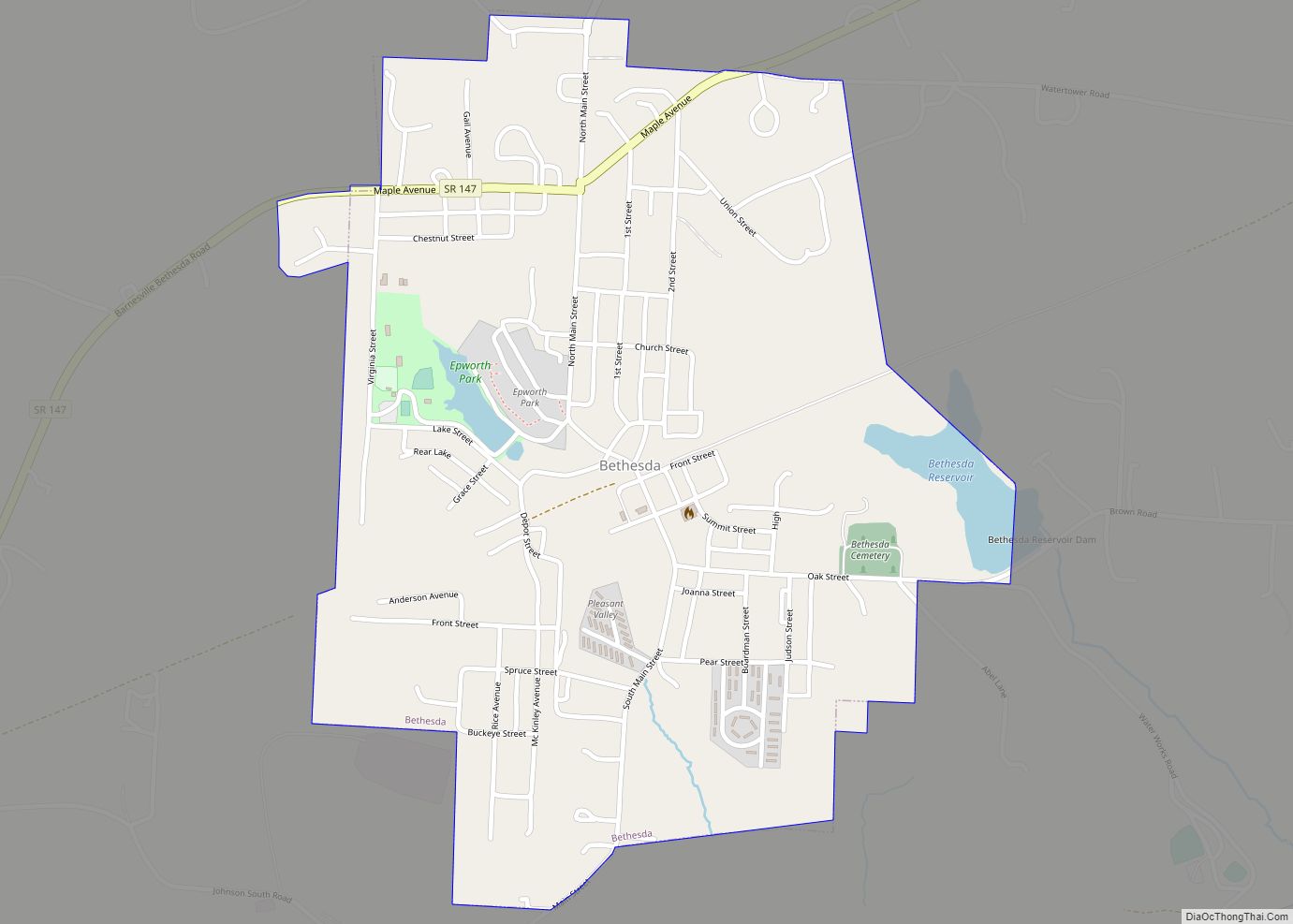
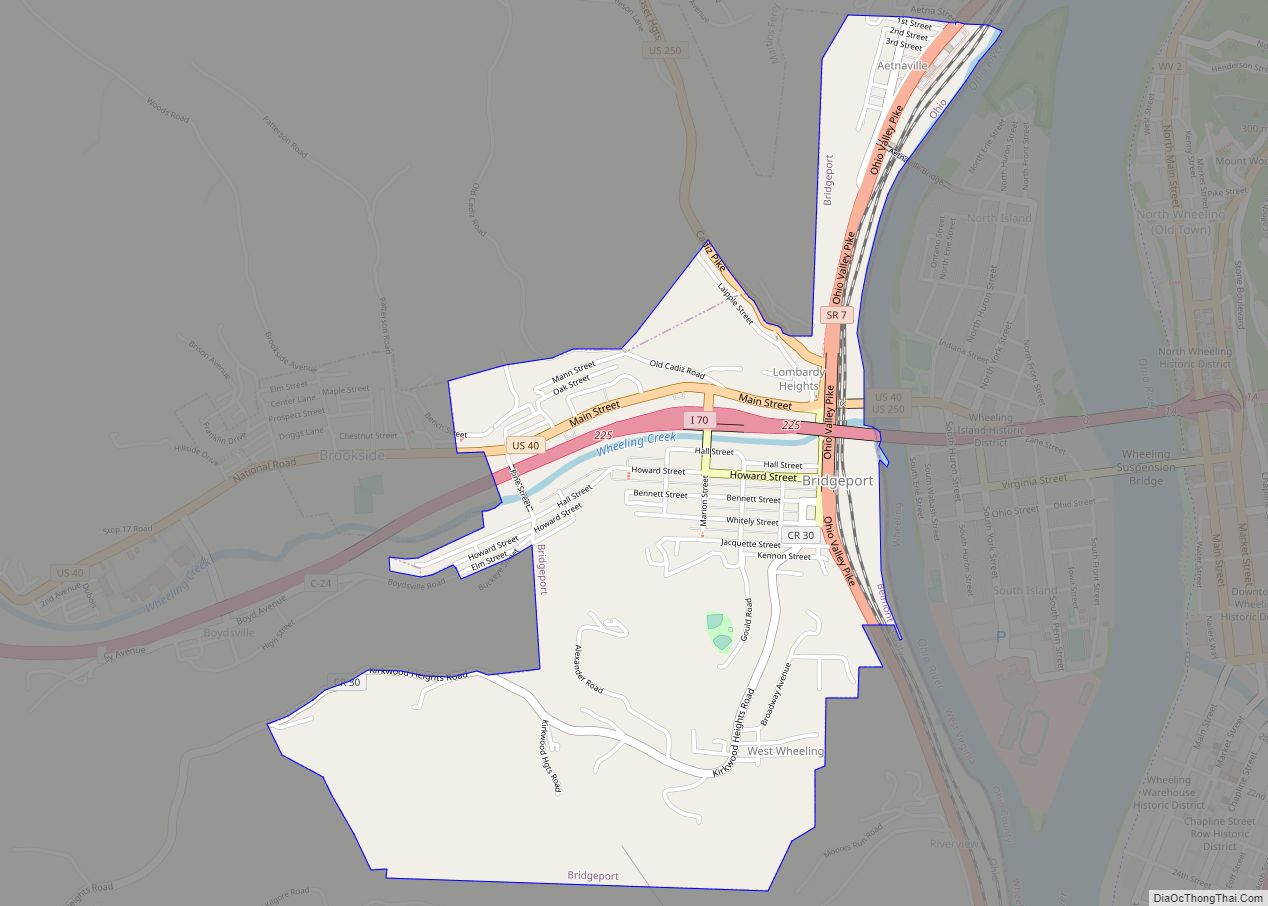
Belmont County is a county in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 66,497. Its county seat is St. Clairsville, while its largest city is Martins Ferry. The county was created on September 7, 1801, and organized on November 7, 1801. It takes its name from the French for “beautiful mountain”.
Belmont County is part of the Wheeling, West Virginia metropolitan area.
| Name: | Belmont County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 39-013 |
| State: | Ohio |
| Founded: | 1801 |
| Named for: | “beautiful mountain” in French |
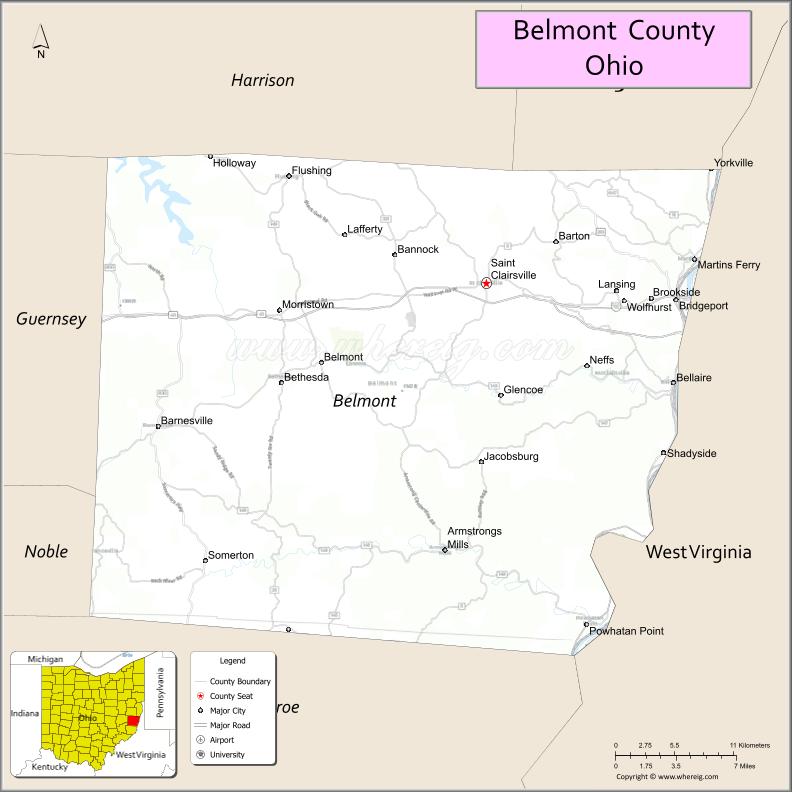
| Seat: | St. Clairsville |
| Largest city: | Martins Ferry |
| Total Area: | 541.27 sq mi (1,401.9 km²) |
| Land Area: | 532.13 sq mi (1,378.2 km²) |
| Total Population: | 66,497 |
| Population Density: | 120/sq mi (50/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Website: | www.belmontcountyohio.org |
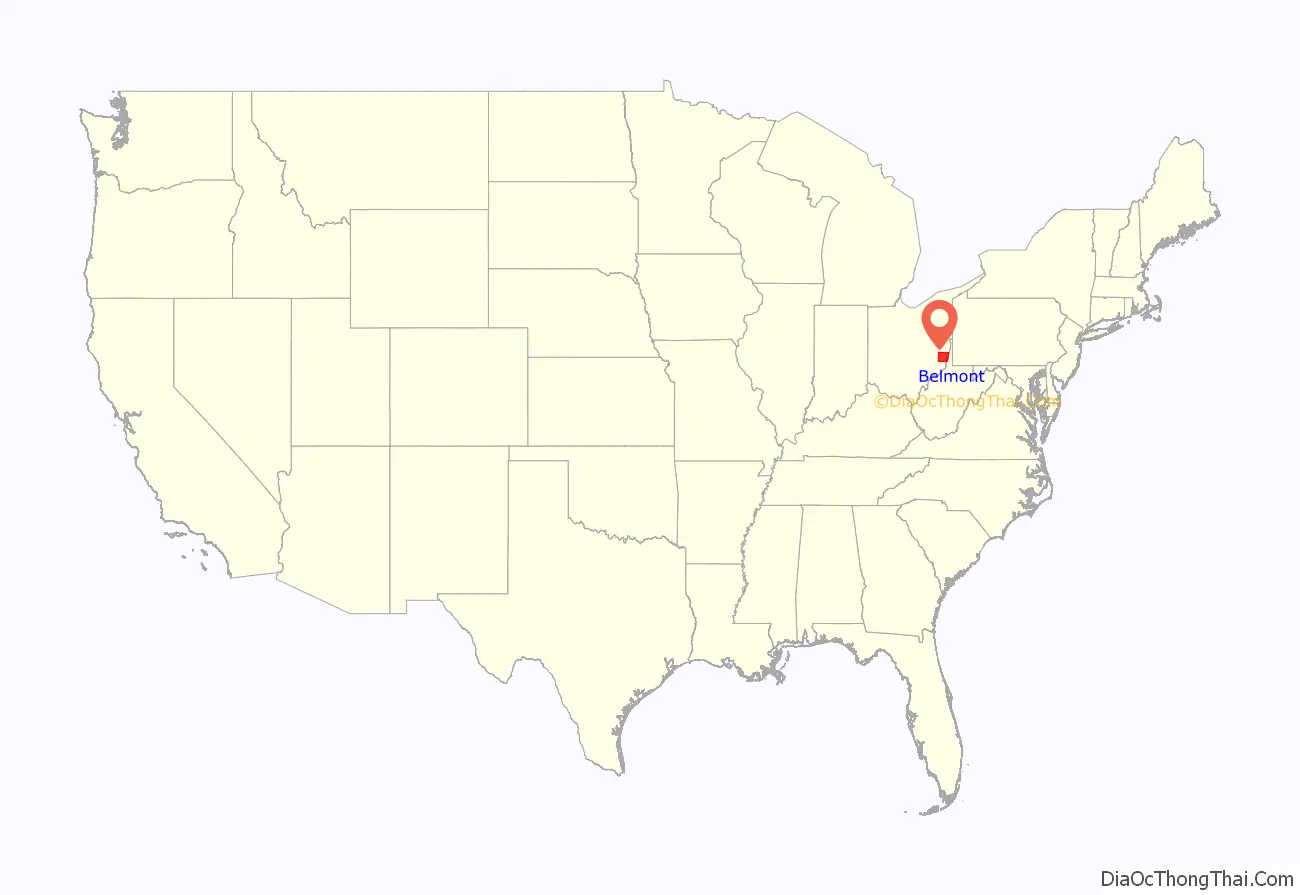
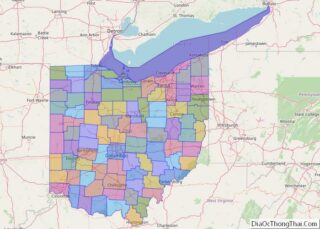
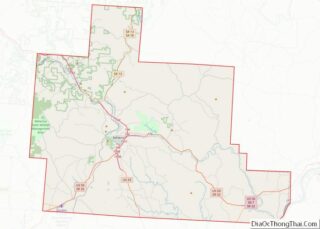
Belmont County location map. Where is Belmont County?
History
Dille, Ohio, also known as Dilles Bottom, was located across the Ohio River from Moundsville, West Virginia. It was founded by the sons of David Dille (b. 1718) around 1790 and was initially a fort called Fort Dille.
Belmont County was authorized in September 1801 by the Northwest Territorial legislature, with area partitioned from Jefferson and Washington counties. The county would be organized two months later. Its area was reduced in 1810 when area was ceded for the formation of Guernsey County and again in 1813 for the formation of Monroe County. It has retained its boundaries unchanged since 1813. Saint Clairsville was named as the county seat in 1815.
Belmont is the French toponym meaning “beautiful mountain”. Settlers migrating westward followed Zane’s Trace through the county. Later, the National Road was built through the county.
Quakers were among the county’s first settlers. Many of these people would become outspoken critics of slavery, including famous abolitionist Benjamin Lundy.
2018 blowout and methane leak
In February 2018, an explosion and blowout in a natural gas well owned by XTO Energy was detected by the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite’s Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument.
About 30 homes were evacuated near the gas well in York Township, and brine and produced water were discharged into streams flowing into the Ohio River.
The blowout lasted 20 days, releasing more than 50,000 tons of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. The blowout leaked more methane than is discharged by most European nations in a year from their oil and gas industries.
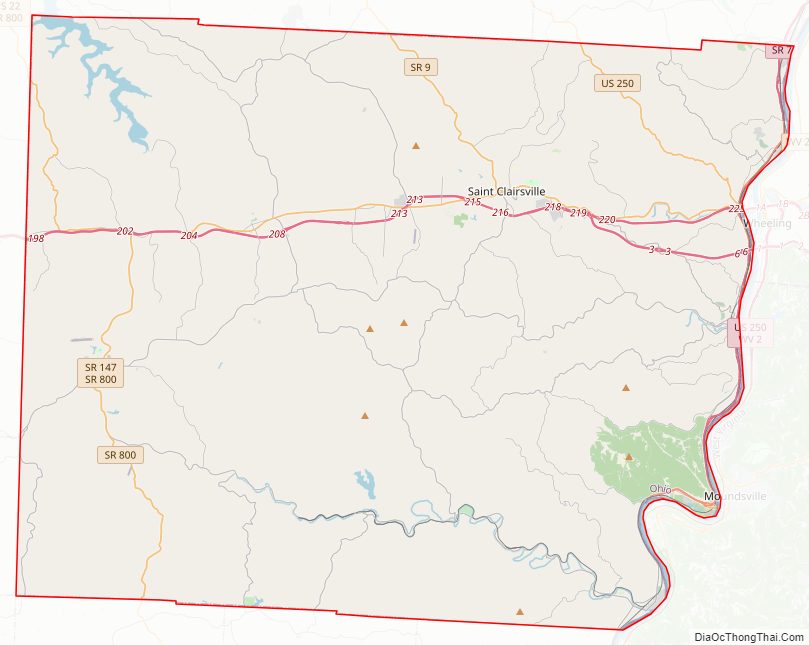
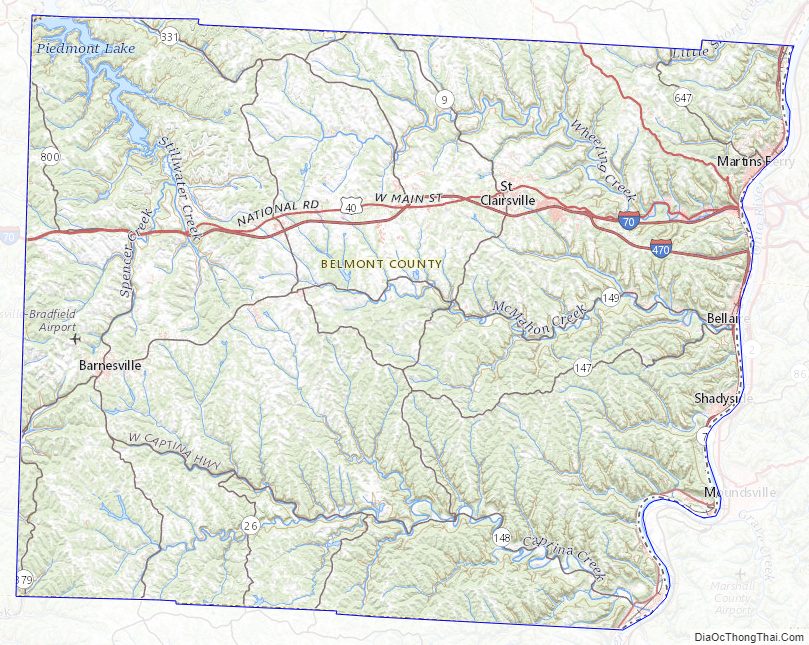
Belmont County Road Map
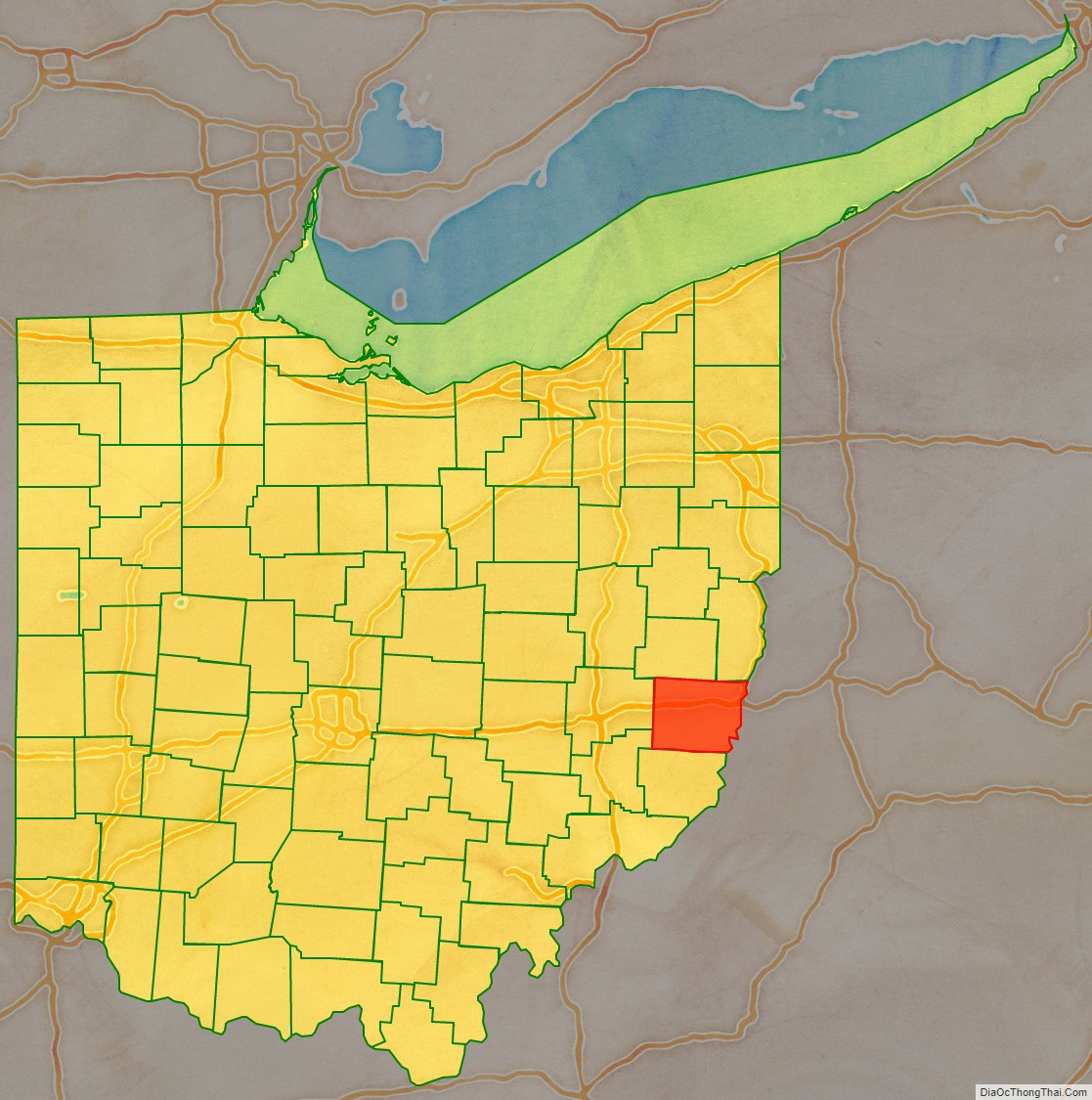
Geography
Belmont County lies on the east side of Ohio. Its east border abuts the west border of West Virginia (across the Ohio River). The Ohio flows southward along the county’s east line. Captina Creek flows eastward through the lower part of the county, discharging into the Ohio at Powhatan Point, and McMahon Creek also flows eastward through the center of the county, discharging into the Ohio at Bellaire. The county terrain consists of low rolling hills, etched with drainages. All available area is devoted to agriculture. The terrain slopes to the east, with its highest point, Galloway Knob (1,396′ or 426m ASL) at 1.2 mile (2 km) southeast of Lamira. The county has a total area of 541.27 sqmi (1492 km), of which 532.13 sqmi (1378 km) is land and 9.14 sqmi (23.69 km) (1.7%) is water.
Adjacent counties
- Harrison County – north
- Jefferson County – northeast
- Ohio County, West Virginia – east
- Marshall County, West Virginia – southeast
- Monroe County – south
- Noble County – southwest
- Guernsey County – west
Major highways
- I-70
- I-470
- US 40
- US 250
- SR 7
- SR 9
- SR 26
- SR 145
- SR 147
- SR 148
- SR 149
- SR 331
- SR 800
- SR 872
Protected areas
- Barkcamp State Park
- Dysart Woods Natural Monument
- Egypt Valley Wildlife Area
Lakes
- Barnesville Lake
- Barnesville Reservoir #3
- Belmont Lake
- Piedmont Lake (part)