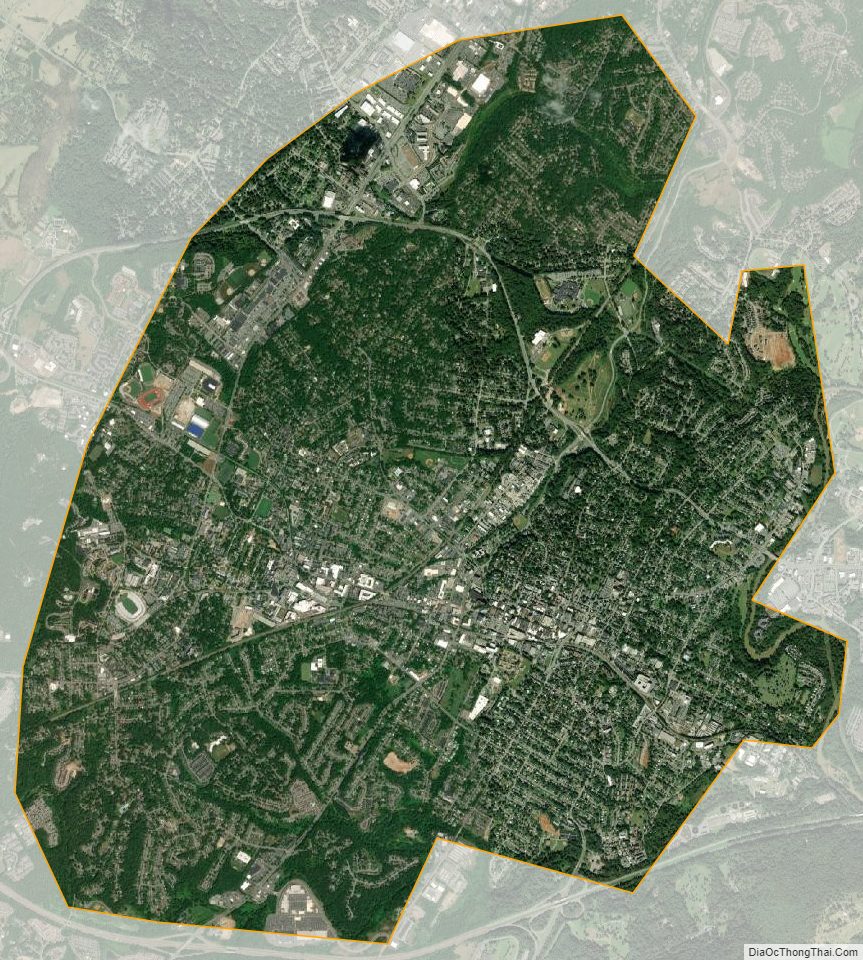
Charlottesville, colloquially known as C’ville, is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. It is the county seat of Albemarle County, which surrounds the city, though the two are separate legal entities. It is named after Queen Charlotte, wife of George III. At the 2020 census, the population was 46,553. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the City of Charlottesville with Albemarle County for statistical purposes, bringing its population to approximately 150,000. Charlottesville is the heart of the Charlottesville metropolitan area, which includes Albemarle, Buckingham, Fluvanna, Greene, and Nelson counties.
Charlottesville was the home of two presidents, Thomas Jefferson and James Monroe. During their terms as Governor of Virginia, they lived in Charlottesville, and traveled to and from Richmond, along the 71-mile (114 km) historic Three Notch’d Road. Orange, located 26 miles (42 km) northeast of the city, was the hometown of President James Madison. The University of Virginia, founded by Jefferson, straddles the city’s southwestern border. Jefferson’s home, Monticello, 3 miles (5 km) southeast of the city, is, along with the University of Virginia, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, attracting thousands of tourists every year.
Charlottesville is consistently ranked by national publications as one of the best places to live in the United States.
| Name: | Charlottesville City |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 51-540 |
| State: | Virginia |
| Founded: | 1762 |
| Named for: | Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz |
| Land Area: | 10.25 sq mi (26.55 km²) |
| Population Density: | 4,541.76/sq mi (1,753.41/km²) |
Charlottesville City location map. Where is Charlottesville City?
History
At the time of European settlement, part of the area that became Charlottesville was occupied by a Monacan village called Monasukapanough.
Founding
An Act of the Assembly of Albemarle County established Charlottesville in 1762. Thomas Walker was named its first trustee. It was situated along a trade route called Three Notched Road (present day U.S. Route 250), which led from Richmond to the Great Valley. The town took its name from the British queen Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
During the American Revolutionary War, Congress imprisoned the Convention Army in Charlottesville at the Albemarle Barracks between 1779 and 1781. The Governor and legislators had to temporarily abandon the capitol and on June 4, 1781, Jack Jouett warned the Virginia Legislature meeting at Monticello of a planned raid by Colonel Banastre Tarleton, allowing a narrow escape.
Civil War and Reconstruction
Unlike much of Virginia, Charlottesville was spared the brunt of the American Civil War. The only battle to take place in Charlottesville was the skirmish at Rio Hill, an encounter in which George Armstrong Custer briefly engaged local Confederate Home Guards before retreating. A year later, the Charlottesville Factory, founded c. 1820–30, was accidentally burnt during General Philip Sheridan’s 1865 raid through the Shenandoah Valley, although the mayor had surrendered the city to Generals Custer and Sheridan to keep the town from being burned. The factory had been taken over by the Confederacy and used to manufacture woolen clothing for the soldiers. It caught fire when some coals taken by Union troops to burn the nearby railroad bridge dropped on the floor. The factory was rebuilt immediately and was known as the Woolen Mills until its liquidation in 1962.
Segregation and Jim Crow laws
After Reconstruction ended, Charlottesville’s African American population suffered under Jim Crow laws that segregated public places and limited opportunity. Schools were racially segregated and African Americans were not served in many local businesses. Public parks were planned separately for the white and African American populations: four for whites, and one for African Americans built on the site of a former dump. The Ku Klux Klan had chapters in the Charlottesville area beginning at least in the early twentieth century, and events such as lynchings and cross burnings occurred in the Charlottesville area. In 1898, Charlottesville resident John Henry James was lynched in the nearby town of Ivy. In August 1950, three white men were observed burning a cross on Cherry Avenue, a street in a mostly African-American neighborhood in Charlottesville. It was speculated that the cross burning might be a reaction to “a white man [who] had been known to socialize with one of the young Negro women in that vicinity.” In 1956, crosses were burned outside a progressive church.
In 1947, Charlottesville organized a local NAACP branch. In 2001, the Charlottesville and Albemarle Branches of the NAACP merged to form the Albemarle-Charlottesville NAACP Branch.
In the fall of 1958, Charlottesville closed its segregated white schools as part of Virginia’s strategy of massive resistance to federal court orders requiring integration as part of the implementation of the Supreme Court of the United States decision Brown v. Board of Education. The closures were required by a new series of state laws collectively known as the Stanley Plan, which prohibited and denied funding to integrated public schools. Segregated schools remained open, however. The first African-American member of the Charlottesville School Board was Raymond Bell in 1963.
In 1963, later than many Southern cities, civil rights activists in Charlottesville began protesting segregated restaurants with sit-ins, such as one that occurred at Buddy’s Restaurant near the University of Virginia.
Destruction of Vinegar Hill
In 1965, the city government razed the downtown African American neighborhood Vinegar Hill as an urban renewal project, after the city council passing a law that “unsanitary and unsafe” properties could be taken over by a housing authority. One hundred thirty homes, five Black-owned businesses, and a church were destroyed. Many displaced community members moved into the Westhaven public housing project. The land was not redeveloped until the late 1970s.
Despite razing this small area comprising about 20 acres abutting West Main Street in the city’s commercial downtown area, Charlottesville maintained its vibrant black community spanning the much larger and still extant Ridge Street and Fifeville neighborhoods to the south, and the Tenth & Page and Rose Hill neighborhoods to the north. Neighborhood civic associations, social clubs and church groups sponsored activities for its residents. The Blue Mints Social Club met at the home of Mrs. Reva Shelton on December 1, 1974. At this meeting, the group planned their annual “Baskets of Cheer,” hosted a Cabaret Dance on New Year’s Eve at Carver Recreation Center, with the Randolph Brothers performing. In 1974, other social clubs listed are the Bethune Art and Literary Club, The Lucky Twenty Club, and the Les Amies Club.
Conflict over Confederate symbols
Starting in the 2010s Charlottesville received national attention because of local conflict between those who do and those who do not want Confederate symbols removed. The Washington Post has reported that “Nowhere has this clash been more fraught than in Charlottesville, where parks have been renamed, then renamed again, streets have been re-christened, and stickers bearing white supremacist slogans go up as quickly as activists can remove them.”
City attempts to remove statues of Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson from downtown parks have been the subject of extensive, unresolved litigation. In August 2017, white supremacist groups opposed to their removal organized the “Unite the Right rally”, to protest against the removal of the Robert E. Lee statue from then Lee Park, subsequently renamed Emancipation Park. After the rally, a white nationalist drove a car into protesters, resulting in the death of counter-protester Heather Heyer and causing injuries to 19 others. The incident became national news and Charlottesville became a symbol of political turbulence nationwide. The city succeeded in the removal of the Lee and Jackson statues on July 10, 2021, in addition to a statue of Lewis and Clark and Sacajawea.
Religious history
Christ Episcopal Church was Charlottesville’s first church. It was begun in 1820 by builders on loan from Thomas Jefferson, and the congregation’s current home was completed in the early 1900s.
The first black church in Charlottesville, the First Baptist Church of Charlottesville, was established in 1864. Previously, it was illegal for African-Americans to have their own churches, although they were allowed to worship in designated areas in white churches, if the white church members allowed it. Its first black pastor (previously, it was required by law that all churches have white pastors), was William D. Gibbons. The date he became pastor is not known with certainty, but was about 1868. A current predominantly African-American church can trace its lineage to that first church.
Congregation Beth Israel’s 1882 building is the oldest synagogue building still standing in Virginia. In 1974, some of the Baptist churches in Charlottesville included the Union Run Baptist Church, the South Garden Baptist Church, and the Ebenezer Baptist Church.
The first Catholic church in Charlottesville was the Church of the Paraclete, built in 1880 and erected as a parish in 1896. In 1906 the church building was renovated and the parish was renamed to Holy Comforter. A second parish was erected for the growing Catholic population in 1976 called the Church of the Incarnation. In 1967 a Dominican-run parish for Catholic students at the University of Virginia was dedicated (replacing a Newman Center begun in 1943), and named St. Thomas Aquinas University Parish. The first Mass of record in Charlottesville was celebrated in the parlor of F. M. Paoli’s residence, presumably on Random Row, now West Main Street. Services were held for about 12 years after that in the Town Hall. The presiders were priests who came from St. Francis Assisi Church in Staunton and then traveled on to other missions in the area.
Charlottesville City Road Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 10.3 square miles (27 km), virtually all of which is land.
Charlottesville is located in the center of the Commonwealth of Virginia along the Rivanna River, a tributary of the James, just west of the Southwest Mountains, itself paralleling the Blue Ridge about 20 miles (32 km) to the west.
Charlottesville is 99 miles (159 km) from Washington, D.C. and 72 miles (116 km) from Richmond.
Climate
Charlottesville has a four-season humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa), with all months being well-watered, though the period from May to September is the wettest. Winters are somewhat cool, with a January average of 36.2 °F (2.3 °C), though lows can fall into the teens (< −7 °C) on some nights and highs frequently (11 days in January) reach 50 °F (10 °C). Spring and autumn provide transitions of reasonable length. Summers are hot and humid, with July averaging 77.6 °F (25.3 °C) and the high exceeding 90 °F (32 °C) on 34.4 or more days per year. Snowfall is highly variable from year to year but is normally moderate, averaging 17.0 inches (43 cm). What does fall does not remain on the ground for long. Extremes have ranged from −10 °F (−23 °C) on January 19, 1994, up to 107 °F (42 °C), most recently on September 7, 1954.
Notes:
- ^ Threaded records maintained at the “Charlottesville 2W” (Leander McCormick Observatory) from January 1893 to November 13, 1998, and at Charlottesville–Albemarle Airport since November 14, 1998.