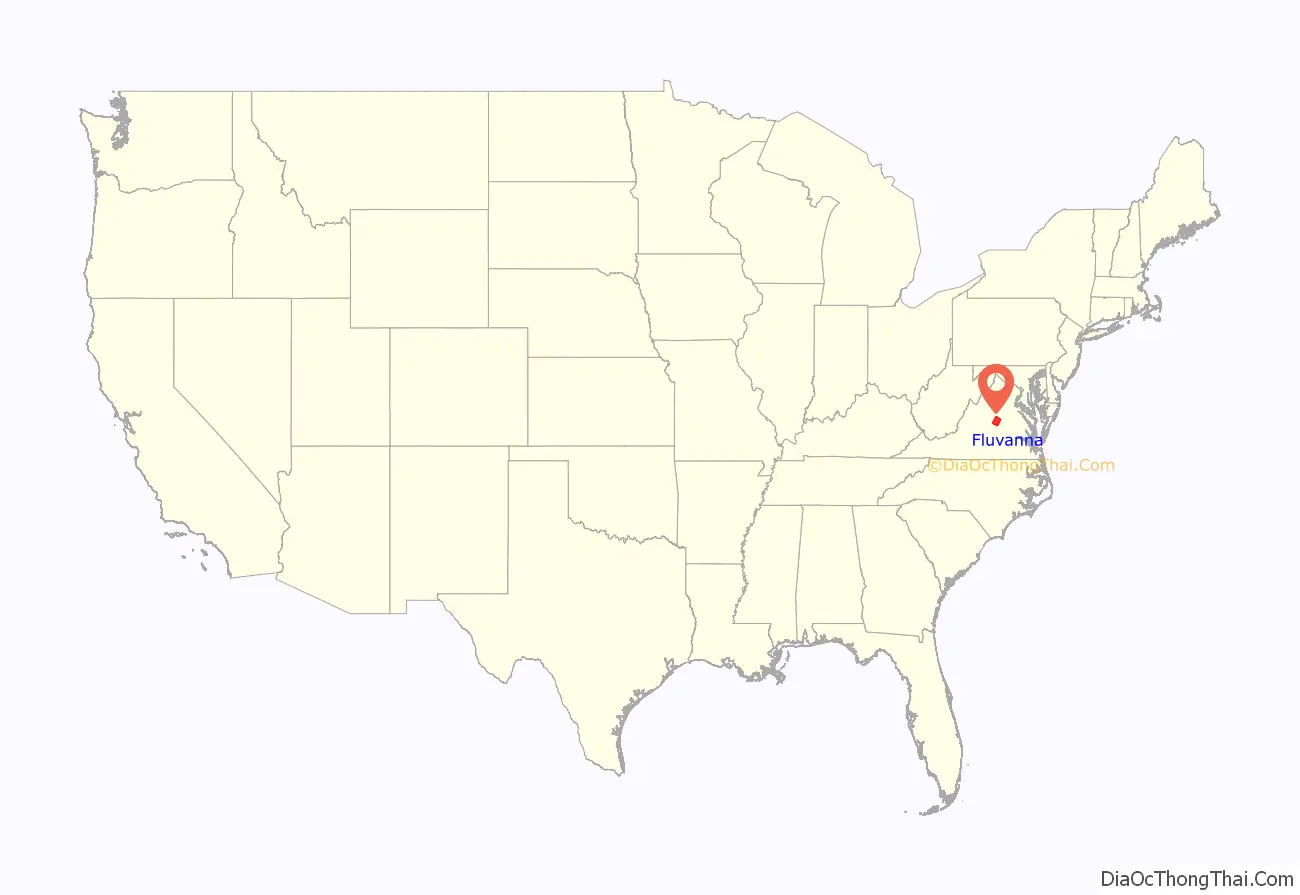
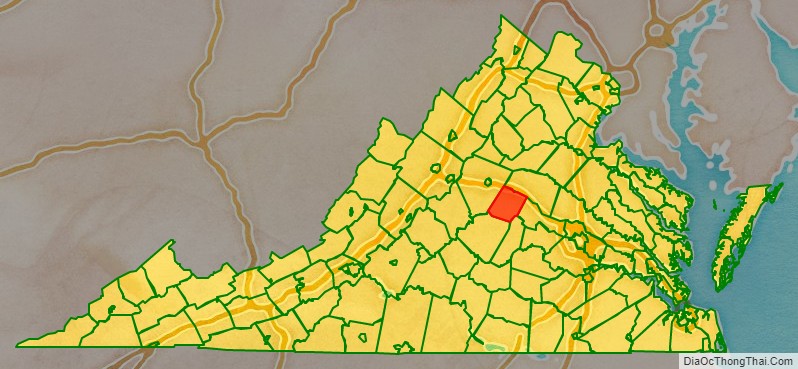
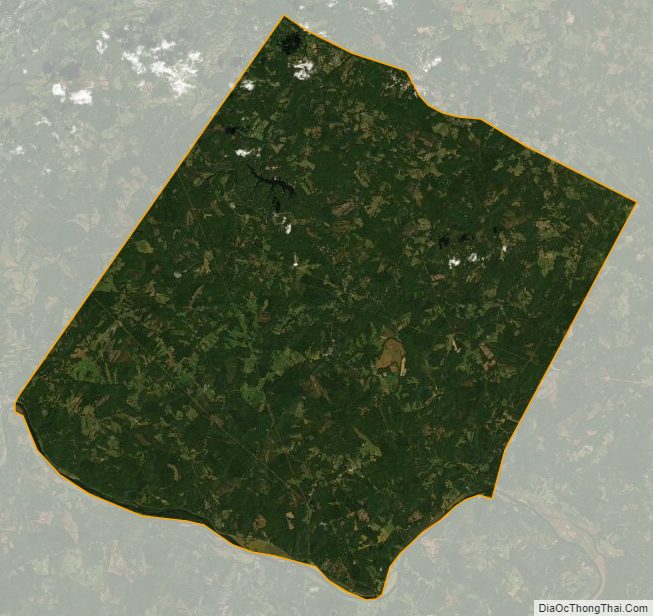
Fluvanna County is a county located in the Piedmont region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 27,249. Its county seat is Palmyra, while the most populous community is the census designated place of Lake Monticello.
Fluvanna County is part of the Charlottesville, Virginia Metropolitan Statistical Area.
| Name: | Fluvanna County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 51-065 |
| State: | Virginia |
| Founded: | 1777 |
| Named for: | Fluvanna River |
| Seat: | Palmyra |
| Total Area: | 290 sq mi (800 km²) |
| Land Area: | 286 sq mi (740 km²) |
| Total Population: | 27,249 |
| Population Density: | 94/sq mi (36/km²) |
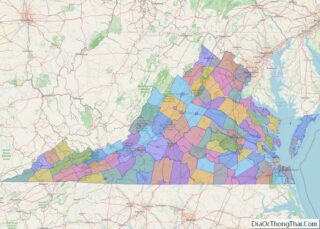
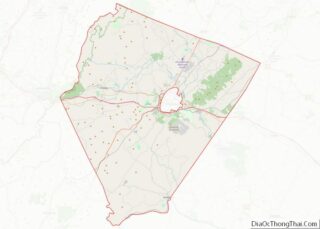
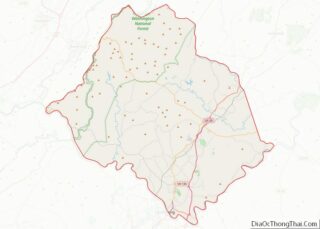
Fluvanna County location map. Where is Fluvanna County?
History
Through the 17th century, the Point of Fork (near Columbia where the James and Rivanna rivers meet) was the site of Rassawek, a major Monacan village of the Native Americans. By 1701, the Seneca Iroquois had overrun the entire Virginia Piedmont, which they sold to Virginia Colony in 1721 at the Treaty of Albany.
The area which is now Fluvanna County was once considered part of Henrico County, one of the original shires of the Virginia Colony. Henrico was divided in 1727 and the Fluvanna County area became a part of Goochland County. In 1744 Goochland was divided and the area presently known as Fluvanna became a part of Albemarle County. When Amherst County, Nelson County and Buckingham County were split off from Albemarle County, the Albemarle County Seat was moved in 1762 from Scottsville to Charlottesville. When the Albemarle County seat was moved citizens in the Fluvanna area would now have to trek over the Southwest Mountains to reach the new seat at Charlottesville. Fluvanna area citizens lobbied the Virginia General Assembly to create a new county. Finally, in 1777, Albemarle County was divided again and Fluvanna County established.
The county was named for the Fluvanna River, a name once given to the James River west of Columbia. “Fluvanna” means “Anne’s River”, in honor of Anne, Queen of Great Britain, who reigned until 1714. Located in the Piedmont above the Fall Line, the county has the James and Rivanna rivers running through it. It was sometimes referred to as “Old Flu.”
Fluvanna was defended by six militia companies during the American Revolutionary War. The county was invaded by British forces in 1781 who destroyed the Point of Fork Arsenal. From an initial 882 “tithables,” the population reached 3,300 by 1782. Columbia was formed in 1788 with Bernardsburg and Wilmington following soon after. Lyles Baptist Church was organized in 1774 and the formation of the Methodist denomination had its roots in a Conference held in Fluvanna in 1779. The “Brick Union” Church was built in 1825 for the use of Episcopalians, Methodists, Baptists and Presbyterians. The village of Fork Union grew up around the Church.
When Palmyra was made the county seat in 1828 it quickly became a thriving town after the new courthouse was completed in 1830.
In the late eighteenth century, Thomas Jefferson improved the navigability of the Rivanna River, as he owned much property along its upper course, e.g. Shadwell and Monticello plantations. Improvements included in the first generation (through 1830) were sluice cuts, small dams and batteaux locks.
Second-generation (1840–1870) improvements made by others included construction of long stretches of canal, serviced by large locks, many of which are still visible along the river. Shortly after the completion of the initial Rivanna navigational works, Virginia requested that the river be opened to public usage. Jefferson reportedly initially refused, but the state insisted and the Rivanna became an integral part of the central Virginian transportation network. The route serviced a large community of farmsteads, plantations throughout Albemarle and Fluvanna counties. It also was lined by increasing numbers of industrial facilities, such as those at Union Mills. Construction of the larger mills prompted the great improvements to navigation. For instance, Union Mills featured a two-and-a-half-mile long canal and towpath, and one upper and two massive lower locks, all directly upon the river.
Where the Rivanna meets the James River at Columbia, the Rivanna Connexion Canal merged with a much longer canal. (The series of locks which connected the two canals lie just outside the Town of Columbia and are mostly buried by sediment today). In 1840, the James River and Kanawha Canal was constructed adjacent to the north bank of the James River and opened to traffic. The new canal was part of a planned link between the Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean via the James and the Kanawha rivers; it was intended to connect via the Ohio River, to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. The canal was used by packet and freight boats, which replaced the earlier shallow-draft batteau for commerce. These boats brought goods and passengers to and from Richmond and points beyond. Long a dream of early Virginians such as George Washington, who was a surveyor early in his career, the canal was never completed as envisioned.
In the batteaux era, Milton was the head of navigation on the river. By the early nineteenth century, horse-drawn canal boats were traveling all the way upstream to Charlottesville. The head of navigation was located at the point where the Fredericksburg Road (now VA 20) and Three Chopt Road (U.S. Route 250), the primary road to Richmond, met and entered the city at the Free Bridge, establishing the city as a major commercial hub.
While no Civil War battles were fought in Fluvanna, Union soldiers burned mills and bridges and damaged the James River and Kanawha Canal to disrupt traffic and commerce. During the American Civil War more than 1,200 of the county’s citizens served in the Confederate forces. Its citizens served in infantry, cavalry, and artillery units during the war, including the Fluvanna Artillery.
The canal was repaired after the war, but traffic never returned to pre-war levels, as railroads were being constructed throughout the state and were more efficient. After many years of trying to compete with the ever-expanding railroad network, the James River and Kanawha Canal was conveyed to a new railroad company by a deed dated March 4, 1880. Railroad construction workers promptly started laying tracks on the towpath. The new Richmond and Allegheny Railroad offered a water-level route from the Appalachian Mountains just east of West Virginia near Jackson’s River Station (now Clifton Forge) through the Blue Ridge Mountains at Balcony Falls to Richmond. In 1888 the railroad was leased, and later purchased, by Collis P. Huntington’s Chesapeake and Ohio Railway.
Fork Union Military Academy (FUMA) was initially founded as Fork Union Academy in October 1898 by Dr. William E. Hatcher, a prominent local Baptist minister. The first class had 19 boys and girls. In 1902, the academy took on a military structure to provide organization, discipline, and physical development for the boys of what was a rapidly growing school. In 1913, the academy became an all-male institution and changed its name to Fork Union Military Academy. That same year, the Academy began receiving support from the Baptist General Association of Virginia, which has continued into the 21st century. FUMA is known for its One Subject Plan as well as Post Graduate Football team that has many NFL players and Heisman Trophy winners as alumni.
Early in the 20th century, the C&O built a new line between the James River Line at Strathmore and the Piedmont Subdivision on the old Virginia Central Railroad’s line at Gordonsville. The Virginia Air Line Railway was built to move loads that were too high or too wide to pass through the tunnels of the Blue Ridge Mountain complex between Charlottesville and Waynesboro. Additionally, coal trains from West Virginia headed eastbound for Washington, D.C. and Northern Virginia were routed on the new line to avoid steep mountain grades. The VAL was completed on September 29, 1909. A new freight station was built at Palmyra. The tracks of the VAL were abandoned in 1975, as railroad freight traffic had declined.
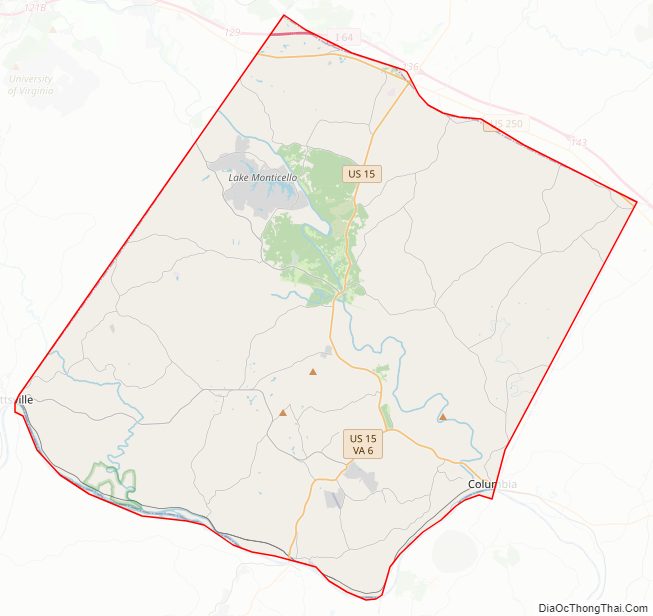
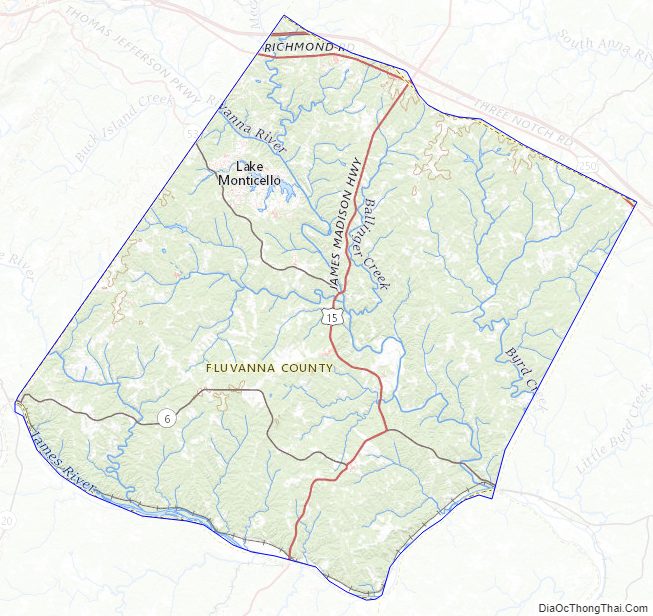
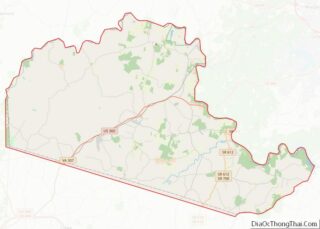
Fluvanna County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 290 square miles (750 km), of which 286 square miles (740 km) is land and 4.1 square miles (11 km) (1.4%) is water. Palmyra, is 54 miles (87 km) from Richmond and 110 miles (180 km) from Dulles International Airport. Lake Monticello, a private community, is 15 miles (24 km) from Charlottesville.
Adjacent counties
- Louisa County – north
- Goochland County – east
- Cumberland County – southeast
- Buckingham County – south
- Albemarle County – west
Major highways
- I-64
- US 15
- US 250
- SR 6
- SR 53