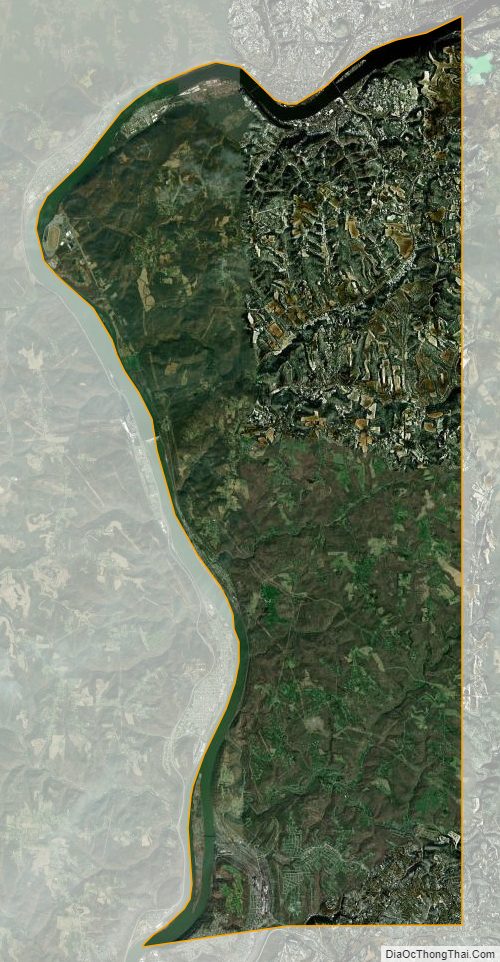
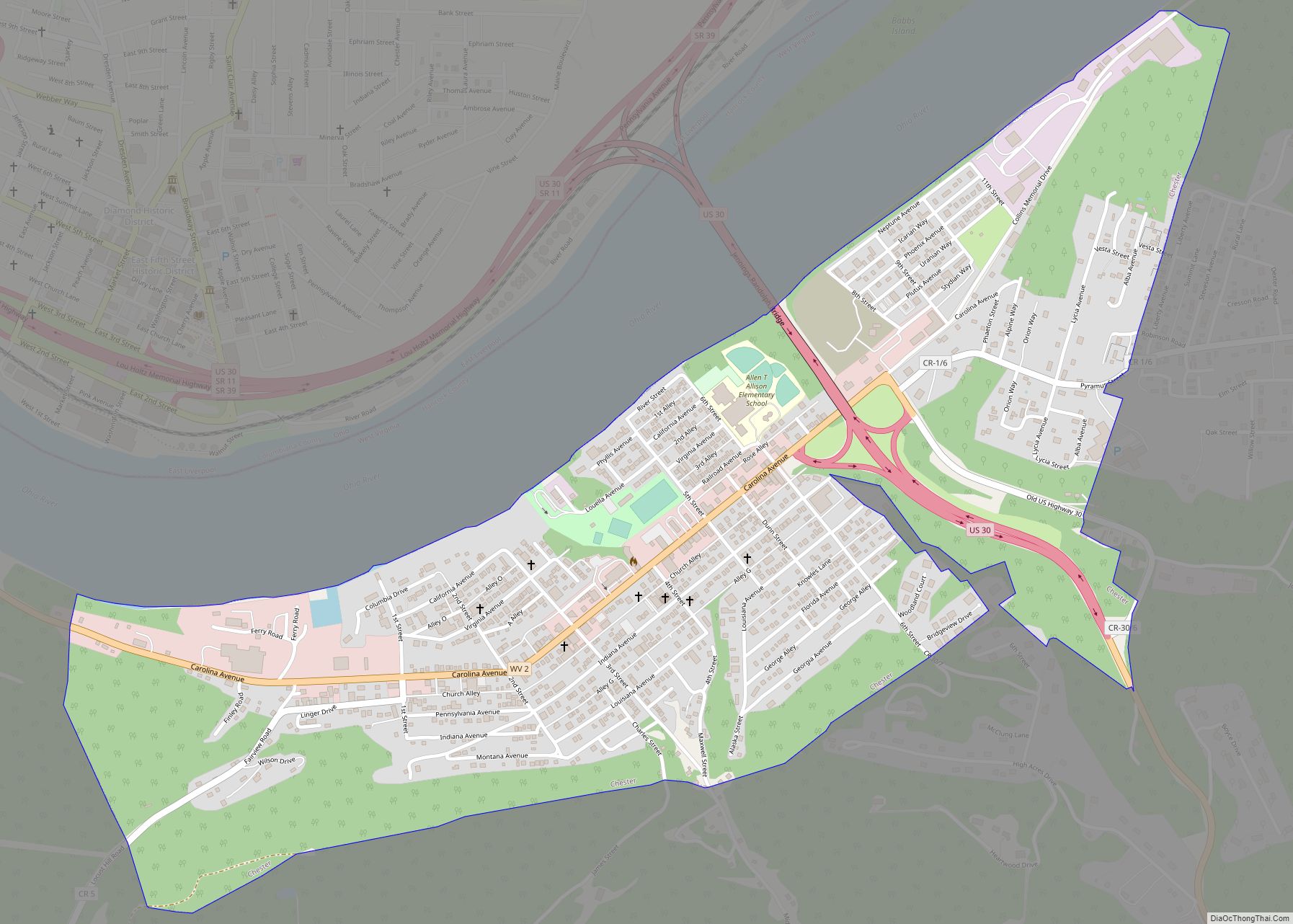
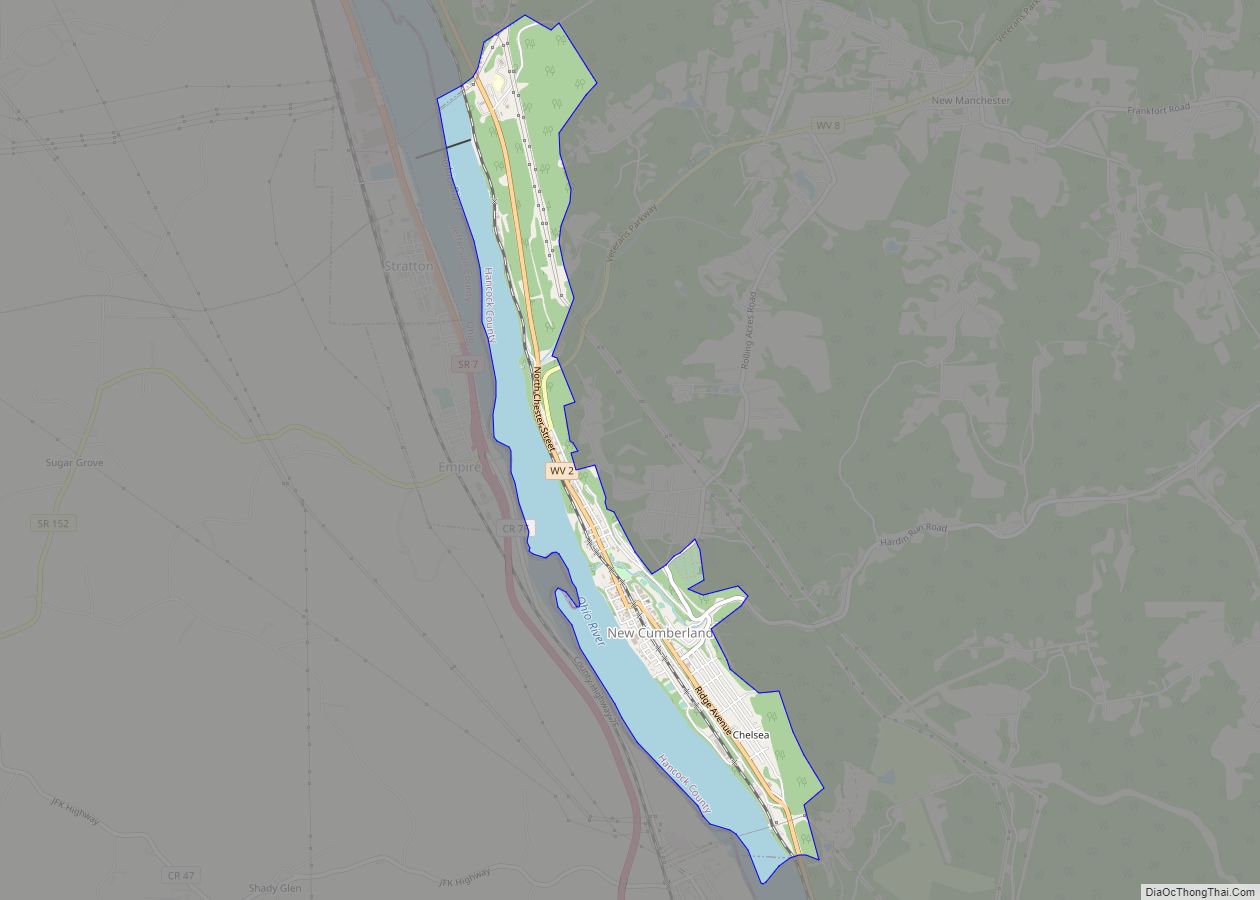
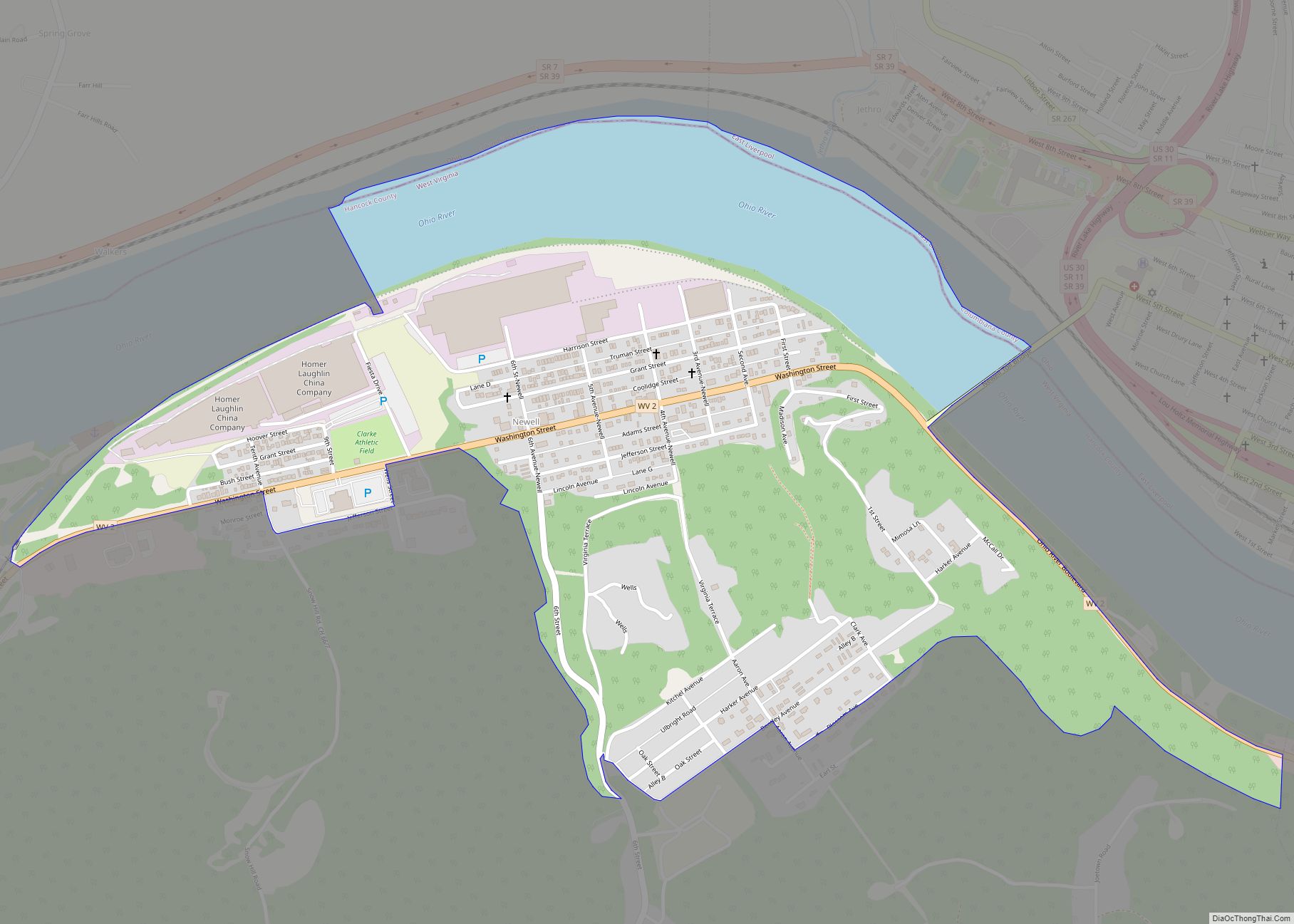
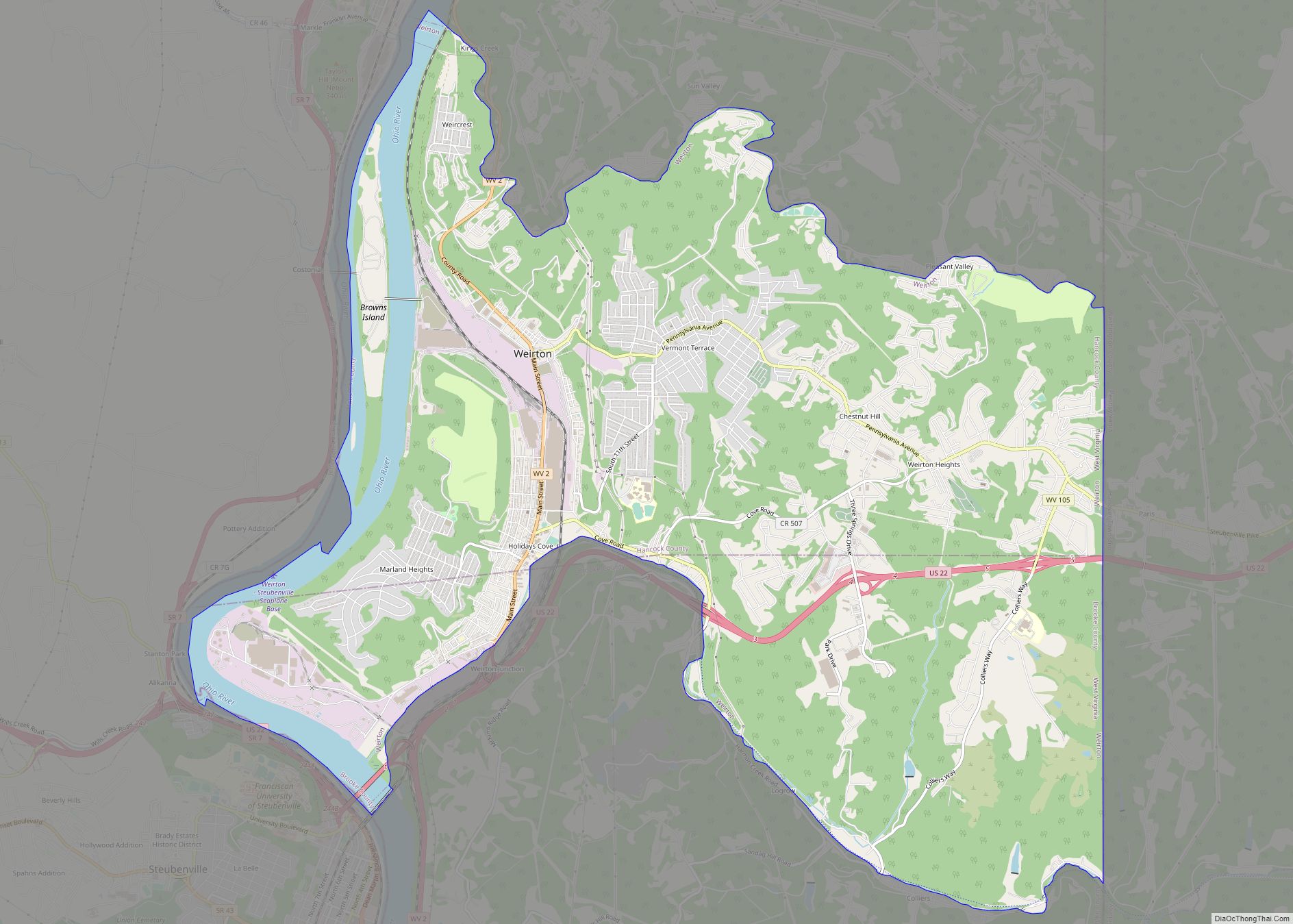
Hancock County is a county in the U.S. state of West Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 29,095. Its county seat is New Cumberland and its largest city is Weirton. The county was created from Brooke County in 1848 and named for John Hancock, first signer of the Declaration of Independence. Hancock County is the northernmost point in both West Virginia and, by some definitions, the Southern United States; being at the tip of the state’s Northern Panhandle. Hancock County is part of the Weirton-Steubenville, WV-OH Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Pittsburgh-New Castle-Weirton, PA-WV-OH Combined Statistical Area.
| Name: | Hancock County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 54-029 |
| State: | West Virginia |
| Founded: | January 15, 1848 |
| Named for: | John Hancock |
| Seat: | New Cumberland |
| Largest city: | Weirton |
| Total Area: | 88 sq mi (230 km²) |
| Land Area: | 83 sq mi (210 km²) |
| Total Population: | 29,095 |
| Population Density: | 330/sq mi (130/km²) |
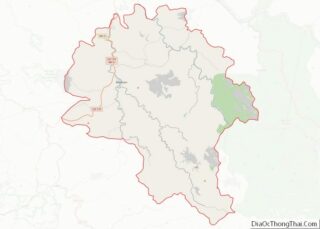
Hancock County location map. Where is Hancock County?
History
Hancock County was formed from Brooke County in 1848, some 15 years before West Virginia became a state. Both counties were once part of Ohio County, Virginia, which had been formed from the District of West Augusta in 1776. Hancock County has significant Revolutionary-period roots due to its location on the Ohio River south of Fort Pitt in Pittsburgh and north of Fort Henry in Wheeling.
Hancock County was the site of the infamous massacre of Iroquois leader Chief Logan’s family in 1774, at Baker’s Tavern across the Ohio River from the mouth of Yellow Creek. The event, known as the Yellow Creek massacre, sparked Lord Dunmore’s War. Adam Poe had his famous fight with the Indian known as Big Foot at the mouth of Tomlinson Run in 1781. Historical markers commemorate both events. Significant Revolutionary War forts and blockhouses in Hancock County included Holliday’s Cove Fort in downtown Weirton and Chapman’s Blockhouse in New Cumberland.
In 1863, West Virginia’s counties were divided into civil townships, with the intention of encouraging local government. This proved impractical in the heavily rural state, and in 1872 the townships were converted into magisterial districts. Hancock County was divided into four districts: Butler, Clay, Grant, and Poe. Poe, the least populous district, was discontinued in the 1920s.
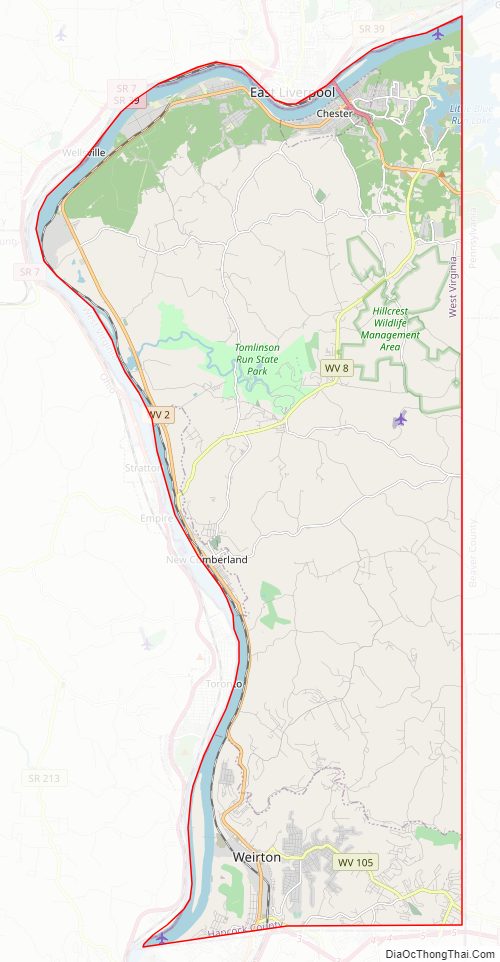
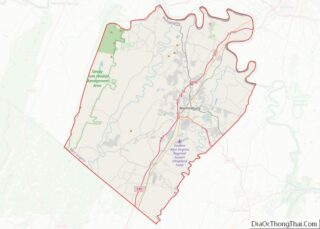
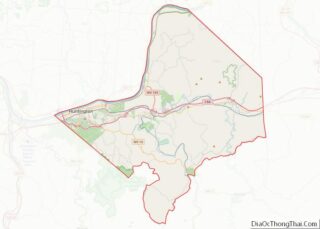
Hancock County Road Map
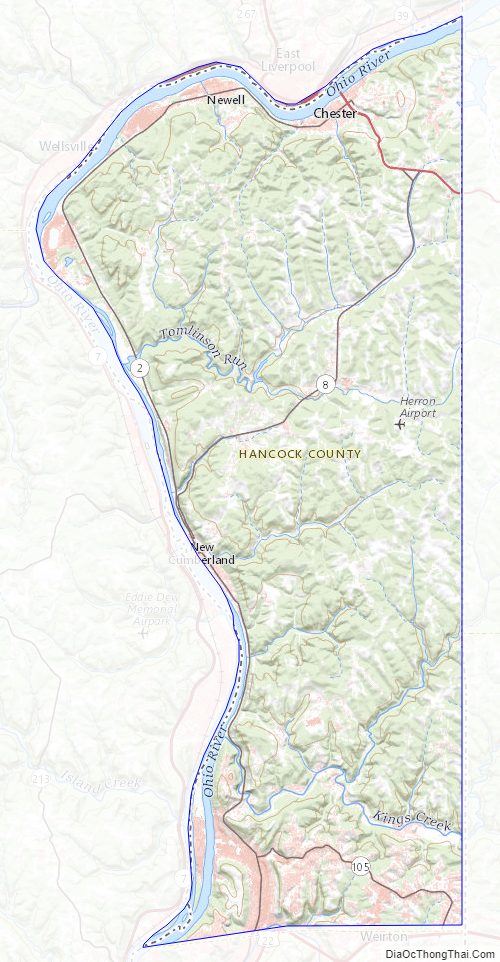
Geography
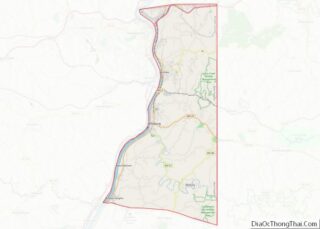
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 88 square miles (230 km), of which 83 square miles (210 km) is land and 5.4 square miles (14 km) (6.1%) is water. It is the smallest county in West Virginia by area, as well as one of the smallest in the United States. The highest point of elevation in Hancock County is approximately 1363 ft. and located about 1800 ft. ESE of Emmanuel Mission Church. [1]
Major highways
- US 22
- US 30
- WV 2
- WV 8
- WV 105
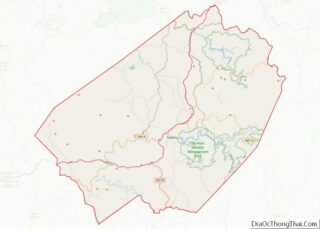
Adjacent counties
- Columbiana County, Ohio (northwest)
- Beaver County, Pennsylvania (east)
- Washington County, Pennsylvania (southeast)
- Brooke County (south)
- Jefferson County, Ohio (west)