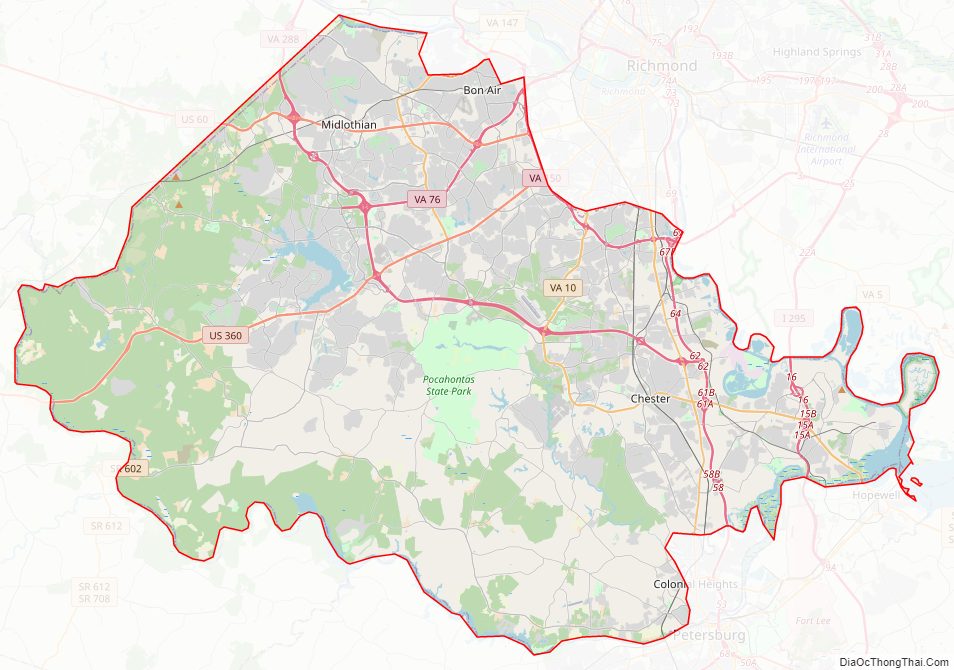
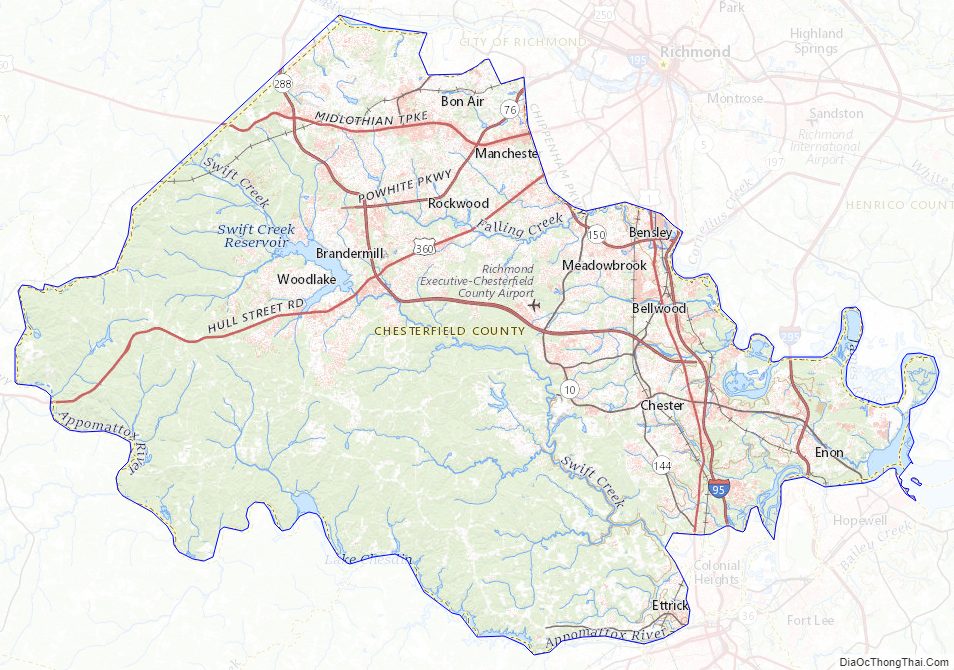
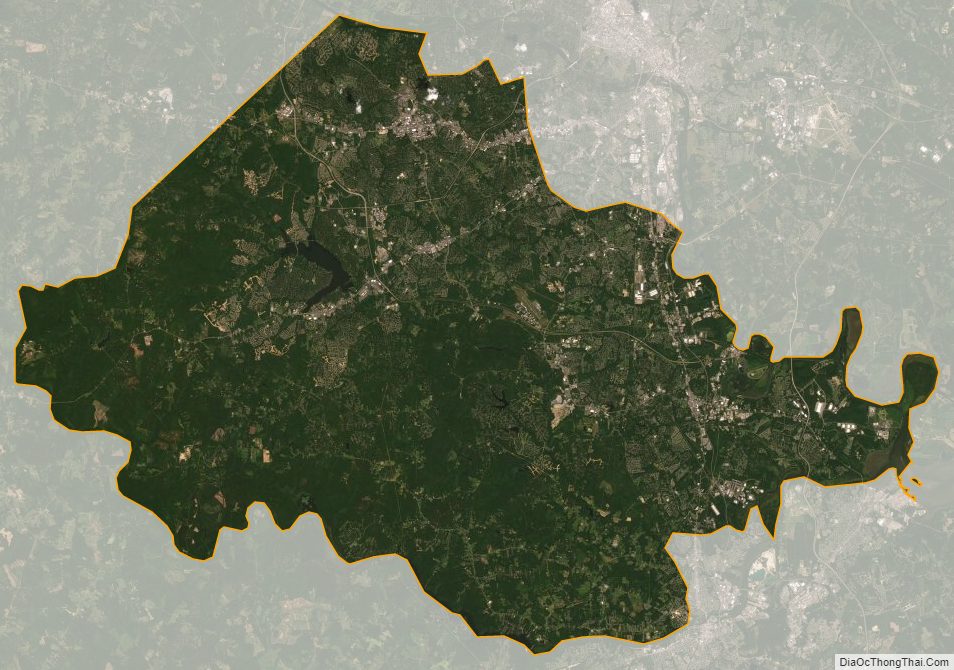
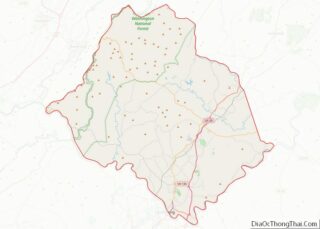
Chesterfield County is located just south of Richmond in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The county’s borders are primarily defined by the James River to the north and the Appomattox River to the south. Its county seat is Chesterfield Court House.
Chesterfield County was formed in 1749 from parts of Henrico County. It was named for Philip Stanhope, 4th Earl of Chesterfield, a prominent English statesman who had been the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland.
As of the 2020 census, the population was 364,548 making it the fourth-most populous county in Virginia (behind Fairfax, Prince William, and Loudoun, respectively). Chesterfield County is part of the Greater Richmond Region, and the county refers to much of the northern portion of the county as “North Chesterfield.”
| Name: | Chesterfield County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 51-041 |
| State: | Virginia |
| Founded: | May 25, 1749 |
| Named for: |
|
| Seat: | Chesterfield Court House |
| Total Area: | 437 sq mi (1,130 km²) |
| Land Area: | 423 sq mi (1,100 km²) |
| Total Population: | 364,548 |
| Population Density: | 830/sq mi (320/km²) |
Chesterfield County location map. Where is Chesterfield County?
History
Part of Henrico Citie, Henrico Shire, Henrico County
During the early 17th century, shortly after the settlement of Jamestown in 1607, English settlers and explorers began settling other areas. One of the more progressive developments in the colony was Henricus, founded under the guidance of Sir Thomas Dale. It was to include a college to help educate Virginia Indians, as well as the children of settlers. Dale was accompanied by men known as the “Hammours”. These veterans of the Low Country wars were heavily armed and better trained than settlers of Jamestown.
Dale wrote about the site: “Eighty miles up our river from Jamestown, I have surveyed a convenient, strong, healthie and sweete site to plant a new towne (according as I had instructions upon my departure) there to build whence might be removed the principal site.” Today known as Farrars Island, the site was on a neck of land with 5,000 acres (20 km) and a shoreline of seven miles (11 km) on the James River. The English settlers soon built a palisade and moat-like ditch to protect entrance to the 174-yard (159 m) wide neck from the shore area.
Dale named the new settlement Henricus in honor of Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, the elder son of King James I. When finished in 1619, “Henricus Citie” contained three streets of well-framed houses, a church, storehouses, a hospital, and watchtowers. 1619 was a watershed year for the Virginia Colony. Henrico and three other large citties (sic) were formed, one of which included what is now Chesterfield County. That year Falling Creek Ironworks, the first in what is now the United States, was established slightly west on the creek near its confluence with the James River. In the Indian Massacre of 1622, Native Americans destroyed Henrico City and the ironworks to try to drive away the English. These were not rebuilt. The colony did not gain a college until 1693, when the College of William and Mary was awarded a royal charter in the capital.
In 1634, the King of England directed the formation of eight shires (or counties) in the colony of Virginia. One of these was Henrico County, which incorporated a large area on both sides of the James River.
Chesterfield County formed
On 25 May 1749, the Virginia House of Burgesses separated Chesterfield from Henrico County and created the new county. The first county seat was established at Chesterfield Court House. It has continued as county seat except for 1870–1876, during Reconstruction, when the county government was located at Manchester. The latter community has been subsumed by South Richmond.
The legislature named the county for the former British Secretary of State, Philip Stanhope, 4th Earl of Chesterfield. Lord Chesterfield was famous for his “good manners and writings”. One of his most frequently used sayings implies avoiding rudeness; “An injury is much sooner forgotten than an insult.” Many years later, Chesterfield Cigarettes were named after this county.
In 1939 during the Great Depression, the Virginia State Police moved their offices from downtown Richmond to a seven-room farmhouse located on 65 acres (260,000 m) of land 3½ miles west on route 60. This structure served as administrative headquarters and barracks. The State Police have since built a new administrative headquarters and an academy here.
Early ports, coal, roads, turnpikes and railroads
Prior to the American Revolutionary War, a thriving port town named Warwick was located at the northwestern confluence of Falling Creek and the James River. It was destroyed during that war, and not rebuilt. (Near the present-day DuPont facility at Ampthill, the site is not open to the public.) Another early port town was Port Walthall on the north shore of the Appomattox River, near the current Point-of-Rocks Park.
Coal mining in the Midlothian area of Chesterfield County began in the 18th century. Around 1701, French Huguenot settlers to the area discovered coal. In a 1709 diary entry William Byrd II, the wealthy planter who had purchased 344 acres (1.4 km) of land in the area, noted that “the coaler found the coal mine very good and sufficient to furnish several generations.” Commercially mined beginning in the 1730s, the coal fueled the production of cannon at Westham (near the present Huguenot Memorial Bridge) during the American Revolutionary War. In 1831, the Chesterfield Railroad was constructed to transport coal by gravity and mule power to Manchester, Virginia on the south side of the James River across from Richmond, Virginia.
From the 1740s through the 1800s rivers above the Fall Line were used for transportation to the West with James River bateau, which could carry about a ton, and boats several times larger from Eppington. The Appomattox River on the Southern border was the lower end of the Upper Appomattox Canal Navigation System connecting to Farmville, Virginia. The James River and Kanawha Canal on the northern border of Chesterfield connected past the Blue Ridge Mountains. Port Walthall connected ships that carried more than 200 tonnes to the East with Ports on the Atlantic Ocean. A canal was built in the Manchester section of Chesterfield to enable transporting coal around the James River falls. Portions are extant and may be seen near the south end of Richmond’s Mayo Bridge.
The Manchester Turnpike in Chesterfield County, completed in 1807, was the first graveled roadway of any length in Virginia. The toll road ran between the coal mining area of Midlothian near the headwaters of Falling Creek and the James River port of Manchester. The current Midlothian Turnpike (U.S. Route 60) generally follows the earlier route.
Created in 1816, the Virginia Board of Public Works was a governmental agency which oversaw and helped finance the development of Virginia’s internal transportation improvements, including canals, during the 19th century. In that era, it was customary to invest public funds in private companies, which were the forerunners of the public service and utility companies of modern times. Claudius Crozet (1789–1864), a civil engineer and educator who helped found the Virginia Military Institute (VMI), was Principal Engineer and later Chief Engineer for the Board of Public Works. He supervised the planning and construction of many of the canals, turnpikes, bridges and railroads in Virginia, including the area which is now West Virginia.
The Board partially engineered and funded new turnpikes, which were operated by private companies to collect tolls. The Manchester and Petersburg Turnpike, which preceded much of the current Jefferson Davis Highway (U.S. Routes 1–301), was one of these.
To improve access to markets, in 1825, a group of mine owners, including Nicholas Mills, Beverley Randolph and Abraham S. Wooldridge, resolved to build a tramway. (The Wooldridge brothers hailed from East Lothian and West Lothian in Scotland, and named their mining company Mid-Lothian, the source of the modern community name). In 1831, the Chesterfield Railroad opened as the first railroad in Virginia; it carried coal from mines near Falling Creek to the docks at the fall line on the James River. By the early 1850s, railroad lines connecting these areas included the Richmond and Danville Railroad (R&D) (which put the Chesterfield Railroad out of business) and the Richmond and Petersburg Railroad. They were both completed before the American Civil War, in which they provided important transportation for Southern supplies and men.
The Clover Hill Railroad was built to haul coal, mined in Chesterfield at the Clover Hill Pits to ports at Osborne’s Landing. This railroad was replaced by the Brighthope Railway, which was, in 1881, narrowed into a narrow gauge railroad and rerouted to the tiny village of Bermuda Hundred, a port on the James River near the mouth of the Appomattox River. The Brighthope Railway was sold in foreclosure and restructured as the Farmville and Powhatan Railroad, later renamed the Tidewater and Western Railroad, extended to Farmville in Prince Edward County. Although long gone, portions of the old rail bed may be seen along Beach Road near the entrance to Pocahontas State Park. A water stop station in the Park remains and Beach Station remains as a national historic landmark.
American Civil War
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), Drewry’s Bluff became a key defensive point for Confederate forces to block the Union’s vastly superior Navy from taking Richmond by way of the James River. During the Siege of Petersburg (1864–65), a long defensive works through the county was part of the Confederacy’s Richmond-Petersburg line of land defenses. Railroad lines passing through Petersburg finally proved the key to the fall of Richmond in 1865, effectively ending the War.
Reconstruction
A normal school founded by the state after the American Civil War primarily to help educate freed men eventually became Virginia State University, located in the Ettrick area near Petersburg and Colonial Heights. The U.S. Government rebuilt damaged railroads.
After Reconstruction, Chesterfield County used Convict lease to build roads in 1878.
The Richmond and Danville Railroad became part of the Southern Railway in 1894. It is now part of Norfolk Southern Railway. The Richmond and Petersburg Railroad became part of the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad. In 1900, a mostly parallel line was built by the Seaboard Air Line Railroad, with a branch line to Hopewell. Through the restructuring of the railroad industry beginning in 1960, the CSX Transportation system eventually absorbed parts of both these lines.
Former areas lost to new independent cities
Manchester (directly across the James River from the City of Richmond) was the county seat of Chesterfield County from 1870 until 1876, when it was moved to the present location at Chesterfield Court House. The City of Manchester had meanwhile left Chesterfield in 1874 to become an independent city, and merged with the City of Richmond by mutual agreement in 1910. It is now known as a part of South Richmond.
Colonial Heights was formerly an incorporated town in Chesterfield County, and became an independent city in 1948. Over half a century later, the two neighbors continued to share provision of some governmental services.
Annexation issues
Chesterfield County shares borders with three independent cities, and was long exposed to annexation suits from any of them under Virginia law. The county lost territory to the City of Richmond through several annexations in the 20th century, including one in 1944. The city tried to annex more of the county in 1970, an action that created controversy.
While the annexation lawsuit filed by Richmond in 1965 was being heard, with the city seeking 51 square miles (132 km) of the county, the leaders of the two jurisdictions, Irvin G. Horner, Chairman of the Chesterfield County Board of Supervisors, and Phil J. Bagley, Jr., the Mayor of Richmond, met privately and agreed to a compromise. In May 1969, the city and Chesterfield County approved what was called the Horner-Bagley Compromise, incorporated in a court decree of 12 July 1969. This effectively shut out a number of third parties attempting to block the annexation, and they believed they had been excluded from the process. A small commuter bus company held operating rights in the county, but the expanded city granted the franchise to a competitor.
Richmond annexed 23 square miles (60 km) of the county, including fire stations, parks, and other infrastructure, such as water and sewer lines. Under the agreement, the county school system also conveyed about a dozen public schools, support buildings, and future school sites to the City of Richmond to be operated by Richmond Public Schools. Residents of the annexed area were unhappy about this change, as Richmond Public Schools was already involved in a contentious racial desegregation lawsuit in the Federal courts because of its failure to integrate. The transferred schools included Huguenot High School, Fred D. Thompson Middle School, Elkhardt Middle School, and eight elementary schools. In 1971, the federal court ordered these schools included in a citywide desegregation busing program. This ended in the 1990s.
Many of the 47,000 residents who lived in the annexed area had been opposed to the action. They fought unsuccessfully for more than 7 years in the courts to have the agreement reversed. Some called the annexed 23 square miles (60 km) area “Occupied Chesterfield.”
Many black residents of Richmond also opposed the annexation, claiming that it violated the National Voting Rights Act of 1965. They said the city had deliberately diminished their voting power by adding the white voters of the annexed area, which diluted the black vote within the city. In 1970 the pre-annexation population of the city was 202,359, of which 104,207 or 52% were black citizens. The annexation added 47,262 people, of whom 45,705 were non-black and 1,557 were black. The total post-annexation population was 249,621 and 42% black.
The plaintiffs prevailed in federal court. The city created an electoral ward system to ensure blacks did not lose their voting power, changing what had been a system of electing all city council positions at large (by which the majority population would more easily prevail). Under the ward system, four wards had a predominantly white population, four wards had a predominantly black population, and one ward had a population that was 59% white and 41% black. Soon after the ward system was established, the city elected its first black mayor.
Revisions in state annexation laws
Many political leaders have long believed that Virginia’s annexation laws have created a barrier to regional cooperation among localities. The issues resulting from the 1970 Richmond-Chesterfield case were considered prime examples of obstacles to regional cooperation as the state legislators considered changes. In 1979, the Virginia General Assembly adopted legislation that allowed any county meeting certain population and density standards to petition the local circuit court to declare the county permanently immune from annexation. In 1981, Chesterfield County and several other counties in the state sought and received such immunity from further annexation by Richmond.
Recognizing the controversy surrounding annexations in Virginia, in 1987, the General Assembly placed a moratorium on future annexations of any county by any city. When this moratorium expires, Chesterfield County remains immune from annexation by Richmond because of the 1981 state grant of immunity. Unless new revenue sharing or other agreements are reached, the county is at risk to annexation suits by any of the smaller independent cities of Colonial Heights, Hopewell, and Petersburg which adjoin it.
Chesterfield County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 437 square miles (1,130 km), of which 423 square miles (1,100 km) is land and 14 square miles (36 km) (3.1%) is water.
Chesterfield County is largely bordered by two rivers which define miles of its boundaries. The major adjoining cities each originated at the head of navigation of these river, called the fall line. There, the hillier and rockier Piedmont region falls to the sandy and mostly flat eastern coastal plain Tidewater region, a change which creates barriers for ships going upstream on the rivers. Chesterfield County includes areas of both regions.
Richmond and Manchester were formed at the fall line of the James River. Most of the northern portion of Chesterfield County is part of what is called Richmond’s “South Side”. As the James River flows east to Richmond and then turns almost due south below the fall line for about 8 miles (13 km) before turning east, Henrico County encompasses much of Richmond’s West End, North Side, and East End areas.
Chesterfield County borders on the Appomattox River to the south. Much of the southern and eastern portions of the county are considered part of the Tri-Cities area, which includes Petersburg, located at the fall line.
Adjacent counties
National protected areas
- Presquile National Wildlife Refuge
- Richmond National Battlefield Park (part)