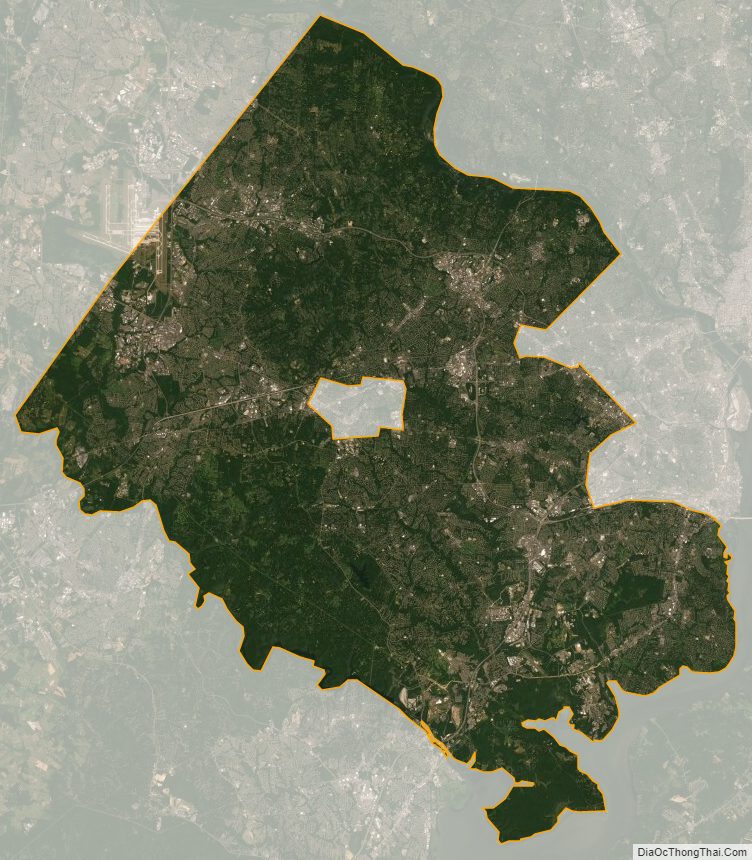
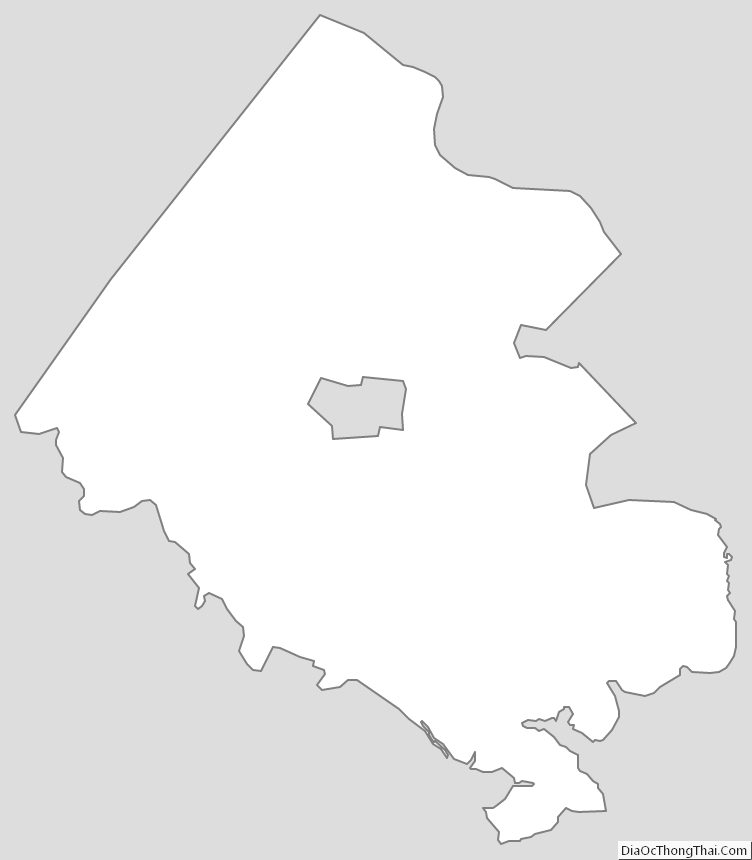
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is part of Northern Virginia and borders both the city of Alexandria and Arlington County and forms part of the suburban ring of Washington, D.C. The county is predominantly suburban in character with some urban and rural pockets.
As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,150,309, making it Virginia’s most populous jurisdiction, with around 13% of the Commonwealth’s population. The county is also the most populous jurisdiction in the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area, with around 20% of the MSA population, as well as the larger Washington-Baltimore-Arlington, DC-MD-VA-WV-PA Combined Statistical Area, with around 13% of the CSA population. The county seat is Fairfax, although because it is an independent city under Virginia law, the city of Fairfax is not part of Fairfax County.
Fairfax was the first U.S. county to reach a six-figure median household income and has the third-highest median household income of any county-level local jurisdiction in the U.S. Fairfax County, as part of the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area, is usually included atop or near the top of lists of the wealthiest areas in the United States.
The county is home to the headquarters of several intelligence agencies such as the Central Intelligence Agency, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, National Reconnaissance Office, National Counterterrorism Center, and Office of the Director of National Intelligence as well as the headquarters of several aerospace manufacturing and defense industry giants. The county is also home to the flagship campus of George Mason University, and headquarters to seven Fortune 500 companies, including three in the Falls Church area, though not in the independent municipality of Falls Church.
| Name: | Fairfax County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 51-059 |
| State: | Virginia |
| Founded: | June 19, 1742 |
| Named for: | Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron |
| Seat: | Fairfax (independent city) |
| Total Area: | 406 sq mi (1,050 km²) |
| Land Area: | 391.02 sq mi (1,012.7 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,150,309 |
| Population Density: | 2,941.82/sq mi (1,135.84/km²) |
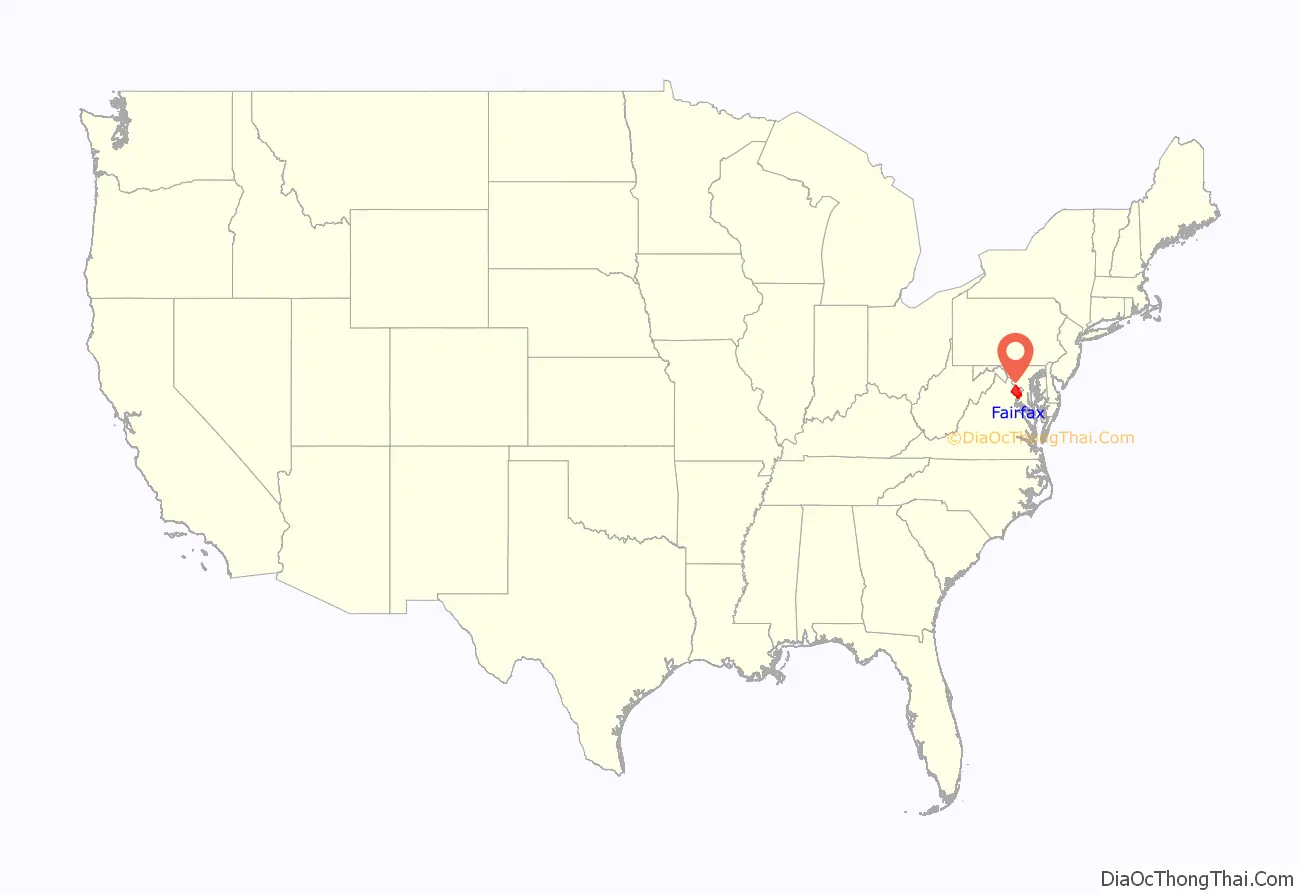
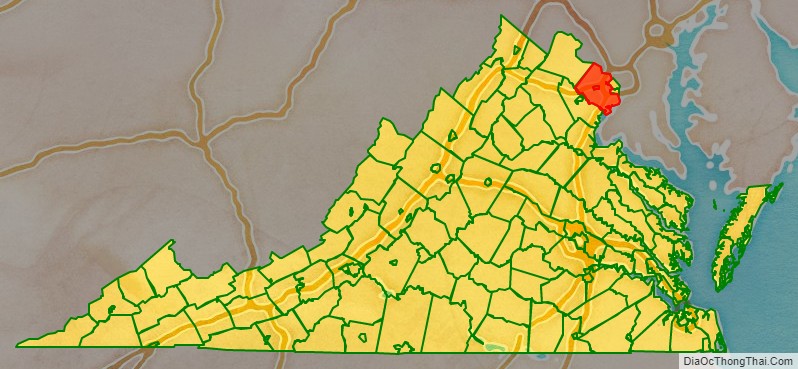
Fairfax County location map. Where is Fairfax County?
History
At the time of first European encounter, the inhabitants of what would become Fairfax County were an Algonquian-speaking subgroup called the Taux, also known as the Doeg or Dogue. Their villages, as recorded by Captain John Smith in 1608, included Namassingakent and Nemaroughquand on the south bank of the Potomac River in what is now Fairfax County. Virginian colonists from the Northern Neck region drove the Doeg out of this area and into Maryland by 1670.
Fairfax County was formed in 1742 from the northern part of Prince William County. It was named after Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron (1693–1781), proprietor of the Northern Neck. The Fairfax family name is derived from the Old English phrase for “blond hair”, Fæger-feax.
The oldest settlements in Fairfax County were along the Potomac River. George Washington settled in Fairfax County and built his home, Mount Vernon, facing the river. Gunston Hall, the home of George Mason, is nearby. Modern Fort Belvoir is partly on the estate of Belvoir Manor, built along the Potomac by William Fairfax in 1741.
Thomas Fairfax, the only member of the British nobility ever to reside in the colonies, lived at Belvoir before moving to the Shenandoah Valley. The Belvoir mansion and several of its outbuildings were destroyed by fire immediately after the Revolutionary War in 1783, and George Washington noted the plantation complex deteriorated into ruins.
In 1757, the northwestern two-thirds of Fairfax County became Loudoun County. In 1789, part of Fairfax County was ceded to the federal government to form Alexandria County of the District of Columbia. Alexandria County was returned to Virginia in 1846, reduced in size by the secession of the independent city of Alexandria in 1870, and renamed Arlington County in 1920. The Fairfax County town of Falls Church became an independent city in 1948. The Fairfax County town of Fairfax became an independent city in 1961.
Located near Washington, D.C., Fairfax County was an important region in the Civil War. The Battle of Chantilly or Ox Hill, during the same campaign as the second Battle of Bull Run, was fought within the county; Bull Run is the border between Fairfax and Prince William Counties. Other areas of activity included Minor’s Hill, Munson’s Hill, and Upton’s Hill, on the county’s eastern border, overlooking Washington, D.C.
The federal government’s growth during and after World War II spurred rapid growth in the county and made it increasingly suburban. Other large businesses continued to settle in Fairfax County and the opening of Tysons Corner Center spurred the rise of Tysons Corner. The technology boom and a steady government-driven economy also created rapid growth and an increasingly large and diverse population. The economy has also made Fairfax County one of the nation’s wealthiest counties.
A general aviation airport along U.S. Route 50 west of Seven Corners called the Falls Church Airpark operated in the county from 1948 to 1960. The facility’s 2,650-foot unpaved runway was used extensively by private pilots and civil defense officials. Residential development, multiple accidents, and the demand for retail space led to its closure in 1960.
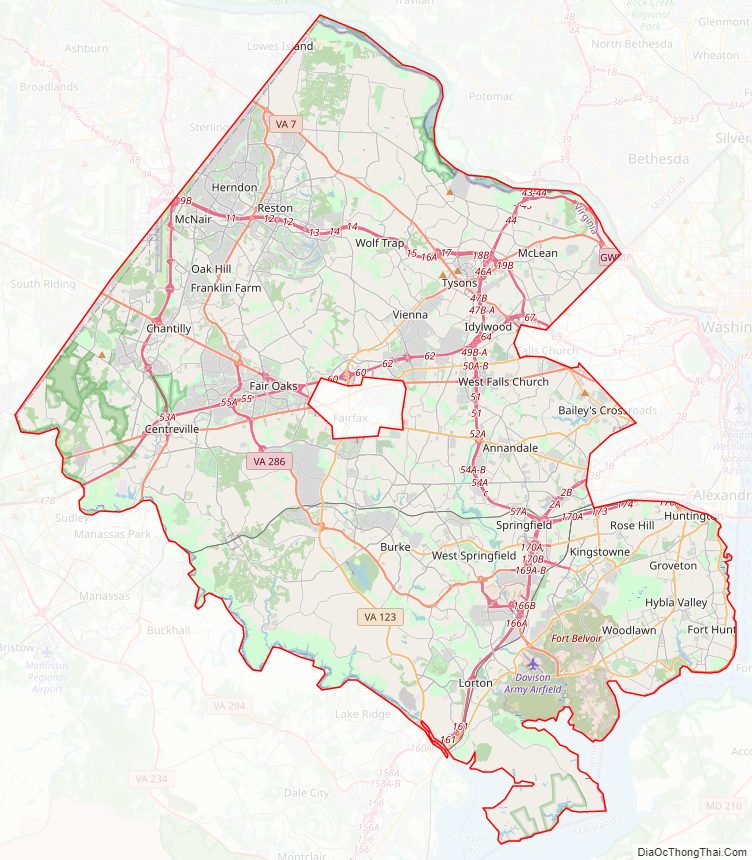
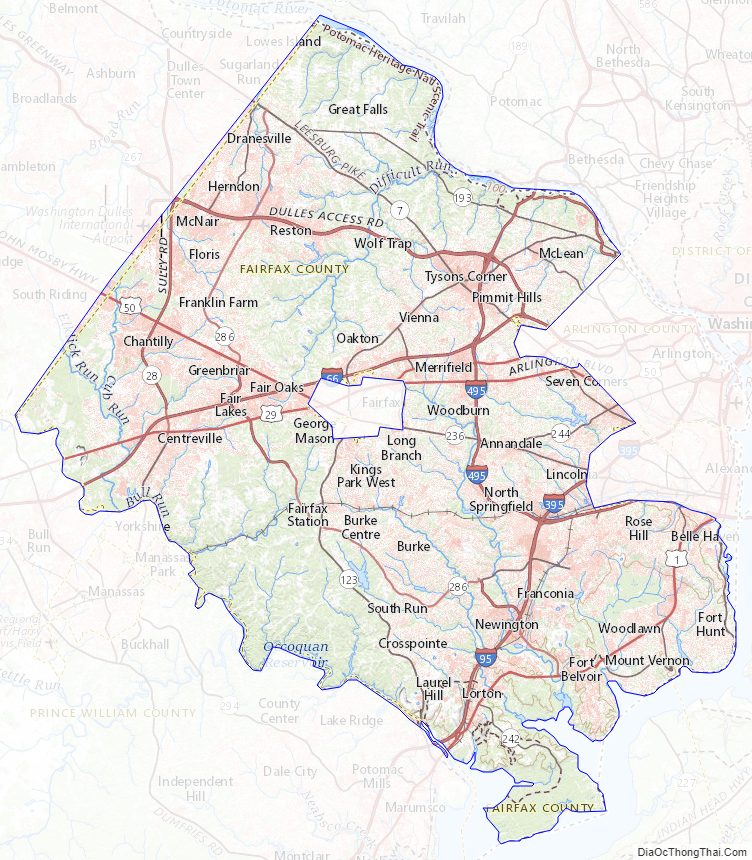
Fairfax County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has an area of 406 square miles (1,050 km), of which 391 square miles (1,010 km) is land and 15 square miles (39 km) (3.8%) is water.
Fairfax County is bounded on the north and southeast by the Potomac River. Across the river to the northeast is Washington, D.C., across the river to the north is Montgomery County, Maryland, and across the river to the southeast are Prince George’s County, Maryland and Charles County, Maryland. The county is partially bounded on the north and east by Arlington County and the independent cities of Alexandria and Falls Church. It is bounded on the west by Loudoun County, and on the south by Prince William County.
Most of the county lies in the Piedmont region, with rolling hills and deep stream valleys such as Difficult Run and its tributaries. West of Route 28, the hills give way to a flat, gentle valley that stretches west to the Bull Run Mountains in Loudoun County. Elevations in the county range from near sea level along the tidal sections of the Potomac River in the southeast portion of the county to more than 500 feet (150 m) in the Tysons Corner area.
Adjacent jurisdictions
- Arlington County – east
- Charles County, Maryland – southeast
- City of Alexandria – east
- City of Fairfax – surrounded by Fairfax County
- City of Falls Church – east
- Loudoun County – northwest
- Montgomery County, Maryland – north
- Prince George’s County, Maryland – east
- Prince William County – southwest