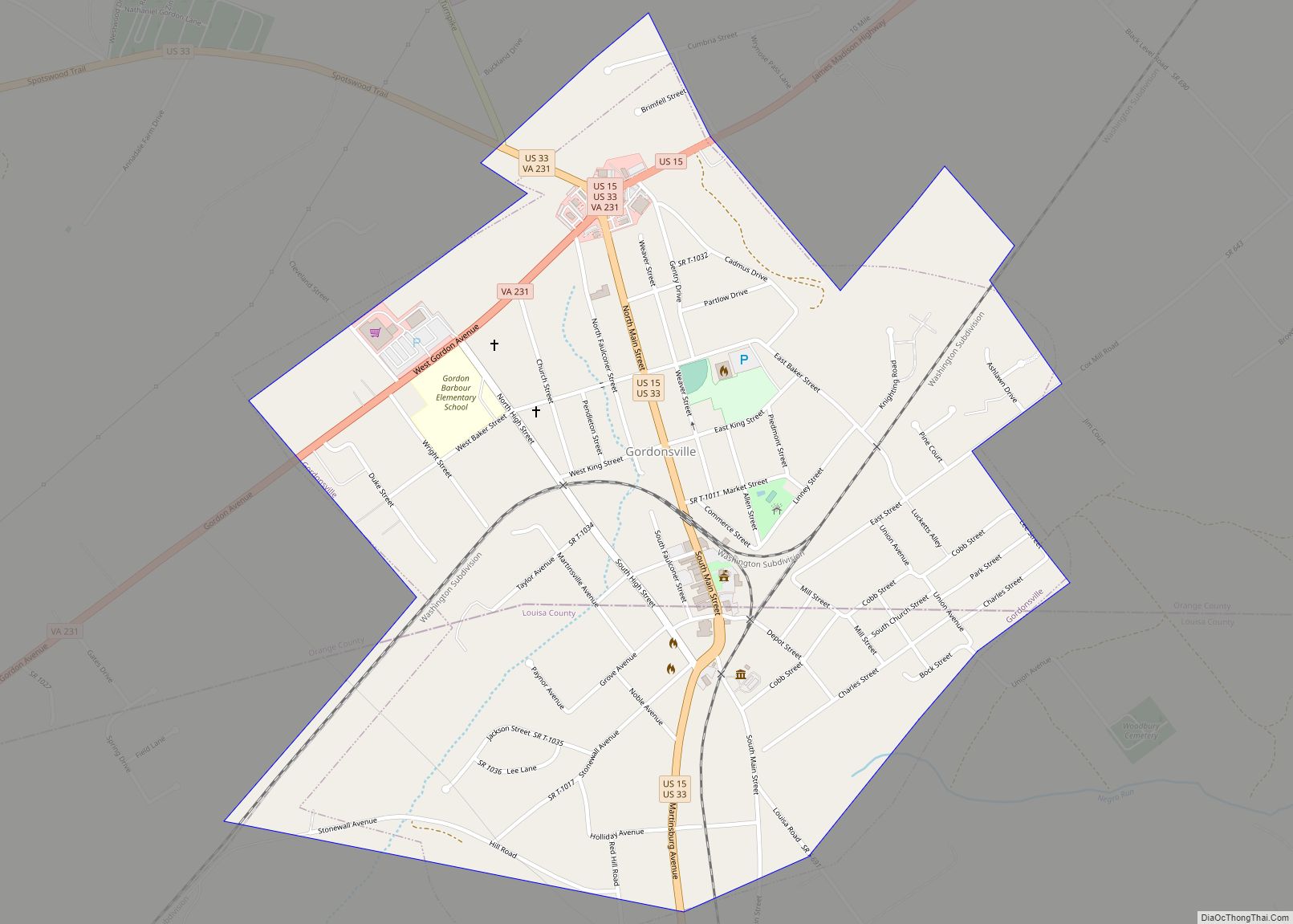
Gordonsville is a town in Orange County in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Located about 19 miles northeast of Charlottesville and 65 miles northwest of Richmond, the population was 1,496 at the 2010 census.
The town celebrated its bicentennial in 2013, two hundred years after local innkeeper Nathaniel Gordon was appointed the area’s first postmaster, thus officially creating the area known as Gordonsville. It was strategically important during the Civil War, due to its location on the Virginia Central Railroad.
Gordonsville claims to have influenced the popularity of fried chicken in the United States; it bills itself as the “Fried Chicken Capital of the World.”
| Name: | Gordonsville town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | Virginia |
| County: | Louisa County, Orange County |
| Elevation: | 499 ft (152 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.95 sq mi (2.46 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.95 sq mi (2.46 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,496 |
| Population Density: | 1,713.08/sq mi (661.28/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 22942 |
| Area code: | 540 |
| FIPS code: | 5131936 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1467264 |
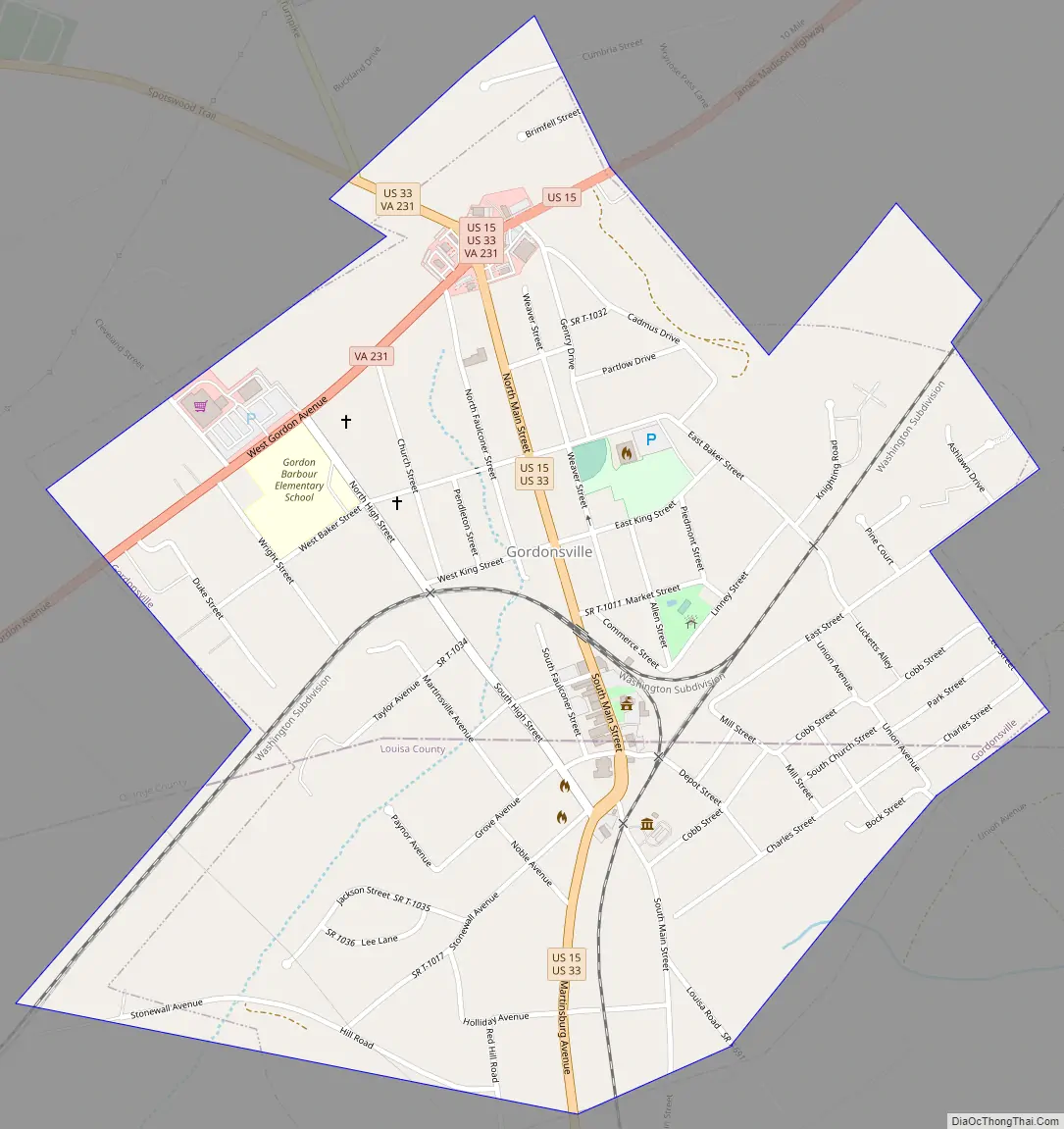
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
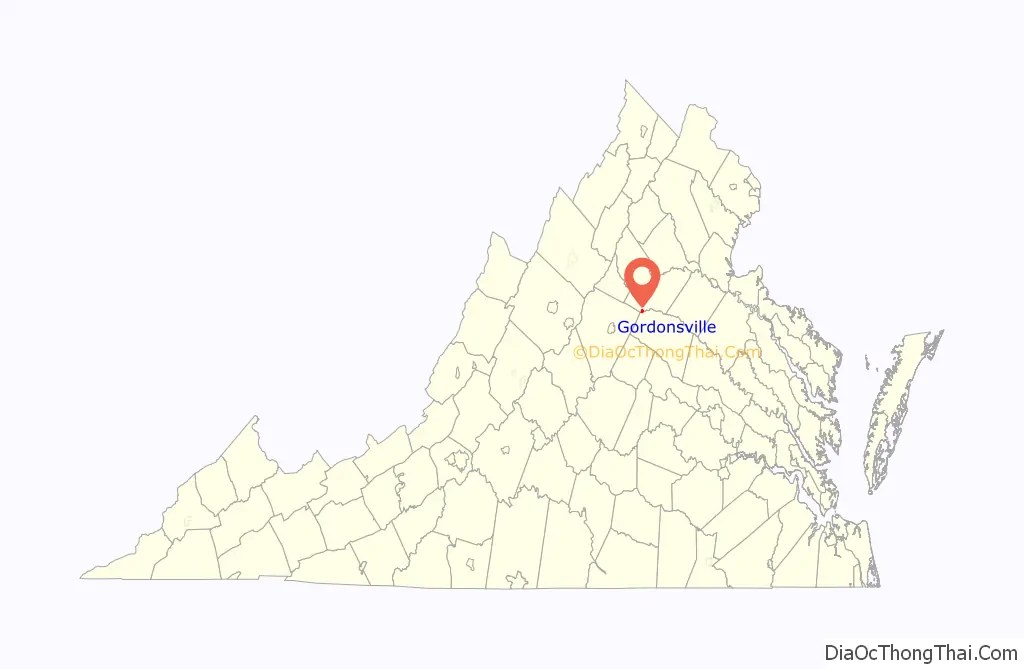
Gordonsville location map. Where is Gordonsville town?
History
Pre-Civil War
In 1787, Nathaniel Gordon purchased 1,350 acres (5.46 square km) of land, then known as “Newville,” from a cousin of President James Madison.
In 1794, or perhaps earlier, Gordon applied for and was granted a license to operate a tavern there, which, as was typical of the time, was used as a place to eat, lodge and discuss local matters. It sat at the intersection of two highways: “The Fredericksburgh Great Road,” a stage route from Charlottesville, through Orange, to Fredericksburg; and “The Richmond Road,” which led from the Virginia capital, through Louisa, west over the Blue Ridge Mountains into the Shenandoah Valley. President Thomas Jefferson described the tavern in 1802 as a “good house” when recommending the best route south to Charlottesville from the recently established national capital on the Potomac. The building was known as Gordon’s Tavern, Gordon Tavern and later as Gordon Inn. The commemorative marker at the site lists prominent Americans as guests at the tavern: George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, James Monroe, James & Philip P. Barbour, James Waddel, William Wirt and Henry Clay. Another famous visitor was Major General the Marquis de Lafayette.
Gordon was named the first postmaster of the area in 1813, and the area became known as Gordonsville. At the time of Gordon’s death in 1820, Gordonsville had, in addition to the tavern, a post office, several homes, a general mercantile store and a blacksmith shop. Nathaniel willed his land and tavern to his son, John, and near that same time Dr. Charles Beale (husband of Nathaniel’s daughter, Mary) purchased adjoining land near what is currently Main Street. The later division and sale of lots from this property, and the construction of adjacent roads, would foster growth of the town up to and during the Civil War.
In 1839, the General Assembly authorized the extension of the Louisa Railroad (later the Virginia Central Railroad) from Louisa Courthouse to Gordonsville, which ushered in growth and prosperity for Gordonsville. It became a center of trade for the plantations and farms in the surrounding countryside. Two new roadways, the Blue Ridge Turnpike and the Rockingham Turnpike, were built to connect the town to New Market and Harrisonburg, respectively.
In 1854, the Orange & Alexandria Railroad completed its line into Gordonsville, connecting the area with northern portion of Virginia. Over the next few years, both railroad lines were extended, increasing Gordonsville’s role as a transportation hub. The rail depots were constructed next to what is now S. Main Street.
Nathaniel Gordon’s original tavern burned down in 1859. Richard F. Omohundro, who owned the land at the time, rebuilt what is now known as the Exchange Hotel. Following its completion in 1860, the hotel offered elegant lodging for rail passengers and other travelers. During the Civil War, it was used as a receiving hospital that saw more than 70,000 patients. It is now known as the Civil War Exchange Museum and is arguably the most historically and architecturally significant building in Gordonsville.
During the Civil War and after
Gordonsville and the railroads which intersected there were of vital importance to the Confederacy for troop mobility and supplies. Troops from Richmond on the way to the First Battle of Bull Run on July 21, 1861, came through town. During the war years, Robert E. Lee, James Longstreet, Stonewall Jackson, Richard S. Ewell and A. P. Hill spent time in Gordonsville. Major Gen. Philip Sheridan led a raid in the direction of Gordonsville and Charlottesville but was stopped by Wade Hampton’s Confederate cavalry in the vicinity of Trevilian Station. Gordonsville was threatened many times but was always successfully defended by the Confederates. The Civil War ended in 1865 and with Gordonsville being largely unscathed, passenger rail service was quickly reestablished.
Gordonsville was officially incorporated into a town in 1870 by an act of the Virginia General Assembly. The population then was approximately 1,500. In the following years it was “a flourishing and fast improving town” and its prosperity gave rise to then-superior educational facilities and fine examples of period architecture, many of which are still standing on N. Main and W. Baker Streets. Gordonsville had the unique reputation as a fast-food emporium in the 1870s, with an active market of food vendors serving rail travelers as they stopped in the town. As alternative rail lines and roads were constructed bypassing Gordonsville, it morphed into a quiet, rural market town. Fires in 1916 and 1920 destroyed much of the downtown, with only a handful of buildings surviving to this day. Damage was repaired and buildings were rebuilt, largely shaping modern-day Gordonsville. The town has remained economically stable through current times, as has its population.
In the early 1970s, following the 100-year anniversary of the town’s incorporation, a nonprofit organization named Historic Gordonsville Inc. was formed. As of August 2013, the company owned a large number of properties downtown, including the Exchange Hotel. Their renovation and preservation efforts have helped maintain the historic commercial core of Gordonsville. House Bill 847 was passed by the Virginia Assembly in 1996, which amended §10.1-2212 of the Virginia Code to add Historic Gordonsville, Inc. to the listing of historical societies eligible to receive appropriations from the Virginia Department of Historical Resources.
Places of historical significance
The Gordonsville Historic District, Black Meadow, Exchange Hotel, and Rocklands are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The historic district and the Exchange Hotel are both within the town limits of Gordonsville; Black Meadow and Rocklands are nearby.
Gordonsville Road Map
Gordonsville city Satellite Map
Geography
Gordonsville is located at 38°8′5″N 78°11′13″W / 38.13472°N 78.18694°W / 38.13472; -78.18694 (38.134628, -78.187068).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 0.9 square miles (2.4 km), all of which is land.
See also
Map of Virginia State and its subdivision:- Accomack
- Albemarle
- Alexandria
- Alleghany
- Amelia
- Amherst
- Appomattox
- Arlington
- Augusta
- Bath
- Bedford
- Bedford City
- Bland
- Botetourt
- Bristol
- Brunswick
- Buchanan
- Buckingham
- Buena Vista
- Campbell
- Caroline
- Carroll
- Charles City
- Charlotte
- Charlottesville
- Chesapeake
- Chesterfield
- Clarke
- Clifton Forge City
- Colonial Heights
- Covington
- Craig
- Culpeper
- Cumberland
- Danville
- Dickenson
- Dinwiddie
- Emporia
- Essex
- Fairfax
- Fairfax City
- Falls Church
- Fauquier
- Floyd
- Fluvanna
- Franklin
- Frederick
- Fredericksburg
- Galax
- Giles
- Gloucester
- Goochland
- Grayson
- Greene
- Greensville
- Halifax
- Hampton
- Hanover
- Harrisonburg
- Henrico
- Henry
- Highland
- Hopewell
- Isle of Wight
- James City
- King and Queen
- King George
- King William
- Lancaster
- Lee
- Lexington
- Loudoun
- Louisa
- Lunenburg
- Lynchburg
- Madison
- Manassas
- Manassas Park
- Martinsville
- Mathews
- Mecklenburg
- Middlesex
- Montgomery
- Nelson
- New Kent
- Newport News
- Norfolk
- Northampton
- Northumberland
- Norton
- Nottoway
- Orange
- Page
- Patrick
- Petersburg
- Pittsylvania
- Poquoson
- Portsmouth
- Powhatan
- Prince Edward
- Prince George
- Prince William
- Pulaski
- Radford
- Rappahannock
- Richmond
- Roanoke
- Roanoke City
- Rockbridge
- Rockingham
- Russell
- Salem
- Scott
- Shenandoah
- Smyth
- Southampton
- Spotsylvania
- Stafford
- Staunton
- Suffolk
- Surry
- Sussex
- Tazewell
- Virginia Beach
- Warren
- Washington
- Waynesboro
- Westmoreland
- Williamsburg
- Winchester
- Wise
- Wythe
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming