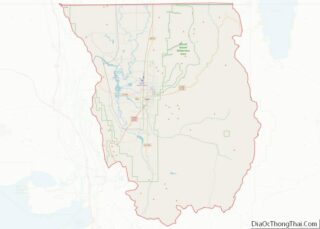
Juab County (/ˈdʒuːæb/ JOO-ab) is a county in western Utah, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 10,246. Its county seat and largest city is Nephi.
Juab County is part of the Provo–Orem, Utah Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Salt Lake City–Provo–Orem, Utah Combined Statistical Area.
| Name: | Juab County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 49-023 |
| State: | Utah |
| Founded: | March 3, 1852 |
| Named for: | Ute word for valley |
| Seat: | Nephi |
| Largest city: | Nephi |
| Total Area: | 3,406 sq mi (8,820 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3,392 sq mi (8,790 km²) |
| Total Population: | 11,786 |
| Population Density: | 3.5/sq mi (1.3/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−7 (Mountain) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−6 (MDT) |
| Website: | www.co.juab.ut.us |
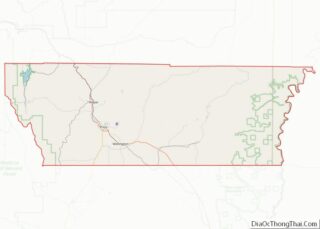
Juab County location map. Where is Juab County?
History
The area of future Juab County was inhabited by nomadic indigenous peoples before the Mormon settlement of Utah beginning in 1847. Soon after, Mormons and others traveling through the area had established a road to California, leading SSW from Great Salt Lake City. It passed Salt Creek, flowing westward through a slough in the Wasatch Mountains. The area around this creek was often used as a stopping or camping spot by travelers, and by 1851 Mormon settlers had begun a settlement in the area. When the Utah Territory legislature created a county (by partitioning territory from Utah County) to oversee the growth and organization of the largely uninhabited and unbearable area, this settlement (called Salt Creek) was the only real settlement worthy of the name, and it was designated as the county seat in a 3 March 1852 legislative act. The new county’s description included considerable territory falling in present-day Nevada. The county name reportedly derived from a Native American word meaning thirsty valley, or possibly only valley.
The county’s boundaries were altered in 1854, 1855, and 1856. Also, in 1856 the Territory legislature, acknowledging the upcoming establishment of Nevada Territory, removed from the boundary description of Juab county all territories west of 114 degrees longitude. Further boundary adjustments were made in 1861, 1862, 1866, 1870, in 1888, and 1913. A small adjustment between Juab and Sanpete counties on March 8, 1919, created the current Juab County configuration.
Early settlers in Salt Creek devoted themselves to agriculture and livestock. However, by 1869 mining of precious metals had begun in the Tintic region. Mining towns, including Diamond, Silver City, and Eureka, appeared. By 1889 it was considered one of the nation’s most productive mining areas. Mining continued as the dominant economic driver through the mid-twentieth century, then subsided. Salt Creek grew apace, although in 1882 the town name (and US Post Office designation) was changed to “Nephi”.
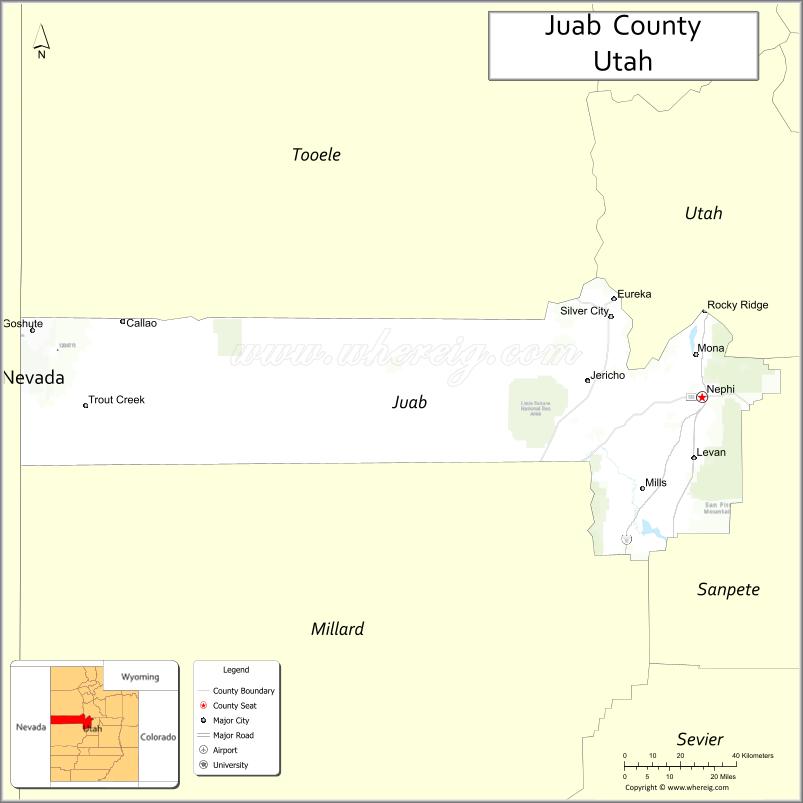
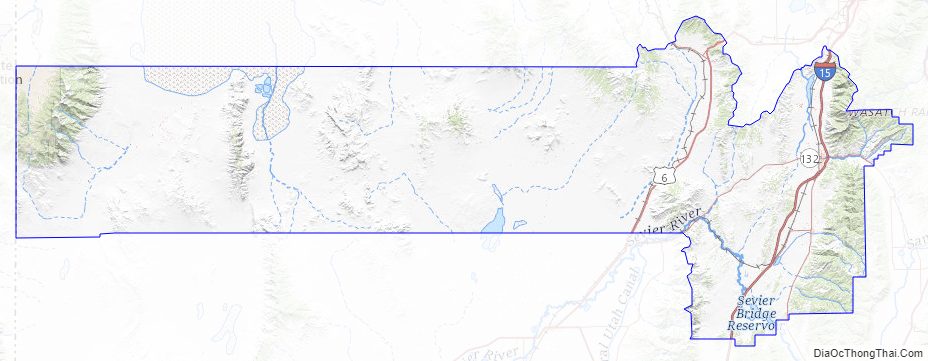
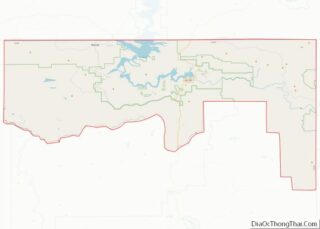
Juab County Road Map
Geography
Juab County lies on the west side of Utah. Its west border abuts the east border of the state of Nevada. Its planar areas consist of rugged, arid semi-arable fine-grain soil, with hills and low mountains. Its eastern border is loosely defined by the ridgeline of an arm of the Wasatch Mountains. The terrain generally slopes to the north, with its highest point on Mount Ibapah, a crest of the East Central Great Basin Range in northwest Juab County. The listed elevation of Mt. Ibapah is 12,087′ (3684m) ASL. The county has a total area of 3,406 square miles (8,820 km), of which 3,392 square miles (8,790 km) is land and 14 square miles (36 km) (0.4%) is water. The county’s shape bears resemblance to the shape of Massachusetts.
Airports
- Nephi Municipal Airport (NPH)
Highways
- Interstate 15
- U.S. Route 6
- Utah State Route 28
- Utah State Route 36
- Utah State Route 78
- Utah State Route 132
Adjacent counties
- Tooele County – north
- Utah County – northeast
- Sanpete County – southeast
- Millard County – south
- White Pine County, Nevada – west
Protected areas
- Deep Creek Wildlife Management Area
- Fish Springs National Wildlife Refuge
- Fishlake National Forest (part)
- Mona Front Wildlife Management Area
- Triangle Ranch Wildlife Management Area
- Uinta-Wasatch-Cache National Forest (part)
- Yuba State Park (part)
- Yuba Lake State Recreation Area
Lakes
- Andys Pond
- Antelope Springs
- Baker Hot Springs
- Big Spring
- Bittner Knoll Reservoir
- Blue Springs
- Brough Reservoir
- Burraston Ponds
- Cane Springs
- CCC Reservoir
- Cherry Creek Reservoir
- Chicken Creek Reservoir
- Coyote Knoll Reservoir
- Crater Bench Reservoir
- Dead Horse Tank
- Desert Mountain Reservoir
- Dog Valley Reservoir
- East Dugway Reservoir
- East Topaz Reservoir
- East Topaz 2 Reservoir
- Fish Springs
- Avocet Pool
- Crater Spring
- Curlew Pool
- Deadman Spring
- Egret Pool
- Gadwall Pool
- Harrison Pool
- House Springs
- Ibis Pool
- Lost Spring
- Mallard Pool
- Middle Spring
- Mirror Spring
- North Springs
- Percy Spring
- Pintail Pool
- Shoveler Pool
- South Springs
- Thomas Springs
- Walter Spring
- Hogback Reservoir
- Hole in Rock Reservoir
- Hole-in-the-Wall Reservoir
- Irons Reservoir
- Laird Spring
- Lime Spring
- Little Red Cedar Spring
- Lower Topaz Reservoir
- Mile Pond
- Molten Spring
- Mona Reservoir
- Monument Reservoir
- Mud Lake Reservoir
- Mud Springs
- North Sugarville Reservoir
- Picture Rock Reservoir
- Picture Rock Wash Reservoir
- Rain Lake
- River Bed Reservoir
- River Bed Reservoir Number 2
- Roadside Reservoir (near Boyd Station)
- Roadside Reservoir (in the Tule Valley)
- South Desert Mountain Reservoir
- Studhorse Springs
- Swasey Point Reservoir
- Table Knoll Reservoir
- Trough Spring
- West Fork Reservoir
- Yuba Lake (or Sevier Bridge Reservoir)(partially)