| Name: | Menard County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 48-327 |
| State: | Texas |
| Founded: | 1871 |
| Named for: | Michel Branamour Menard |
| Seat: | Menard |
| Largest city: | Menard |
| Total Area: | 902 sq mi (2,340 km²) |
| Land Area: | 902 sq mi (2,340 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,962 |
| Population Density: | 2.2/sq mi (0.84/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | co.menard.tx.us |
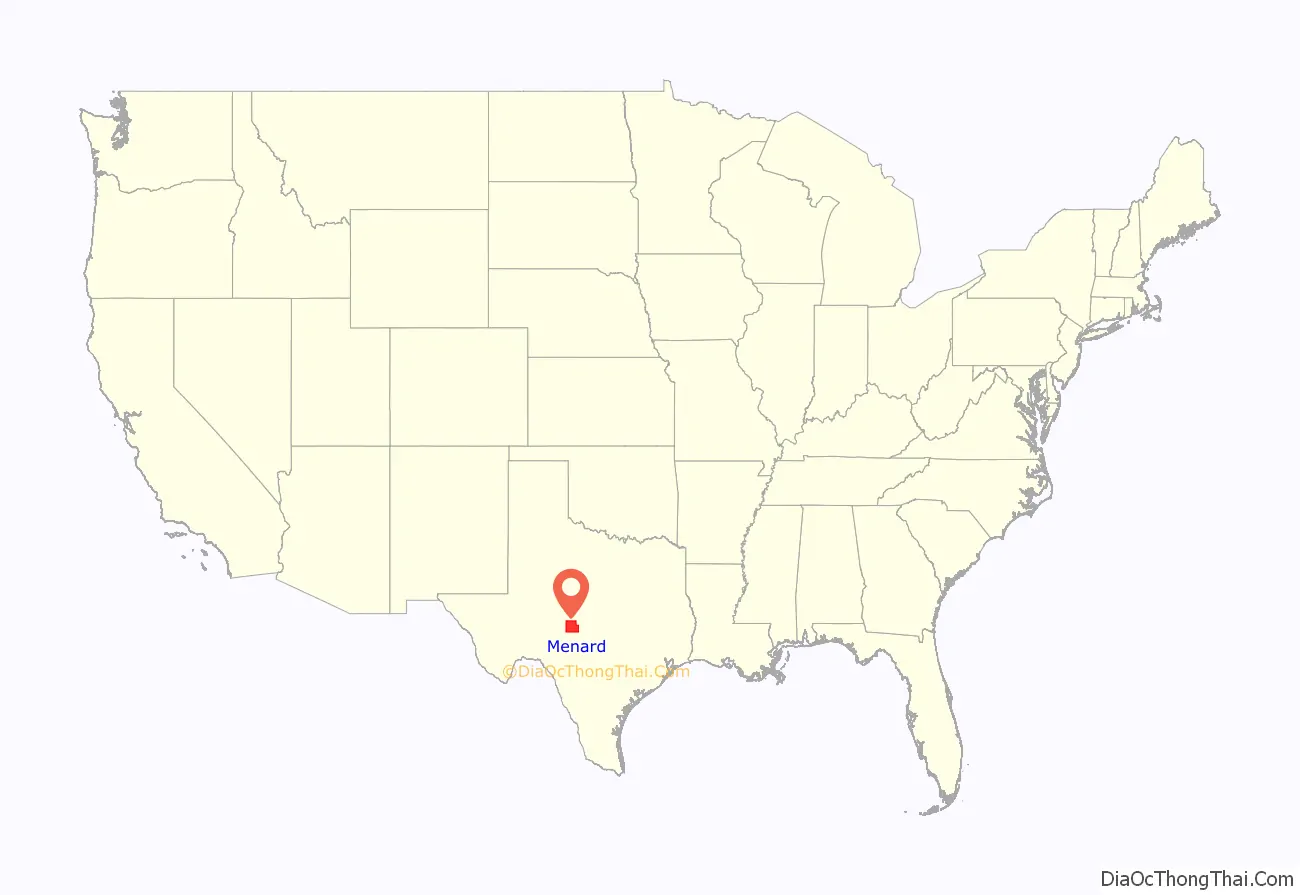
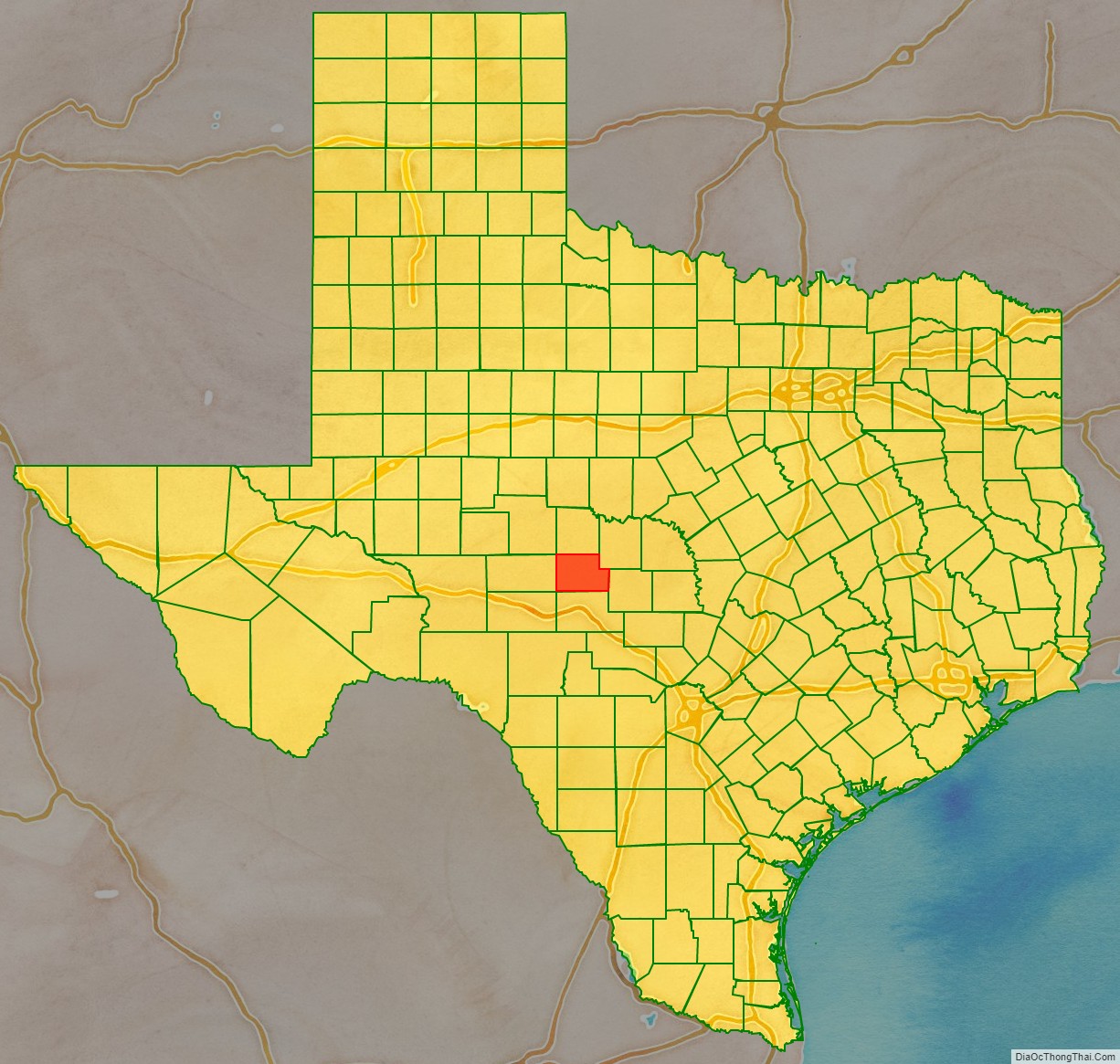
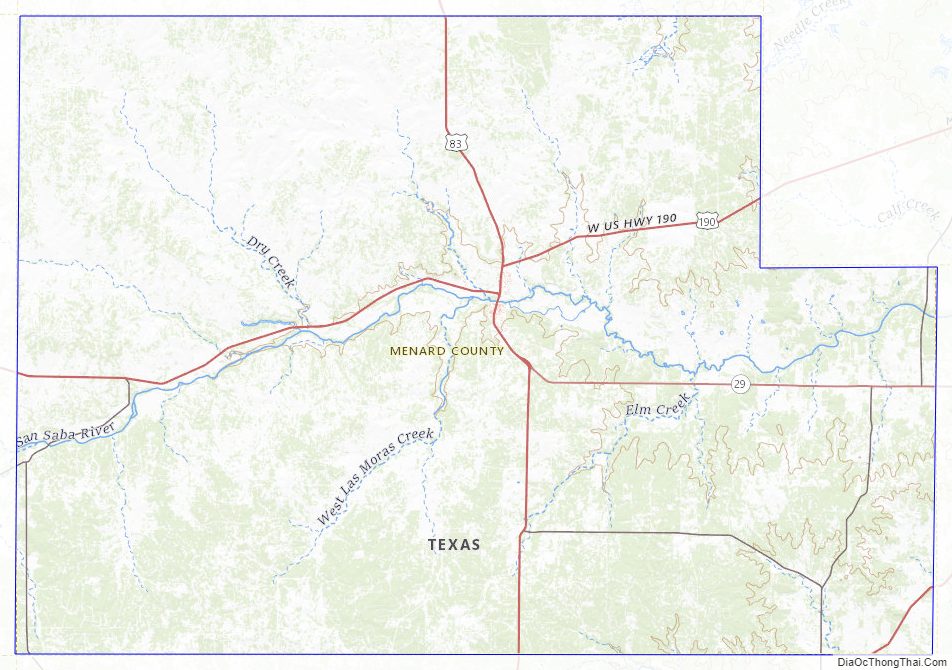
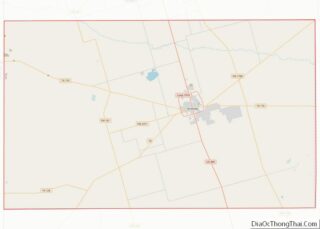
Menard County location map. Where is Menard County?
History
Around 8000, early Native American inhabitants arrived. Later Native Americans included Comanche and Lipan Apache. In 1757, Father Alonso Giraldo de Terreros founded Presidio San Luis de las Amarillas, as a support for Santa Cruz de San Sabá Mission, for the Apache Indians. In the 1830s, James Bowie and Rezin P. Bowie, scoured the San Saba valley seeking a silver mine that the Spanish had believed to be in the area. They are unsuccessful, but the legend of the Lost Bowie Mine, also known as the Lost San Saba Mine or the Los Almagres Mine, fed the imagination of treasure-seekers for the next 150 years.
Camp San Saba was established in 1852 to protect settlers from Indian attacks. The state legislature formed Menard County from Bexar County in 1858. The county was named for Michel Branamour Menard, the founder of Galveston. Menardville, later known as Menard, became the county seat.
By 1870, the county population was 667: 295 were white, and 372 were black, possibly due to the Buffalo Soldiers at Fort McKavett. The next year, county residents elected their own officials. The county had an immigrant influx from Mexico. In 1911, the Fort Worth and Rio Grande Railroad Company arrived. Gas deposits were tapped in 1929, but plugged for lack of a market. The local Parent-Teacher Association offered free lunches for needy children in 1931.
In 1934, the Texas Relief Cannery was in operation. The Drought Relief Program bought cattle and sheep from area ranchers. A gas well was redrilled in 1941, and produced about seven million cubic feet of gas. In 1946, a small oilfield was discovered northeast of Fort McKavett, but was abandoned the following year. By the 1960s, oil and gas production had an average annual yield more than 270,000 barrels (43,000 m). In the 1980s, of the county’s 40 oilfields, about 20 were still active, producing 132,000 to 185,000 barrels (29,400 m) annually.
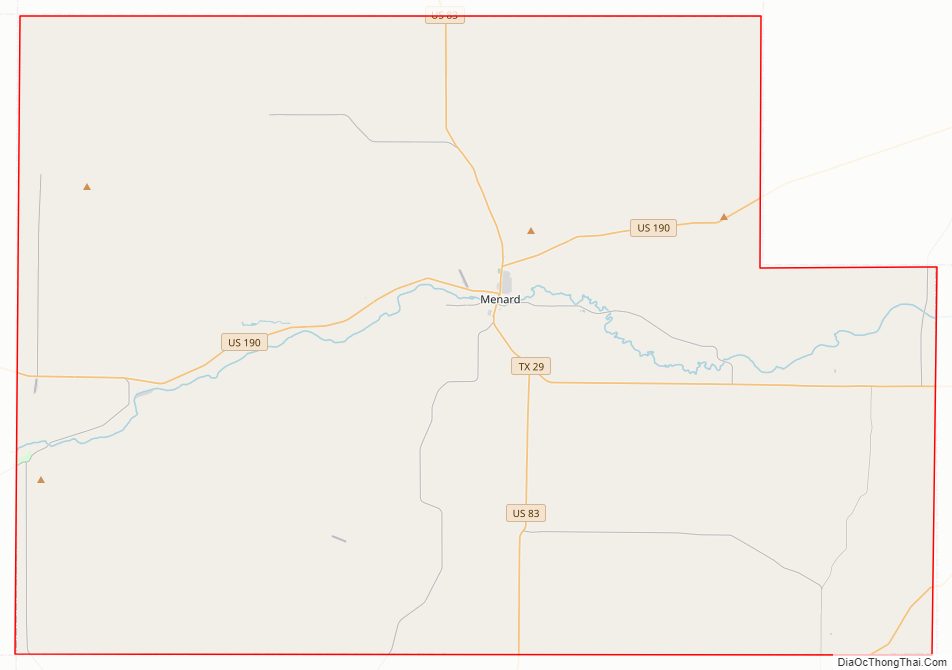
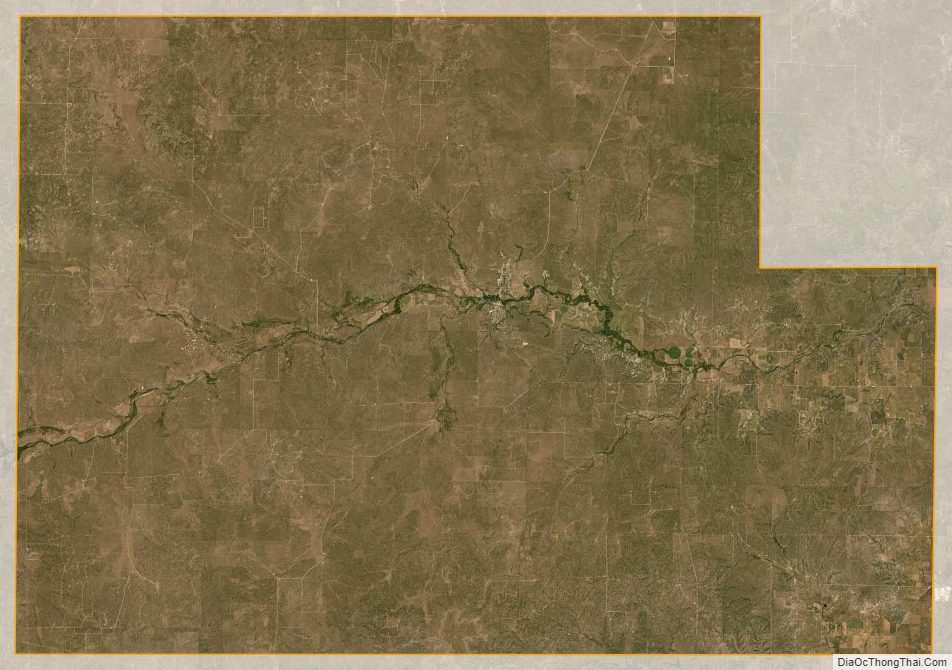
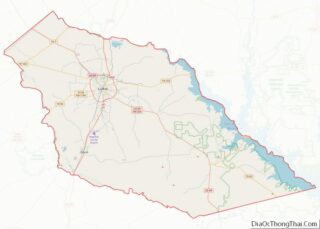
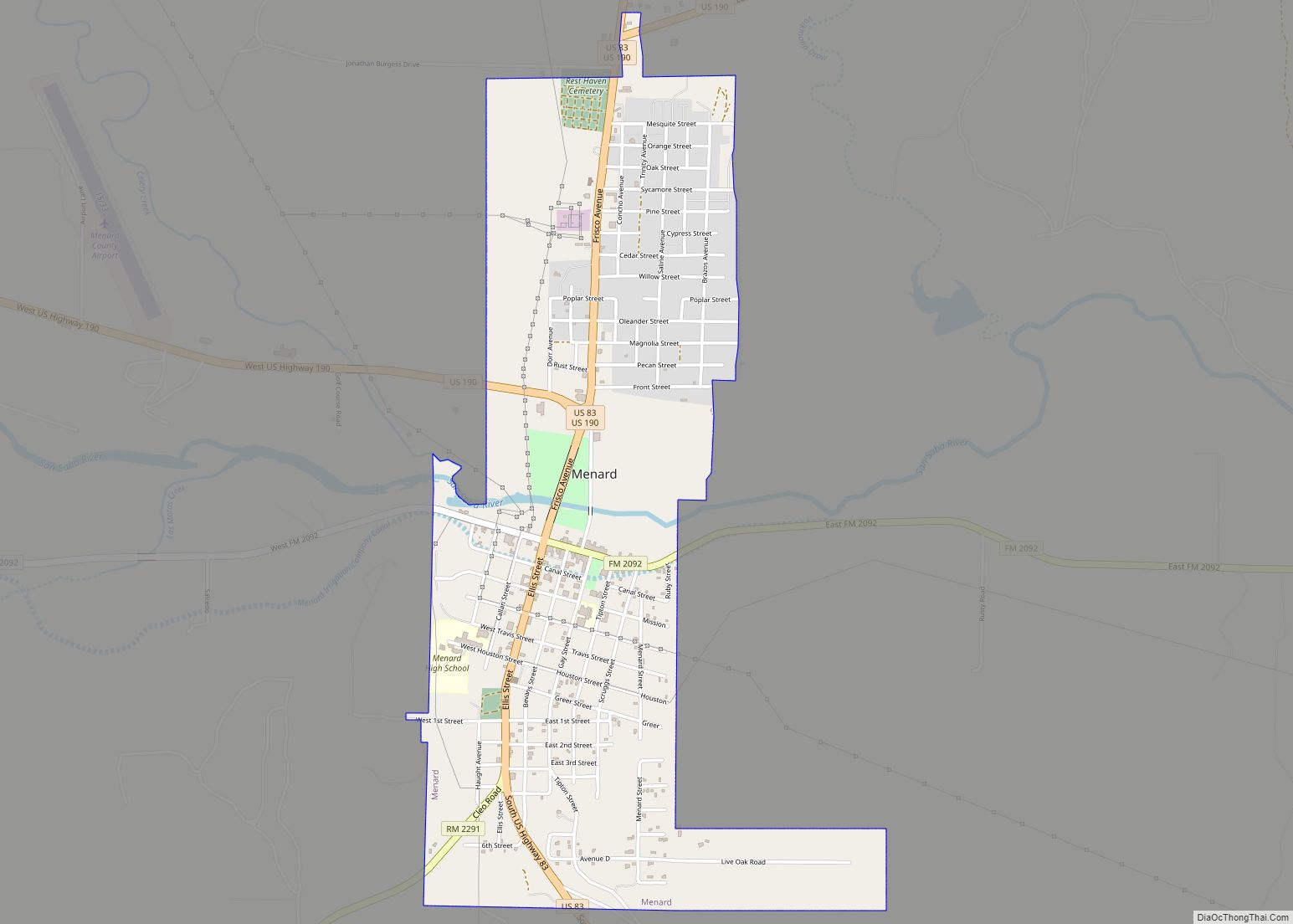
Menard County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 902 square miles (2,340 km), of which 902 square miles (2,340 km) are land and 0.2 square miles (0.52 km) (0.03%) is covered by water.
Major highways
- U.S. Highway 83
- U.S. Highway 190
- U.S. Highway 377
- State Highway 29
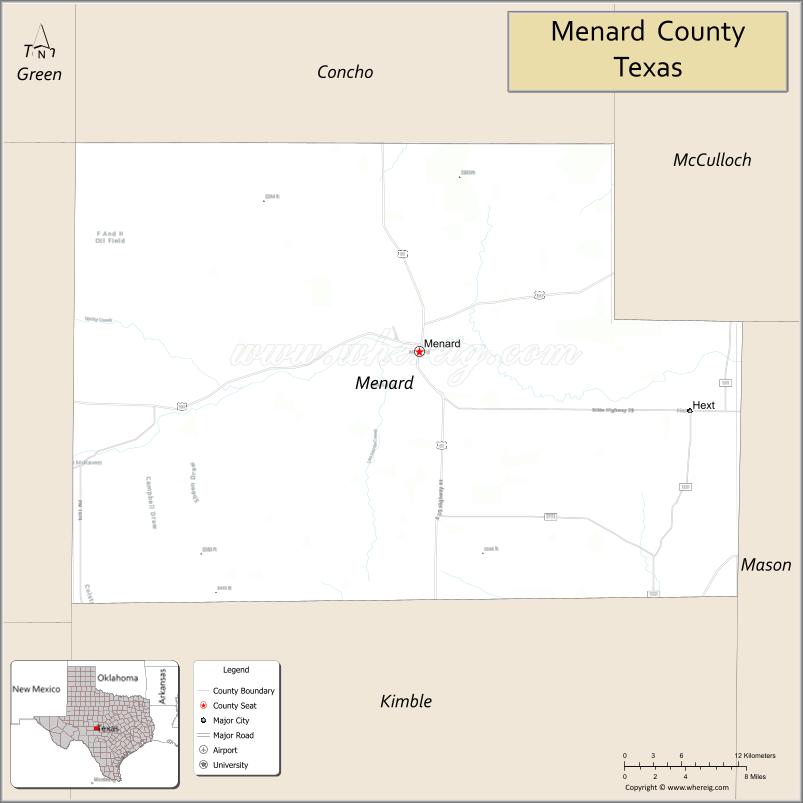
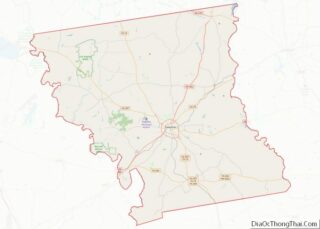
Adjacent counties
- Concho County (north)
- McCulloch County (northeast)
- Mason County (east)
- Kimble County (south)
- Schleicher County (west)
- Sutton County (southwest)
- Tom Green County (northwest)