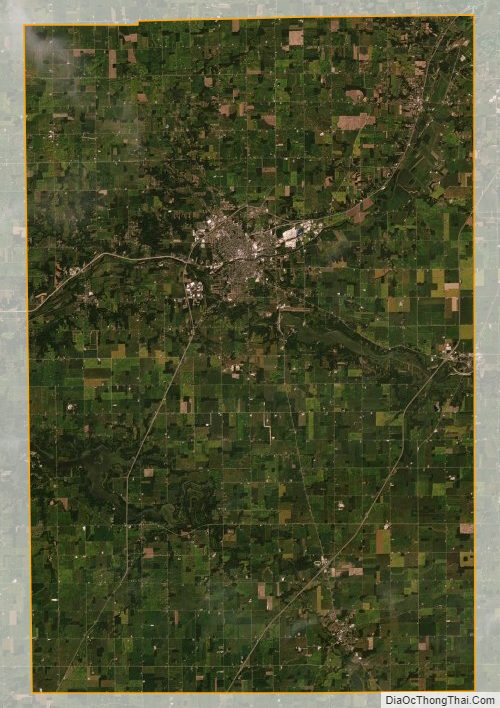
Huntington County is a county in the U.S. state of Indiana. According to the 2020 United States Census, the population was 36,662. The county seat (and only city) is Huntington.
Huntington County comprises the Huntington, Indiana micropolitan statistical area and is included in the Fort Wayne–Huntington–Auburn Combined Statistical Area.
| Name: | Huntington County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 18-069 |
| State: | Indiana |
| Founded: | 2 February 1832 (authorized) 5 May 1834 (organized) |
| Named for: | Samuel Huntington |
| Seat: | Huntington |
| Largest city: | Huntington |
| Total Area: | 387.72 sq mi (1,004.2 km²) |
| Land Area: | 382.65 sq mi (991.1 km²) |
| Total Population: | 36,662 |
| Population Density: | 95.8/sq mi (37.0/km²) |
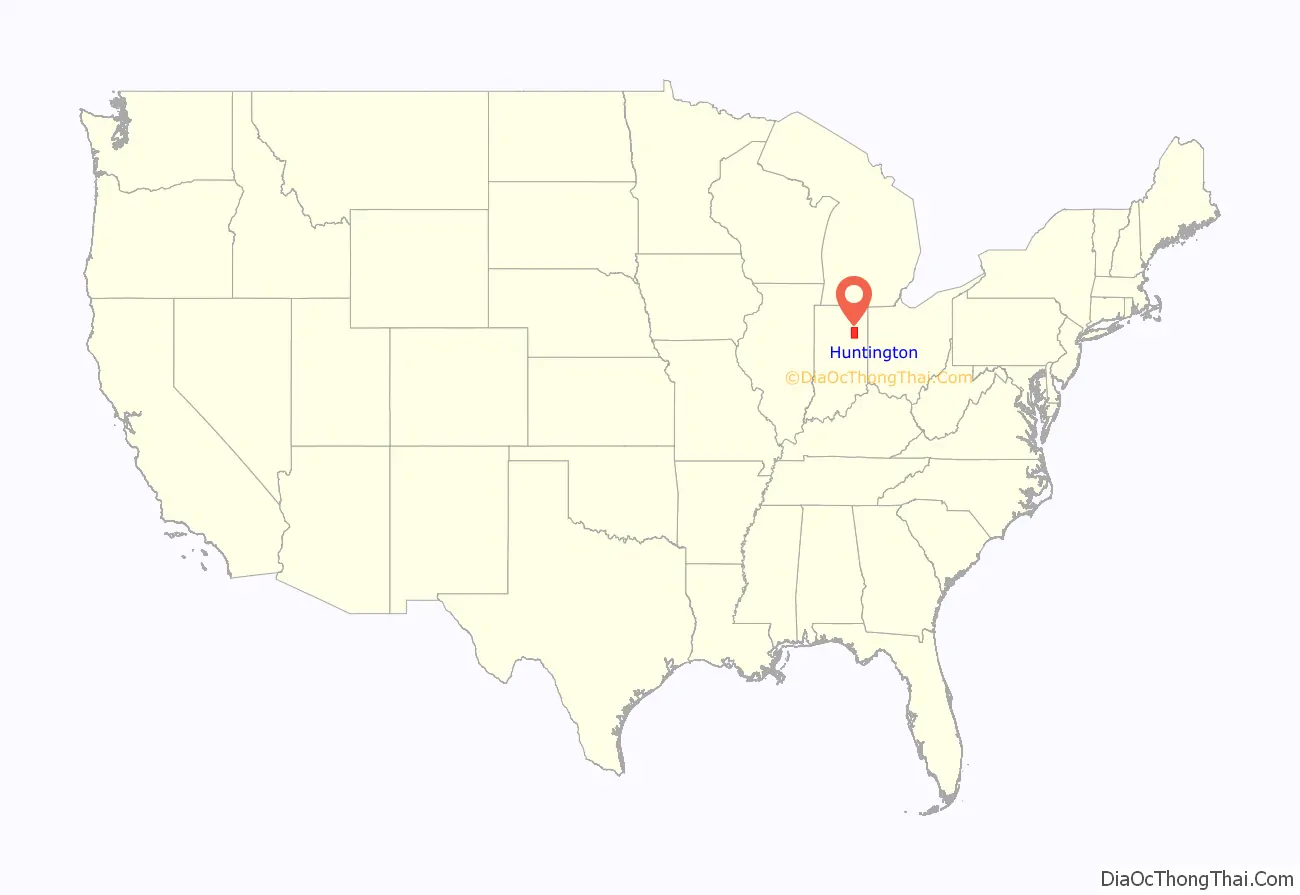
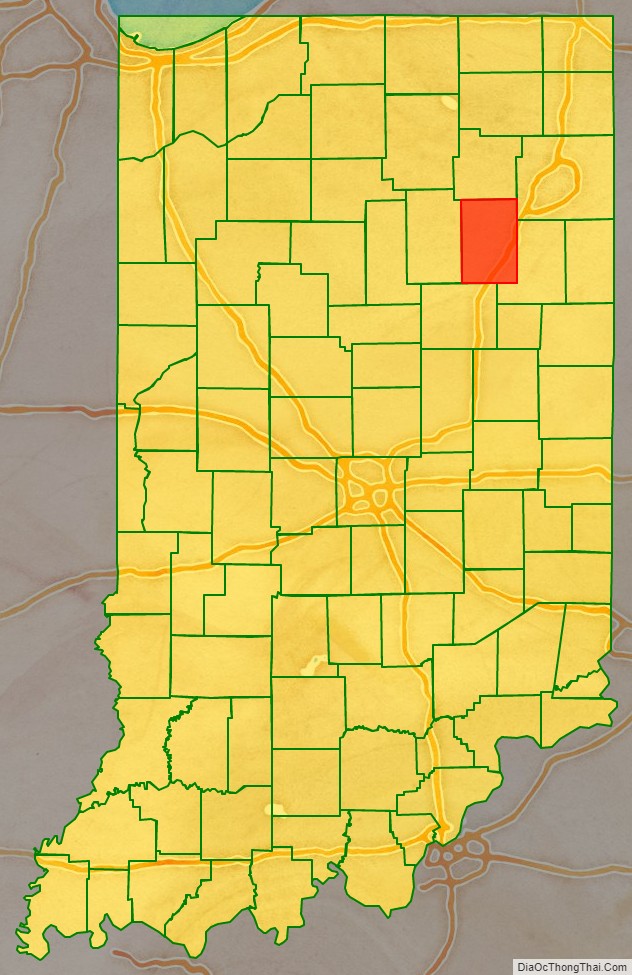
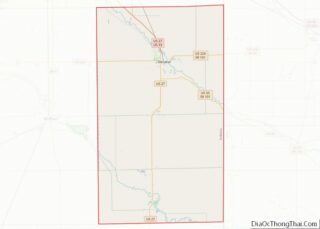
Huntington County location map. Where is Huntington County?
History
Huntington County was organized from the previously unorganized Indiana Territory and lands gained by the Adams New Purchase of 1818. The county’s creation was authorized by an act of the Indiana state legislature dated 2 February 1832. Organization of the county’s governing structure began on 5 May 1834. The first non–Native American settlers in what has since become Huntington County were a group of 29 farm families from Connecticut who arrived in the early 1830s. These were “Yankee” settlers, meaning they were descended from the English Puritans who settled New England in the colonial era. These settlers were able to get to what has since become Huntington County due to the construction of the Wabash and Erie Canal, which was a shipping canal that connected the Great Lakes to the Ohio River by way of a manmade waterway. When they arrived in what has since become Huntington County, the settlers from Connecticut found dense virgin forest and wild prairie. The original 29 “Yankee” families from Connecticut laid out roads; built a post office; established post routes; and built a town hall, a church, and a schoolhouse from the trees in the area that they cut down. The county was named for Samuel Huntington, who signed the Declaration of Independence and the Articles of Confederation. He was also president of the Continental Congress under the Articles of Confederation.
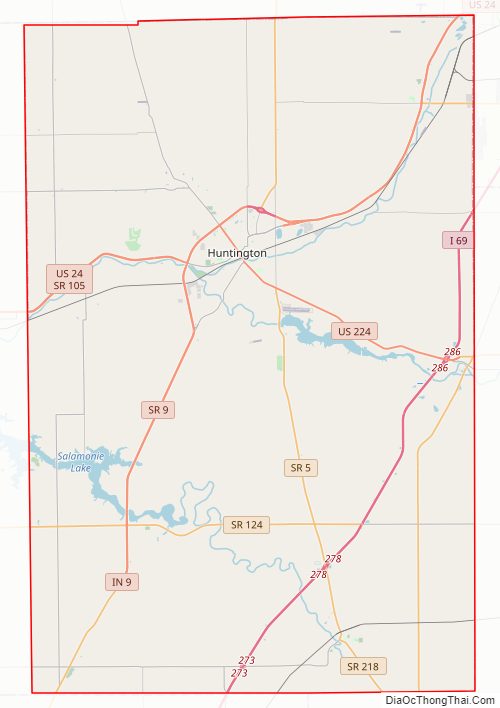
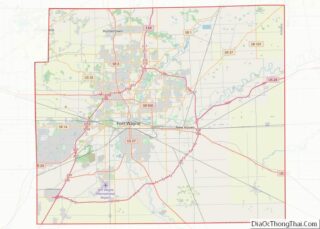
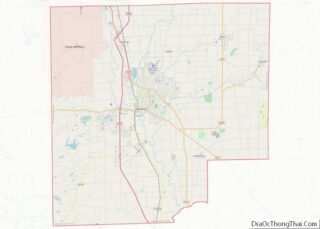
Huntington County Road Map
Geography
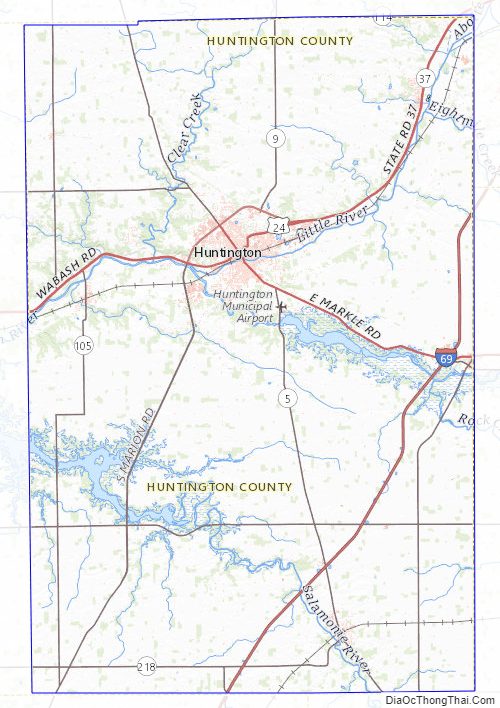
The terrain of Huntington County consists of low rolling hills, completely devoted to agriculture or urban development. The Wabash River flows to the west through the upper-central part of the county, while the Salamonie River flows to the west through the lower part. Its highest point (about 925 feet (282 m) above sea level) is at the southwest corner. According to the 2010 census, the county has a total area of 387.72 square miles (1,004.2 km), of which 382.65 square miles (991.1 km) (or 98.69%) is land and 5.07 square miles (13.1 km) (or 1.31%) is water.
Adjacent counties
- Whitley County – north
- Allen County – northeast
- Wells County – east
- Grant County – south
- Wabash County – west
Highways
- Interstate 69
- U.S. Route 24
- U.S. Route 224
- State Road 3
- State Road 5
- State Road 9
- State Road 16
- State Road 105
- State Road 114
- State Road 116
- State Road 124
- State Road 218
City and towns
- Andrews
- Banquo
- Bippus
- Goblesville
- Huntington (city)
- Lancaster
- Majenica
- Markle (partial)
- Monument City
- Mount Etna
- Plum Tree
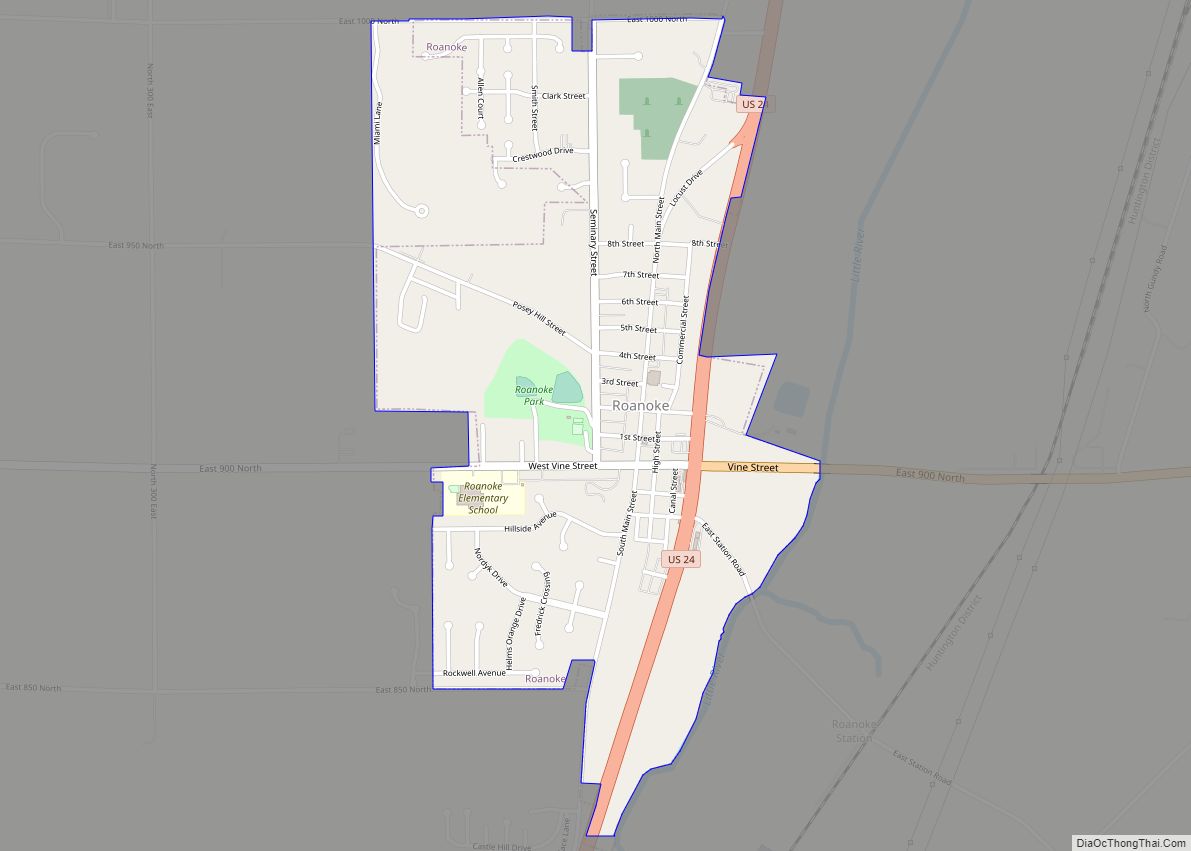
- Roanoke
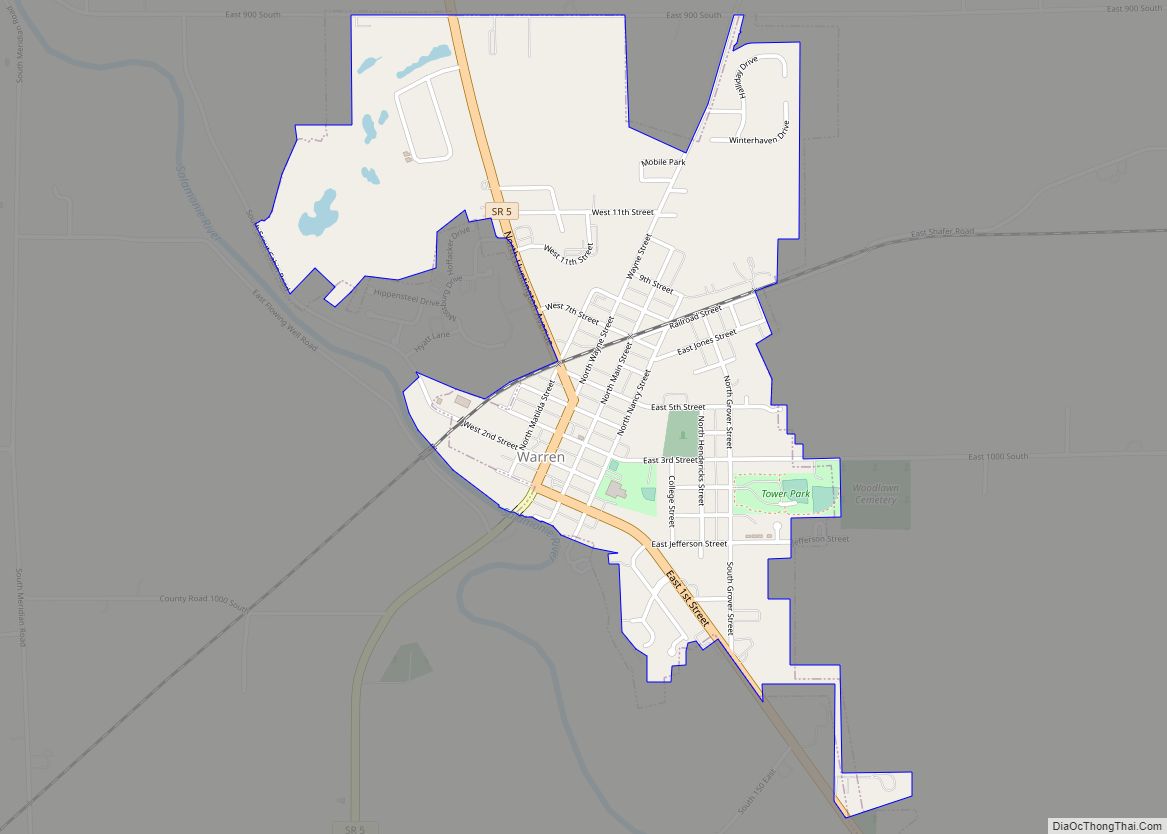
- Warren
Townships
- Clear Creek
- Dallas
- Huntington
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lancaster
- Polk
- Rock Creek
- Salamonie
- Union
- Warren
- Wayne
Unincorporated communities
- Banquo
- Bippus
- Bowerstown
- Bracken
- Buckeye
- Goblesville
- Harlansburg
- Lancaster
- Mahon
- Majenica
- Makin
- Mardenis
- Milo
- Pleasant Plain
- Plum Tree
- Roanoke Station
- Rock Creek Center
- Simpson
Protected areas
- JE Roush Fish and Wildlife Area
- Lost Bridge State Recreation Area