Indiana (/ˌɪndiˈænə/ (listen)) is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th state on December 11, 1816. It is bordered by Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the south and southeast, and the Wabash River and Illinois to the west.
Various indigenous peoples inhabited what would become Indiana for thousands of years, some of whom the U.S. government expelled between 1800 and 1836. Indiana received its name because the state was largely possessed by native tribes even after it was granted statehood. Since then, settlement patterns in Indiana have reflected regional cultural segmentation present in the Eastern United States; the state’s northernmost tier was settled primarily by people from New England and New York, Central Indiana by migrants from the Mid-Atlantic states and adjacent Ohio, and Southern Indiana by settlers from the Upland South, particularly Kentucky and Tennessee.
Indiana has a diverse economy with a gross state product of $352.62 billion in 2021. It has several metropolitan areas with populations greater than 100,000 and a number of smaller cities and towns. Indiana is home to professional sports teams, including the NFL’s Indianapolis Colts and the NBA’s Indiana Pacers. The state also hosts several notable competitive events, such as the Indianapolis 500, held at Indianapolis Motor Speedway.
| Before statehood: | Indiana Territory |
|---|---|
| Admitted to the Union: | December 11, 1816 (19th) |
| Capital: | Indianapolis |
| Capital – largest city: | largest city |
| Largest metro and urban areas: | Indianapolis |
| Elevation: | 700 ft (210 m) |
| Total Area: | 36,418 sq mi (94,321 km) |
| Area Rank: | 38th |
| Total Population: | 6,785,528 |
| Population Rank: | 17th |
| Population Density: | 189/sq mi (73.1/km) |
| Population Density Rank: | 16th |
| Median Household Income: | $54,181 (2,017) |
| Income Rank: | 37th |
| Demonym(s): | Hoosier |
| USPS abbreviation: | IN |
| ISO 3166 code: | US-IN |
| Website: | www.in.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
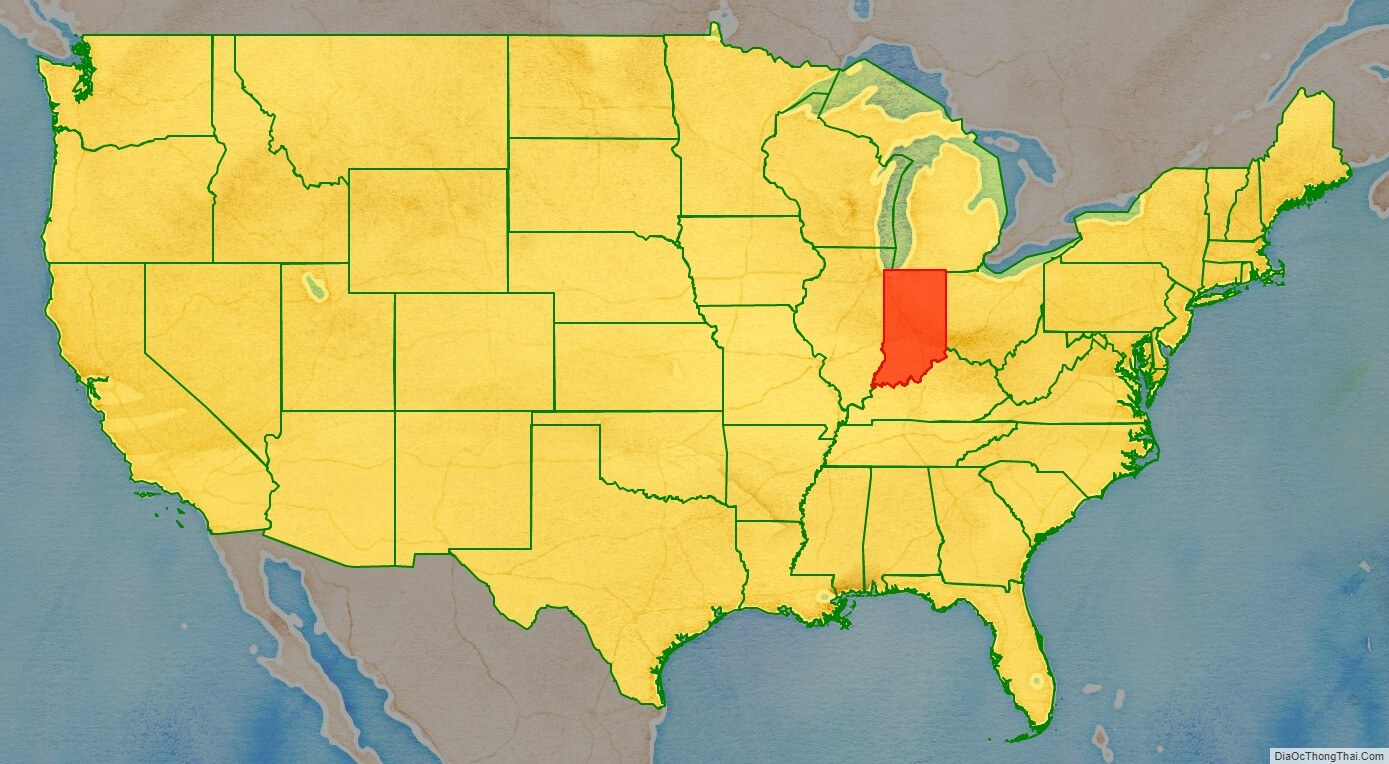
Indiana location map. Where is Indiana state?
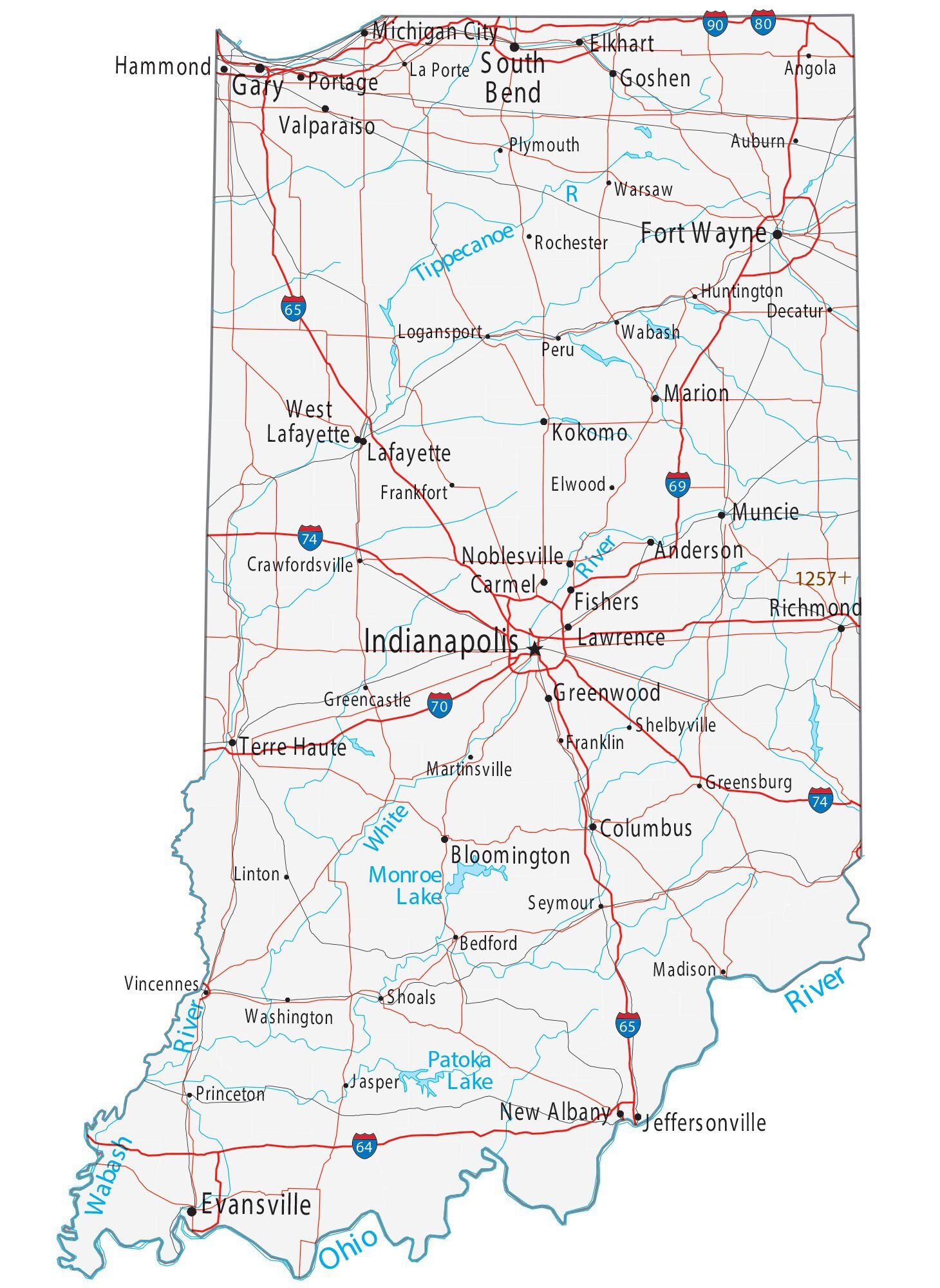
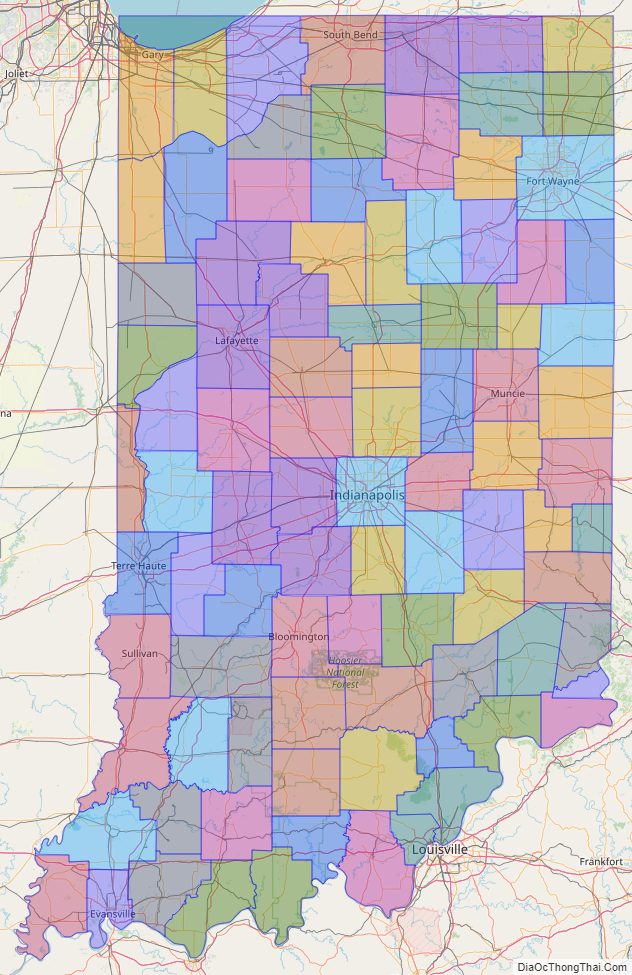
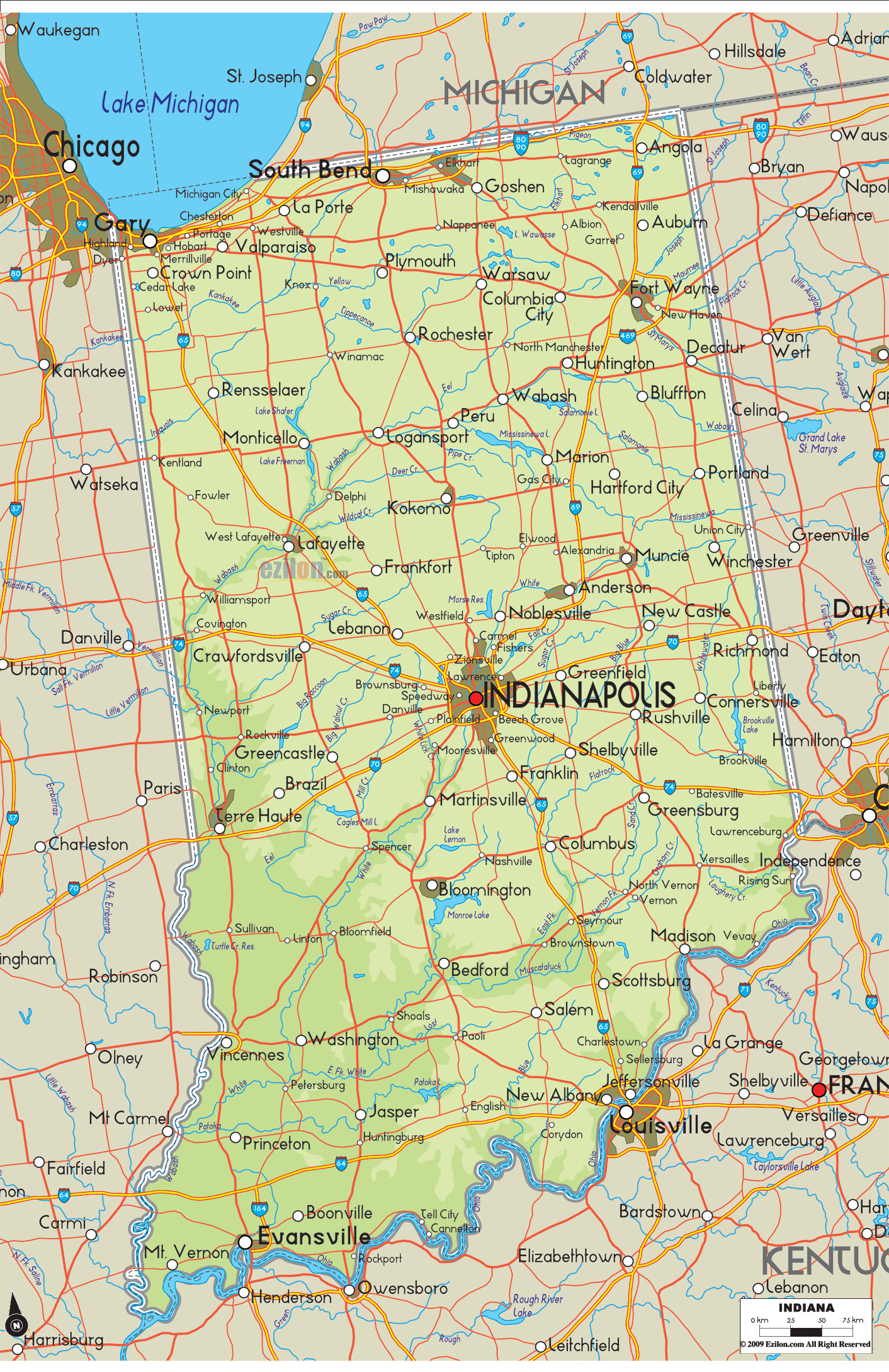
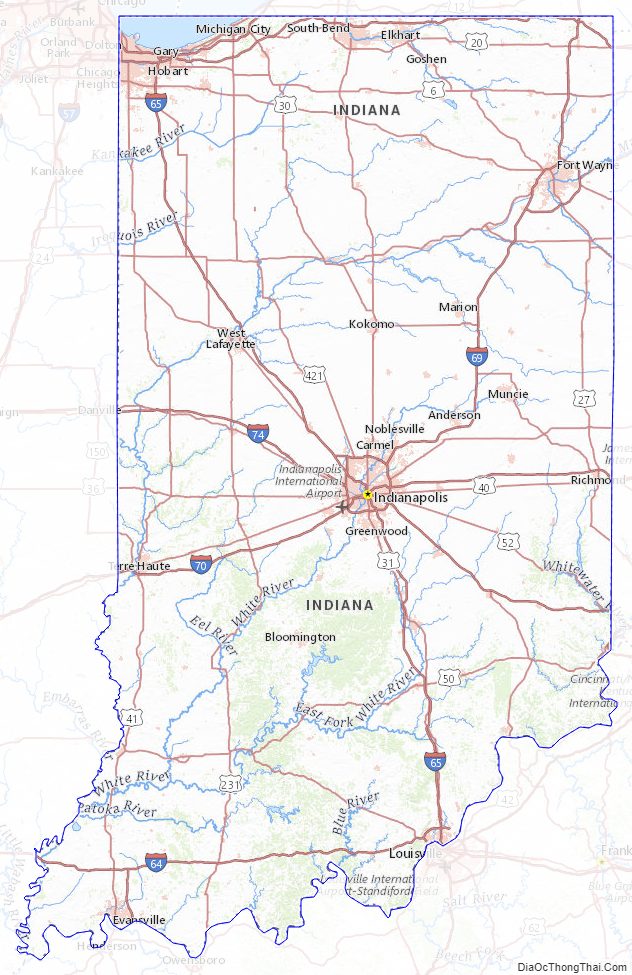
Indiana Road Map
Indiana Map – Roads & Cities
Indiana Street Map
Indiana State Map – Places and Landmarks
Indiana Political Map
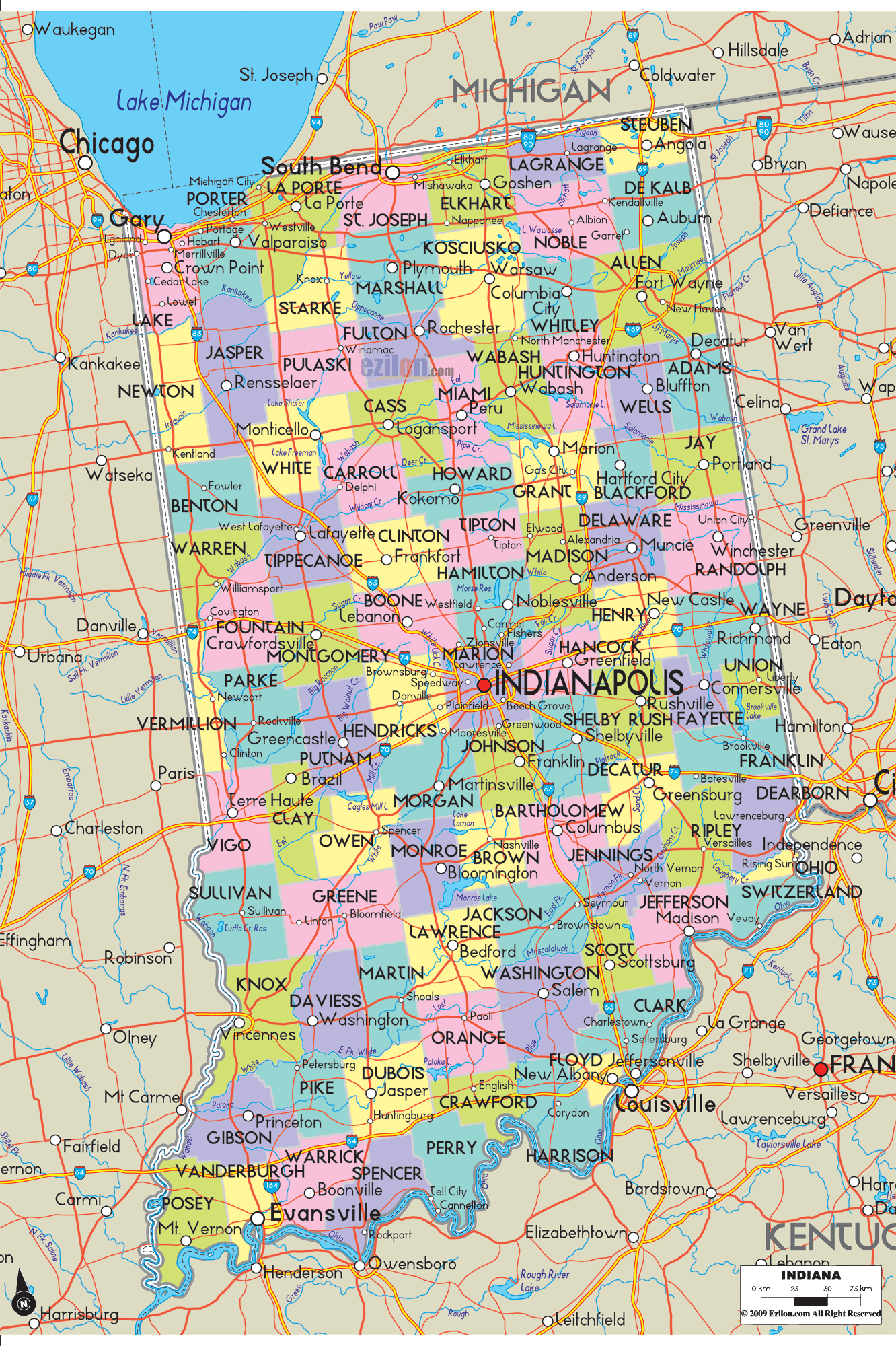
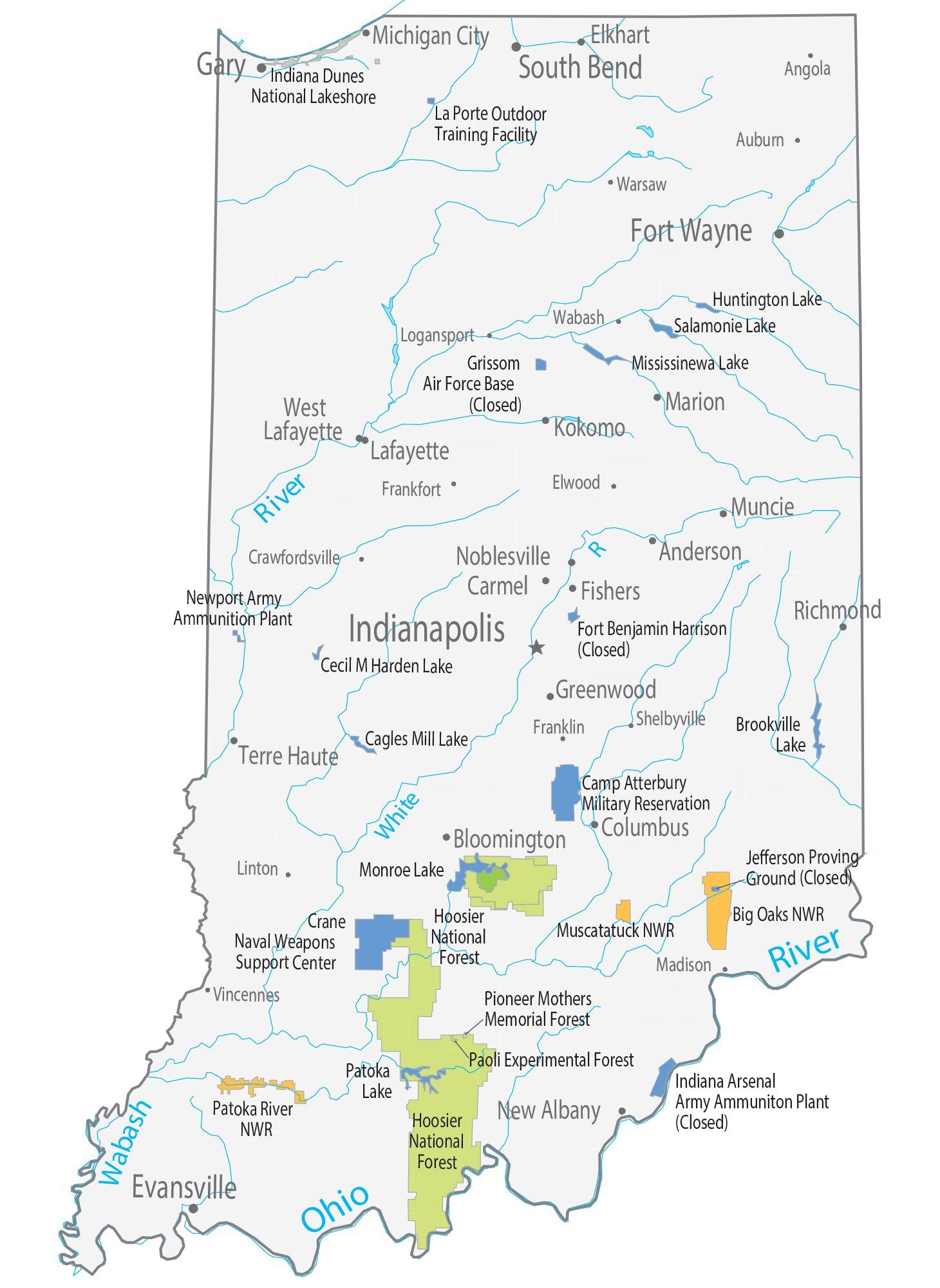
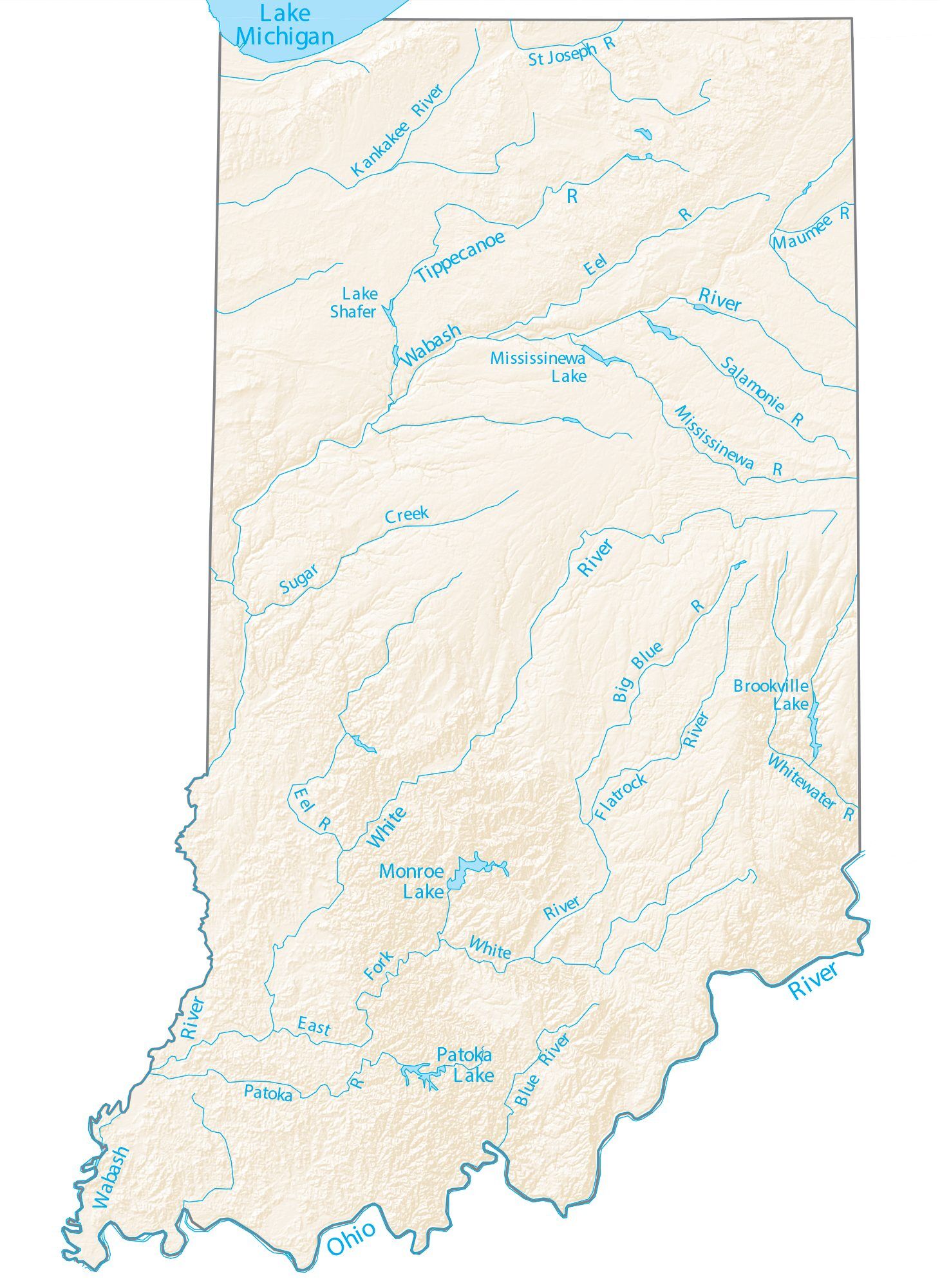
Indiana Lakes and Rivers Map
Geography
With a total area (land and water) of 36,418 square miles (94,320 km), Indiana ranks as the 38th largest state in size. The state has a maximum dimension north to south of 250 miles (400 km) and a maximum east to west dimension of 145 miles (233 km). The state’s geographic center (39° 53.7’N, 86° 16.0W) is in Marion County.
Located in the Midwestern United States, Indiana is one of eight states that make up the Great Lakes Region. Indiana is bordered on the north by Michigan, on the east by Ohio, and on the west by Illinois, partially separated by the Wabash River. Lake Michigan borders Indiana on the northwest and the Ohio River separates Indiana from Kentucky on the south.
Geology and terrain
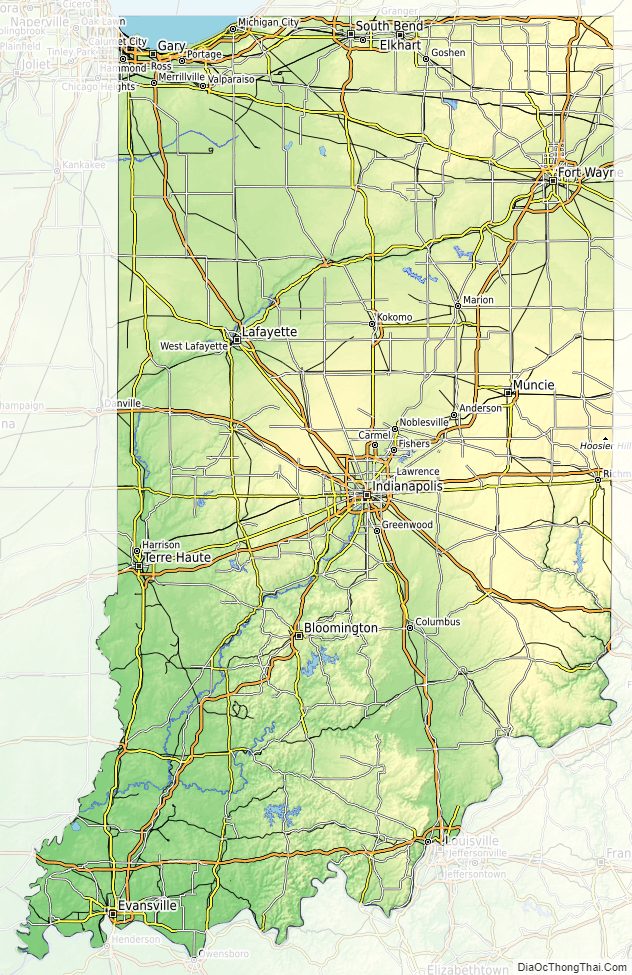
The average altitude of Indiana is about 760 feet (230 m) above sea level. The highest point in the state is Hoosier Hill in Wayne County at 1,257 feet (383 m) above sea level. The lowest point at 320 feet (98 m) above sea level is in Posey County, where the Wabash River meets the Ohio River. The resulting elevation span, 937 feet (286 m), is the narrowest of any non-coastal U.S. state. Only 2,850 square miles (7,400 km) have an altitude greater than 1,000 feet (300 m) and this area is enclosed within 14 counties. About 4,700 square miles (12,000 km) have an elevation of less than 500 feet (150 m), mostly concentrated along the Ohio and lower Wabash Valleys, from Tell City and Terre Haute to Evansville and Mount Vernon.
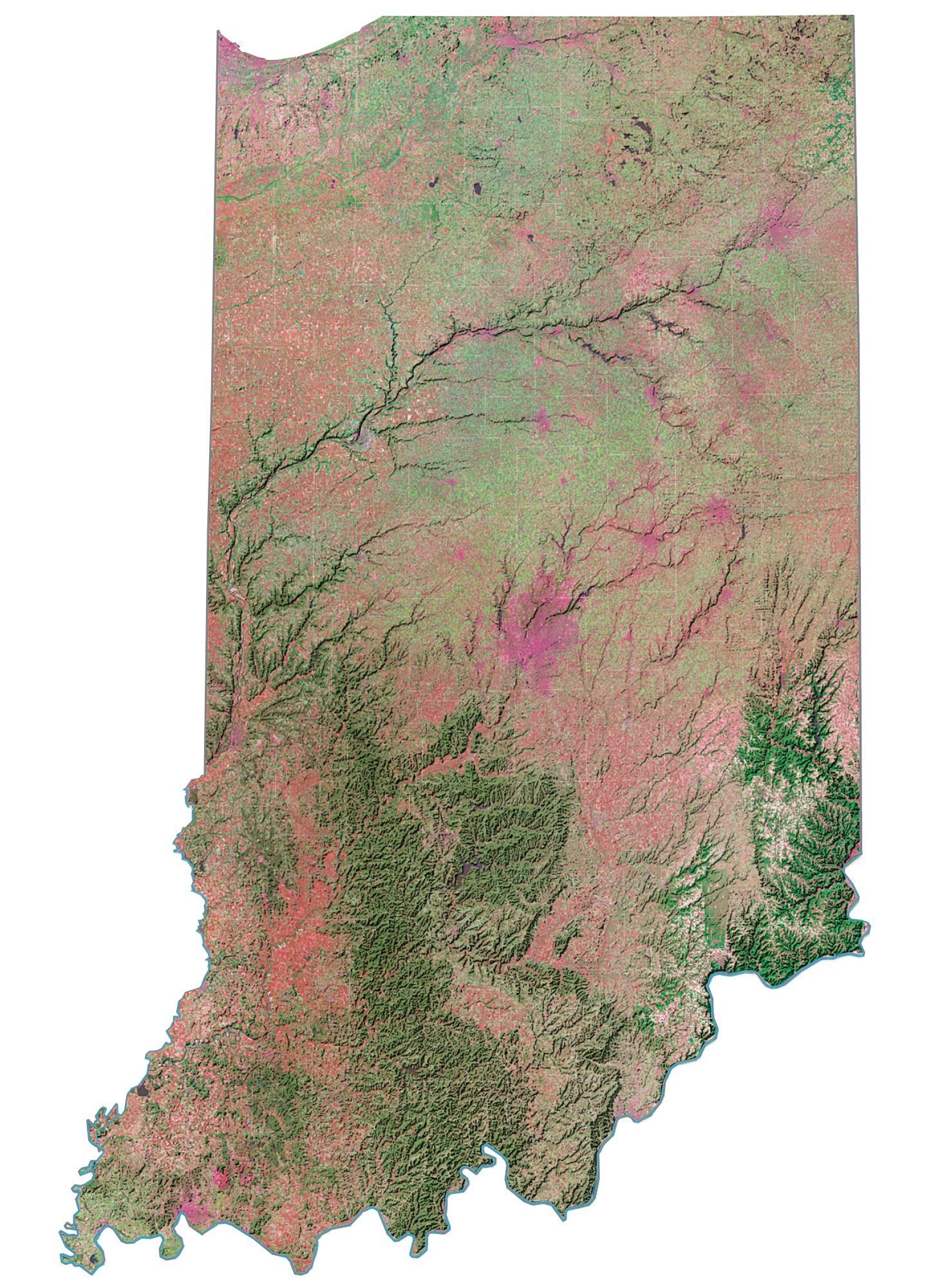
The state includes two natural regions of the United States: the Central Lowlands and the Interior Low Plateaus. The till plains make up the northern and central regions of Indiana. Much of its appearance is a result of elements left behind by glaciers. Central Indiana is mainly flat with some low rolling hills (except where rivers cut deep valleys through the plain, like at the Wabash River and Sugar Creek) and soil composed of glacial sands, gravel and clay, which results in exceptional farmland. Northern Indiana is similar, except for the presence of higher and hillier terminal moraines and hundreds of kettle lakes. In northwest Indiana there are various sand ridges and dunes, some reaching nearly 200 feet in height; most of them are at Indiana Dunes National Park. These are along the Lake Michigan shoreline and also inland to the Kankakee Outwash Plain.
Southern Indiana is characterized by valleys and rugged, hilly terrain, contrasting with much of the state. Here, bedrock is exposed at the surface. Because of the prevalent Indiana limestone, the area has many caves, caverns, and quarries.
Hydrology
Major river systems in Indiana include the Whitewater, White, Blue, Wabash, St. Joseph, and Maumee rivers. According to the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, as of 2007, there were 65 rivers, streams, and creeks of environmental interest or scenic beauty, which included only a portion of an estimated 24,000 total river miles within the state.
The Wabash River, which is the longest free-flowing river east of the Mississippi River, is the official river of Indiana. At 475 miles (764 kilometers) in length, the river bisects the state from northeast to southwest, forming part of the state’s border with Illinois, before converging with the Ohio River. The river has been the subject of several songs, such as On the Banks of the Wabash, The Wabash Cannonball and Back Home Again, In Indiana.
There are about 900 lakes listed by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources. To the northwest, Indiana borders Lake Michigan, one of five lakes comprising the Great Lakes, the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world. Tippecanoe Lake, the deepest lake in the state, reaches depths at nearly 120 feet (37 m), while Lake Wawasee is the largest natural lake in Indiana. At 10,750 acres (summer pool level), Lake Monroe is the largest lake in Indiana.
Climate
In the past, almost all of Indiana had a humid continental climate (Dfb), with cold winters and hot, wet summers; only the extreme southern portion of the state lay within the humid subtropical climate (Cfb), which receives more precipitation than other parts of Indiana. But as of the 2016 update, about half the state is now classified as humid subtropical. Temperatures generally diverge from the north and south sections of the state. In midwinter, average high/low temperatures range from around 30 °F/15 °F (−1 °C/−10 °C) in the far north to 41 °F/24 °F (5 °C/−4 °C) in the far south.
In midsummer there is generally a little less variation across the state, as average high/low temperatures range from around 84 °F/64 °F (29 °C/18 °C) in the far north to 90 °F/69 °F (32 °C/21 °C) in the far south. Indiana’s record high temperature was 116 °F (47 °C) set on July 14, 1936, at Collegeville. The record low was −36 °F (−38 °C) on January 19, 1994 at New Whiteland. The growing season typically spans from 155 days in the north to 185 days in the south.
While droughts occasionally occur in the state, rainfall totals are distributed relatively equally throughout the year. Precipitation totals range from 35 inches (89 cm) near Lake Michigan in northwest Indiana to 45 inches (110 cm) along the Ohio River in the south, while the state’s average is 40 inches (100 cm). Annual snowfall in Indiana varies widely across the state, ranging from 80 inches (200 cm) in the northwest along Lake Michigan to 14 inches (36 cm) in the far south. Lake effect snow accounts for roughly half the snowfall in northwest and north central Indiana due to the effects of the moisture and relative warmth of Lake Michigan upwind. The mean wind speed is 8 miles per hour (13 km/h).
In a 2012 report, Indiana was ranked eighth in a list of the top 20 tornado-prone states based on National Weather Service data from 1950 through 2011. A 2011 report ranked South Bend 15th among the top 20 tornado-prone U.S. cities, while another report from 2011 ranked Indianapolis eighth.Despite its vulnerability, Indiana is not part of Tornado Alley.
Time zones
Indiana is one of 13 U.S. states that are divided into more than one time zone. Indiana’s time zones have fluctuated over the past century. At present most of the state observes Eastern Time; six counties near Chicago and six near Evansville observe Central Time. Debate continues on the matter.
Before 2006, most of Indiana did not observe daylight saving time (DST). Some counties within this area, particularly Floyd, Clark, and Harrison counties near Louisville, Kentucky, and Ohio and Dearborn counties near Cincinnati, Ohio, unofficially observed DST by local custom. Since April 2006 the entire state observes DST.
Indiana Physical Map
Indiana Topographic Map
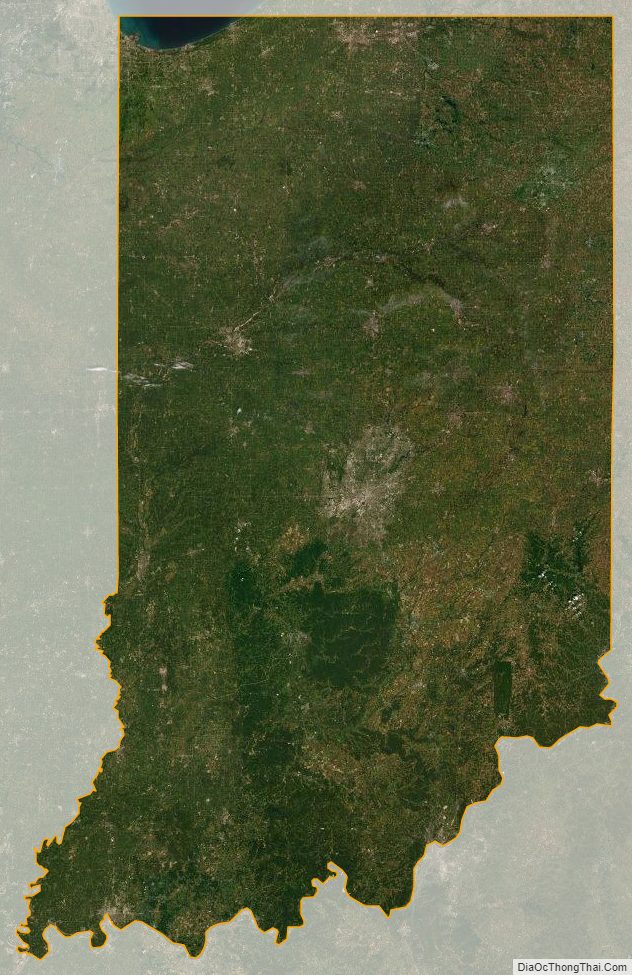
Indiana Satellite Map
Others printable maps
Indiana Outline Map
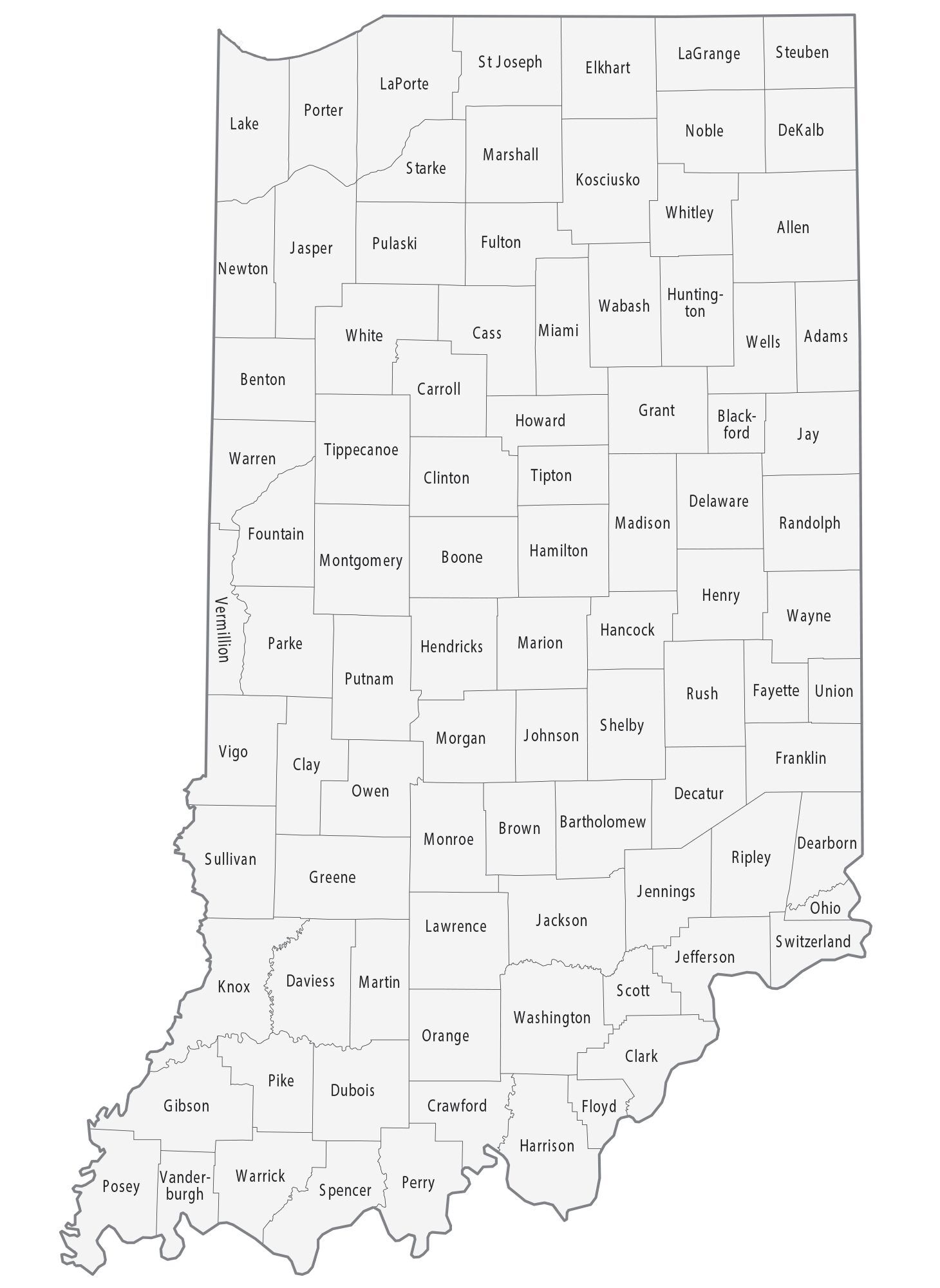
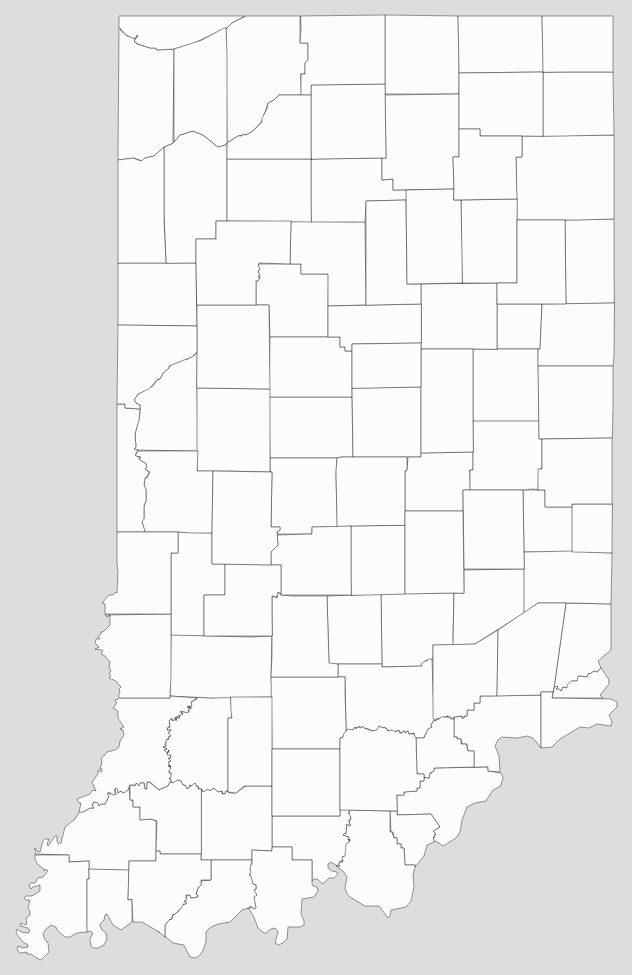
Blank Indiana County Map
See also
Map of Indiana State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Bartholomew
- Benton
- Blackford
- Boone
- Brown
- Carroll
- Cass
- Clark
- Clay
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Daviess
- De Kalb
- Dearborn
- Decatur
- Delaware
- Dubois
- Elkhart
- Fayette
- Floyd
- Fountain
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gibson
- Grant
- Greene
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Harrison
- Hendricks
- Henry
- Howard
- Huntington
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jay
- Jefferson
- Jennings
- Johnson
- Knox
- Kosciusko
- LaGrange
- Lake
- Lake Michigan
- LaPorte
- Lawrence
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Martin
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Newton
- Noble
- Ohio
- Orange
- Owen
- Parke
- Perry
- Pike
- Porter
- Posey
- Pulaski
- Putnam
- Randolph
- Ripley
- Rush
- Saint Joseph
- Scott
- Shelby
- Spencer
- Starke
- Steuben
- Sullivan
- Switzerland
- Tippecanoe
- Tipton
- Union
- Vanderburgh
- Vermillion
- Vigo
- Wabash
- Warren
- Warrick
- Washington
- Wayne
- Wells
- White
- Whitley
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming