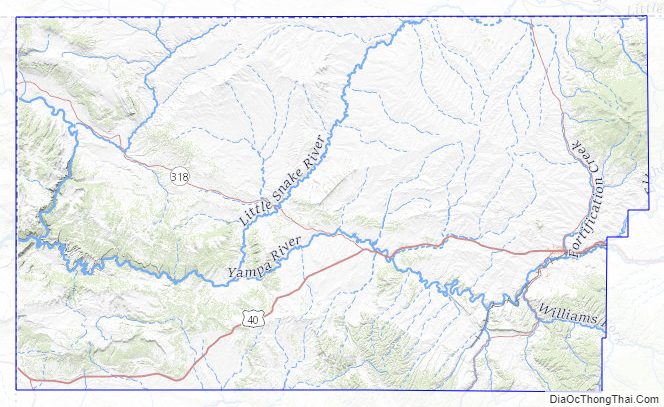
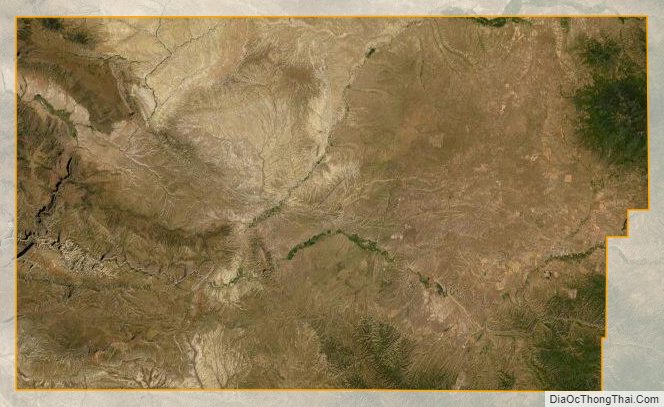
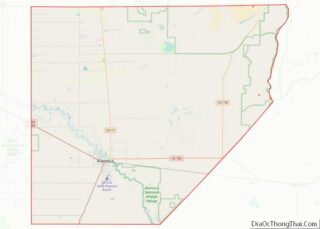
Moffat County is a county located in the U.S. state of Colorado. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,292. The county seat is Craig. With an area of 4,751 square miles, it is the 2nd largest county by area in Colorado, behind Las Animas County.
Moffat County comprises the Craig, CO Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Steamboat Springs-Craig, CO Combined Statistical Area.
| Name: | Moffat County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 08-081 |
| State: | Colorado |
| Founded: | February 27, 1911 |
| Named for: | David H. Moffat |
| Seat: | Craig |
| Largest city: | Craig |
| Total Area: | 4,751 sq mi (12,310 km²) |
| Land Area: | 4,743 sq mi (12,280 km²) |
| Total Population: | 13,185 |
| Population Density: | 2.8/sq mi (1.1/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−7 (Mountain) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−6 (MDT) |
| Website: | moffatcounty.colorado.gov |
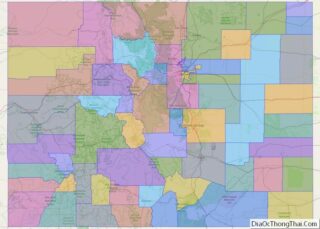
Moffat County location map. Where is Moffat County?
History
Displacement of the Native People
The first recorded humans in northwestern Colorado were the Ute tribes. The Spanish expedition of Dominguez-Escalante of 1776 reached just south of what would be Moffat County and noted the area and inhabitants, but did not offer detailed information. In the early 1820s, William H. Ashley organized a major expedition of trappers into the Green River area of the county beginning the first use of the area’s resources by Europeans. John C. Freemont would lead the first organized exploration of Moffat County on his return from California during his second expedition. His party crossed into the future Moffat County on 6 June 1844.
Despite the encroachment by trappers, miners, and explorers, the Ute Treaty of 1868 (a.k.a. The Kit Carson Treaty) and the Brunot Treaty of 1873 identified northwestern Colorado as part of the Ute nation and ‘agencies’ were established to act as representatives of the U.S. government within the Ute Nation. In 1879, a new agent, Nathan Meeker, was appointed to serve at the White River Agency in northwestern Colorado. Meeker had founded a Christian-based European agricultural colony in 1870 in eastern Colorado and had strong ideas of how a community should be structured. As the ‘Indian Agent’ he felt compelled to change the nomadic lifestyle of the Ute Indians and attempted to ‘civilize’ them by converting them into farmers. His efforts to impose an agricultural lifestyle on the native people created a conflict that ultimately led to the murder of Meeker and all of the staff at the Agency. The U.S. government’s reaction to the massacre resulted in the relocation of most of the Ute tribes to Utah by force. After the removal of the Ute tribes, the U.S. government opened up northwestern Colorado for mining, commercial cattle ranching, and homesteading.
Northwestern Colorado County Reorganizations of Territory/State
In 1861, the Colorado Territory was organized and northwestern Colorado became Summit County. In 1874, Grand County was created out of the northern half of Summit County, and in 1877, Grand County was further subdivided, creating Routt County. It would be another 34 years before Moffat County would be carved out of the western portion of Routt County. The county was named for David H. Moffat, a Colorado tycoon who died in 1911.
Development and Growth
David Moffat had been the primary force driving the establishment of a railroad from Denver to Salt Lake City. He established the Denver, Northwestern & Pacific Railway, and attempted to build a route from Denver to Salt Lake City. Construction on the ‘Moffat Road’ track began in the early 1900s but it faced constant delays and challenges. It finally reached Moffat County in 1913, ending in the town of Craig. The railroad was important for cattle ranchers in Moffat County’s early years; however, the track was never extended into Utah. In 1934, another more direct route was established to Salt Lake City, and Moffat County remained a branch line and never part of the main commerce rail artery between Denver and Salt Lake City.
In the 1920s, U.S. 40, a major cross-country highway, began construction. The route selected put Moffat County, and the County Seat of Craig on the ‘Victory Highway’ and almost exactly halfway between Denver and Salt Lake City. In 1938, the final section over the Rocky Mountains was completed and paved, with the exception of Rabbit Ears Pass in Routt County. That section would was paved before 1950. This expanded Craig’s economy by adding lodging and tourism. Unfortunately, Moffat County was excluded from the initial Interstate Highway System plans as I-80 was routed through southern Wyoming and I-70 was planned to end in Denver and not cross the Rocky Mountains. Then Colorado Governor and former Moffat County resident, Edwin C. Johnson lobbied for I-70 to continue through Denver and connect to Salt Lake City. Eventually, the federal highway agency approved I-70 to continue through Colorado but routed it through Grand Junction, Colorado, and leaving Moffat County as a secondary highway isolated between the two main east/west Interstate arteries.
The population in Moffat County stabilized at just over 5,000 people by the first census in 1920; however, remained stagnant until the 1970s when construction of three coal-fired electrical power plants began. Those three plants are now scheduled to be closed in 2025, 2028, and 2030, respectively creating a severe impact on the County’s economy. Beyond the energy industries, Moffat County’s ranching, agricultural, and tourism industries round out its primary economy. The 2020 census data has the population at almost the same as the post-power plant boom in the 1980s at 13,292 people. The 2021 estimated about 100 fewer people in the county.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 4,751 square miles (12,310 km), of which 4,743 square miles (12,280 km) is land and 7.6 square miles (20 km) (0.2%) is water. It is the second-largest county by area in Colorado.
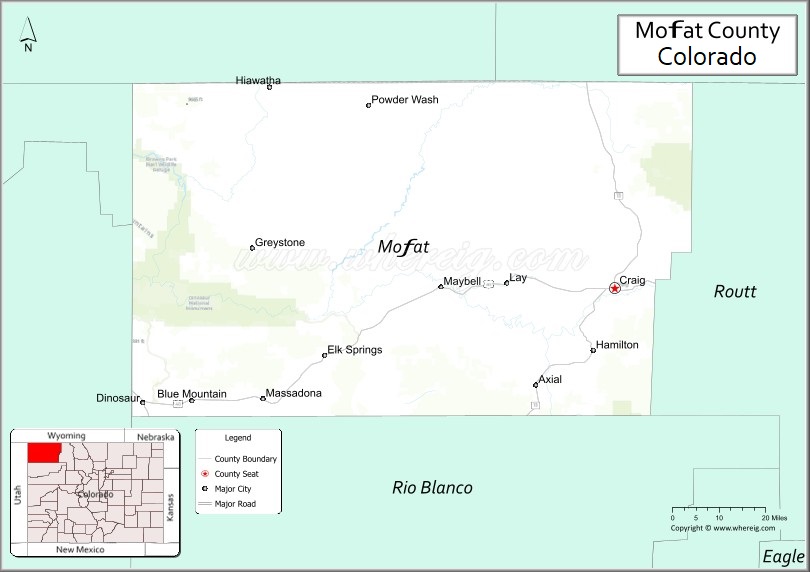
Adjacent counties
- Routt County – east
- Rio Blanco County – south
- Uintah County, Utah – west
- Daggett County, Utah – west
- Sweetwater County, Wyoming – north
- Carbon County, Wyoming – north
Major highways
- U.S. Highway 40
- State Highway 13
- State Highway 317
- State Highway 318
- State Highway 394
- Wyoming Highway 70
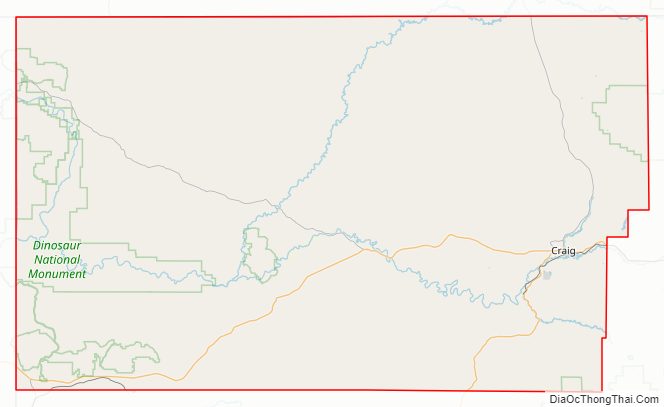
National protected areas
- Browns Park National Wildlife Refuge
- Dinosaur National Monument
- Routt National Forest
- White River National Forest
- Yampa River State Park
Scenic byway
- Dinosaur Diamond Prehistoric Highway National Scenic Byway
Summit
- Cold Spring Mountain