Shasta County (/ˈʃæstə/ (listen)), officially the County of Shasta, is a county in the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Its population is 182,155 as of the 2020 census, up from 177,223 from the 2010 census. The county seat is Redding.
Shasta County comprises the Redding, California metropolitan statistical area. The county occupies the northern reaches of the Sacramento Valley, with portions extending into the southern reaches of the Cascade Range.
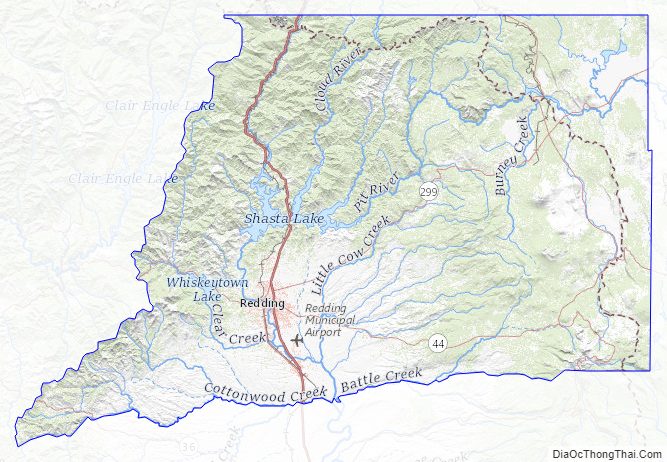
Points of interest in Shasta County include Shasta Lake, Lassen Peak, and the Sundial Bridge.
| Name: | Shasta County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 06-089 |
| State: | California |
| Founded: | 1850 |
| Named for: | Mount Shasta, which was named after the Shasta people |
| Seat: | Redding |
| Largest city: | Redding |
| Total Area: | 3,847 sq mi (9,960 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3,775 sq mi (9,780 km²) |
| Total Population: | 182,155 |
| Population Density: | 47/sq mi (18/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−8 (Pacific Standard Time) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) |
| Website: | www.shastacounty.gov |
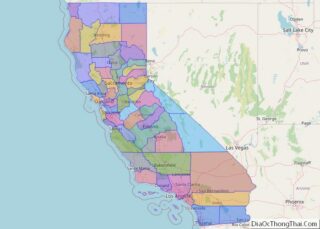
Shasta County location map. Where is Shasta County?
History
Shasta County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. The county was named after Mount Shasta; the name is derived from the English equivalent for the Shasta people. Their population declined in the 1850s due to disease, low birth rates, starvation, killings, and massacres, as White settlers moved in. The name of the tribe was spelled in various ways until the present version was used when the county was established. Originally, Mt. Shasta was within the county, but it is now part of Siskiyou County, to the north. Its 14,179-foot (4,322 m) peak is visible throughout most of Shasta County. Parts of the county’s territory were transferred to Siskiyou County in 1852, and to Tehama County in 1856.
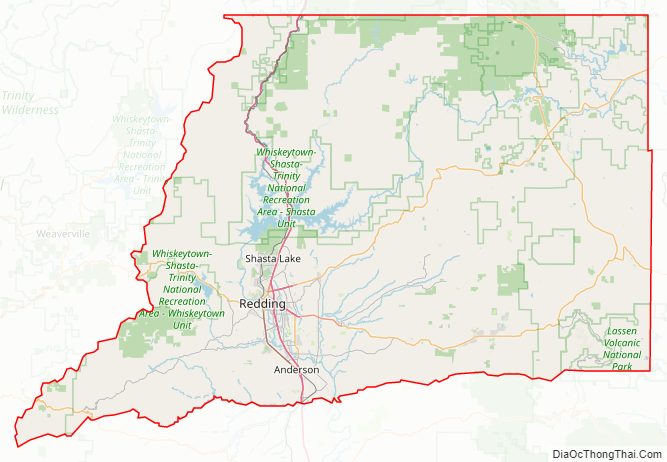
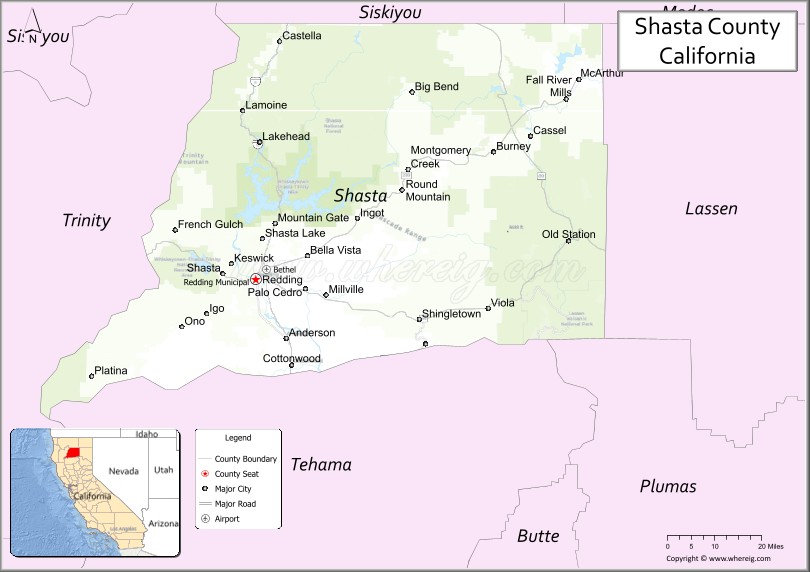
Shasta County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 3,847 square miles (9,960 km), of which 72 square miles (190 km) (1.9%) are covered by water. Mountains line the county on the east, north, and west. The Sacramento River flows out of the mountains to the north, through the center of the county, and toward the Sacramento Valley to the south.
Flora and fauna
According to Willis Linn Jepson, the biota of Shasta County was not explored in a scientific manner until just before 1900. Until the 1920s, the Southern Pacific Railroad Company owned vast tracts of natural grasslands, but during the 1920s, the railroad sold off much of its grassland holdings, leading to the rapid clearing of brush and large-scale conversion from habitat to agricultural uses. Shasta County has extensive forests, which cover over one half the land area with commercially productive forest systems. Common forest alliances include mixed-oak woodland and mixed conifer-oak woodland, as well as Douglas fir forest. Common trees found include white-bark pine, California black oak, and California buckeye.
Adjacent counties
- Siskiyou County – north
- Modoc County – northeast
- Lassen County – east
- Plumas County – southeast
- Tehama County – south
- Trinity County – west
National protected areas
- Shasta-Trinity National Forest (part)
- Whiskeytown National Recreation Area (part)