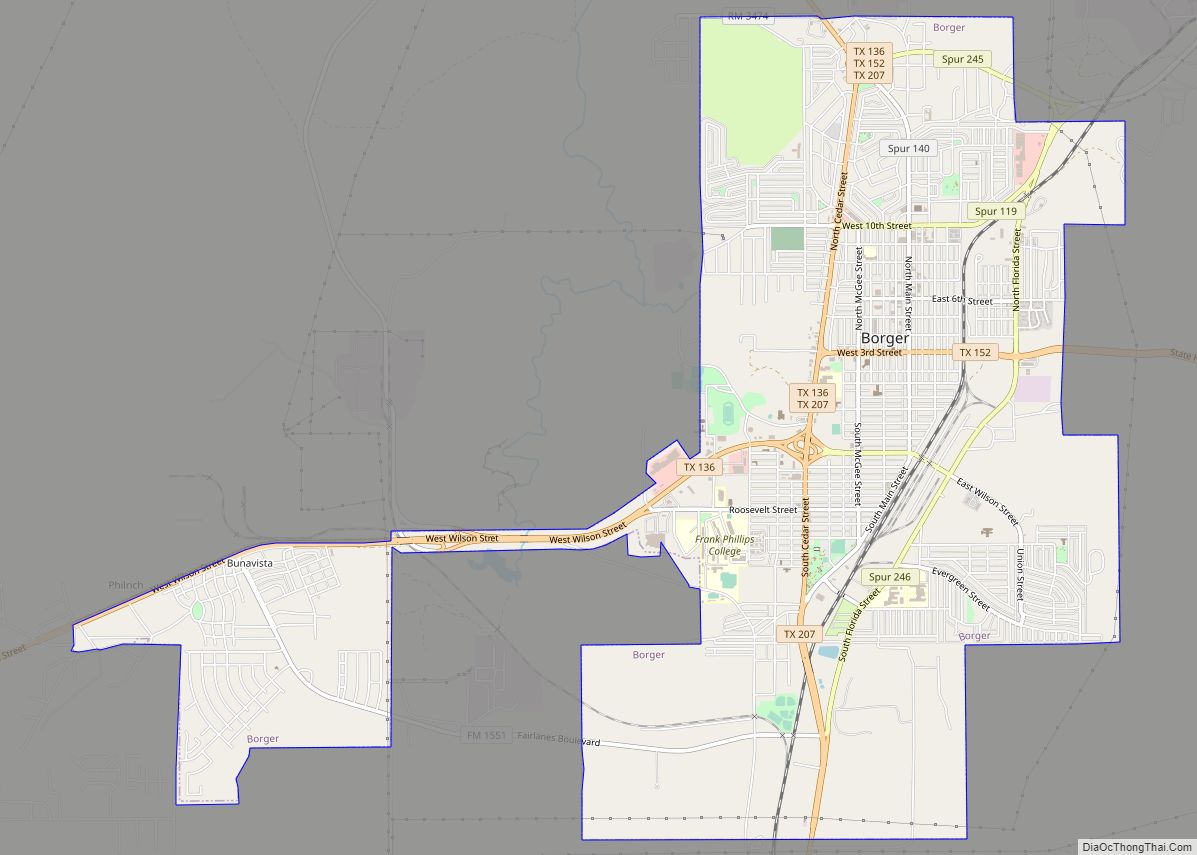
Hutchinson County is a county in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 20,617. Its county seat is Stinnett. The county was created in 1876, but not organized until 1901. It is named for Andrew Hutchinson, an early Texas attorney.
Hutchinson County comprises the Borger, TX Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Amarillo-Borger, TX Combined Statistical Area. It is located in the northern portion of the Texas Panhandle. The history of Hutchinson County is accented in downtown Borger in the Hutchinson County Historical Museum, also known as Boomtown Revisited. Hutchinson County is the county with the most ghost towns in the Texas Panhandle.
| Name: | Hutchinson County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 48-233 |
| State: | Texas |
| Founded: | 1901 |
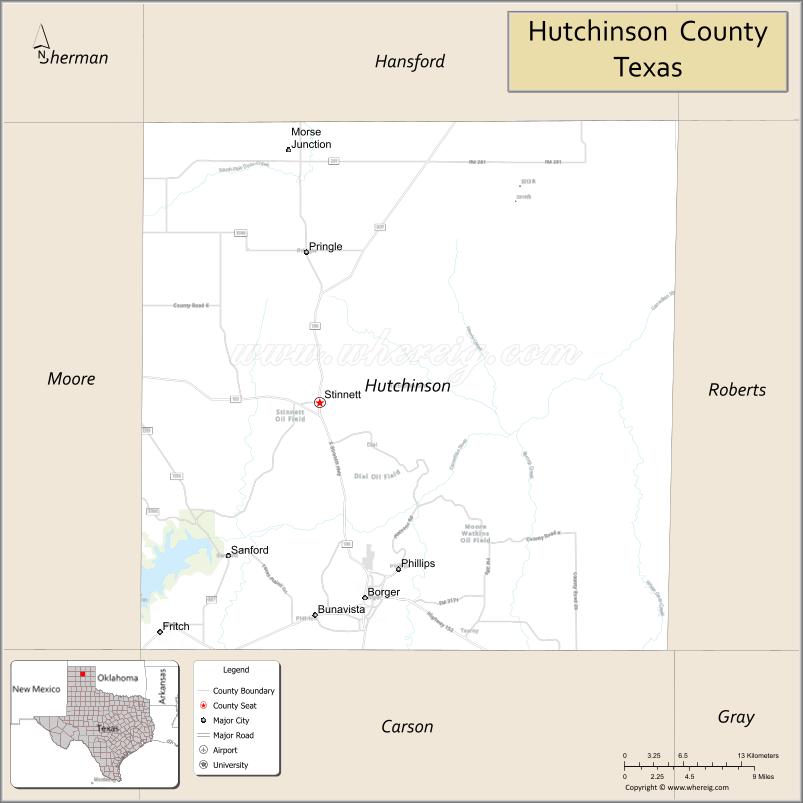
| Seat: | Stinnett |
| Largest city: | Borger |
| Total Area: | 895 sq mi (2,320 km²) |
| Land Area: | 887 sq mi (2,300 km²) |
| Total Population: | 20,617 |
| Population Density: | 23/sq mi (8.9/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | www.co.hutchinson.tx.us |
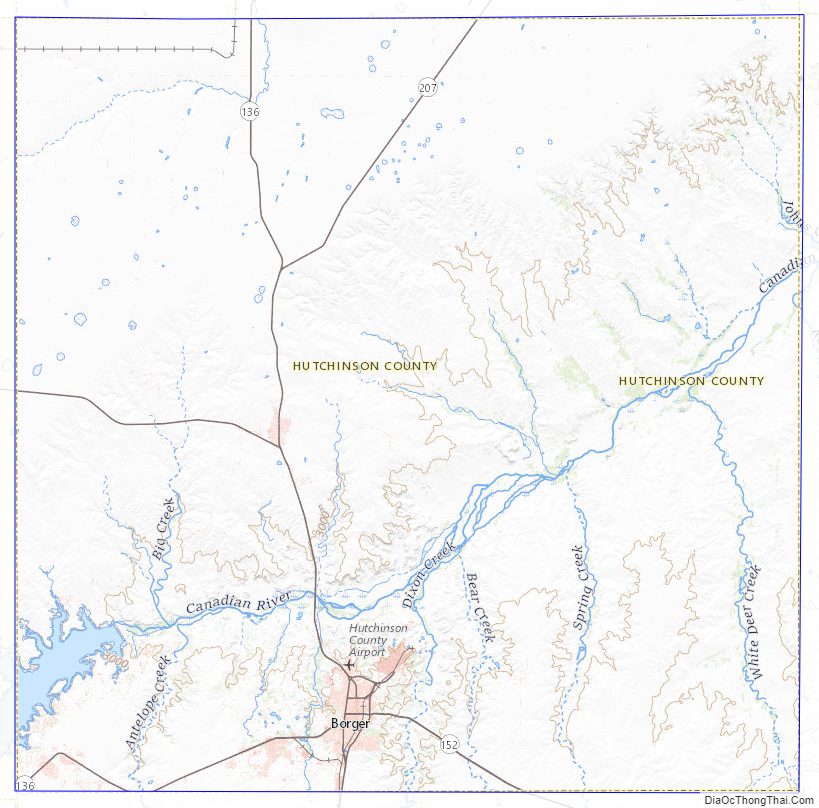
Hutchinson County location map. Where is Hutchinson County?
History
Native Americans
Artifacts of the Antelope Creek Indian culture abound along the Canadian River valley in Hutchinson County. Archaeologists have found 1,300 acres (5.3 km) of Alibates flint in the area that was used as a quarry for shaping flint tools. Nomadic Plains Apache also camped in this area, as did Comanche, Arapaho, Kiowa, and Cheyenne.
Bent, St. Vrain and Company established a trading post in this area to tap into Indian trading. Known as Fort Adobe, it was blown up by traders three years later due to Indian depredations. The ruins became known as Adobe Walls.
The First Battle of Adobe Walls took place in 1864 when General James H. Carleton sent Colonel Kit Carson into the area to avenge for repeated Indian attacks. Carson and several hundred cavalry soldiers were greatly outnumbered by Kiowa and Comanche and forced to retreat. The Second Battle of Adobe Walls took place in 1874. A group of buffalo hunters attempted a revitalization of Fort Adobe. The Comanches, Cheyenne, Arapaho, and Kiowa saw the fort and the decimation of the buffalo herd as a threat to their existence. Comanche medicine man Isa-tai prophesied a victory and immunity to the white man’s bullets in battle. Quanah Parker lead several hundred in a raid on the fort. The buffalo hunters were able to force the Indians into retreat.
Early explorations
In 1541, an expedition led by Francisco Vásquez de Coronado traversed the area on its Great Plains quest for Quivira on the search for the mythical Seven Cities of Gold. Spanish conquistador Juan de Oñate passed through in 1601 on his Kansas expedition. Buffalo hunters and Comanchero from New Mexico hunted and traded in the vicinity until the 1870s. The first Anglo-American expedition to come through the county was led by Stephen H. Long, who mistook the Canadian River for the Red River, in August 1820. Josiah Gregg brought his Santa Fe caravan through in March 1840. During the month of December 1858, Lt. Edward Beale with 100 men passed through the county constructing a federally funded military road, the first to be constructed in the American Southwest. The road went from Fort Smith, Arkansas, to Los Angeles. It was named the Beale Wagon Road by Secretary of War John B. Floyd.
Early ranch entrepreneurs
In November 1876, Kansan Thomas Sherman Bugbee established the Quarter Circle T Ranch. The Scissors Ranch was begun in 1878 by William E. Anderson at the Adobe Walls site. The ranch was named after the brand, which looked like a pair of scissors. Coloradan Richard E. McNalty moved to Texas and began the Turkey Track Ranch, which he sold to Charles Wood and Jack Snider in 1881. Scotland-born James M. Coburn formed the Hansford Land and Cattle Company. The Quarter Circle T Ranch and Scissors Ranch were sold to Coburn in 1882. Coburn acquired the Turkey Track Ranch in 1883.
County established
Hutchinson County was established in 1876. The county was not organized until 1901, when Plemons became the county seat. For the next four decades, ranching dominated the county’s economy, while crop cultivation made gradual headway.
The Panhandle oilfield was discovered in the 1920s. On June 1, 1923, the Sanford No. 1 J. C. Whittington well in southwestern Hutchinson County reached a depth of 3,077 feet (938 m) and found flowing oil. Towns sprang up in response. The population mushroomed from 721 in 1920 to 14,848 in 1930 as a result of the oil boom. By 1990, 526,670,107 barrels (83,733,855.6 m) of oil had been taken from Hutchinson County lands since 1923.
Stinnett became the county seat after a special election on September 18, 1926.
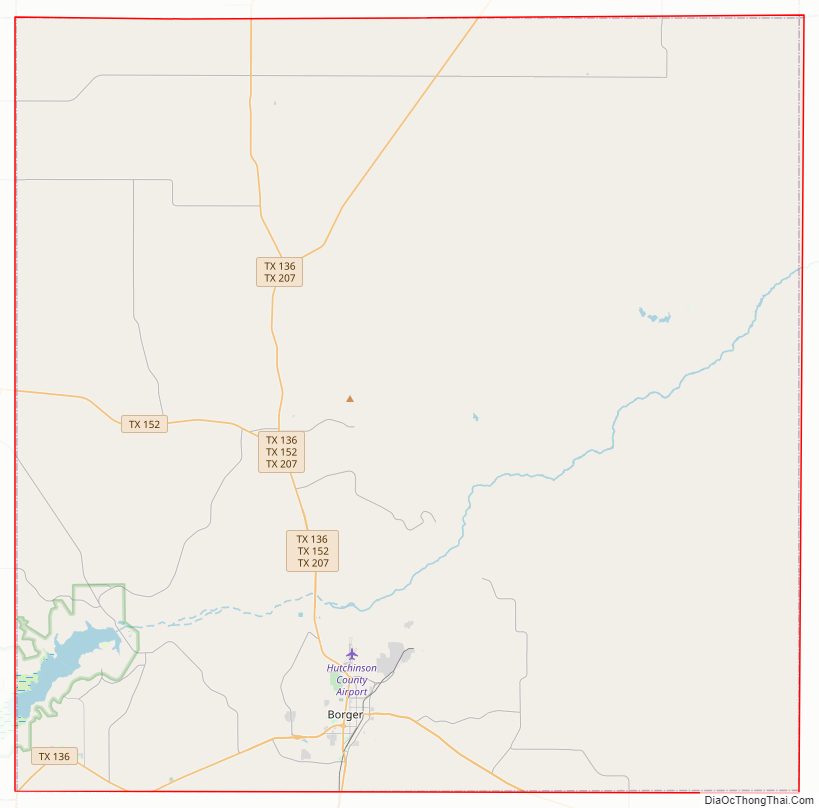
Hutchinson County Road Map
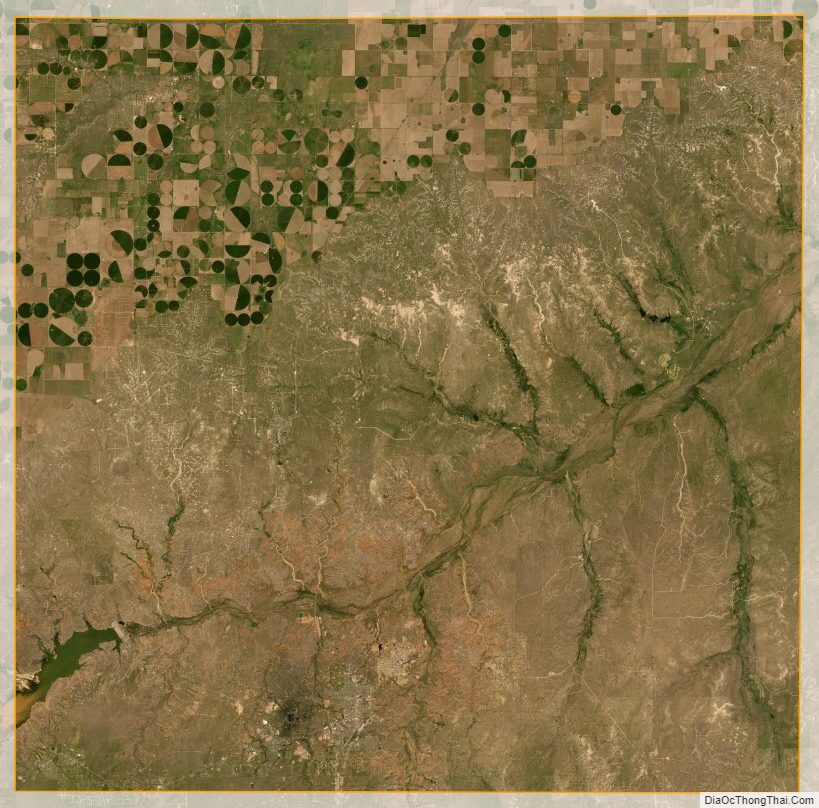
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 895 square miles (2,320 km), of which 887 square miles (2,300 km) are land and 7.5 square miles (19 km) (0.8%) are covered by water.
Major highways
- State Highway 136
- State Highway 152
- State Highway 207
Adjacent counties
- Hansford County (north)
- Roberts County (east)
- Carson County (south)
- Moore County (west)
- Potter County (southwest)
- Gray County (southeast)
- Sherman County (northwest)
- Ochiltree County (northeast)
National protected area
- Lake Meredith National Recreation Area (part)