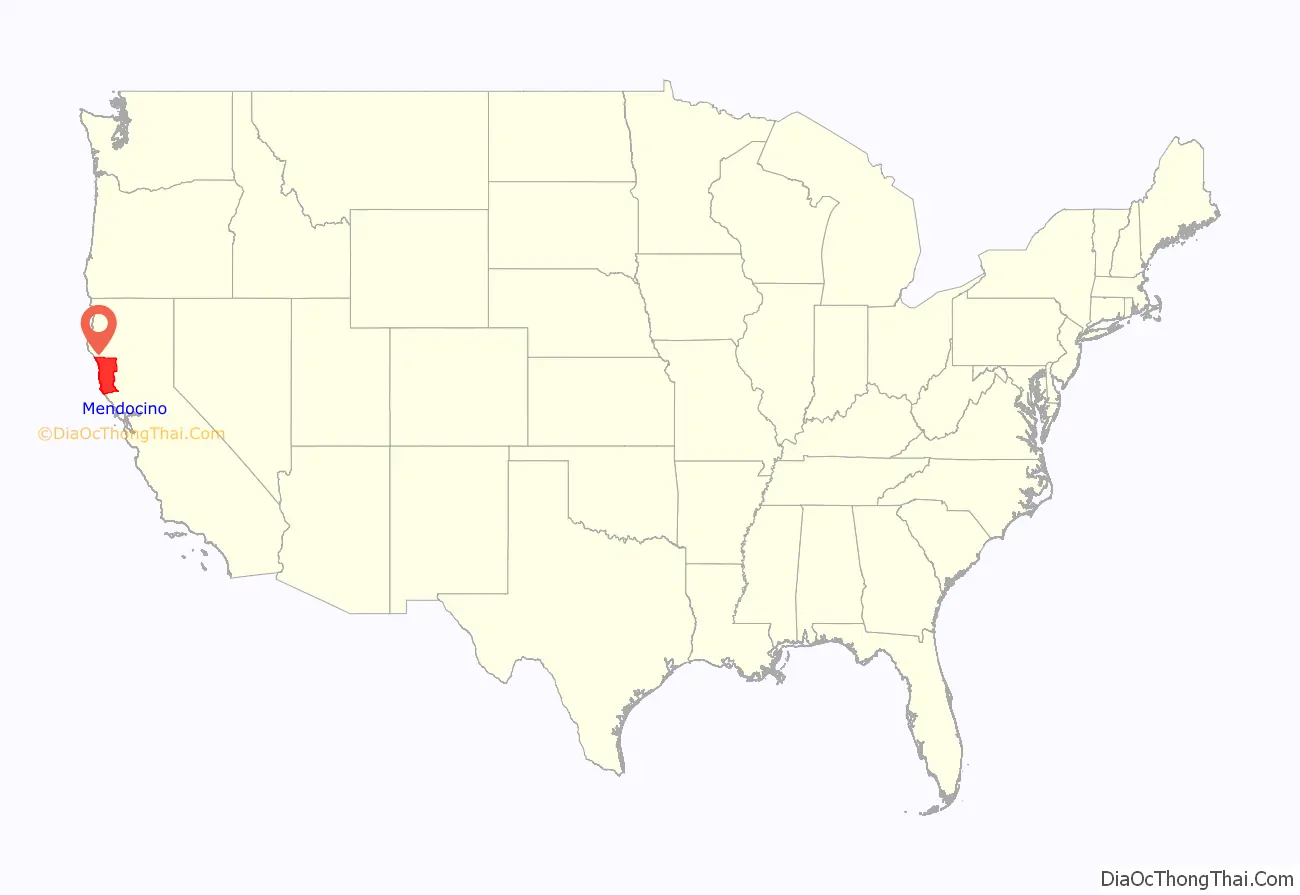
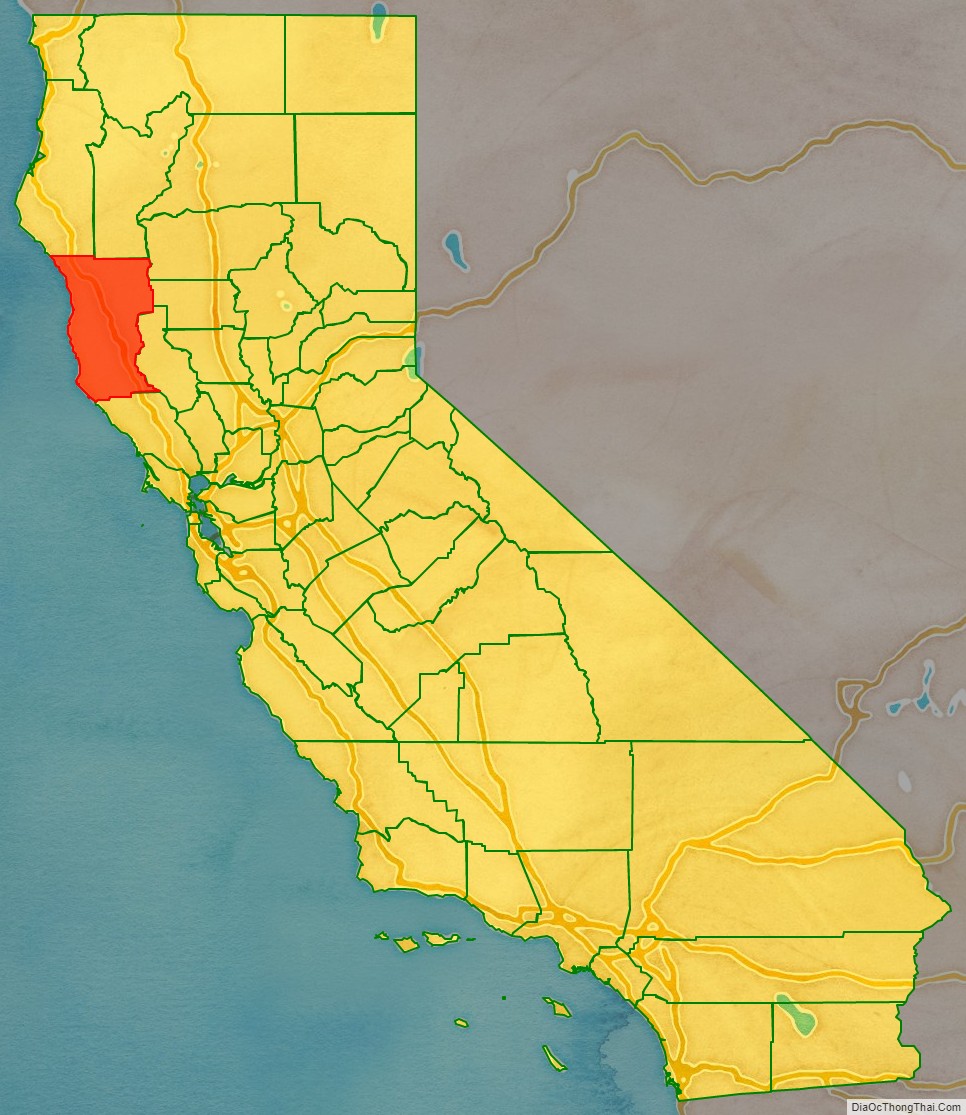
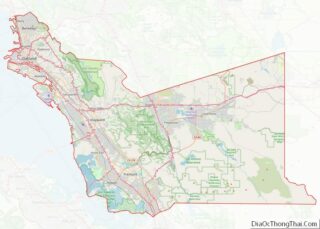
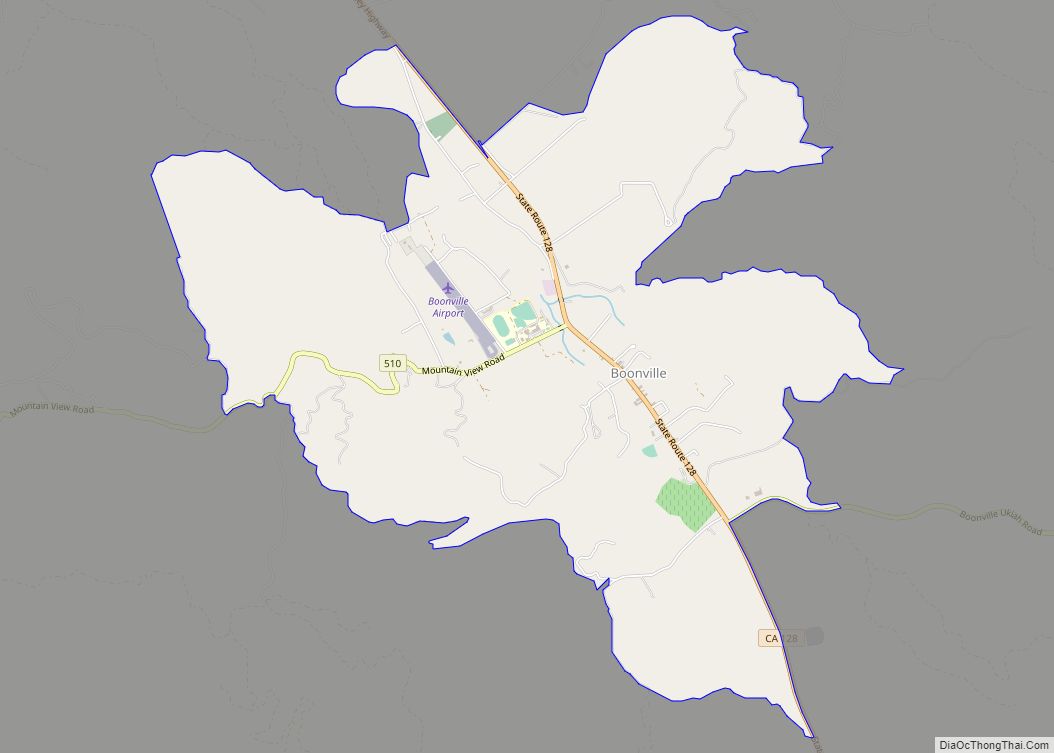
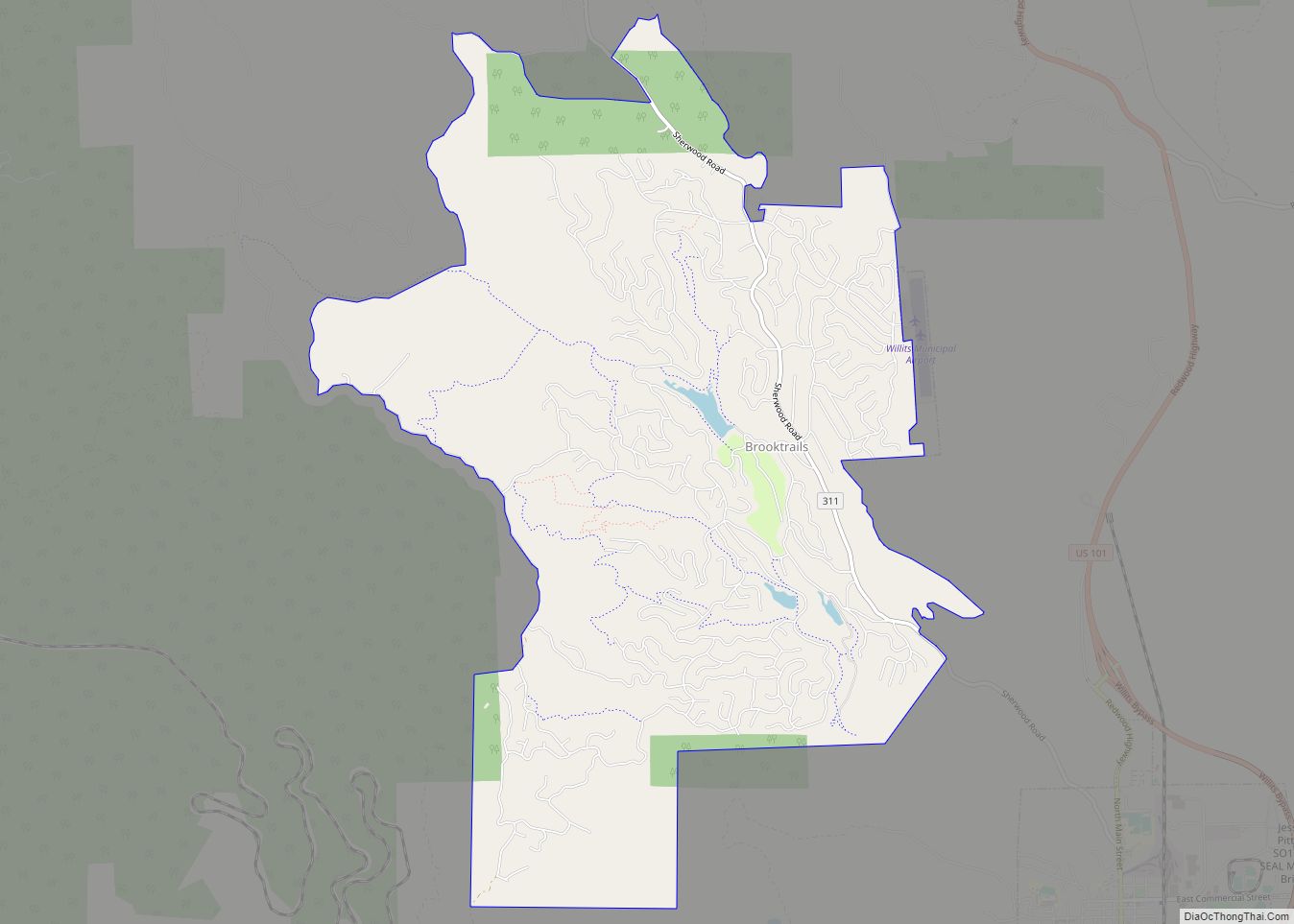
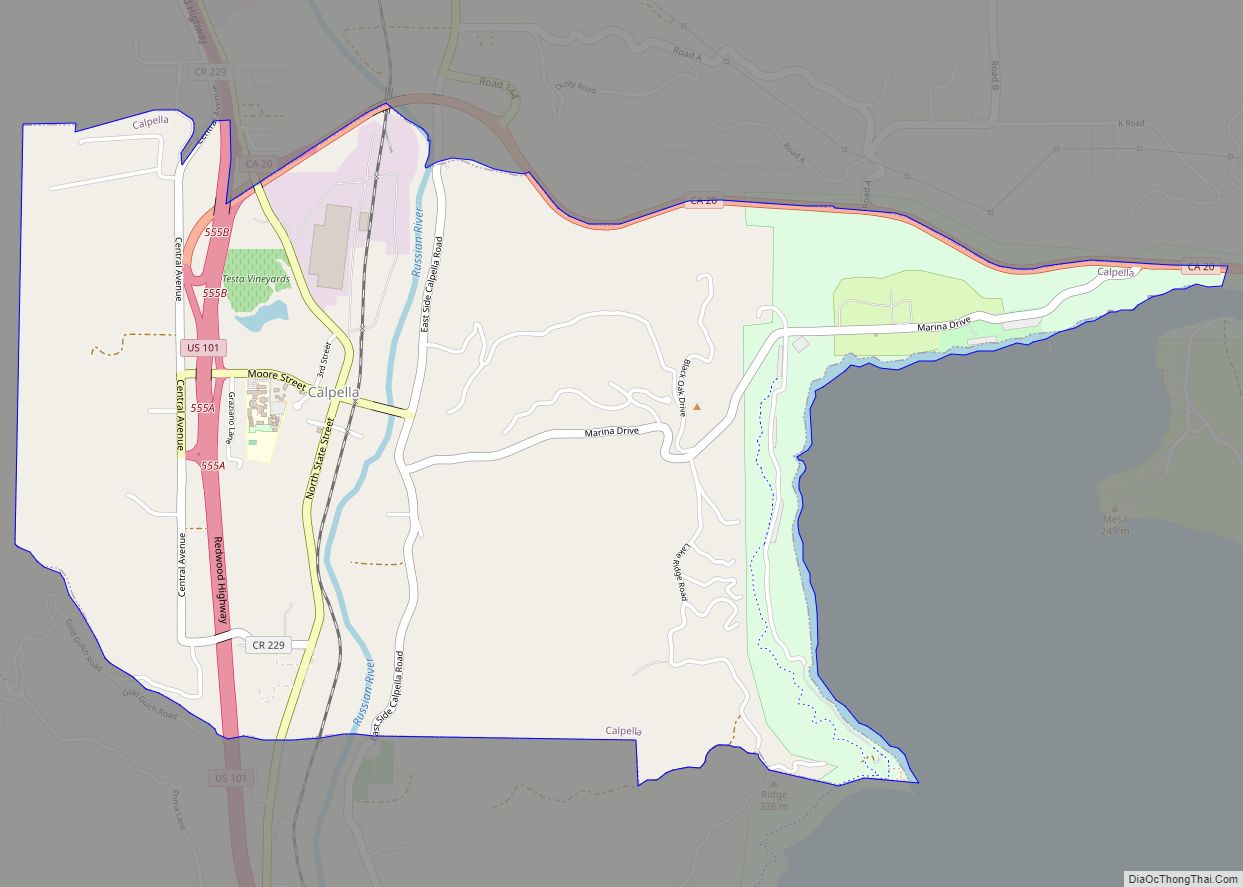
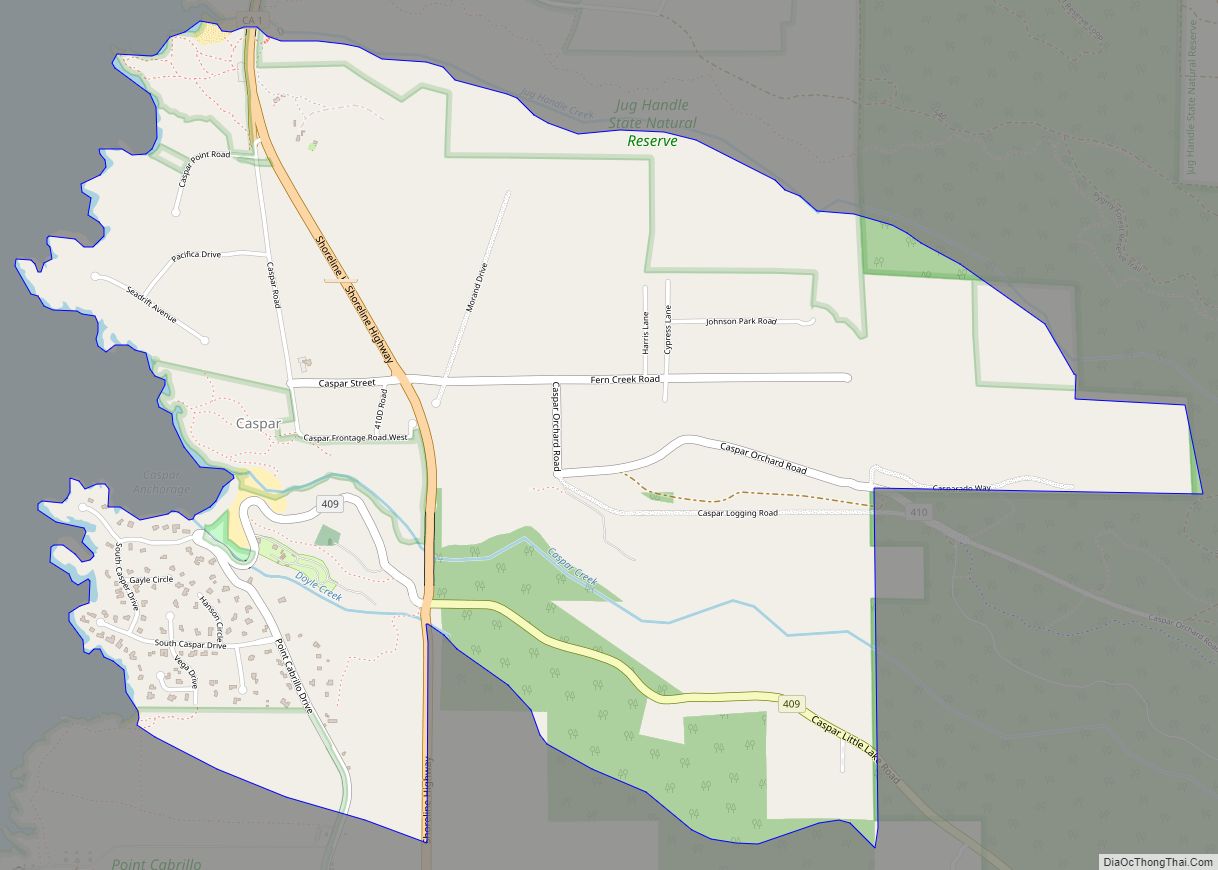
Mendocino County (/ˌmɛndəˈsiːnoʊ/ (listen); Mendocino, Spanish for “of Mendoza) is a county located on the North Coast of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 91,601. The county seat is Ukiah.
Mendocino County consists wholly of the Ukiah, CA Micropolitan Statistical Area (μSA) for the purposes of the U.S. Census Bureau. It is located approximately equidistant from the San Francisco Bay Area and California/Oregon border, separated from the Sacramento Valley to the east by the California Coast Ranges. While smaller areas of redwood forest are found further south, it is the southernmost California county to be included in the World Wildlife Fund’s Pacific temperate rainforests ecoregion, the largest temperate rainforest ecoregion on the planet.
The county is noted for its distinctive Pacific Ocean coastline, its location along California’s “Lost Coast”, Redwood forests, wine production, microbrews, and liberal views about the use of cannabis and support for its legalization. In 2009, it was estimated that roughly one-third of the economy was based on the cultivation of marijuana.
The notable historic and recreational attraction of the “Skunk Train” connects Fort Bragg with Willits in Mendocino County via a steam-locomotive engine, along with other vehicles.
Mendocino is one of three Northern California counties to make up the “Emerald Triangle”, along with Humboldt and Trinity counties.
| Name: | Mendocino County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 06-045 |
| State: | California |
| Founded: | 1850 |
| Named for: | Antonio de Mendoza, Viceroy of New Spain, 1535–42 |
| Seat: | Ukiah |
| Largest city: | Ukiah |
| Total Area: | 3,878 sq mi (10,040 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3,506 sq mi (9,080 km²) |
| Total Population: | 91,601 |
| Population Density: | 26/sq mi (10/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−8 (Pacific Time Zone) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) |
| Website: | www.mendocinocounty.org |
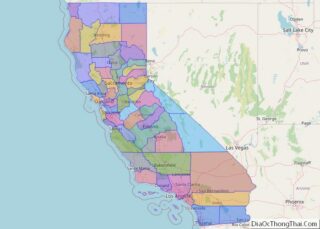
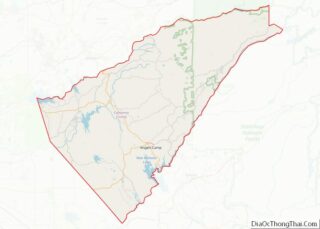
Mendocino County location map. Where is Mendocino County?
History
Mendocino County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. Due to an initially minor settler American population, it did not have a separate government until 1859 and was under the administration of Sonoma County prior to that. Some of the county’s land was given to Sonoma County between 1850 and 1860.
The county derives its name from Cape Mendocino (most of which is actually located in adjacent Humboldt County), which was probably named in honor of either Antonio de Mendoza, Viceroy of New Spain, 1535–1542 (who sent the Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo Expedition to this coast in 1542), or Lorenzo Suárez de Mendoza, Viceroy from 1580 to 1583. Mendocino is the adjectival form of the family name of Mendoza.
Neither Spanish nor Mexican influence extended into Mendocino County beyond the establishment of two Mexican land grants in southern Mendocino County: Rancho Sanel in Hopland, in 1844 and Rancho Yokaya that forms the majority of the Ukiah Valley, in 1845.
In the 19th century, despite the establishment of the Mendocino Indian Reservation and Nome Cult Farm in 1856, the county witnessed many of the most serious atrocities in the extermination of the Californian Native American tribes who originally lived in the area, like the Yuki, the Pomo, the Cahto, and the Wintun. The systematic occupation of their lands, the reduction of many of their members into slavery and the raids against their settlements led to the Mendocino War in 1859, where hundreds of Indians were killed. Establishment of the Round Valley Indian Reservation on March 30, 1870, did not prevent the segregation that continued well into the 20th century. Other tribes from the Sierra Nevada mountains were also relocated to the Round Valley Indian Reservation during the “California Trail Of Tears”, where the Natives were forced to march in bad conditions to their new home in Round Valley. Many of these tribes thrown together were not on good terms with the other tribes they were forced to live with on the reservation, resulting in tensions still evident today.
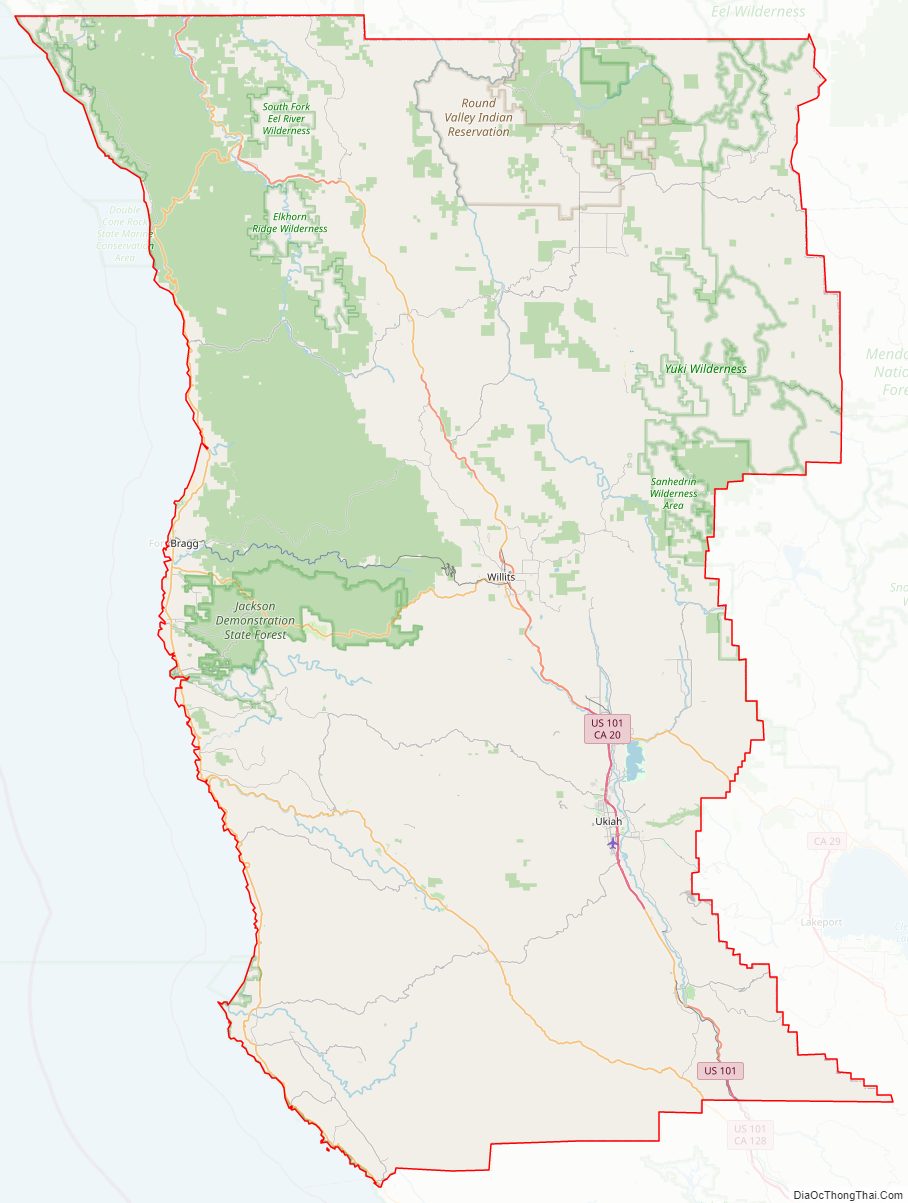
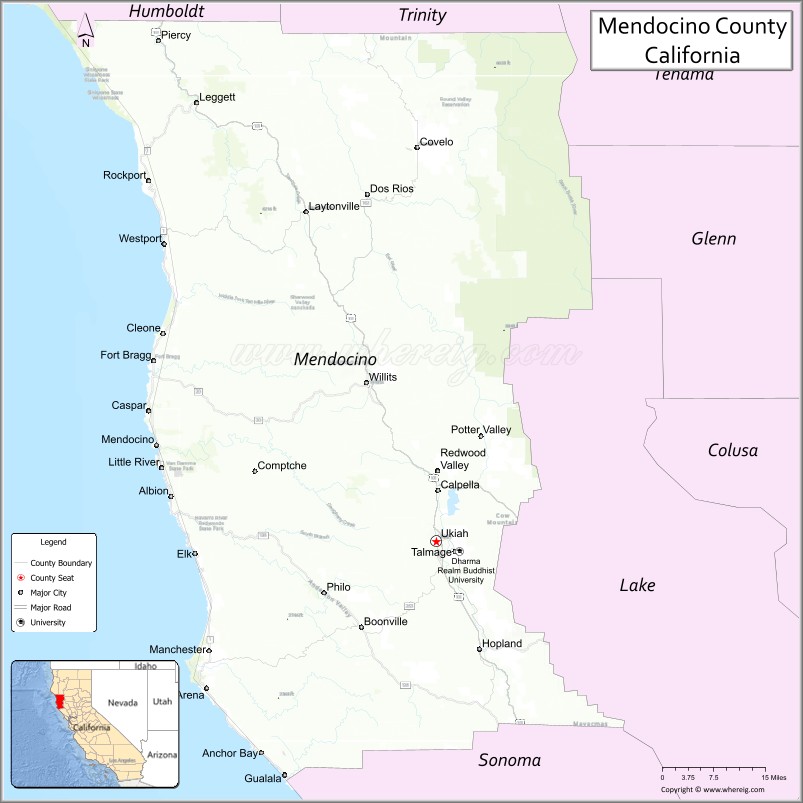
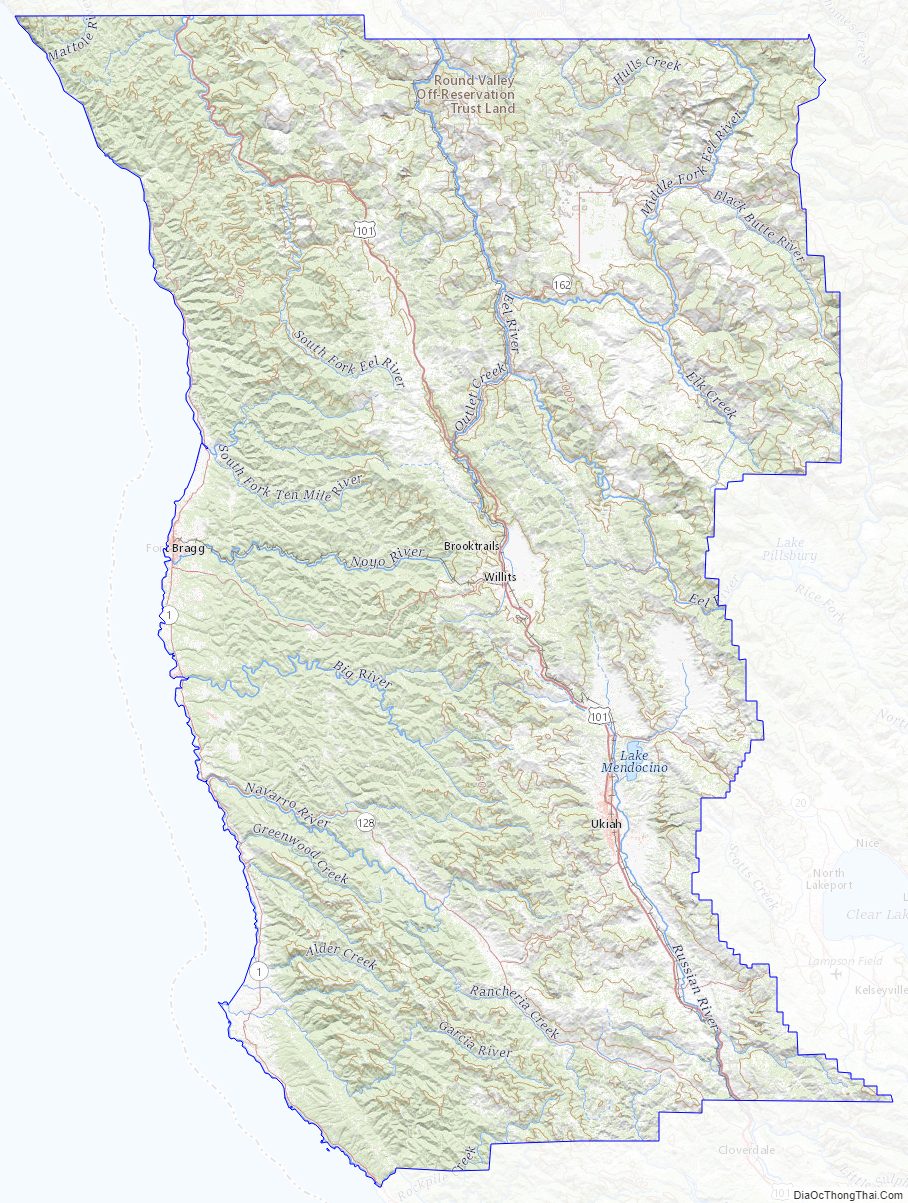
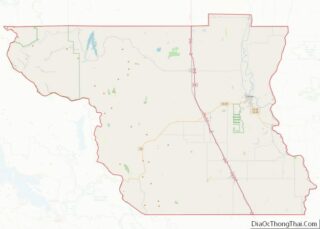
Mendocino County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 3,878 square miles (10,040 km), of which 3,506 square miles (9,080 km) is land and 372 square miles (960 km) (9.6%) is water.
Adjacent counties
- Humboldt County – north
- Trinity County – north
- Tehama County – northeast
- Glenn County – east
- Lake County – east
- Sonoma County – south
Rivers
- Russian River (inland)
- Gualala River
- Garcia River
- Elk Creek
- Navarro River
- Albion River
- Little River
- Big River
- Big Salmon Creek
- Little Salmon Creek
- Noyo River
- Pudding Creek
- Virgin Creek
- Ten Mile River
- Usal Creek
- Eel River (inland)
Beaches
- Big River Beach
- Caspar Headlands State Beach
- Van Damme Beach
- Greenwood State Beach
- Seaside Beach
- Westport-Union Landing State Beach
- Manchester State Beach
- Navarro Beach
- Portuguese Beach
- Schooner Gulch State Beach
- Long Valley Creek
- 10 Mile Creek
- Glass Beach
National and state protected areas
- Admiral William Standley State Recreation Area
- Caspar Headlands State Recreation Area
- Hendy Woods State Park
- Jug Handle State Reserve
- MacKerricher State Park
- Mailliard Redwoods State Reserve
- Manchester State Park
- Mendocino Coast Botanical Gardens
- Mendocino Headlands State Park
- Mendocino National Forest
- Mendocino Woodlands State Park
- Montgomery Woods State Reserve
- Navarro River Redwoods State Park
- Point Arena State Marine Reserve & Point Arena State Marine Conservation Area
- Point Cabrillo Light Station
- Reynolds Wayside Campground
- Round Valley Indian Reservation
- Russian Gulch State Park
- Saunders Reef State Marine Conservation Area
- Sea Lion Cove State Marine Conservation Area
- Sinkyone Wilderness State Park
- Smythe Redwoods State Reserve
- Standish-Hickey State Recreation Area
- Van Damme State Park