Scott County is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 150,928. Its county seat is Shakopee. Shakopee is also the largest city in Scott County, the twenty-third-largest city in Minnesota, and the sixteenth-largest Twin Cities suburb. The county was organized in 1853 and named in honor of General Winfield Scott. Scott County is part of the Minneapolis–St. Paul–Bloomington, MN-WI Metropolitan Statistical Area. It is a member of the Metropolitan Council, and shares many of the council’s concerns about responsible growth management, advocating for progressive development concepts such as clustering, open-space design, and the preservation of open space and rural/agricultural land.
The Shakopee-Mdewakanton Indian Reservation is entirely within the county and within the cities of Prior Lake and Shakopee. Due to its proximity to major cities, the tribe has earned revenues at its gaming casinos and hotel; it has used funds to reinvest in economic development for the tribe, founding numerous other enterprises. The tribe is also committed to philanthropy, having donated more than $350 million to organizations and causes in Scott County and across the country.
Scott County was one of Minnesota’s fastest-growing counties, having increased 55% since 1990. However, according to US Census data released in 2011, Scott County saw the steepest drop in median income of all of Minnesota’s populous counties. Scott County is 365 square miles (950 km) and is bounded on the west and north by the Minnesota River.
The Minnesota River had supported the county’s fur trading, lumbering, and farming industries in the 19th century. Today, Scott County experiences a growing mix of commercial, industrial, and housing development, but is still primarily rural. Scott County is home to several historical, scenic, and entertainment destinations including Canterbury Park, The Landing, Elko Speedway, Mystic Lake Casino run by the Shakopee-Mdewakanton Dakota; the Renaissance Festival, and Valleyfair Amusement Park.
| Name: | Scott County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 27-139 |
| State: | Minnesota |
| Founded: | March 5, 1853 |
| Named for: | Winfield Scott |
| Seat: | Shakopee |
| Largest city: | Shakopee |
| Total Area: | 368 sq mi (950 km²) |
| Land Area: | 356 sq mi (920 km²) |
| Total Population: | 150,928 |
| Population Density: | 424.0/sq mi (163.7/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | www.scottcountymn.gov |
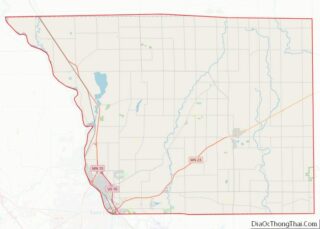
Scott County location map. Where is Scott County?
History
Scott County was first inhabited by two bands of the Santee Sioux (Dakota) Indians, the Mdewakanton and Wahpeton. Their semi-nomadic life followed a seasonal cycle. They gathered food, hunted, fished, and planted corn. In the summer the Dakota villages were occupied but in the winter the groups separated for hunting. They had many permanent villages along the Minnesota River. They had many trails leading to these settlements and to the Red River Valley in the North, and the Prairie du Chien to the Southeast. These trails were later used by the fur traders and settlers, and were known as the “ox cart trails.” The area of Scott County, as well as much of southern Minnesota, was opened for settlement by two treaties signed at Mendota and Traverse des Sioux, in 1851 and 1853. These treaties removed the Dakota Indians to reservations in upper Minnesota.
Scott County was established and organized by an Act passed in the legislature on March 5, 1853. The 369-square-mile (960 km) county was named after General Winfield Scott. Settlers started entering the area in the mid-1850s. The Minnesota River and the ox cart trails were the primary transportation routes. The first settlers were Yankees, followed by groups of Germans, Irish, Czechs, and Scandinavians. They each brought their own traditions and religions. Most of these settlers became farmers. Fur trading, lumbering, and farming were Minnesota’s major industries all throughout the 19th century. With the fast-growing farms, sprang up towns. Shakopee, the County Seat, began in 1851 as a trading post by the Dakota Village of Chief Shakopee (or Shakpay). Other towns were established alongside transportation routes. When the railroads came to Minnesota, they became the primary mode of transportation, and eventually highways were developed along the ox cart trails between the communities.
Due to urban sprawl and suburbanization this rural county is changing dramatically. Cities are continually growing, causing an increase in population from roughly 90,000 in 2000 to 130,000 today, making Scott County Minnesota’s fastest-growing county.
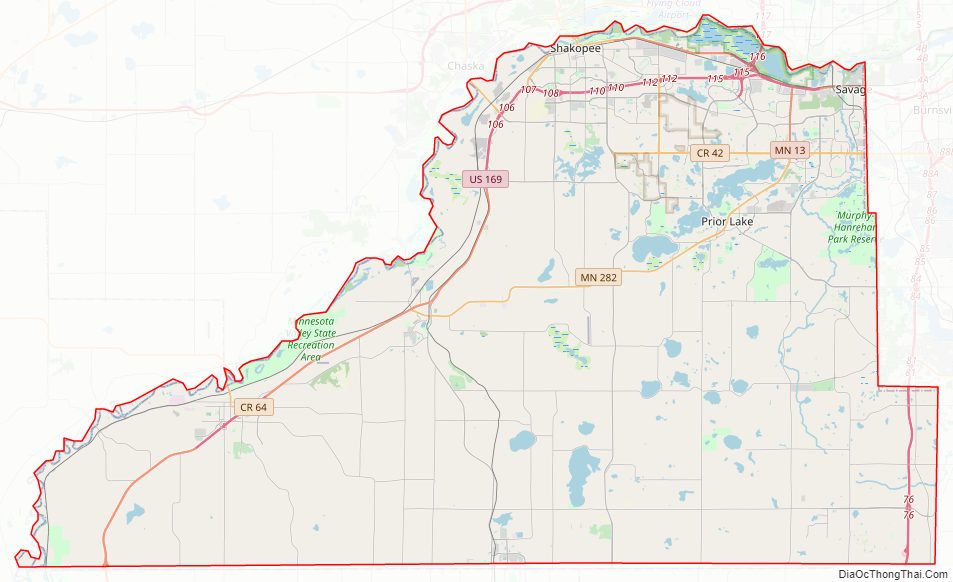
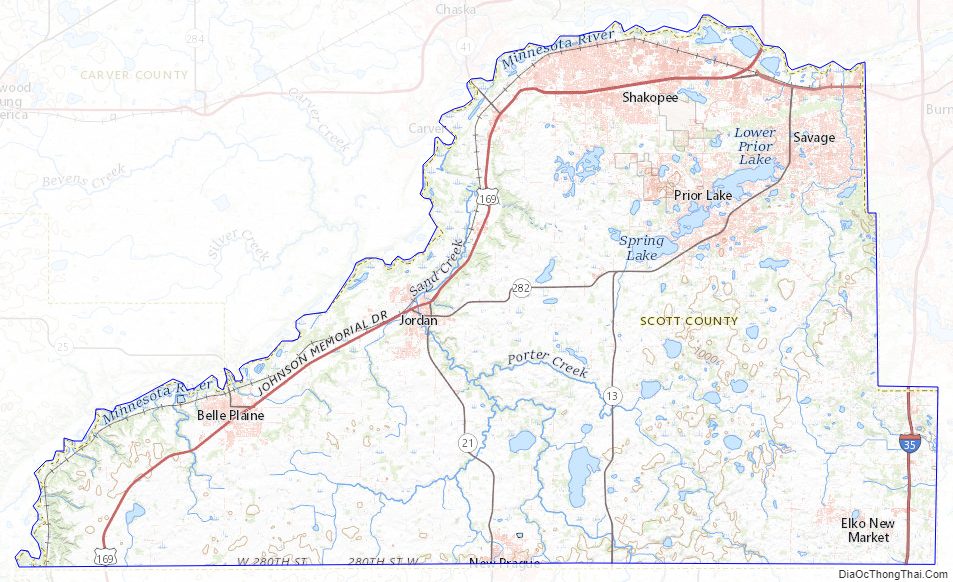
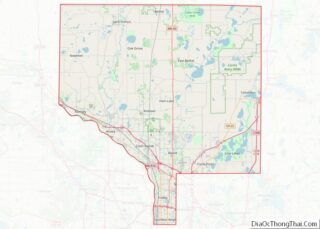
Scott County Road Map
Geography
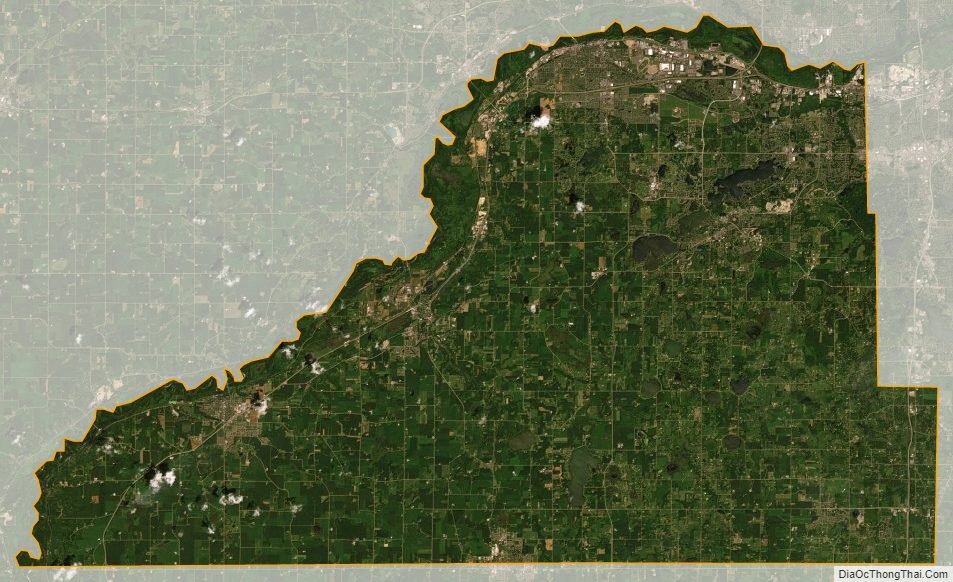
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has an area of 368 square miles (950 km), of which 356 square miles (920 km) is land and 12 square miles (31 km) (3.2%) is water. It is the third-smallest county in Minnesota by land area and second-smallest by total area.
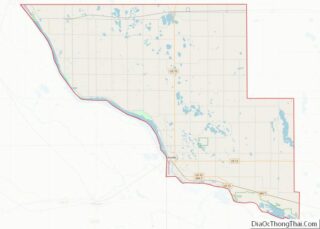
The Minnesota River is the county’s boundary in both the north and the west. The broad river valley juts through glacial sediment into some of the oldest rock known. Now mostly farmland, it was an oak savanna and a mixture of grass and clusters of trees that grew parallel to the river valley. The savanna bordered the “Big Woods”, a “closed-forest savanna” that covered most of Minnesota before it was logged in the mid-19th century. Scott is one of 17 Minnesota savanna counties with more savanna soils than either forest or prairie soils. One example of native vegetation in Scott County:
Lakes
- Ahlswede Lake: in St. Lawrence Township
- Blue Lake: in Jackson Township
- Browns Lake: in St. Lawrence Township
- Campbell Lake: in Spring Lake Township
- Cedar Lake: western two-thirds is in Helena Township; eastern third is in Cedar Lake Township
- Cedar Lake: there is a smaller Cedar Lake in the eastern part of Cedar Lake Township
- Clark Lake: in Blakely Township
- Cleary Lake: mostly in Credit River; the western part stretches into Spring Lake Township
- Crystal Lake: in Spring Lake Township
- Cynthia Lake: northern two thirds is in Spring Lake Township; the rest is in Cedar Township
- Deans Lake: in Jackson Township
- Fish Lake: in Spring Lake Township
- Fisher Lake: in Jackson Township
- Gifford Lake: in Jackson Township
- Hanrahan Lake: in Jackson Township
- Hickey Lake: eastern two thirds is in Helena Township; western third is in Cedar Lake Township
- Horseshoe Lake: in St. Lawrence Township
- Howard Lake: in Jackson Township
- Kane Lake: in Spring Lake Township
- Lennon Lake: in Cedar Lake Township
- Lower Prior Lake: in the city of Prior Lake
- Markley Lake: eastern half is in Credit River; the western half is in Prior Lake
- McMahon Lake: in Spring Lake Township
- Mud Lake: in Cedar Lake Township
- Murphy Lake: in Credit River
- O’Dowd Lake: western third is in Louisville Township; eastern two thirds is in Jackson Township
- Pike Lake: in Jackson Township
- Pleasant Lake: in Helena Township
- Rice Lake: west half is in Cedar Lake Township; east half is in Dakota County
- Rice Lake: there is another Rice Lake in Jackson Township
- Rice Lake: there is a third Rice Lake in Spring Lake Township
- Schneider Lake: in Louisville Township
- Spring Lake: in Spring Lake Township and Prior Lake
- St. Catherine Lake: in Cedar Lake Township
- Thole Lake: in Louisville Township
- Upper Prior Lake: in Prior Lake
Major highways
- Interstate 35
- U.S. Highway 169
- Minnesota State Highway 13
- Minnesota State Highway 19
- Minnesota State Highway 21
- Minnesota State Highway 25
- Minnesota State Highway 41
- Minnesota State Highway 282
- County Road 42
- County Road 101
- Other County Roads
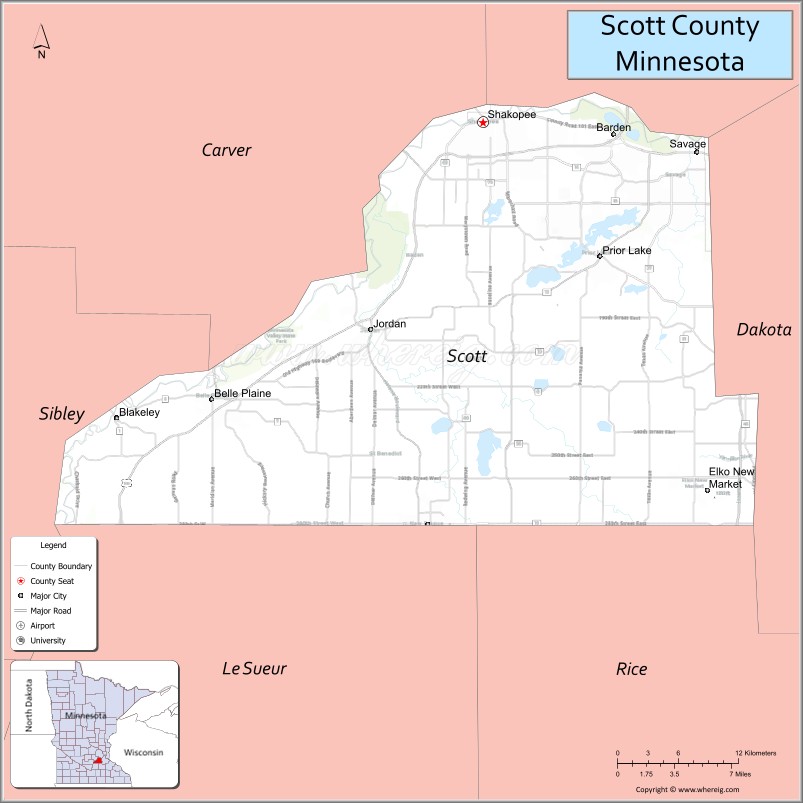
Adjacent counties
- Hennepin County (north)
- Dakota County (east)
- Rice County (southeast)
- Le Sueur County (southwest)
- Sibley County (west)
- Carver County (northwest)
National protected area
- Minnesota Valley National Wildlife Refuge (part)