Tensas Parish (French: Paroisse des Tensas) is a parish located in the northeastern section of the State of Louisiana; its eastern border is the Mississippi River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 4,147. It is the least populated parish in Louisiana. The parish seat is St. Joseph. The name Tensas is derived from the historic indigenous Taensa people. The parish was founded in 1843 following Indian Removal.
The parish was developed for cotton agriculture, which dominated the economy through the early 20th century. There has also been some cattle ranching in the 1930s and timber extraction.
| Name: | Tensas Parish |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 22-107 |
| State: | Louisiana |
| Founded: | March 17, 1843 |
| Named for: | Taensa people |
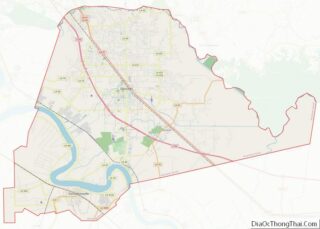
| Seat: | St. Joseph |
| Largest town: | Newellton |
| Total Area: | 641 sq mi (1,660 km²) |
| Land Area: | 603 sq mi (1,560 km²) |
| Total Population: | 4,147 |
| Population Density: | 6.5/sq mi (2.5/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | louisiana.gov/Government/Parish_Tensas/ |
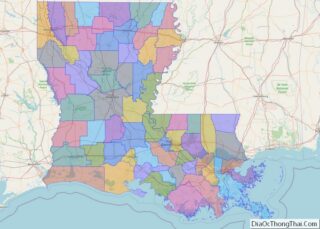
Tensas Parish location map. Where is Tensas Parish?
History
Pre-history
Tensas Parish was the home to many successive indigenous groups in the thousands of years before European settlements began. Some village and mound sites once built by these various peoples are preserved today as archaeological sites.
One example is the Flowery Mound, a rectangular platform mound just east of St. Joseph. It measures 10 feet (3.0 m) in height and 165 by 130 feet (50 by 40 m) at its base; the summit measures 50 feet (15 m) square. Core samples taken during investigations at the site have revealed the mound was built in a single stage. Because the fill types can still be differentiated, the mound is thought to be relatively young. Radiocarbon dating of charcoal found in a midden under the mound reveals that the site was occupied from 996 to 1162 during the Coles Creek period. The mound was built over the midden between 1200 and 1541 during the Plaquemine/Mississippian culture period. The corners of the mound are oriented in the four cardinal directions. Related ancient sites include Balmoral Mounds, Ghost Site Mounds, and Sundown Mounds.
Historic tribes in this area were the Choctaw and Natchez, in addition to smaller groups such as the Taensa people.
Antebellum development
Following Indian Removal by the United States government in the 1830s, the land was sold and this area was developed by European Americans for cotton plantations, the leading commodity crop before the Civil War. Planters moved into the area from the eastern and upper South, either bringing or purchasing numerous enslaved African Americans as workers. They developed plantations along the river and Lake St. Joseph, as waterways were required for transportation routes and access to markets. In 1861, according to the United States Coast Survey map, 90.8% of the parish’s inhabitants were slaves.
Reconstruction
During and after the Reconstruction era, white Democrats acted to suppress black and Republican voting in the state and in this parish with its large black majority. They enforced Jim Crow laws and rules through intimidation and violence, including lynchings.
From 1877 to 1950, there were 30 lynchings of blacks in Tensas Parish, most in the decades around the turn of the 20th century; Tensas was among the four parishes in Louisiana with the highest number of lynchings in this period, and Louisiana was among the states with the highest number of such murders.
But from 1878 through 1920, the Mississippi Delta area of northern Louisiana legally executed more blacks than did any other part of the state, after they had been convicted by all-white juries. For instance, between 1880 and 1920, twelve persons were executed in Tensas Parish, at least seven of them black.
20th century to present
By the turn of the 20th century, the parish seat of St. Joseph had 720 residents. Tensas Parish had 19,070. Most of the population was still engaged in cotton agriculture, where numerous African Americans worked as sharecroppers and tenant farmers. Others worked in trades associated with river traffic.
While mechanization was gradually introduced, blacks left Tensas Parish before its full effects had taken place, to escape the violence of lynchings and executions. In the 1900 census Tensas Parish had 17,839 African Americans (94 percent) and 1,231 whites (6 percent). By 1920, the number of African Americans had declined by 42% to 10,314 (making up 85 percent of the parish population). Whites numbered 1771 (15 percent).
Twenty years later, by 1940, the number of blacks in the parish had risen only to 11,194 (70 percent) while the whites had increased markedly to 4,746 (30 percent). These differences likely reflected a continuing outmigration by blacks, as well as in-migration of whites from other areas, who settled in the hill country during the 1920s–1930s. Both blacks and whites left the parish to move to defense industry jobs on the West Coast during and after World War II.
In 1962, when only whites could vote, Tensas Parish gave Republican Taylor W. O’Hearn 48.2 percent of the vote in a race for the U.S. Senate against powerful incumbent Democrat Russell B. Long. Long overwhelmingly defeated O’Hearn statewide.
Prior to January 1964, when fifteen African Americans were permitted to register, there had been no black voters on the Tensas Parish rolls since the state passed a constitution in 1898 to disenfranchise blacks. In 1964 the parish consisted of 7,000 blacks and 4,000 whites. Whites had controlled the political system since the late 19th century and excluded blacks from the political system for more than 60 years. Tensas was the last of Louisiana’s parishes in the 20th century to allow African Americans to register to vote.
In the fall of 1964 O’Hearn was elected to an at-large seat from Caddo Parish as a state representative from Shreveport. Another white Republican was also elected from Caddo Parish, as were three Democrats, all running for at-large seats. In 1964 Tensas Parish, with mostly only conservative whites voting, supported Republican presidential nominee Barry M. Goldwater rather than incumbent Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson, who was supporting civil rights. Few of the parish’s thousands of black residents were yet enabled to vote.
After the passage of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, large numbers of Tensas Parish blacks began registering to vote. These new black voters were staunchly Democratic, as the national party had supported their drive for civil rights. Since then, the black majority of the parish has made it a Democratic stronghold. Some white Democrats have been elected to public offices in the parish, including Sheriff Rickey A. Jones and several school board members.
In November 2019, Alex “Chip” Watson Jr., who is African American, was elected to the District 1 police jury seat. Watson defeated incumbent Larry W. Foster, who is white and the police jury president, and challenger “Johnny” Daves, who is also white. With Watson’s victory, the Tensas Parish Police Jury will be majority African American for the first time in the parish’s history.
Tensas Parish was de jure desegregated until the fall of 1970. Although the state officially desegregated, the schools are largely de facto segregated, as many white parents have sent their children to private academies founded at that time. The majority of white students attend the private Tensas Academy in St. Joseph. Nearly all African-American pupils attend the public schools, where few whites are registered.
Enrollment in the public system, now based in St. Joseph, has declined in recent years as parish population has declined. The former Newellton High School in Newellton and Waterproof High School and Lisbon Elementary School in Waterproof have closed because of decreased enrollments. Tensas High School in St. Joseph was consolidated in 2006 from the former Joseph Moore Davidson High School of St. Joseph, as well as Newellton and Waterproof high schools.
In May 2010, the graduating class of forty students at Tensas High School included three whites. Ten white students graduated from Tensas Academy, and four whites from the private Newellton Christian Academy.
Historically, Tensas Parish has been heavily Democratic in orientation, although the make-up of the party has changed markedly in terms of demographics.
In the 1860 presidential election, the parish supported by plurality the Constitutional Union Party candidate, U.S. Senator John Bell of Tennessee, who pledged to support the Constitution of the United States, the Union of states, and the “enforcement of the laws.” Louisiana as a whole narrowly cast its electoral votes for the Southern Democratic choice, Vice President John C. Breckinridge of Kentucky. Regular Democratic nominee Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois ran poorly in Louisiana, and the Republican candidate, Abraham Lincoln, also of Illinois, was not even listed on the state ballot.
The end of the war was followed by emancipation of millions of enslaved African Americans in the South. After gaining the franchise, most black men joined the Republican Party, electing candidates who made up a biracial legislature in Louisiana during Reconstruction. White Democratic groups worked through intimidation and fraud to suppress black and white Republican voting during and after the Reconstruction era. In 1898 Louisiana passed a new state constitution with provisions that created barriers to voter registration in order to disenfranchise African-American voters and cripple the Republican Party. Louisiana was effectively a one-party state and part of the Solid South for the next several decades.
In 1988, Vice President George H. W. Bush, the Republican presidential nominee, prevailed in Tensas Parish with 1,645 votes (50 percent). Governor Michael Dukakis of Massachusetts trailed with 1,556 (47.3 percent).
In 1996, native son of the South U.S. President Bill Clinton obtained 1,882 votes (60.7 percent) in Tensas Parish, and the Republican Bob Dole of Kansas polled 1,000 votes (32.3 percent).
In 2000, the Democratic nominee, Vice President Al Gore, won Tensas Parish by 250 votes. The Democratic electors polled 1,580 votes that year to 1,330 for the George W. Bush-Dick Cheney ticket. In 2004, the Democratic ticket of U.S. Senators John F. Kerry of Massachusetts and John Edwards of North Carolina carried Tensas Parish, 1,460 (49.6 percent) to 1,453 (49 percent) for Bush-Cheney.
In the 2008 presidential contest, Democratic nominee Barack Obama of Illinois won Tensas Parish, 1,646 (54.1 percent) to 1,367 (45 percent) for Republican Senator John McCain of Arizona. In 2012, President Obama again carried the parish, with 1,564 votes (55.6 percent), while rival Mitt Romney polled 1,230 votes (43.7 percent). The Obama-McCain and Obama-Romney voter divisions in 2008 and 2012 reflect the demographics of the political parties in Tensas Parish.
In the 2004 U.S. Senate primary election, Tensas Parish gave a plurality to the Republican candidate, U.S. Representative David Vitter of St. Tammany Parish, who polled 1,145 votes (41 percent) compared to 881 ballots (32 percent) for his chief Democratic rival, Congressman Chris John of Crowley. He won statewide. There was no general election in Tensas Parish to determine if Vitter would have surpassed 50 percent plus one vote to obtain an outright majority in this traditionally Democratic parish.
In 2007, the successful Republican gubernatorial candidate, U.S. Representative Bobby Jindal, polled 40 percent in Tensas Parish. Tensas gave a plurality of 48 percent to Secretary of State Democrat Jay Dardenne. Two Republican candidates ran for a seat on the Tensas Parish Police Jury, the parish governing body, and Emmett L. Adams Jr., won over fellow Republican Patrick Glass, 207-179 votes (54–46 percent).
Under the state constitution, prior to 1968, each parish -regardless of population- elected at least one member to the Louisiana House of Representatives. That year the US Supreme Court ruled that states had to develop legislative districts that were based on roughly equal populations and had to be redistricted after each decennial census, based on the principle of “one man, one vote”. It said there was no constitutional basis for state legislatures to be based on geographical districts (such as one representative per parish), as that system had resulted in inequities: particularly marked under-representation of more populated, urbanized areas and an unequal dominance of state legislatures by rural areas. Louisiana and numerous other states had not regularly conducted redistricting, although there had been dramatic population shifts since the turn of the 20th century.
The last member to represent only Tensas Parish was Democrat S. S. DeWitt of Newellton and later St. Joseph. DeWitt won the legislative post in 1964 by unseating 20-year incumbent J.C. Seaman of Waterproof. Because of Tensas Parish’s small population, the state house district was made to include part of Franklin Parish. In the 1971 primary, DeWitt lost the seat to Lantz Womack of Winnsboro in Franklin Parish.
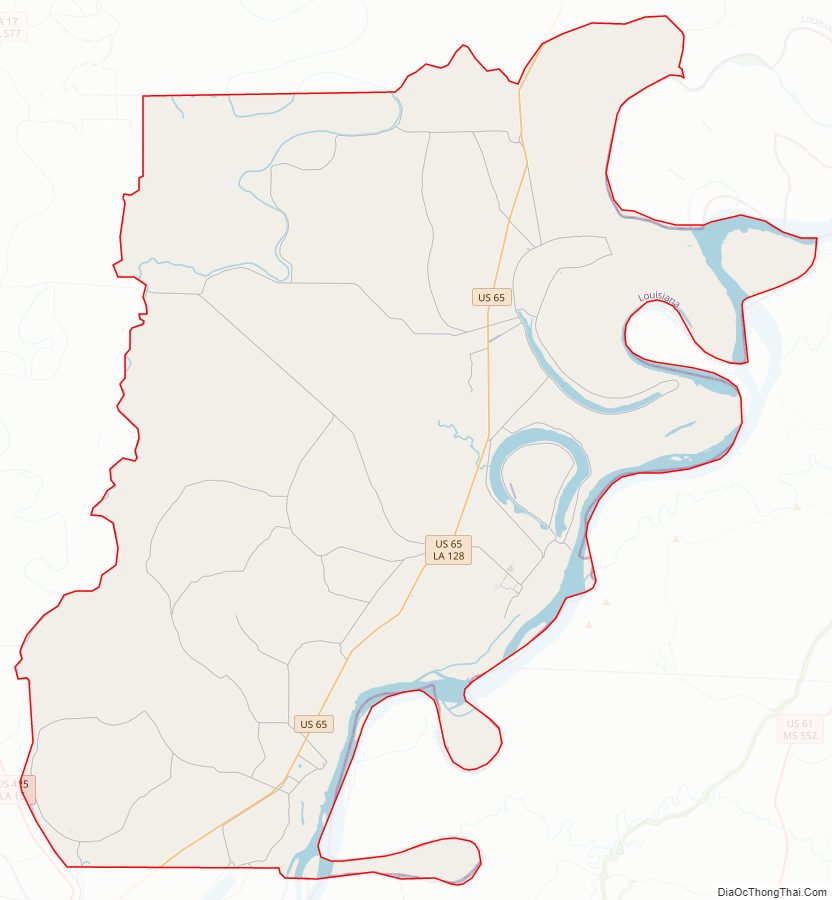
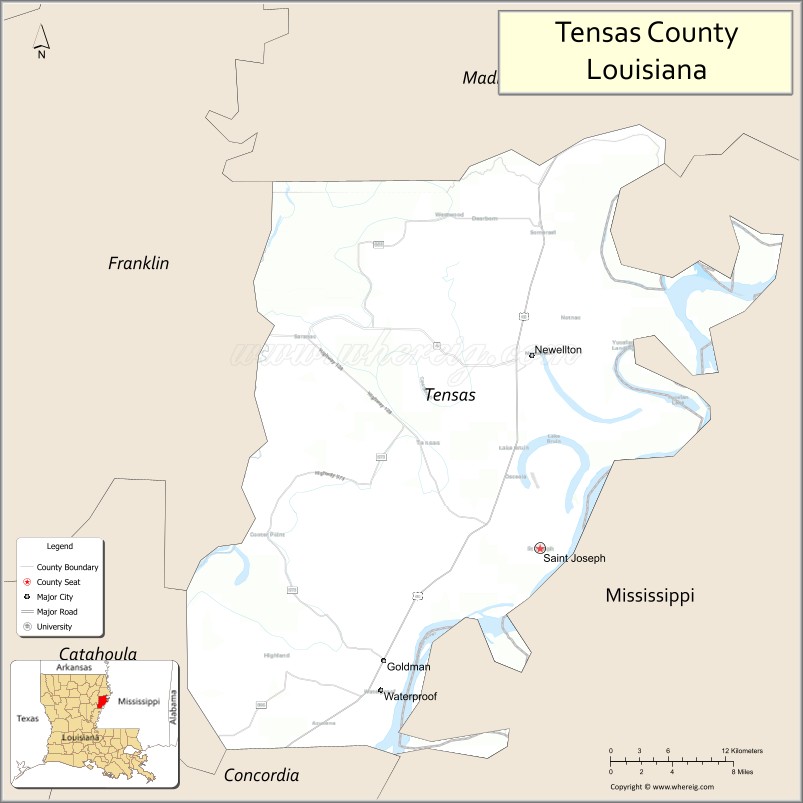
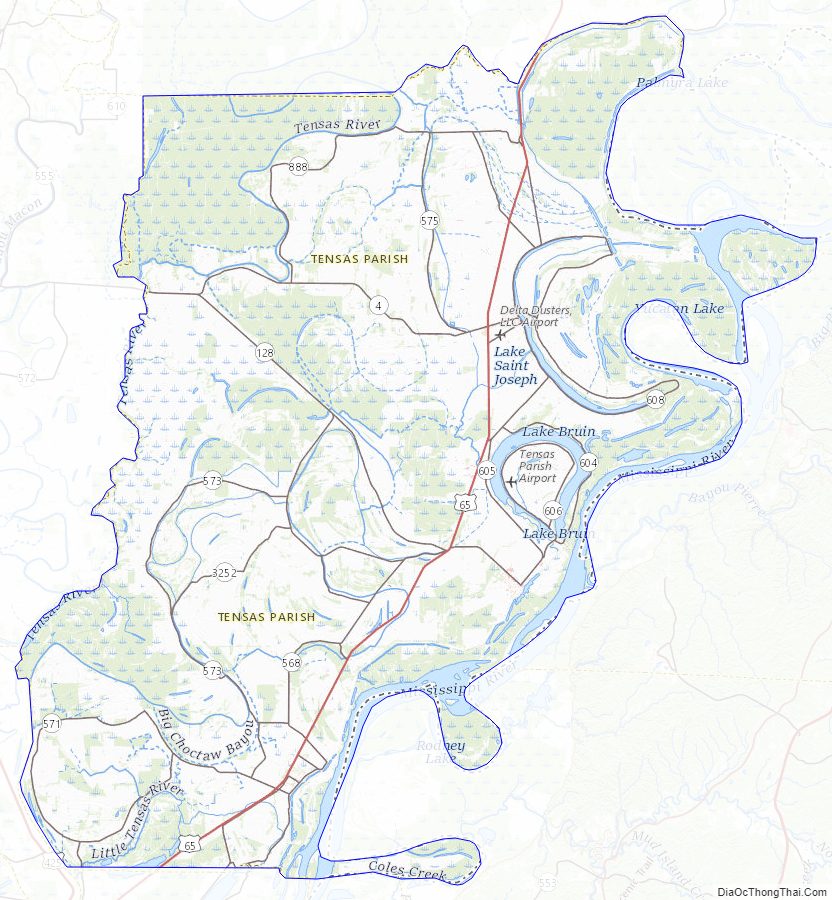
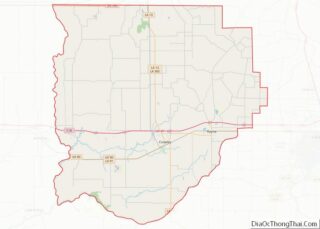
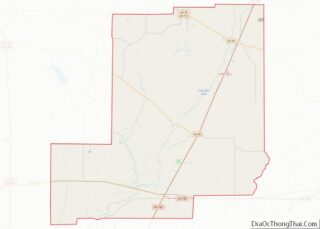
Tensas Parish Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the parish has a total area of 641 square miles (1,660 km), of which 603 square miles (1,560 km) is land and 38 square miles (98 km) (6.0%) is water.
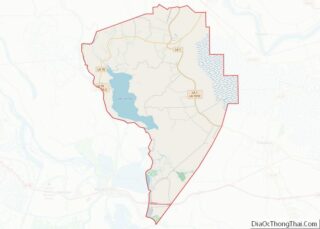
The parish seat of St. Joseph is located adjacent to the Mississippi River levee system, which protects the eastern border of the parish along the river.
The developed Lake Bruin State Park lies near St. Joseph. Lake Bruin is an oxbow lake created by the meandering of the Mississippi River; there are two other oxbow lakes in the parish.
Adjacent parishes and counties
- Madison Parish (north)
- Warren County, Mississippi (northeast)
- Claiborne County, Mississippi (east)
- Jefferson County, Mississippi (east)
- Adams County, Mississippi (southeast)
- Concordia Parish (south)
- Catahoula Parish (southwest)
- Franklin Parish (west)