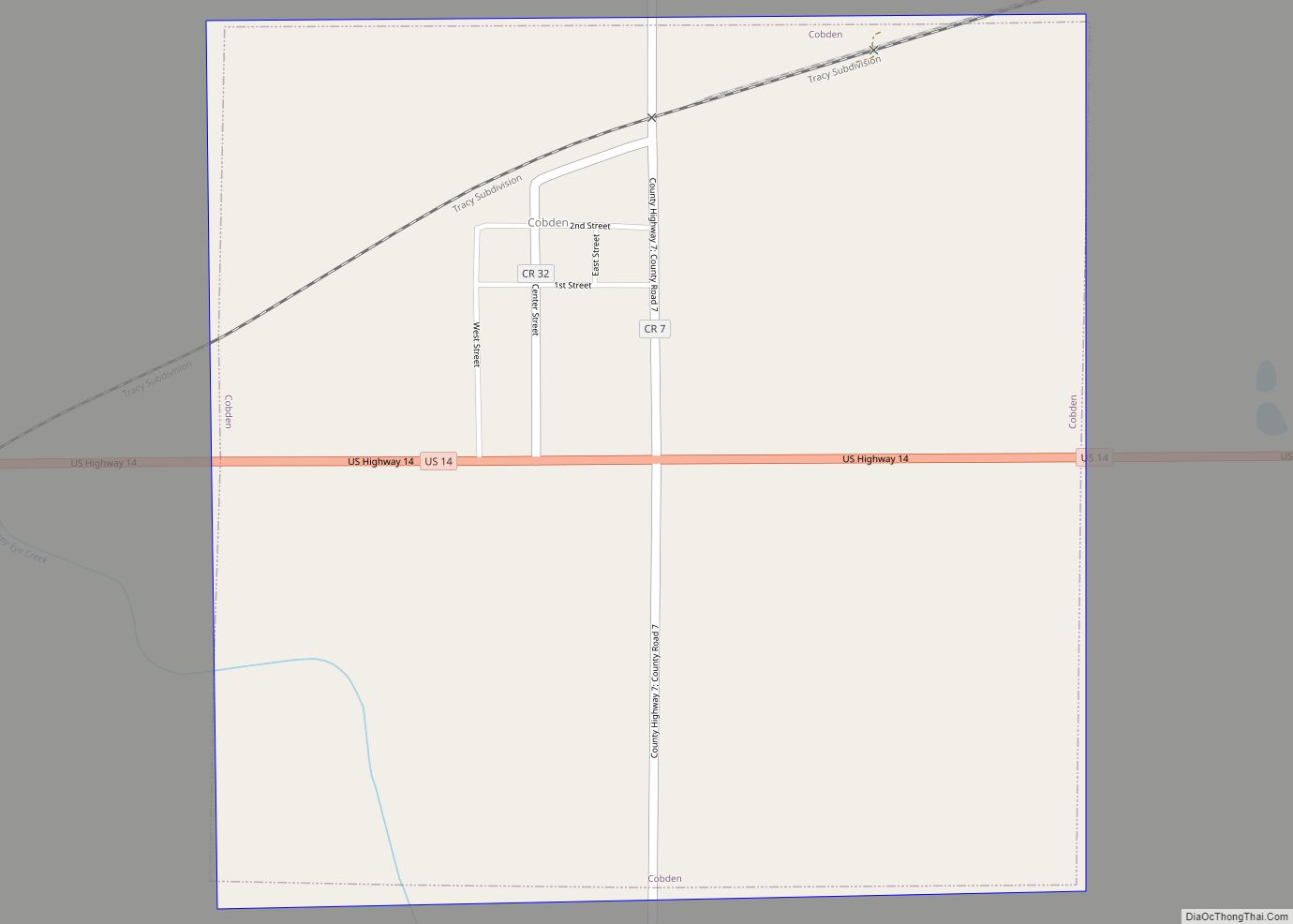
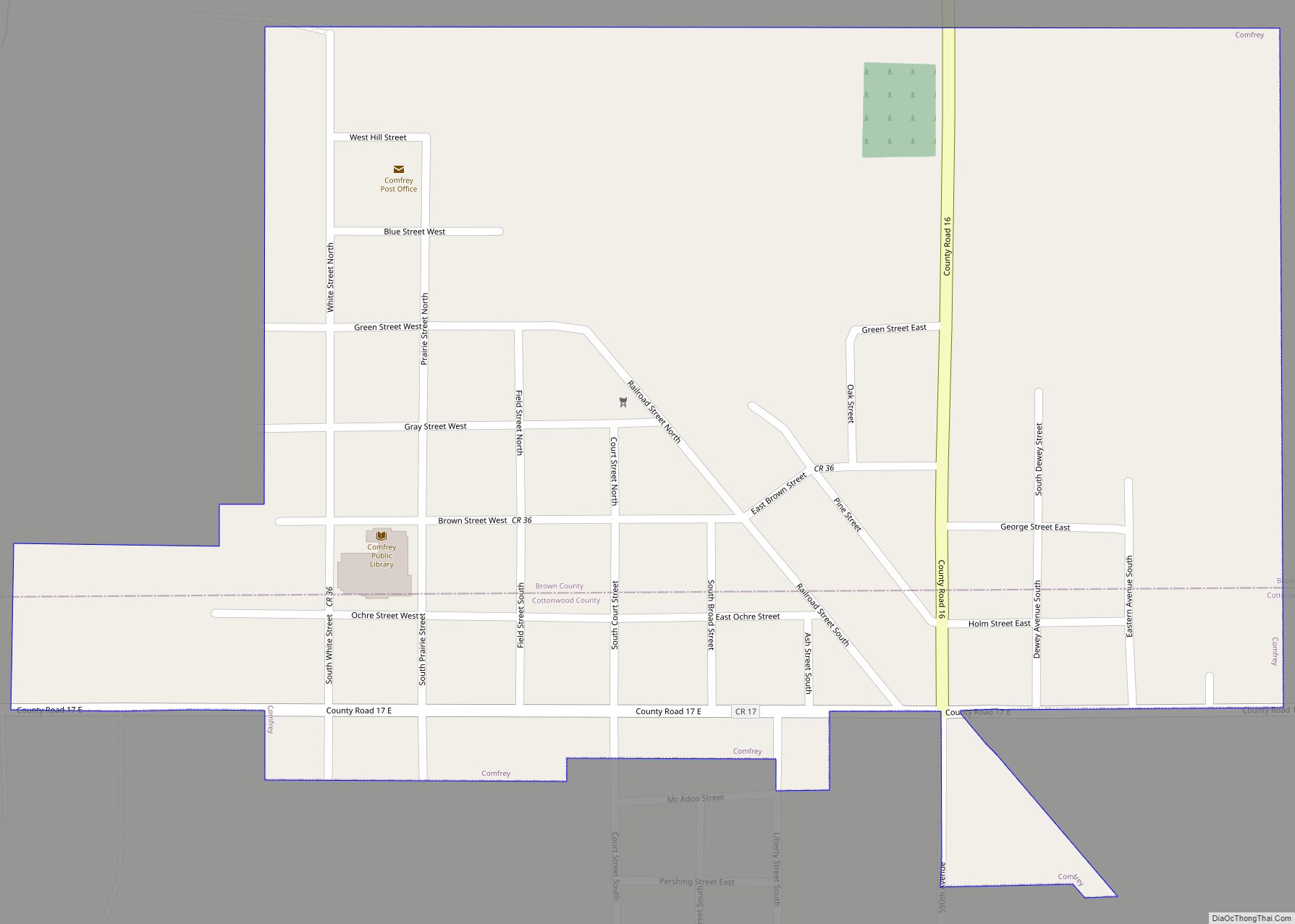
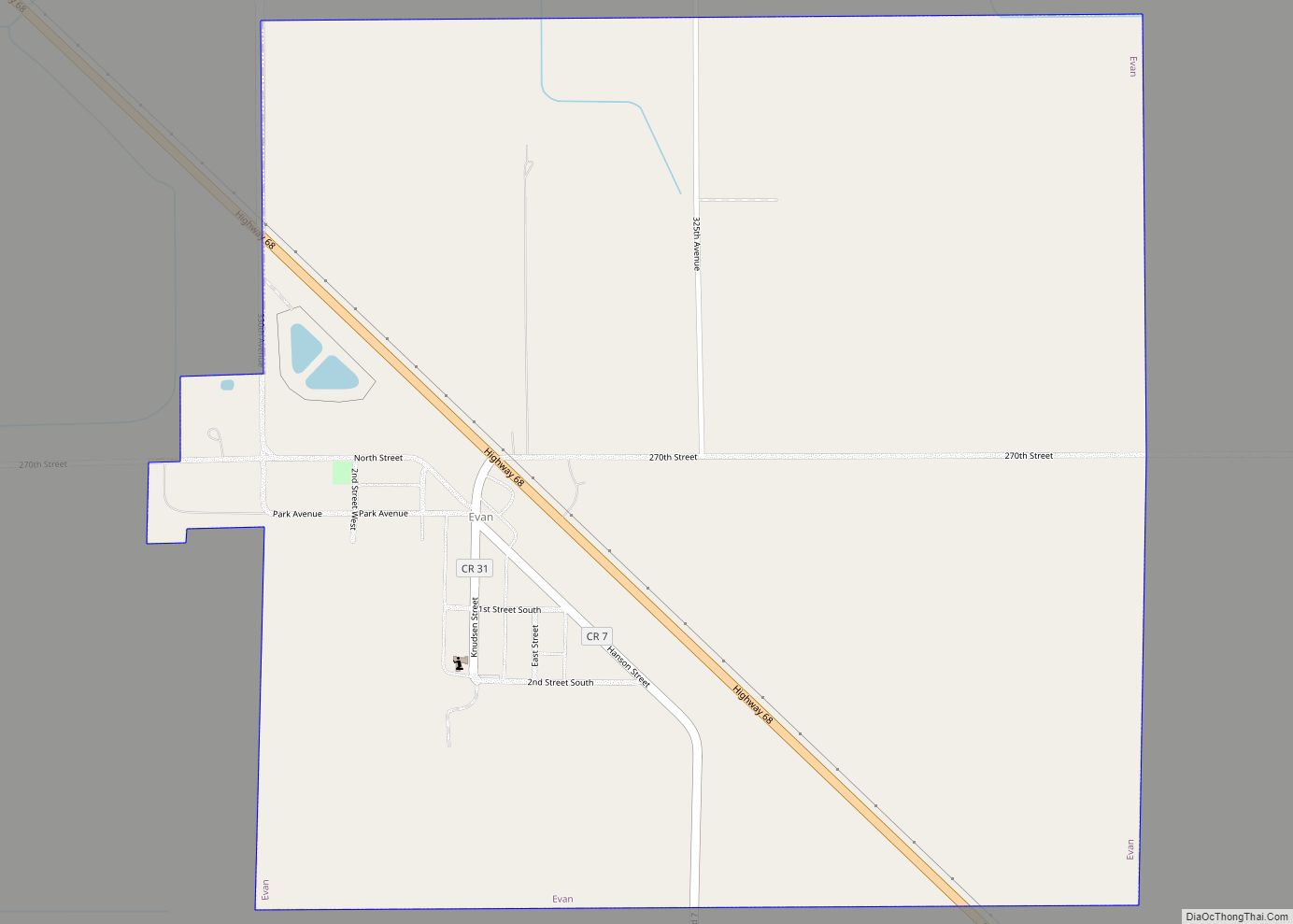
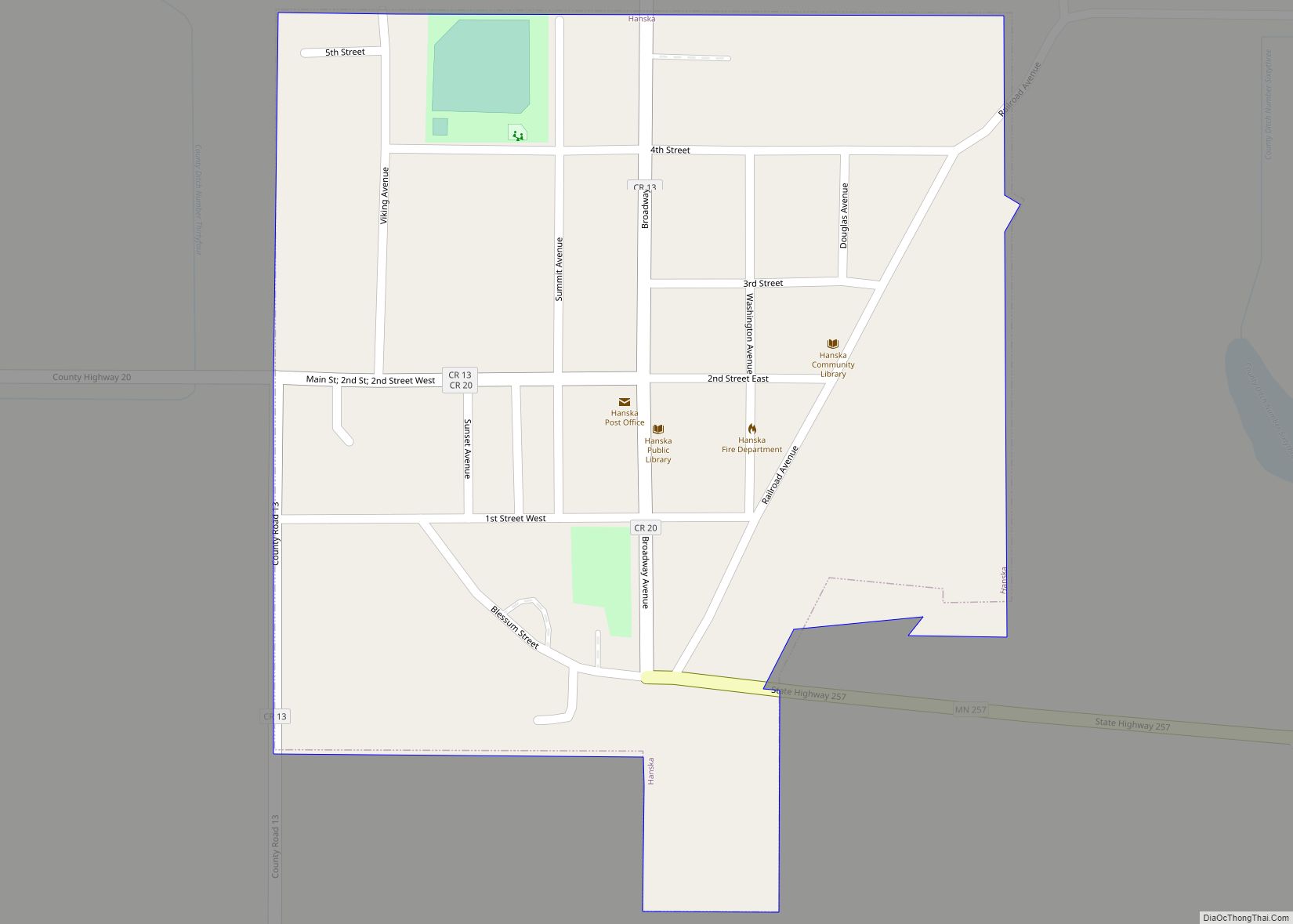
| Name: | Brown County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 27-015 |
| State: | Minnesota |
| Founded: | 1855 |
| Named for: | Joseph Renshaw Brown |
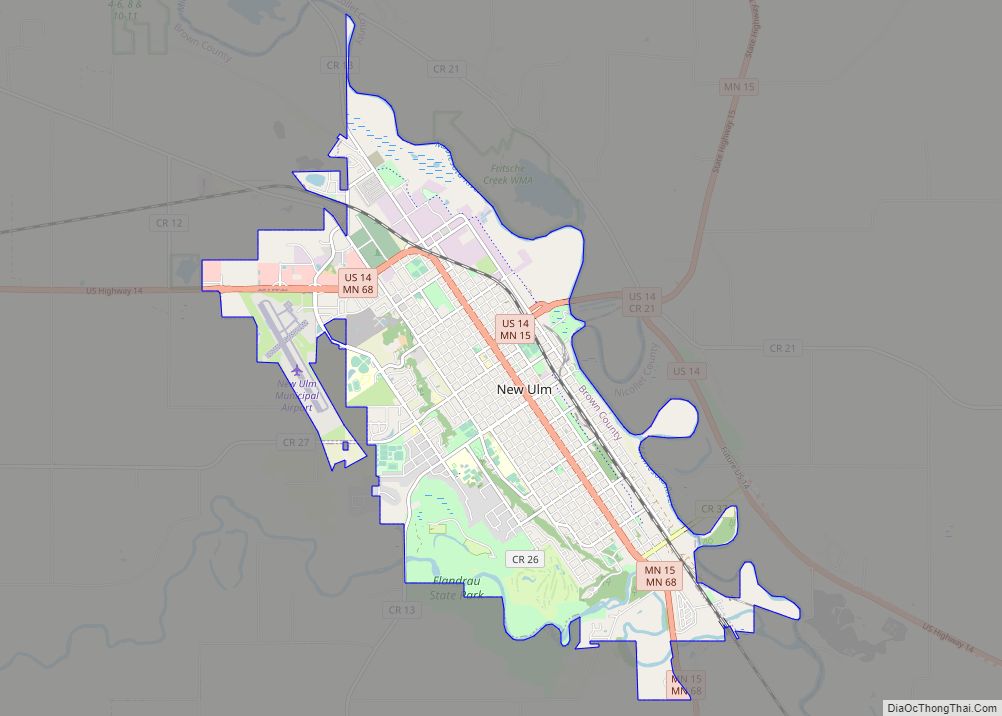
| Seat: | New Ulm |
| Largest city: | New Ulm |
| Total Area: | 618 sq mi (1,600 km²) |
| Land Area: | 611 sq mi (1,580 km²) |
| Total Population: | 25,912 |
| Population Density: | 41.9/sq mi (16.2/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | www.co.brown.mn.us |
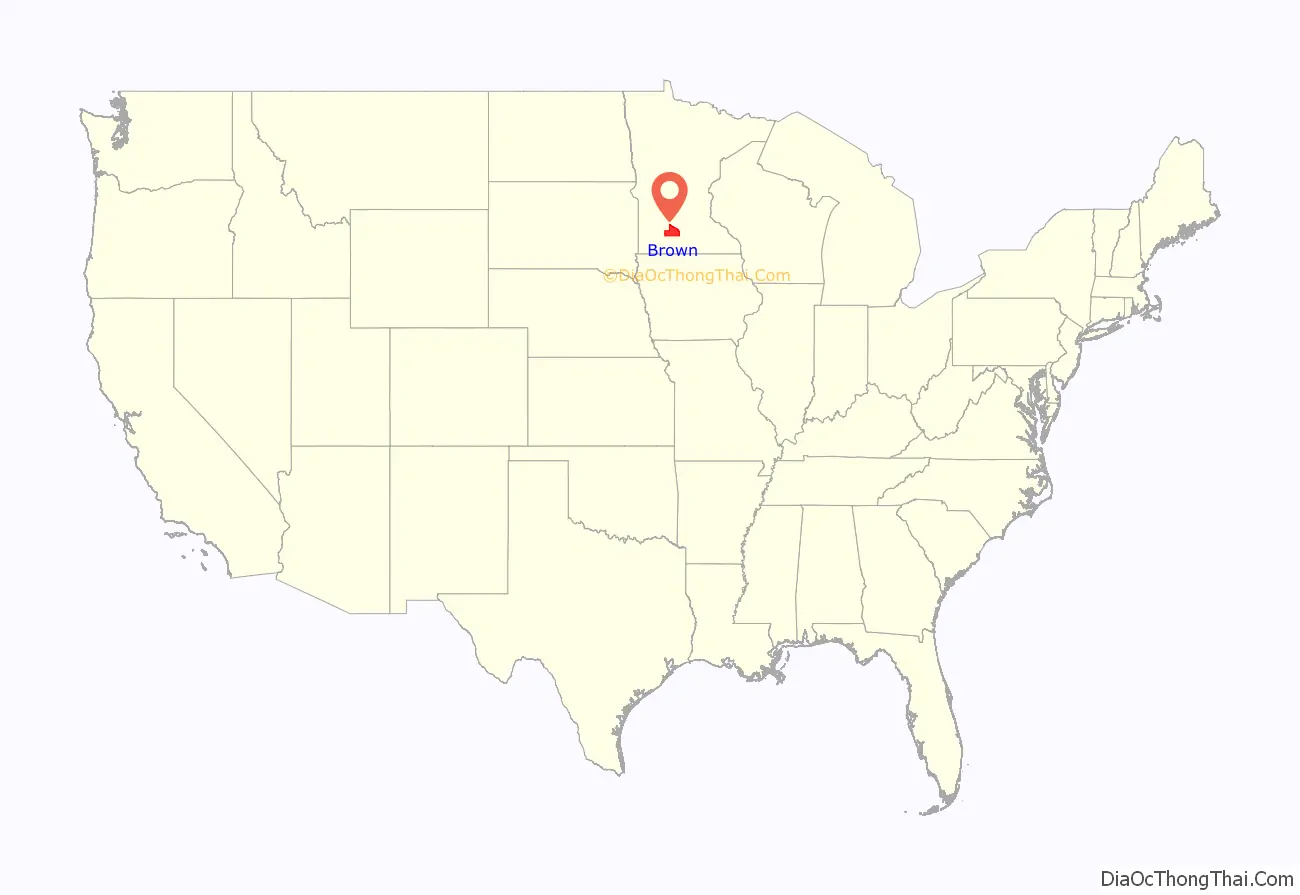
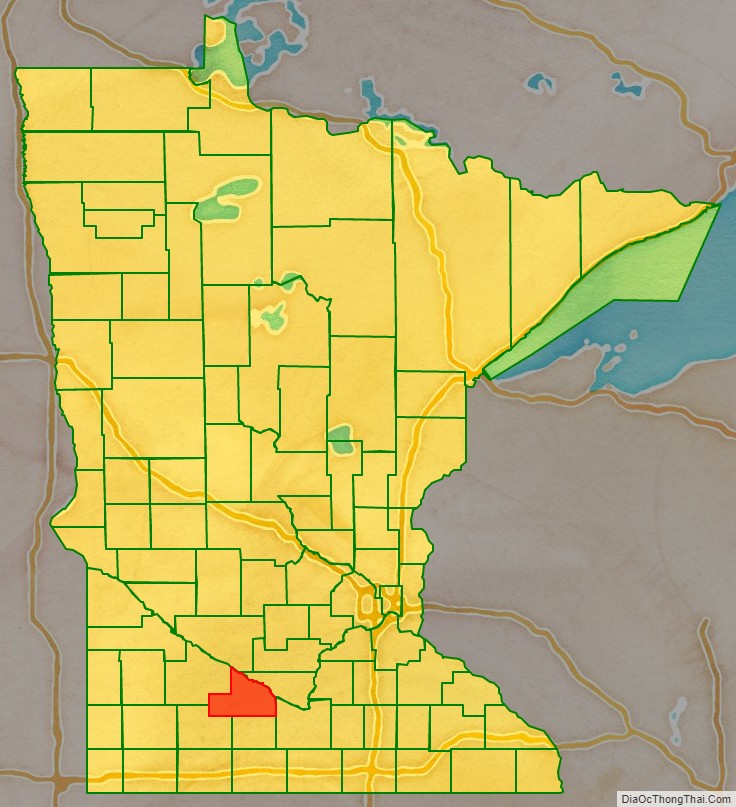
Brown County location map. Where is Brown County?
History
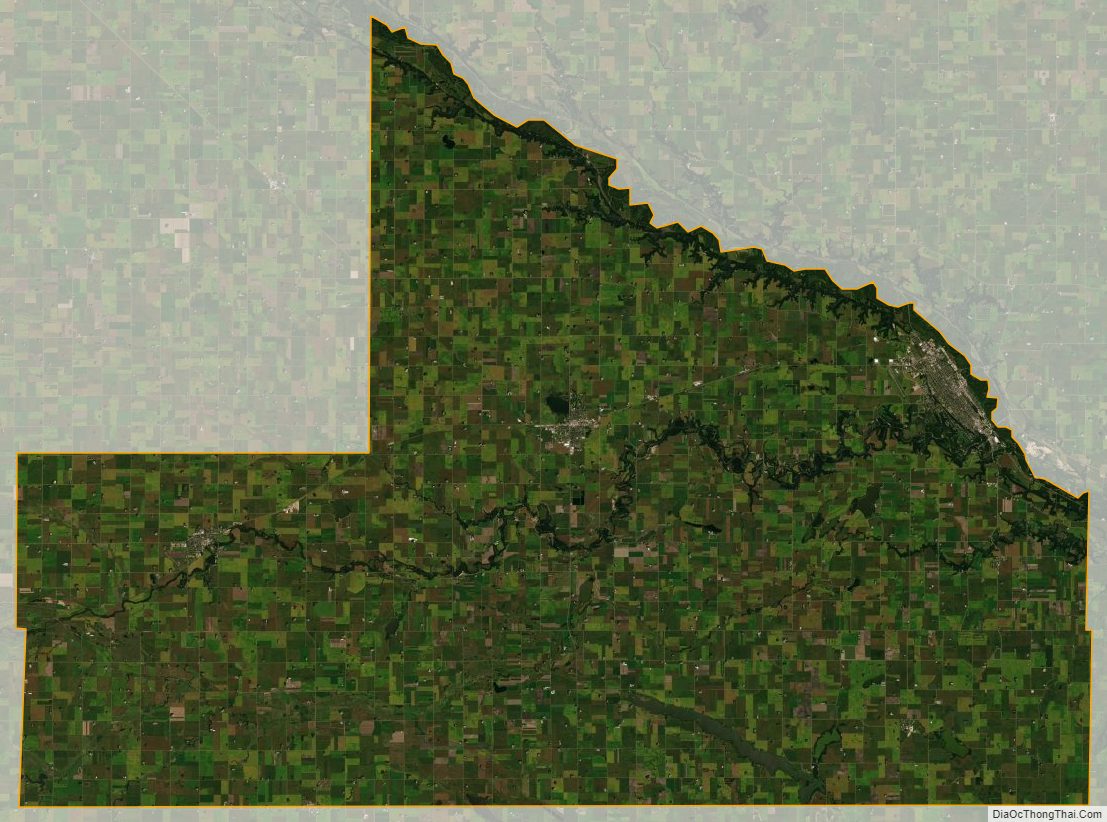
Brown County was founded in 1855 in the southwest corner of what was Minnesota Territory. It was named for Joseph Renshaw Brown, a member of the Governor’s Council of the Territory in 1855. In 1857, Brown County was divided, creating Cottonwood, Jackson, Martin, Murry, Nobles, Pipestone, and Rock counties. Watonwan was broken off in 1860. Redwood was created from a large portion of Brown County in 1862. Redwood was further divided into Lac qui Parle, Lincoln, Lyon and Yellow Medicine Counties in the 1870s. In 1862, the county’s 150-mile northern border was the boundary line of the Upper and Lower Sioux reservations when hostilities broke out. New Ulm, the county seat, came under heavy attack twice by a superior Mdewakanton Dacotah force that was repulsed. Most of the town was torched and most of the population fled to St. Peter and Mankato. The town took many casualties, with the dead buried in the streets. In 1863, when the treaties with the eastern Dacotah were annulled and the two reservations were dissolved, the county border was moved north 10 miles to the Minnesota River.
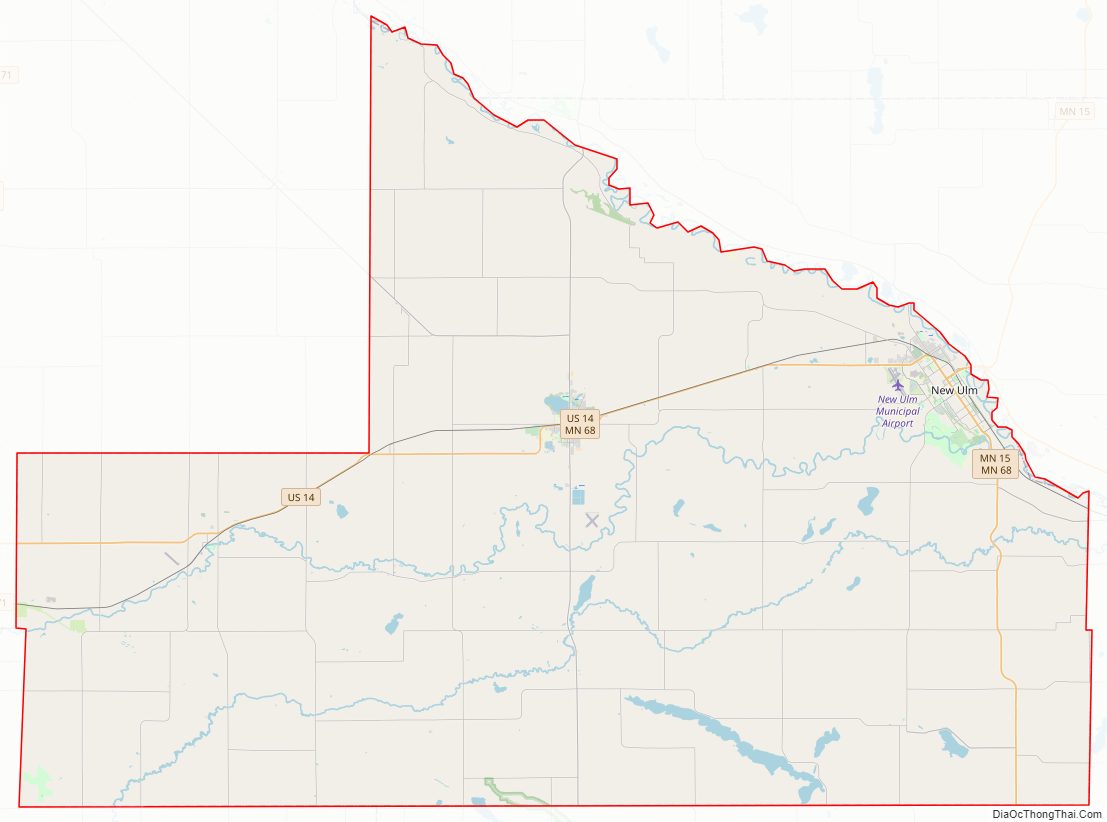
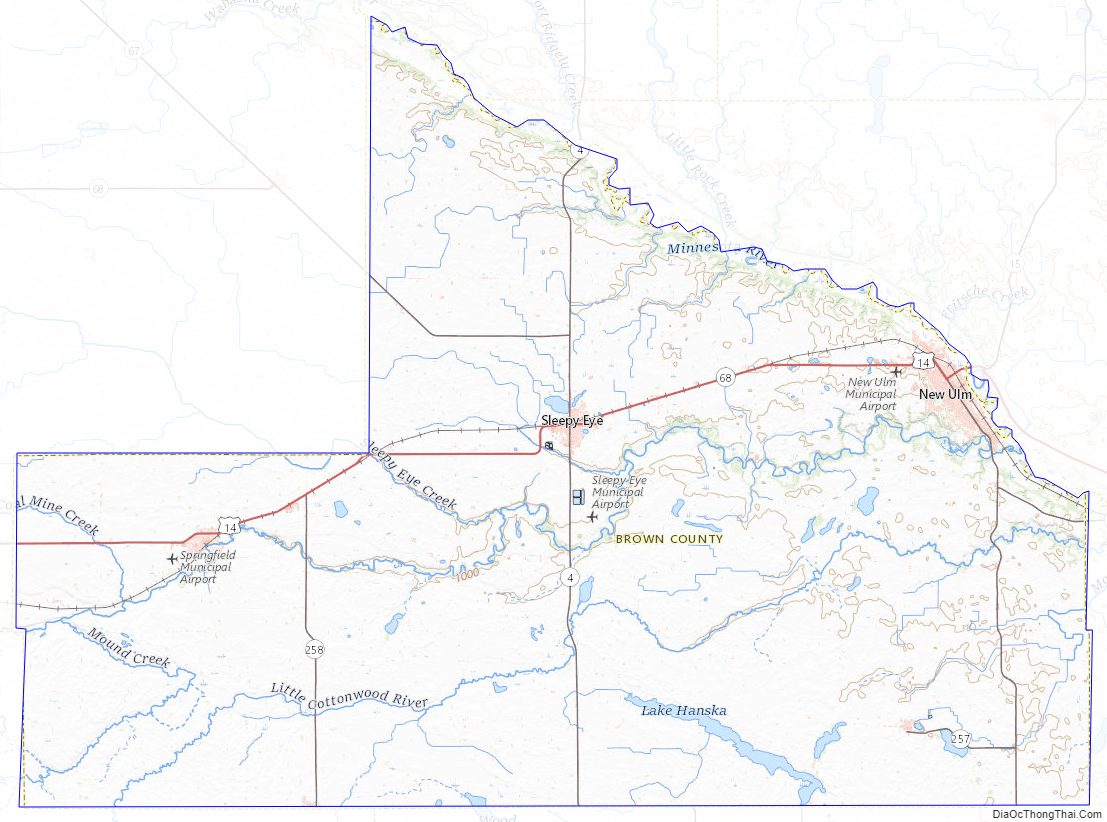
Brown County Road Map
Geography
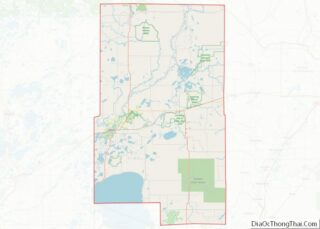
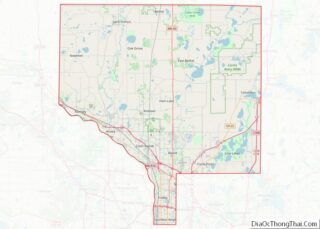
The Minnesota River flows east-southeast along the county’s northern border. The Cottonwood River flows east-northeast through the county’s central and upper area, discharging into the Minnesota at the northern border. The Little Cottonwood River flows east through the lower portion of the county, on its way to discharge into the Minnesota in neighboring Blue Earth County. The terrain consists of rolling hills, mostly devoted to agriculture, and generally slopes to the east, tending to drop into the river valleys. Its highest point is at its southwestern corner, at 1,263′ (385m) ASL.
The county has an area of 618 square miles (1,600 km), of which 611 square miles (1,580 km) is land and 7.4 square miles (19 km) (1.2%) is water.
Major highways
- U.S. Highway 14
- Minnesota State Highway 4
- Minnesota State Highway 15
- Minnesota State Highway 68
- Minnesota State Highway 257
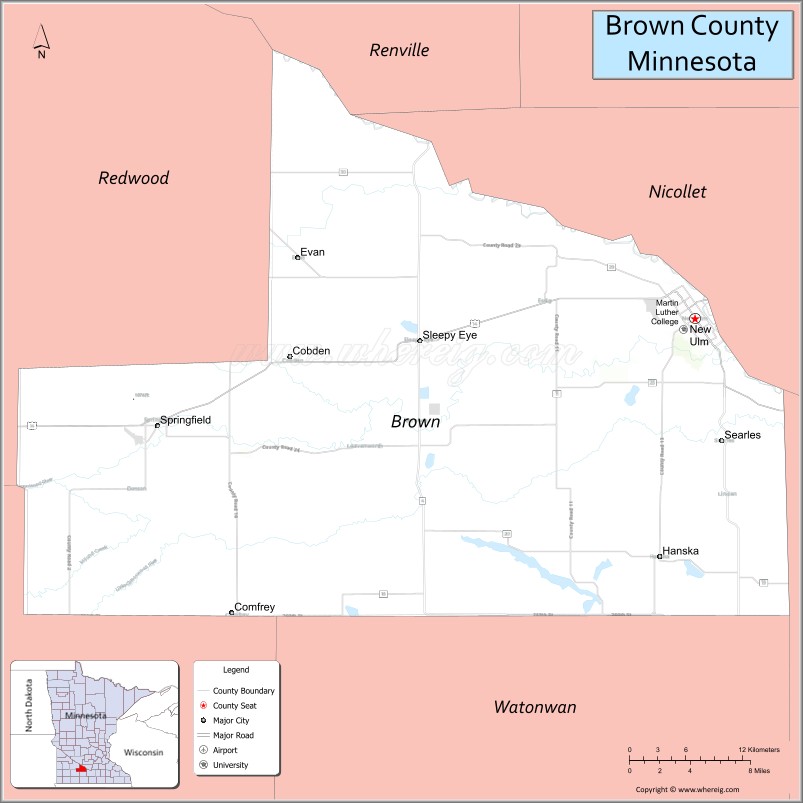
Adjacent counties
- Nicollet County – northeast
- Blue Earth County – southeast
- Watonwan County – south
- Cottonwood County – southwest
- Redwood County – west
- Renville County – northwest
Lakes
Most of the county is an area of rich farm land; most of its wetlands were drained for use in agriculture, leaving a number of lakes. The county has at least 32 lakes, some of which are deemed to be “protected waters” of the State of Minnesota; these are designated with “(p)” below.
The lakes occupy “hollows in the driftsheet”; many have neither an inflow nor an outflow.
Lakes in the county include:
- Altermatt Lake (p)
- Bachelor Lake (p), in Stark township
- Boise Lake (p)
- Clear Lake (p)
- Gilman Lake (p)
- Horseshoe Lake
- Juni Lake (p), named for Benedict Juni, a Swiss settler.
- Lake Cottonwood (p)
- Lake Hanska (p)
- Linden Lake (p)
- Lone Tree Lake (p)
- Omsrud Lake (p)
- School Lake (p), named for its location in school section 16.
- Sleepy Eye Lake (p)
- Zanders Lake (p)