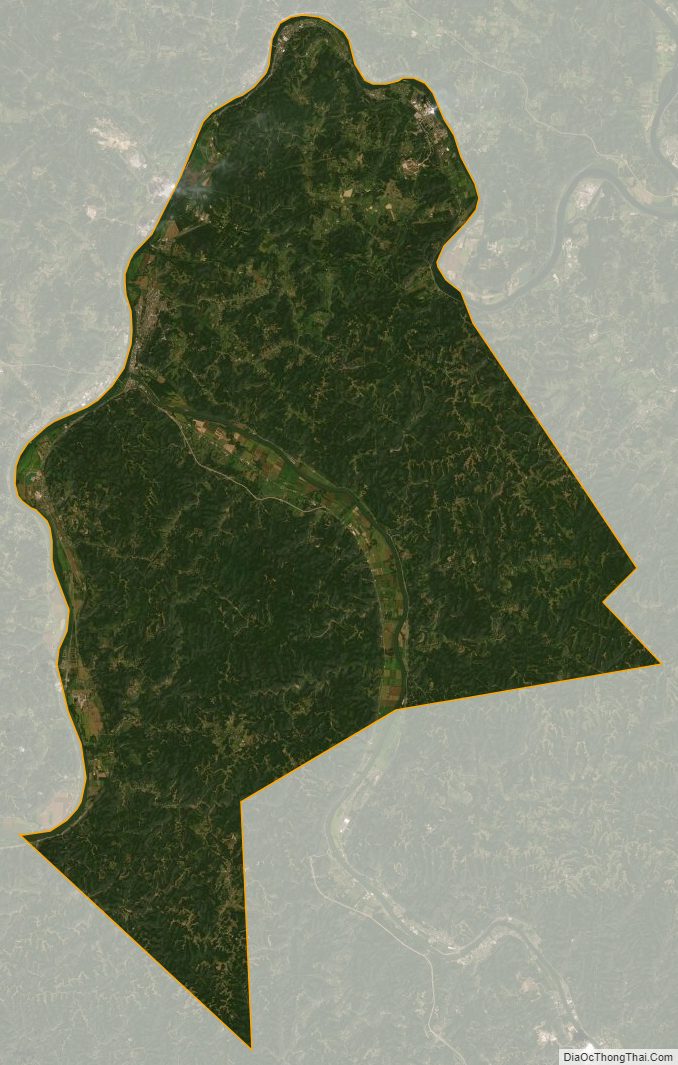
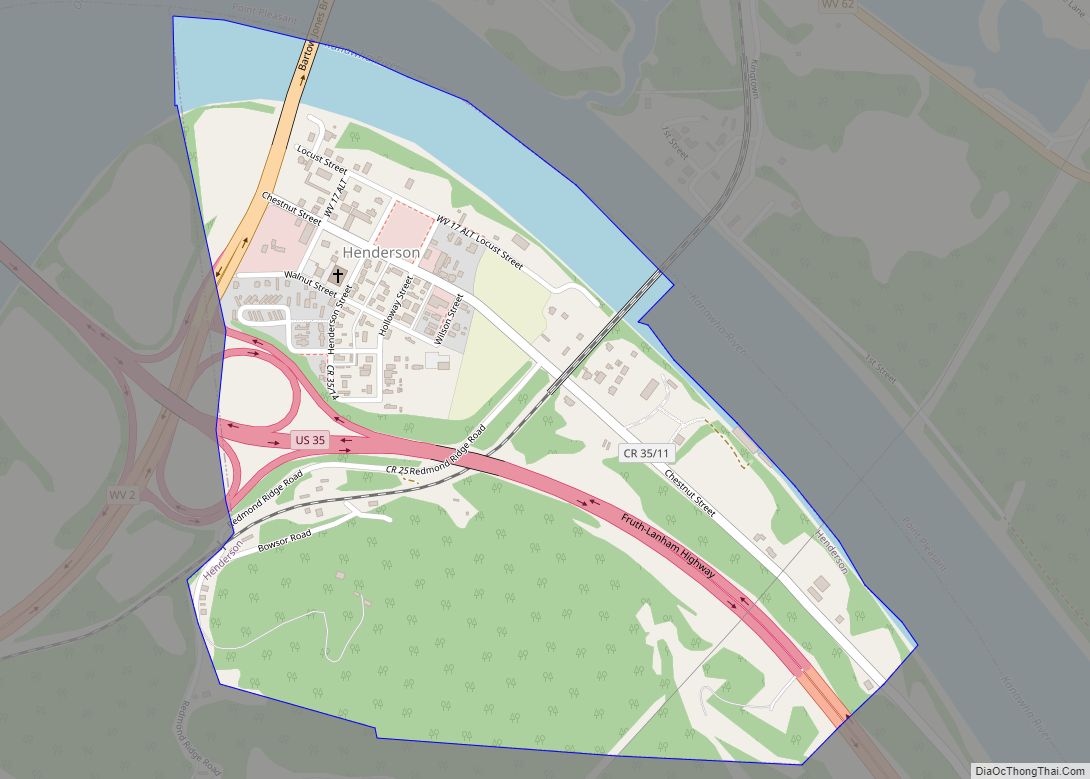
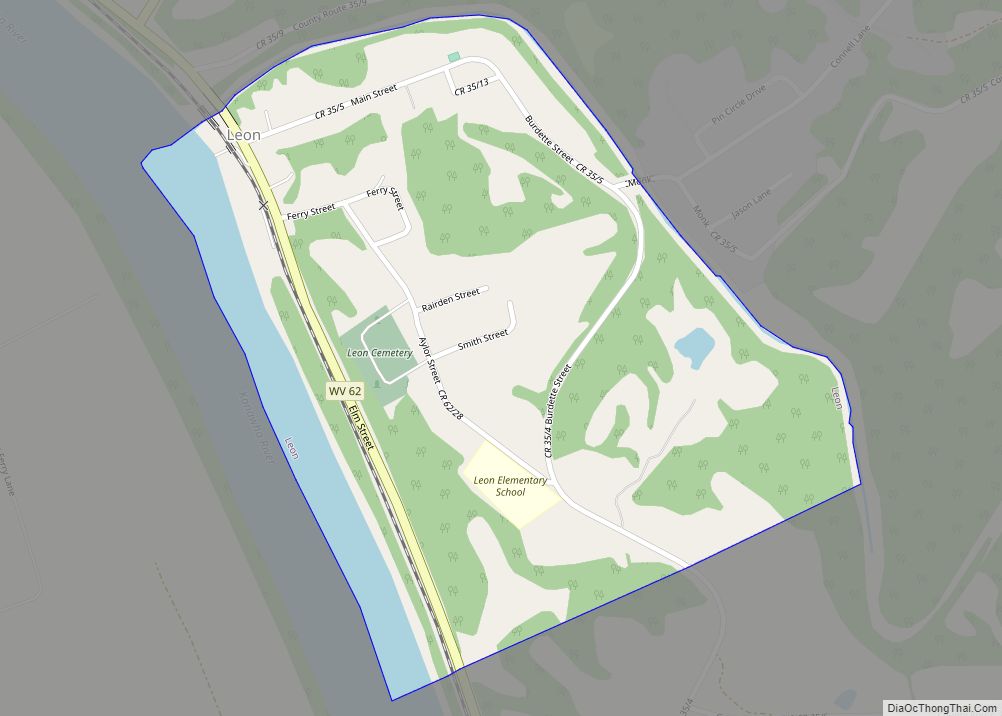
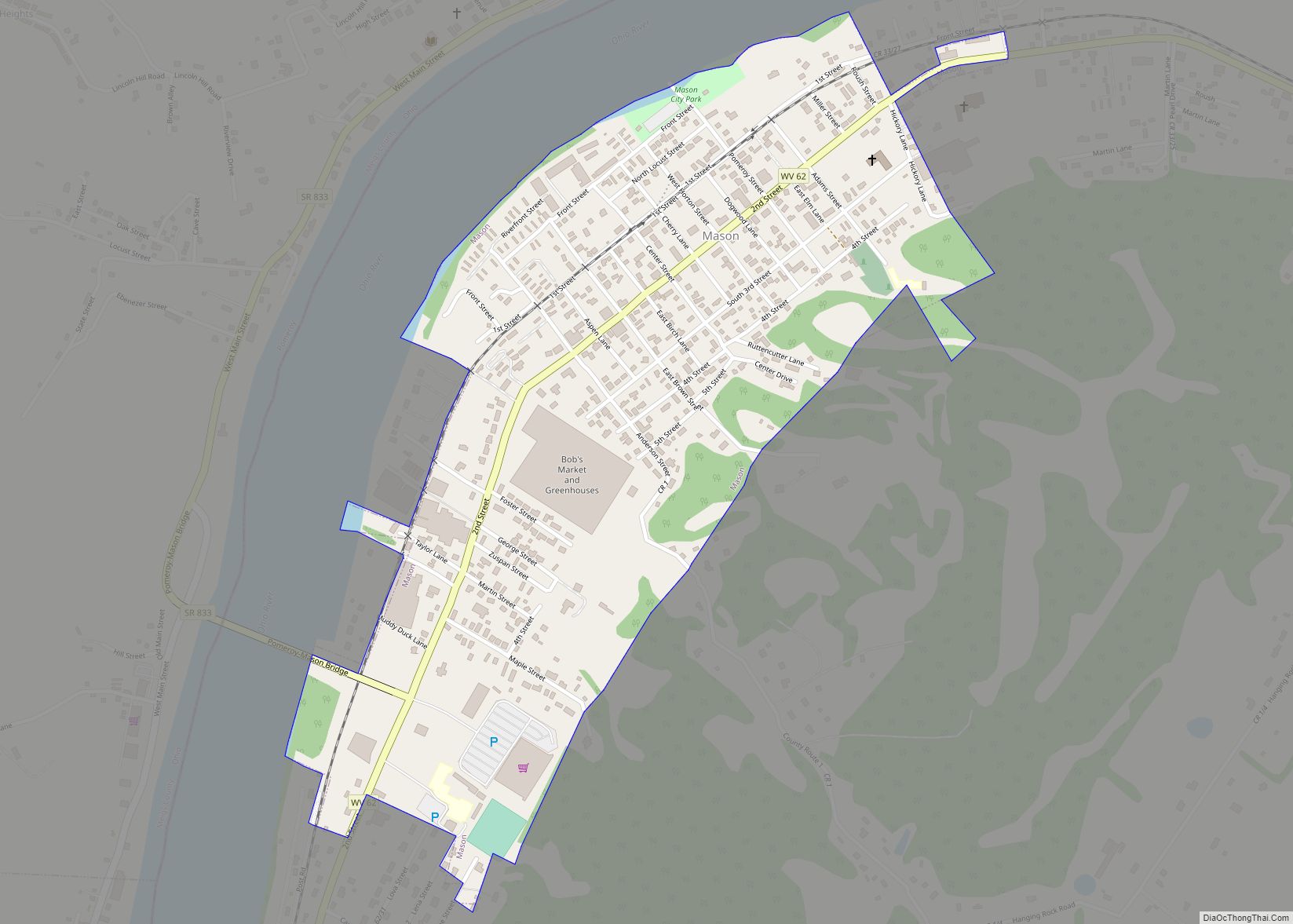
Mason County is a county in the U.S. state of West Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 25,453. Its county seat and largest city is Point Pleasant. The county was founded in 1804 and named for George Mason, delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention. Before the Civil War, the county was in the State of Virginia.
Mason County is part of the Point Pleasant, WV-OH Micropolitan Statistical Area.
| Name: | Mason County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 54-053 |
| State: | West Virginia |
| Founded: | January 2, 1804 |
| Seat: | Point Pleasant |
| Largest city: | Point Pleasant |
| Total Area: | 445 sq mi (1,150 km²) |
| Land Area: | 431 sq mi (1,120 km²) |
| Total Population: | 25,453 |
| Population Density: | 57/sq mi (22/km²) |
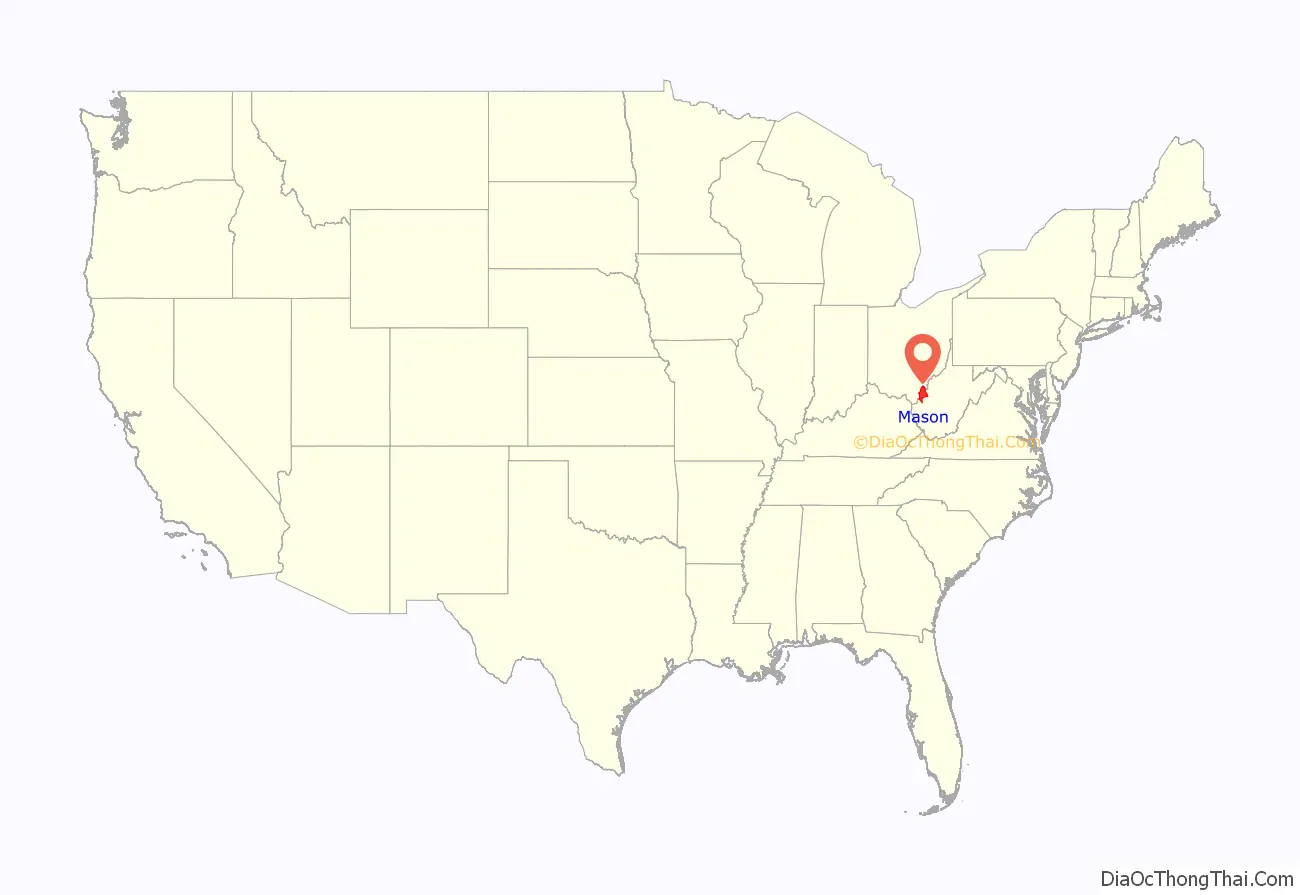
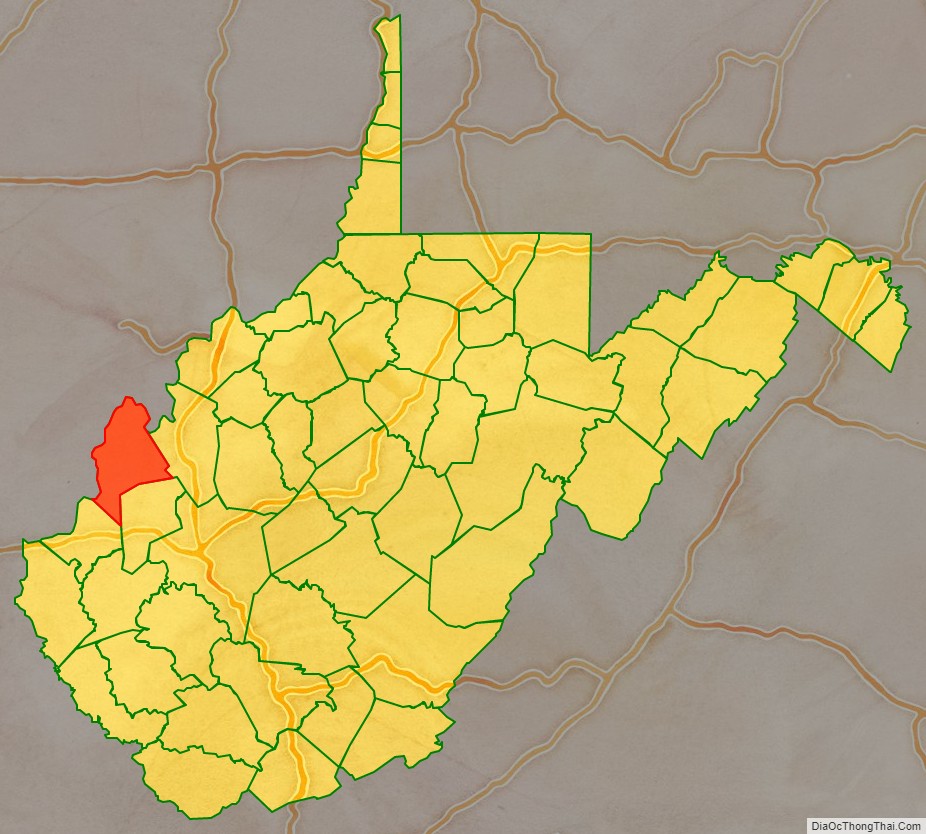
Mason County location map. Where is Mason County?
History
In the second half of 1749, the French explorer, Pierre Joseph Céloron de Blainville, claimed French sovereignty over the Ohio Valley, burying a lead plaque at the meeting point of the Ohio and Kanawha Rivers, naming the place Point Pleasant.
In the Battle of Point Pleasant (October 10, 1774), fought on the future site of the town, over one thousand Virginia militiamen, led by Colonel Andrew Lewis (1720–1781), defeated a roughly equal force of an Algonquin confederation of Shawnee and Mingo warriors led by Shawnee Chief Cornstalk (ca. 1720–1777). The event is celebrated locally as the “First Battle of the American Revolutionary War” and in 1908 the U.S. Senate authorized erection of a local monument to commemorate it as such. Most historians, however, regard it not as a battle of the Revolution (1775–1783), but as a part of Lord Dunmore’s War (1774). White settlers may have established their permanent settlement by 1774, for Col. Lewis had established “Camp Point Pleasant” at the time of the Battle and the settlement that followed also took that name.
According to Hardesty’s West Virginia Counties (1883), regarding the first white settlers in Mason County south of Point Pleasant:
The settlement at Point Pleasant did not receive an official charter until 1794. The first road through what later became Mason County was laid out by Thomas Hannan (1757-1835) in 1798 under contract to the federal government. It traversed the distance from present-day St Albans, (West) Virginia to Chillicothe, Ohio. This road (parts are still known as “Hannan Trace Road”) is one of the oldest roads in Ohio. It became a main highway connecting Chillicothe and points east during the time when that settlement served as the capital of the Northwest Territory and the first capital of Ohio.
The Virginia General Assembly officially created Mason County from Kanawha County on January 2, 1804. It was named for George Mason IV (1725–1792), known as the “Father of the United States Bill of Rights” and a Founding Father of the United States. By 1810, the total county population stood at almost two thousand people. Before the American Civil War it developed as a river port (farmers upstream on the Kanawha River could ship their goods to Point Pleasant and from there down the Ohio River and sometimes the Mississippi River to market) as well as coal.
In the Virginia Secession Convention of 1861, Mason County’s delegate, lawyer James H. Couch (1821-1899), although a slaveholder, voted against secession. Mason County then sent no delegates to the Virginia House of Delegates until West Virginia’s statehood, which Virginia’s House of Delegates refused to recognize, thus seating James Hutcheson who had been elected by Confederate soldiers in their camp. Meanwhile, William W. Newman claimed to represent Mason as well as nearby Jackson, Cabell, Wayne and Wirt counties throughout the war. Mason County sent more than 1000 men to the Union army and one company of 61 men to the Confederate Army (the 37th Virginia Infantry). In March 1863, in the only wartime skirmish in Mason County, during the Jones-Imboden Raid, the 6th Virginia Cavalry and 8th Virginia Cavalry attacked the Mason County Courthouse, where they believed munitions stored, leaving bullet holes in the walls until a replacement was built in 1954.
Point Pleasant’s Battle Monument State Park, also known as Tu-Endie-Wei, was dedicated on October 10, 1901, to commemorate the Battle of Point Pleasant, at the time claimed to have been the first battle of the Revolutionary War. It significantly predates the 1928 establishment of the West Virginia state park system. The park includes the tavern begun in 1796 by Walter Newman, later operated as a museum of local history by the Daughters of the American Revolution.
The Marietta Manufacturing Company (shipbuilders) moved to Point Pleasant in 1915; the facility continued to build mine-planting vessels and other small ships through World War II, but closed in 1970. During World War II the West Virginia Ordnance Works manufactured TNT in Mason County about 5 miles north of Point Pleasant; it was later repurposed as the McClintic Wildlife Management Area as well as an industrial park. The county’s worst disaster occurred on December 15, 1967, when the Silver Bridge, a link-suspension bridge which had connected Point Pleasant to Kanauga, Ohio along U.S. Route 35 since 1928, collapsed during the rush hour commute. The disaster killed 46 people and injured nine others, and drew attention to poor bridge maintenance practices, as well as bridge loads greatly exceeding their original tolerances. The important bridge was replaced two years later by the Silver Memorial Bridge, which stands today.
In 1981, the West Virginia Department of Agriculture acquired land that had been farmed after the Civil War by General John McCausland, the last fully confirmed Confederate general to die. Added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2003, it now operates as Smithland Farm. The River Museum opened on May 1, 2004, but closed in 2018 after a disastrous fire.
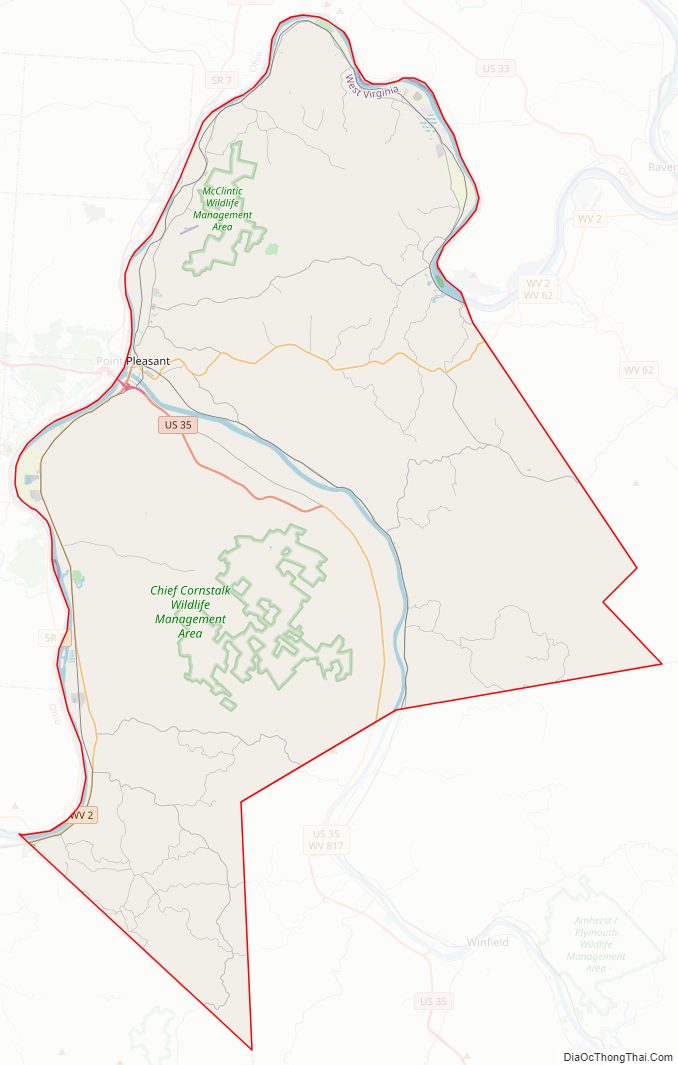
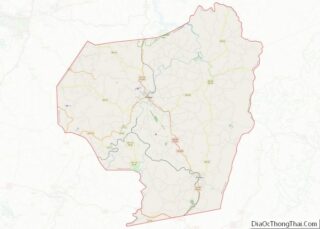
Mason County Road Map
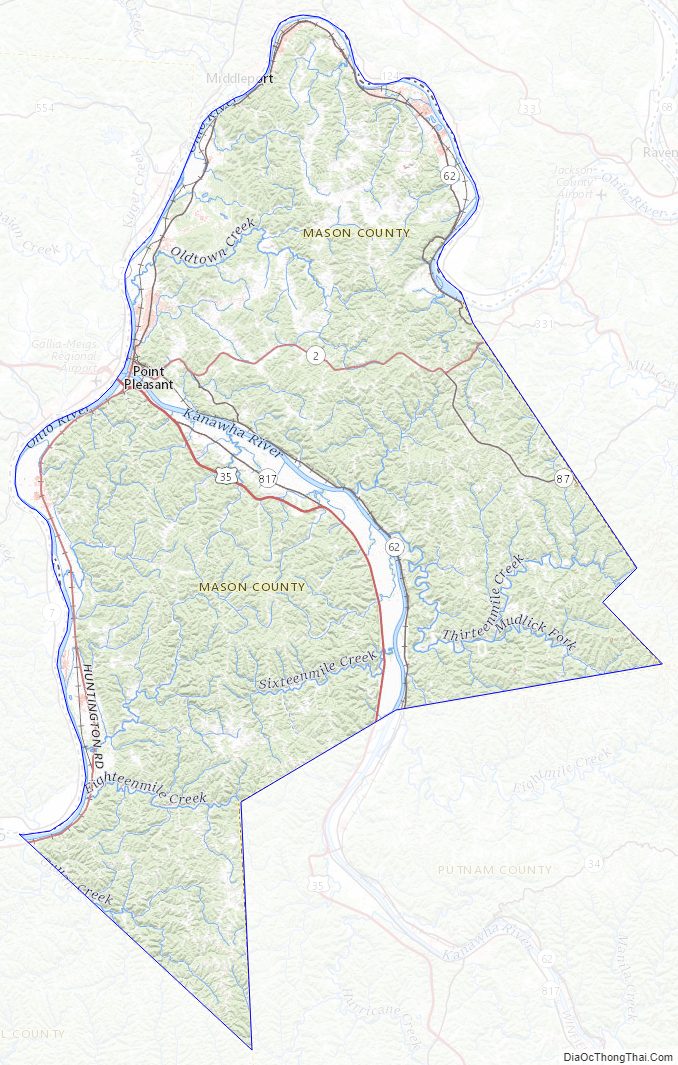
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 445 square miles (1,150 km), of which 431 square miles (1,120 km) is land and 14 square miles (36 km) (3.1%) is water.
Territorial evolution
Prior to its establishment in 1804, the land that would become Mason County was part of the vast and largely unorganized territory claimed by Virginia west of the Alleghenies. It was attached to various counties beginning with Orange in 1734, Augusta in 1738, and Botetourt in 1770. Beginning in 1772, the portion of Mason County south of the Kanawha River was part of Fincastle County, the West Virginia portion of which became Monroe County in 1777. The remaining West Virginia portion of Botetourt County, including the northern part of present-day Mason County, became Greenbrier County in 1778. In 1789, the western portions of Greenbrier and Monroe Counties, extending to the Ohio and Big Sandy Rivers, were combined to form Kanawha County.
Mason County was separated from Kanawha County in 1804, including all of its current territory, as well as portions of what are now Jackson, Putnam, and Roane Counties. The northern and western boundaries were formed by the Ohio River, and the county’s southwestern boundary, originally with Kanawha County, and now with Cabell, remains unchanged. Until 1831, Mason County shared a boundary with Wood County, running southeasterly from the Ohio River north of Ravenswood to the northwestern boundary of Kanawha County, thence in a southwesterly direction to the present border with Cabell County. The formation of Jackson County in 1831 from portions of Mason, Wood, and Kanawha Counties removed the eastern portion of Mason County, including the part now in Roane County, while the formation of Putnam County from portions of Mason, Cabell, and Kanawha Counties in 1848 removed the southeastern portion of the county. This was the last major change to Mason County’s boundaries.
After West Virginia gained its independence from Virginia in 1863, the state’s counties were divided into civil townships, with the goal of placing authority in the hands of local governments. Mason County was divided into ten townships, each of which was named after a pioneer settler of Mason County. However, township government proved impractical across the heavily rural state, with citizens unable to meet on a regular basis, and inadequate tax revenue to meet township responsibilities. Following the adoption of the Constitution of West Virginia in 1872, the townships were converted into magisterial districts, and the county courts (later county commissions) empowered to establish, consolidate, or otherwise modify them.
Major highways
- U.S. Route 35
- West Virginia Route 2
- West Virginia Route 62
- West Virginia Route 87
- West Virginia Route 817
Adjacent counties
- Meigs County, Ohio (north)
- Jackson County (east)
- Putnam County (southeast)
- Cabell County (southwest)
- Gallia County, Ohio (west)
National protected area
- Ohio River Islands National Wildlife Refuge (part)