Osage County (/ˈoʊseɪdʒ/) is the largest county by area in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Created in 1907 when Oklahoma was admitted as a state, the county is named for and is home to the federally recognized Osage Nation. The county is coextensive with the Osage Nation Reservation, established by treaty in the 19th century when the Osage relocated there from Kansas. The county seat is in Pawhuska, one of the first three towns established in the county. The total population of the county is 47,987.
| Name: | Osage County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 40-113 |
| State: | Oklahoma |
| Founded: | 1907 |
| Named for: | Osage Nation |
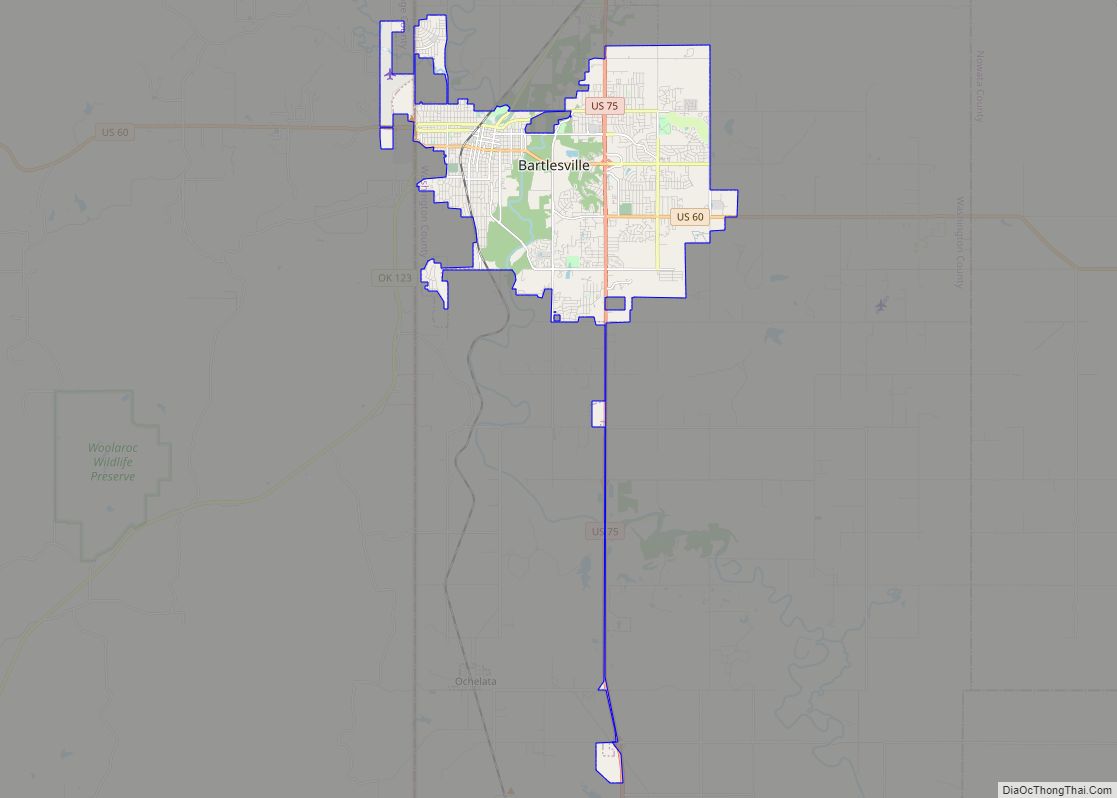
| Seat: | Pawhuska |
| Largest city: | Tulsa |
| Total Area: | 2,304 sq mi (5,970 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2,246 sq mi (5,820 km²) |
| Total Population: | 47,472 |
| Population Density: | 21/sq mi (8/km²) |
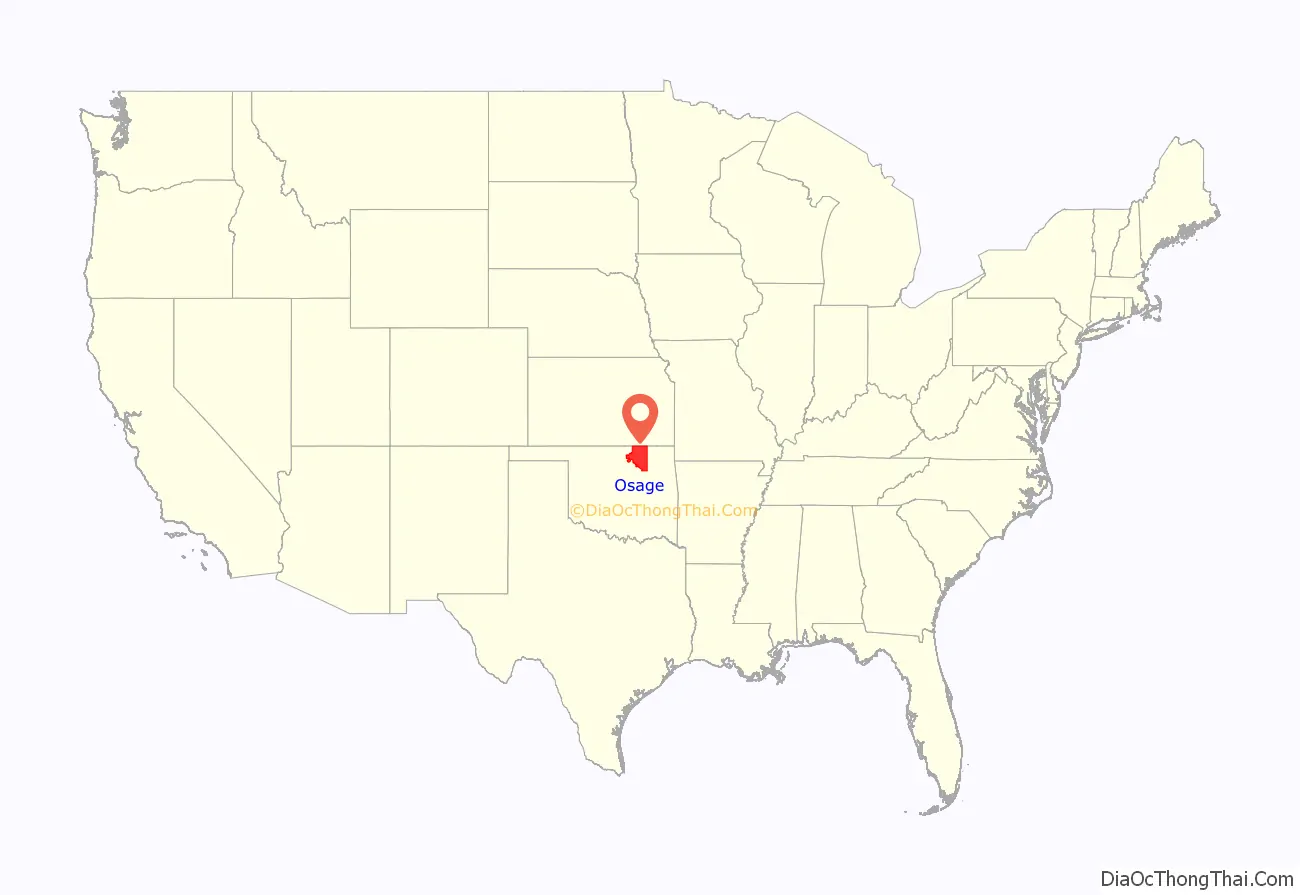
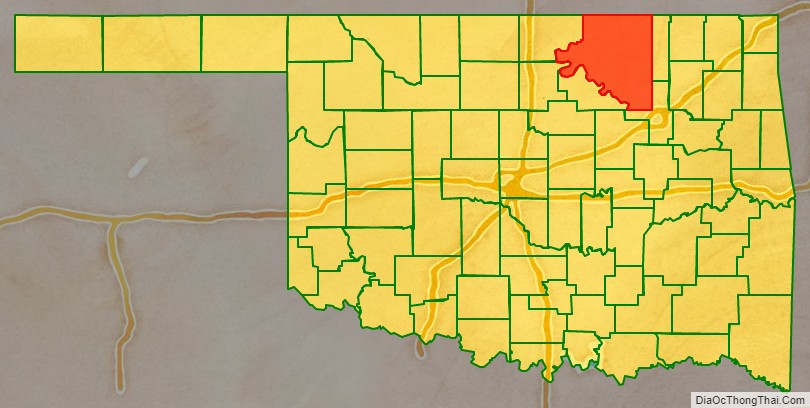
Osage County location map. Where is Osage County?
History
During the 17th century, the Osage and other Dhegihan Siouan tribes were displaced westward from the Ohio Country following the Beaver Wars. The Osage became established as a powerful nation in the areas of present-day Missouri and Arkansas between the Missouri and Red rivers, as well as extending to the west. By 1760, they had increased their range to include the present Osage County. Historically one of the most powerful Great Plains tribes, their numbers were reduced by infectious disease and warfare after encounter with Europeans.
In 1825, they ceded their claim to the land in present-day Oklahoma to the United States government, which included it in a “perpetual outlet to the west given to the Cherokee Nation by the Treaty of New Echota” in 1835. This treaty was to accomplish Cherokee removal to the Indian Territory. During the American Civil War, on December 26, 1861, a band of pro-Union Creek and Seminole fought with a Confederate Army unit at the Battle of Chustenahlah on Bird Creek, near the present town of Skiatook. Generally the Five Civilized Tribes were allied with the Confederacy.
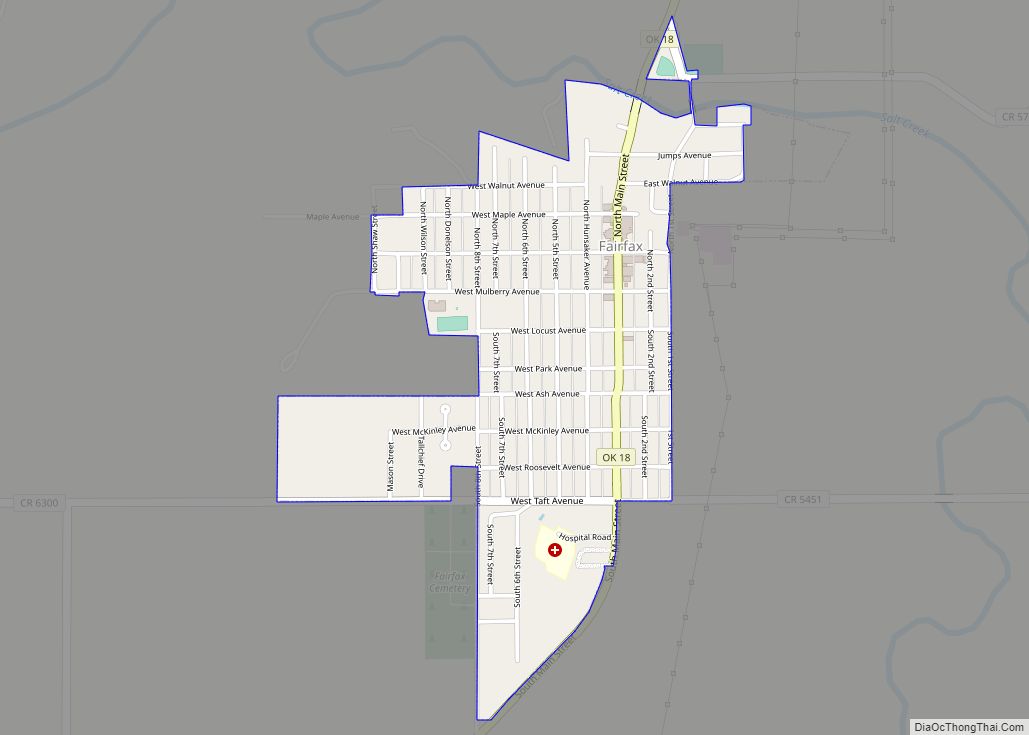
In 1870, the Osage finally prepared for removal from Kansas, after having negotiated payment for their land. They purchased 1.57 million acres (6,400 km) of their former territory in present-day Oklahoma from the Cherokee. By owning it by title, they had a stronger position in relation to the US government than did other tribes. The Osage Agency was established in 1872 at Deep Ford, later renamed as Pawhuska. It was designated as the county seat when Oklahoma was admitted as a state. The other chief settlements in the 1870s were Hominy and Fairfax; each of the three was settled by a major Osage band.
In 1875, the US designated their land as the Osage Reservation. Because the tribe owned the land directly, they retained more control over their affairs than did tribes whose land was held “in trust” by the United States government. This reservation became part of the Oklahoma Territory under the Oklahoma Organic Act of 1890. It became a semi-autonomous district by the Oklahoma Enabling Act of 1906, and Osage County at the time of Oklahoma Statehood in 1907. At that time, there were 2,229 registered Osage members.
As owners, the Osage negotiated the retention of the communal mineral rights to their reservation lands. In October 1897, the Phoenix Oil Company drilled the first successful oil well on the Osage reservation and in Oklahoma Territory. It was located along Butler Creek. In 1901, Phoenix Oil and Osage Oil companies combined their assets to form the Indian Territory Illuminating Oil Company (ITIO). It arranged with the Bureau of Indian Affairs to sub-lease the eastern part of the Osage reservation until 1916. When ITIO’s lease expired, the United States government supervised the public auctioning of leases for 160-acre (65 ha) tracts.
All subsurface minerals, including oil, are owned by the Osage Nation and held in trust for them by the Federal Government. Each mineral lease was negotiated by the Osage National Council and approved by the U.S. Secretary of the Interior. While the government forced allotment of lands and distribution of 160-acre (65 ha) plots to tribal members for farming in the early 20th century, the tribe continued to hold their “surplus” land after the distribution. Other tribes were forced to give up such “surplus” and allow for sales to non-Indians. The Osage distributed their surplus communal land to tribal members, so that in 1906 each Osage was given a total of 657 acres (266 ha), nearly four times the amount that other Indian households received in the allotment process. Later the enrolled Osage and their descendants received oil and other mineral royalties as payments based on these “headrights”.
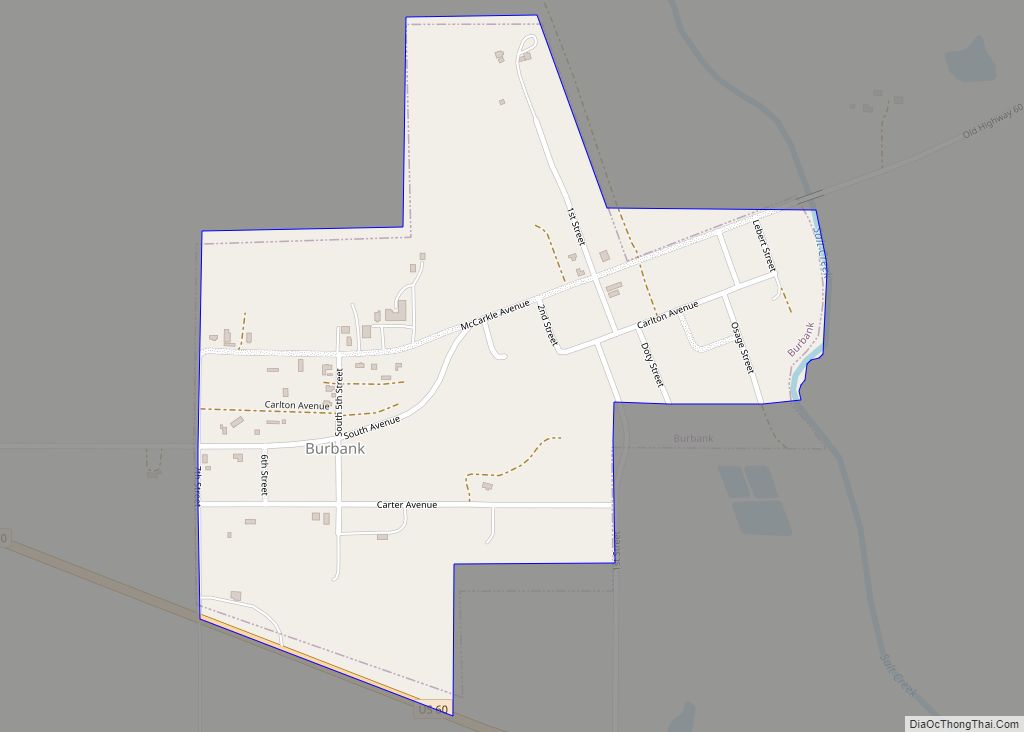
The Burbank Oil Field was discovered in May 1920 with the Marland Oil Company’s well 1 discovery. Peak production from the dome was in July 1923 at 88,950 barrels from 1020 wells, with total production of 200 million barrels by the end of 1938. Most production is from the Burbank Sand at a depth of 2700–3000 feet.
By 1920, the Osage were receiving lucrative revenues from royalties and were counted as the richest people in the country. During the 1920s, Osage County was the site of the infamous Osage Indian murders. Because of the great wealth being generated by oil, an estimated 60 tribal members were killed as whites tried to gain their headrights, royalties or land. The FBI believed that several white husbands of Osage women had committed or ordered murders of their wives. Other Osage were tricked out of their legal rights by unscrupulous white opportunists. Congress had passed a law in 1921 requiring all Osage of half or more Indian ancestry to have a guardian appointed by the court until the person proved to be “competent.” Guardians were appointed by the courts even for minors with living parents. There was extensive corruption as such guardians manipulated people to give or bequeath land to them in order to get access to oil rights.
The Osage called in the FBI to help solve several murders in the Kyle family. Three white men were ultimately convicted and sentenced. But, many murders were never solved. To try to protect the Osage, Congress passed a law in 1925 limiting the inheritance of headrights only to persons who were half or more Osage in ancestry.
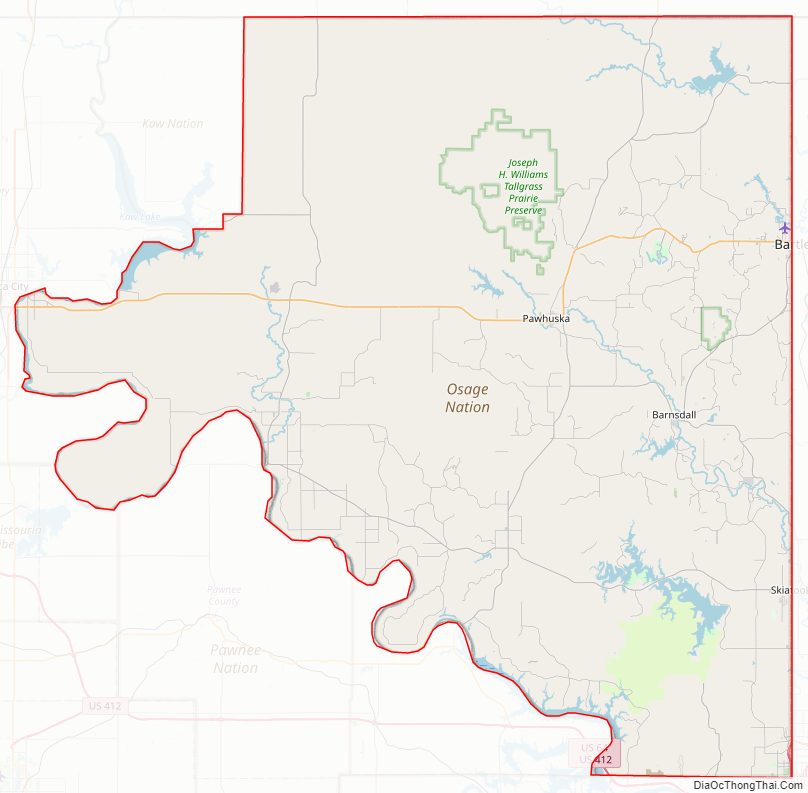
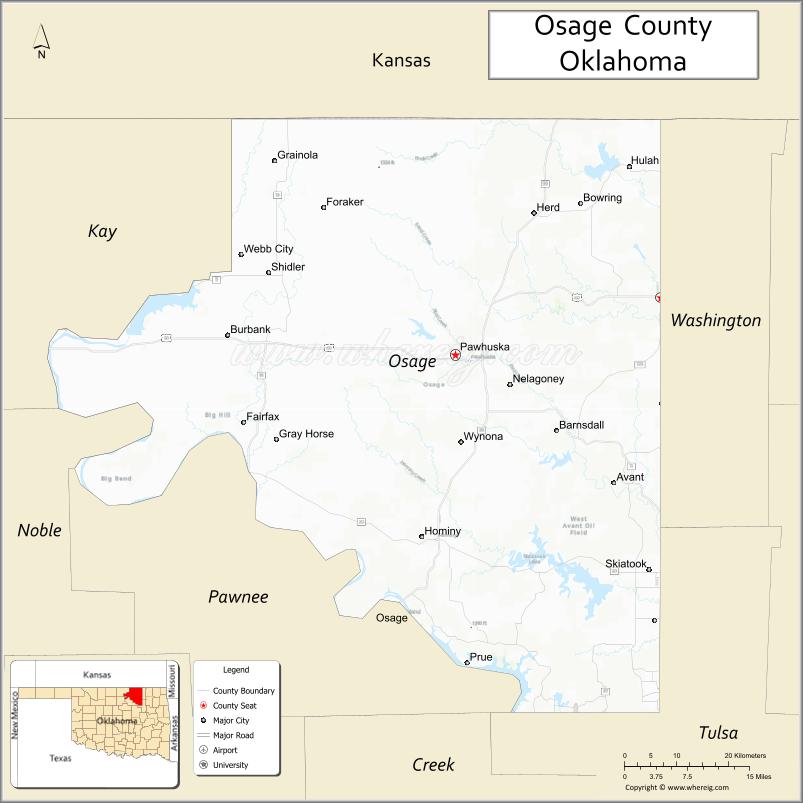
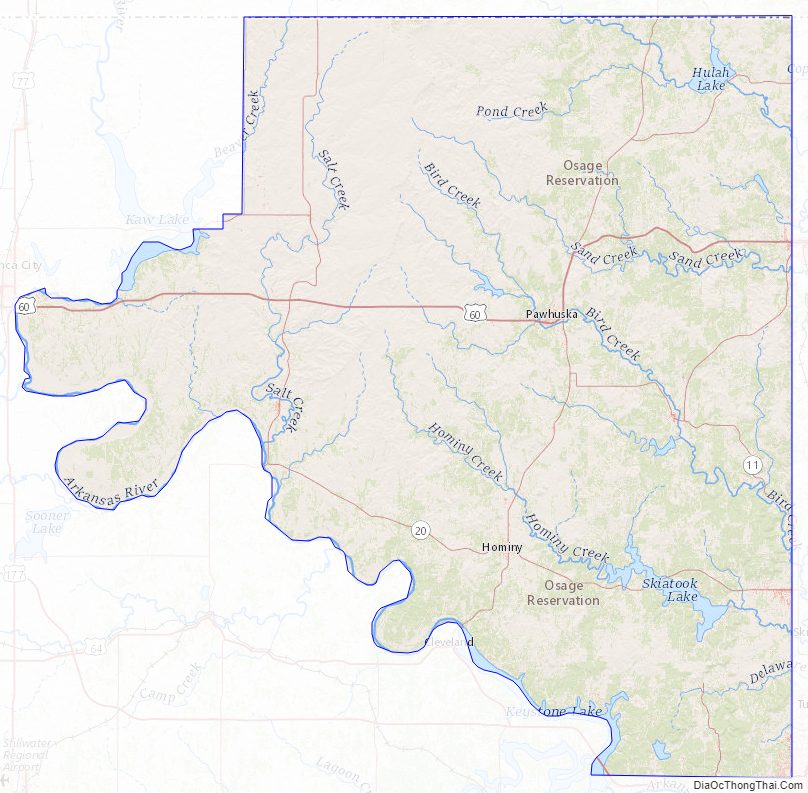
Osage County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 2,304 square miles (5,970 km), of which 2,246 square miles (5,820 km) is land and 58 square miles (150 km) (2.5%) is water. It is the largest county in Oklahoma by area. Most of the county is in the Osage Plains, and consists of open prairie. The eastern part of the county contains the Osage Hills, an extension of the Flint Hills in Kansas. Tallgrass Prairie Preserve is north of Pawhuska.
Holmes Peak is a mountain northwest of Tulsa in Osage County. It was named by the United States Board on Geographic Names on October 5, 1983, for the fictional detective, Sherlock Holmes. The name was proposed by Richard S. Warner. Holmes Peak is the highest point in the Tulsa Metropolitan area, with an elevation of 1,030 feet (310 m), though it ranks only as the 379th highest point in the state.
Gray Horse Creek, Drum Creek and Salt Creek all drain the southwestern part of the county and flow into the Arkansas River, which is part of the county’s southern and western boundaries. Eastern Osage County drains into Caney River, Bird Creek, Hominy Creek, and Delaware Creek. All of these streams flow into the Verdigris River.
Lakes and reservoirs in the county include:
- Birch Lake
- Bluestem Lake
- Hulah Lake (Oklahoma)
- Kaw Lake
- Keystone Lake
- Skiatook Lake
In 2012, the Osage Nation took over management of Wah-Sha-She State Park, which includes Hulah Lake, after state budget cuts would have closed it. Hunting is allowed there. The land is owned by the US Army Corps of Engineers, which developed the lake. In 2015, the Osage subleased the renamed Wah-Sha-She Park to the Hulah Lake Osage Association (HLOA), a non-profit group which took on the task of maintaining the park through volunteer efforts. As of 2020 HLOA still had the park open, supported by campground fees.
It is the most populous and the second-largest county geographically (after Corson County, South Dakota) of the six U.S. counties that lie entirely within an Indian reservation. (The six counties in descending order of area are Corson; Osage; Oglala Lakota and Todd in South Dakota; Sioux in North Dakota; and Mahnomen in Minnesota.) Three other counties, Thurston in Nebraska; and Dewey and Ziebach in South Dakota, lie entirely in parts of two separate Indian reservations. A total of nine US counties lie entirely within reservation territory. Dewey County is slightly larger in area than Osage.
Adjacent counties
- Cowley County, Kansas (northwest)
- Chautauqua County, Kansas (north)
- Washington County (east)
- Tulsa County (southeast)
- Pawnee County (southwest)
- Kay County (west)
- Noble County (west)