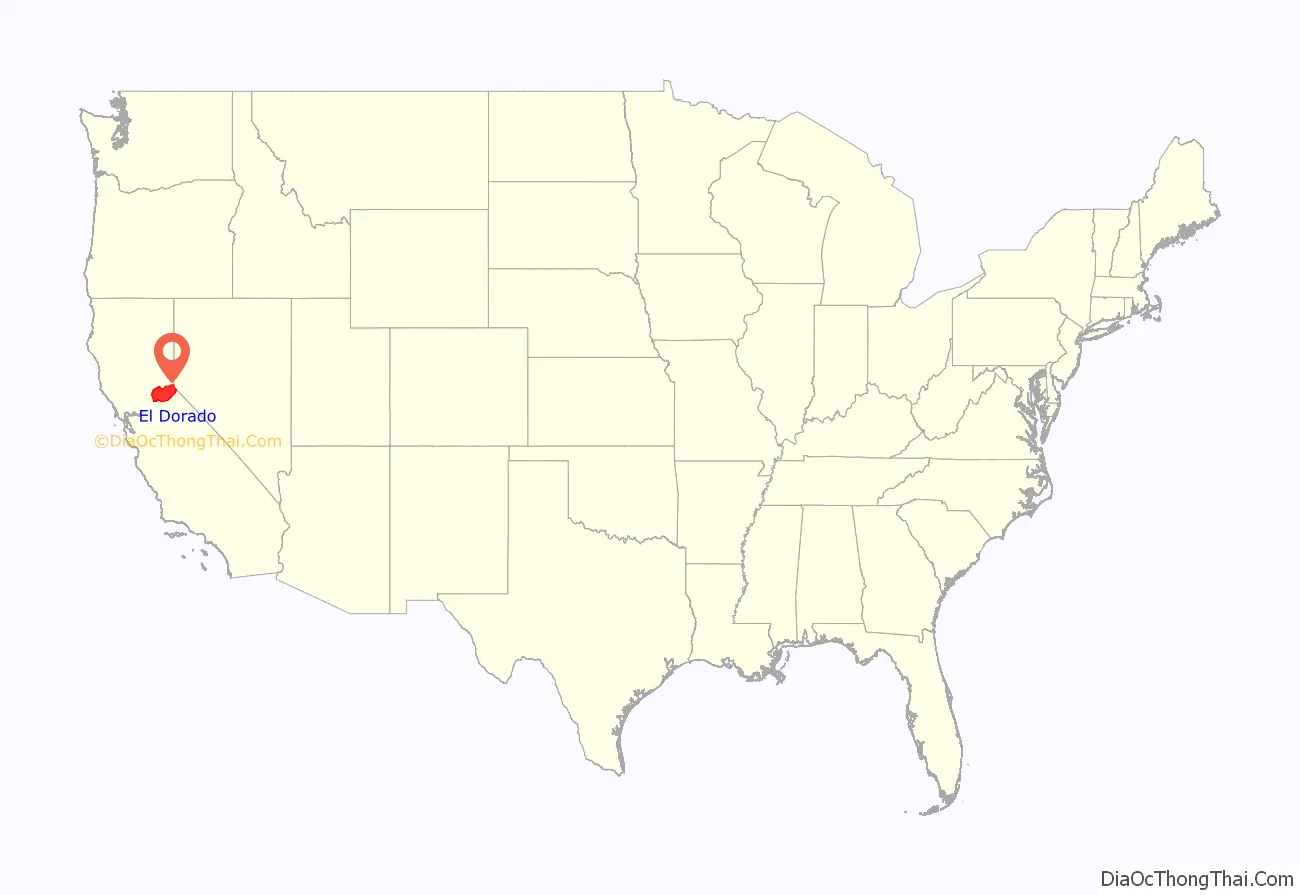
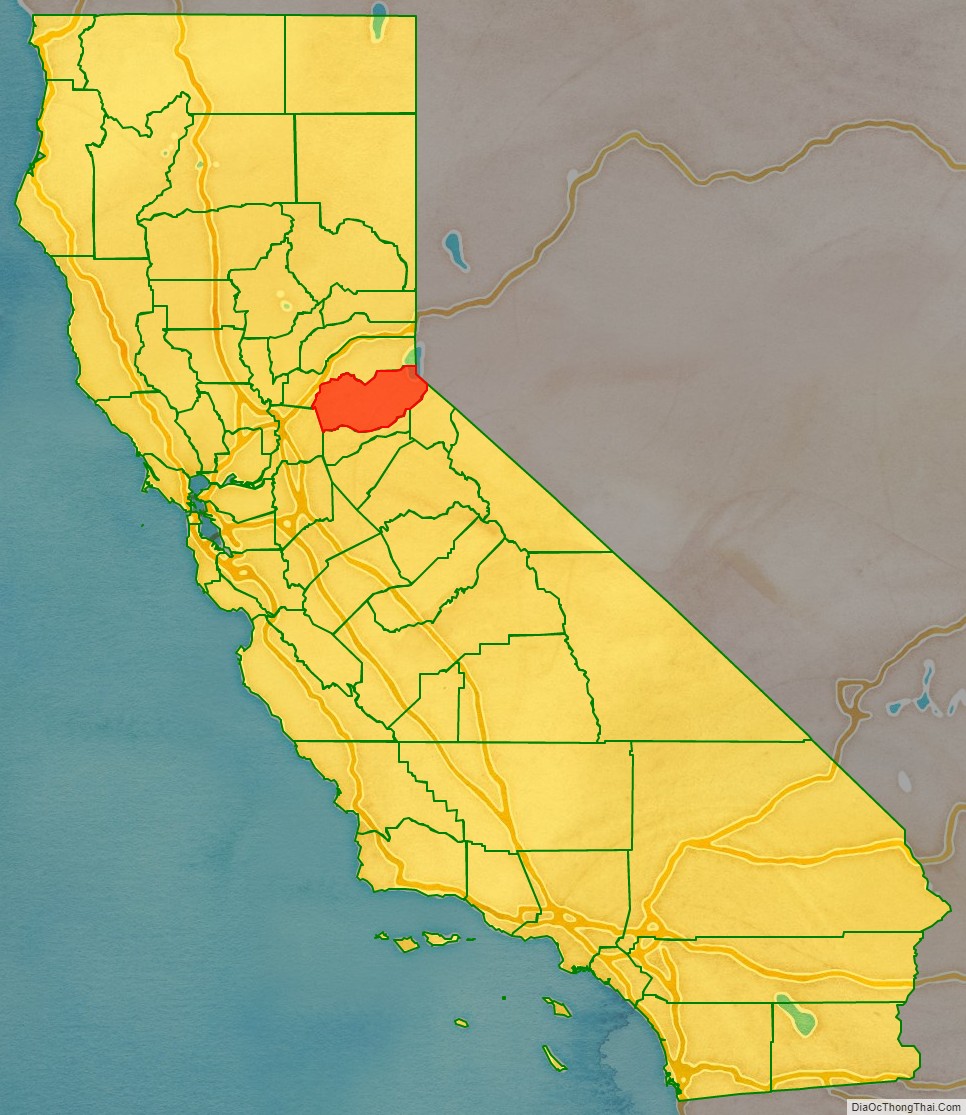
El Dorado County (/ˌɛl dəˈrɑːdoʊ/ (listen)), officially the County of El Dorado, is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 191,185. The county seat is Placerville. The County is part of the Sacramento–Roseville–Arden-Arcade, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area. It is located entirely in the Sierra Nevada, from the historic Gold Country in the western foothills to the High Sierra in the east. El Dorado County’s population has grown as Greater Sacramento has expanded into the region. Where the county line crosses US 50 at Clarksville, the distance to Sacramento is 15 miles. In the county’s high altitude eastern end at Lake Tahoe, environmental awareness and environmental protection initiatives have grown along with the population since the 1960 Winter Olympics, hosted at the former Squaw Valley Ski Resort in neighboring Placer County.
| Name: | El Dorado County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 06-017 |
| State: | California |
| Founded: | 1850 |
| Named for: | Spanish for “the golden” and El Dorado |
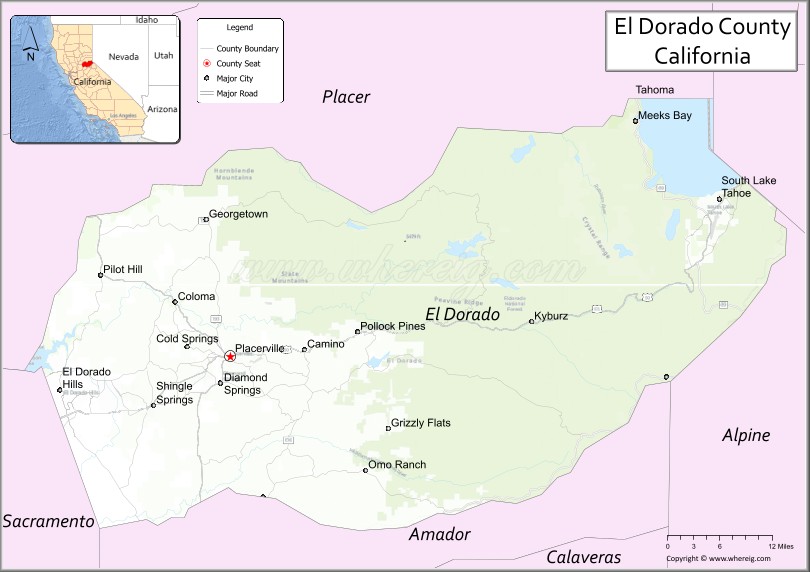
| Seat: | Placerville |
| Total Area: | 1,786 sq mi (4,630 km²) |
| Land Area: | 1,708 sq mi (4,420 km²) |
| Total Population: | 191,185 |
| Population Density: | 110/sq mi (41/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−8 (Pacific Time Zone) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) |
| Website: | www.edcgov.us |
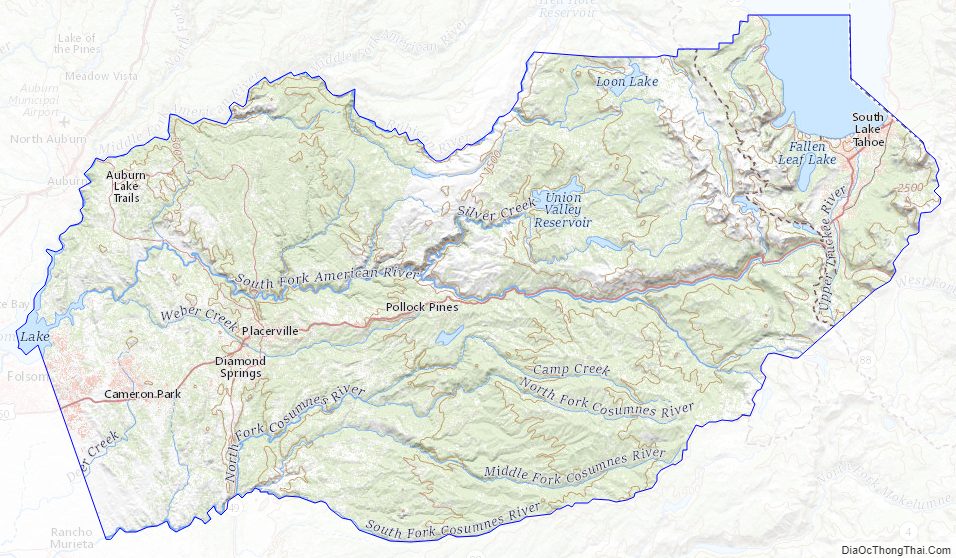
El Dorado County location map. Where is El Dorado County?
History
What is now known as El Dorado County has been home to the Maidu, Nisenan, Washoe, and Miwok Indigenous American nations for centuries. Because of colonization, their numbers dropped severely. Today many indigenous people in El Dorado County, like the Nissenan are telling their stories and culture, praying in their languages sharing their history; Once seen as struggling to survive to now on their way to having once broken treaties re-recognized and honored. Indigenous stories did not begin at the gold rush, and they will continue long after. According to a California census, by 1870, there were only 100 indigenous people left in El Dorado County due to violent California laws that paid white settlers a small fee for the scalps of Indigenous children and adults in an attempt to strategically wipe out the existing communities. Along with intentional genocide, excessive resource degradation such as logging, trapping bears and other animals for fur, water and soil contamination from mining played a part in the attempt to “starve out” indigenous communities. A settler looking to start a company processing cut trees found gold on the land he started using. The region became famous for being the site of the 1848 gold discovery that sparked the California Gold Rush. The County of El Dorado was one of California’s original 27 counties created effective February 18, 1850 (the number has risen to 58 today). Its name is derived from the Spanish meaning “the gilded/golden”.
The final segments of the Pony Express mail route ran through El Dorado County until its replacement with the telegraph service in 1861; U.S. Highway 50 follows the Pony Express route today.
- Mother lode
- James W. Marshall
- California Mining and Mineral Museum
- Marshall Gold Discovery State Historic Park
- Confidence Hall
- Fountain-Tallman Soda Works
- John Pearson Soda Works
- Combellack-Blair House
- Rubicon Point Light
The Placerville Mountain Democrat, California’s oldest surviving newspaper, serves El Dorado County.
The Caldor Fire started on August 14, 2021, near Little Mountain, south of Pollock Pines in El Dorado County, about two miles East of Omo Ranch and four miles south of Grizzly Flats. It initially burned slowly, but exploded in size on August 16 due to high winds. By the night of August 16 it was 6,500 acres (2,600 ha). On August 17 the fire grew to 30,000 acres (12,000 ha) as it expanded rapidly north and east, crossing the North Fork Cosumnes River and approaching Sly Park Reservoir. By August 20 the fire had burned nearly to Highway 50, forcing a closure of the highway. Over the next few days, the fire crossed Highway 50 in the vicinity of Kyburz. Starting on August 27 winds drove the fire rapidly east towards the Lake Tahoe Basin. By August 30, it had reached Echo Summit, less than 5 miles (8.0 km) from South Lake Tahoe.
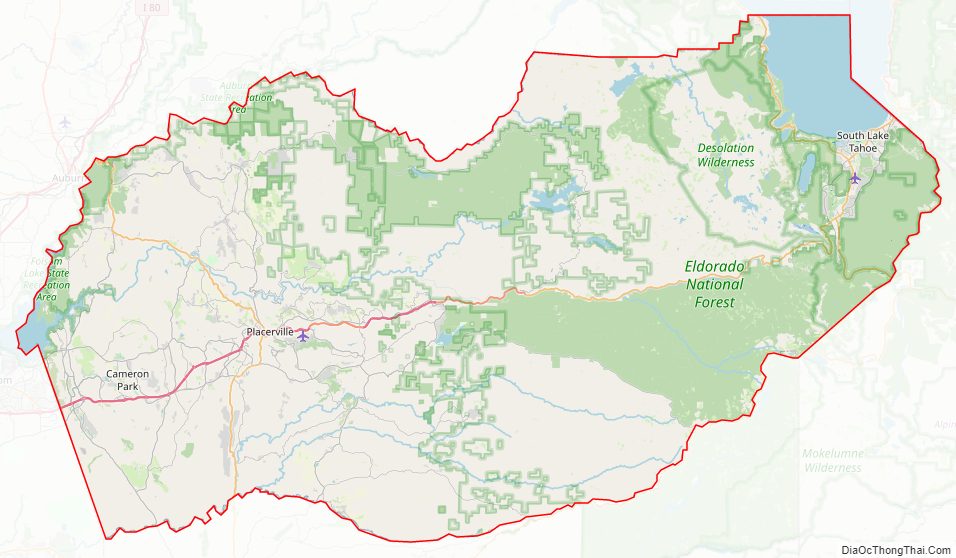
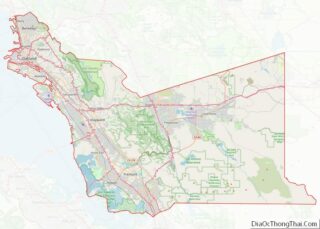
El Dorado County Road Map
Geography
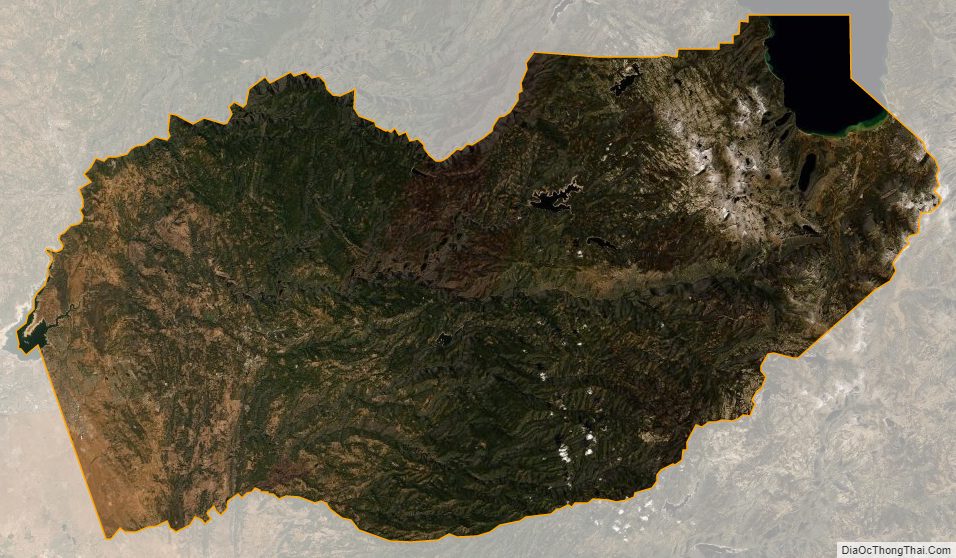
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,786 square miles (4,630 km), of which 1,708 square miles (4,420 km) is land and 78 square miles (200 km) (4.4%) is water.
The county, owing to its location in the Sierra Nevada, consists of rolling hills and mountainous terrain. The northeast corner is in the Lake Tahoe Basin (part of the Great Basin), including a portion of the lake itself. Across the Sierra crest to the west lies the majority of the county, referred to as the “western slope.” A portion of Folsom Lake is in the northwest corner of the county.
Much of the county is public land. The Eldorado National Forest comprises a significant portion (approximately 43%) of the county’s land area, primarily on the western slope. The Lake Tahoe Basin Management Unit, formerly part of the Eldorado and two other National Forests, manages much of the land east of the crest. The Pacific Crest Trail runs through the eastern part of the county, along or roughly paralleling the Sierra crest. The county is home to the Desolation Wilderness, a popular destination for hiking, backpacking, and fishing.
Adjacent counties
- Placer County – north
- Douglas County, Nevada – northeast
- Alpine County – southeast
- Amador County – south
- Sacramento County – southwest
Geographic features
- American River
- Carson Range
- Crystal Range
- Echo Lake
- Fallen Leaf Lake
- Folsom Lake
- Francis Lake
- Freel Peak as its highest point at 10,886 feet (3,318 m)
- Gilmore Lake
- Green Springs Ranch
- Lake Tahoe
- Loon Lake
- Lost Lake
- Mount Price
- Mount Tallac
- Pyramid Lake
- Sierra Nevada
- Silver Peak
- Talking Mountain
- Union Valley Reservoir
- Waca Lake