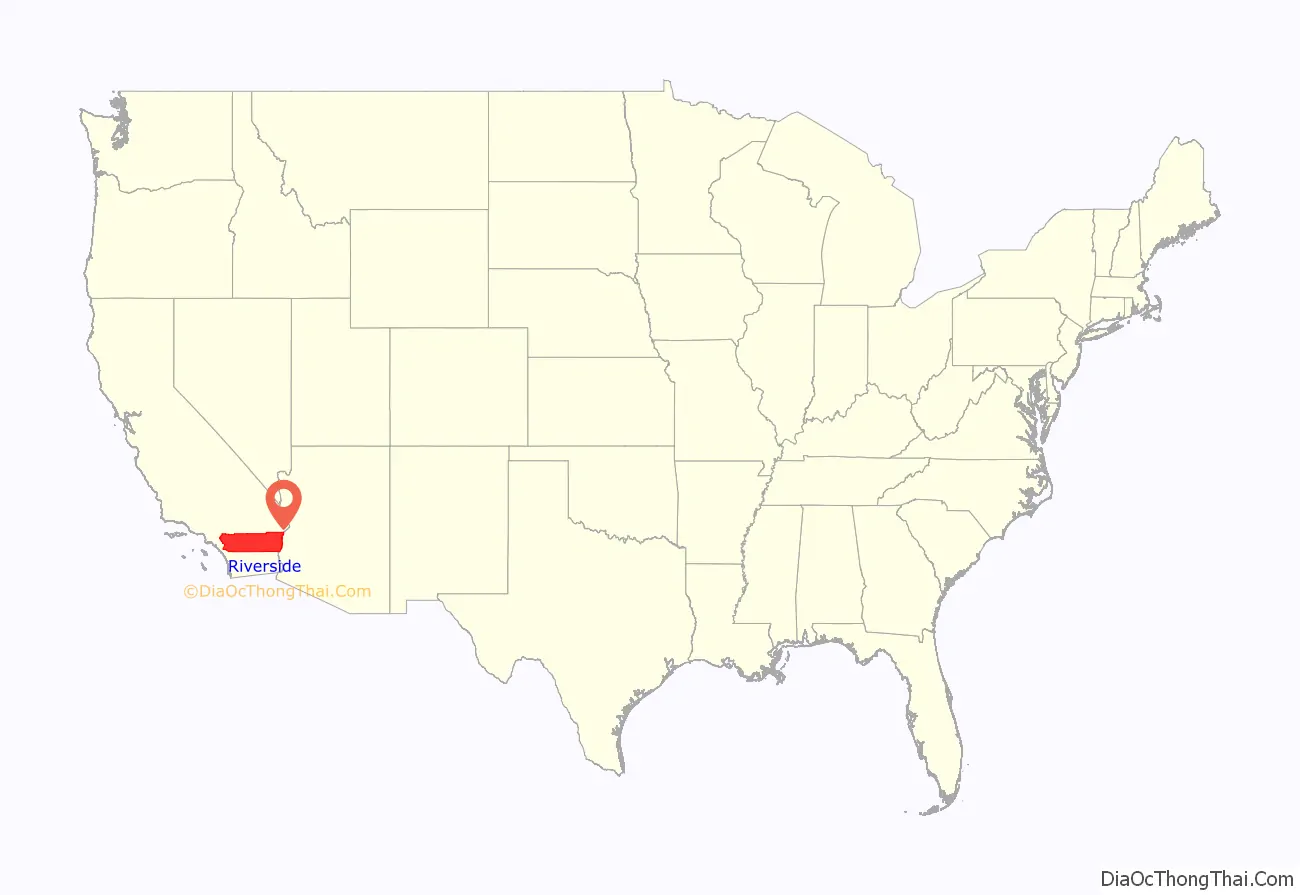
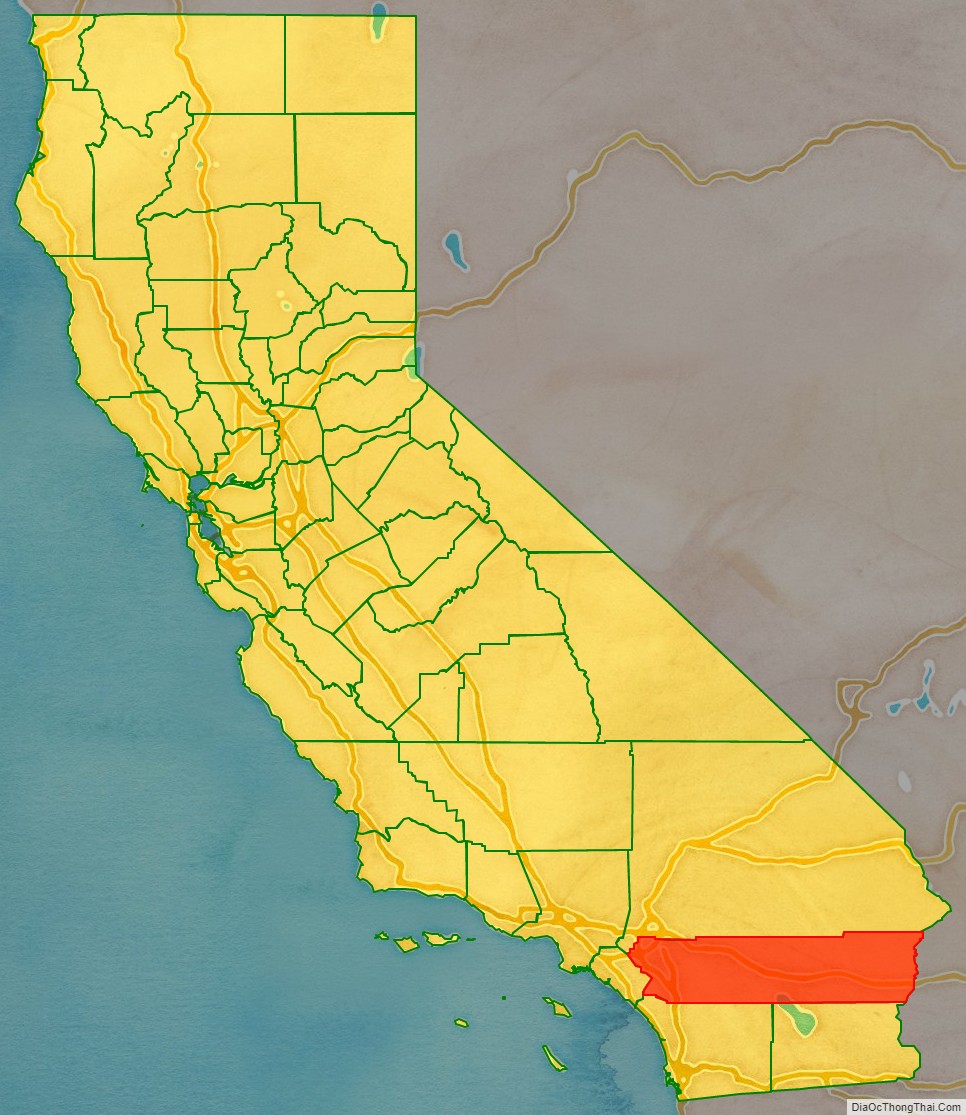
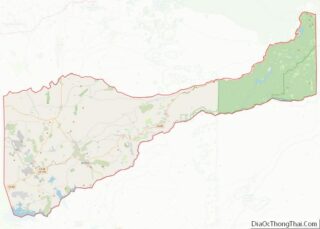
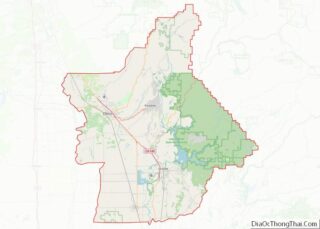
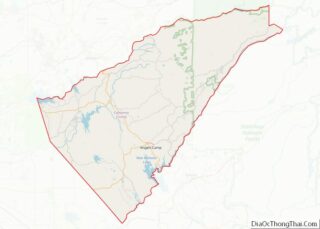
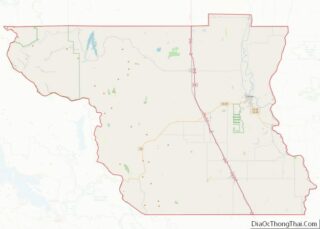
Riverside County is a county located in the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,418,185, making it the fourth-most populous county in California and the 10th-most populous in the United States. The name was derived from the city of Riverside, which is the county seat.
Riverside County is included in the Riverside-San Bernardino–Ontario Metropolitan Statistical Area, also known as the Inland Empire. The county is also included in the Los Angeles–Long Beach Combined Statistical Area.
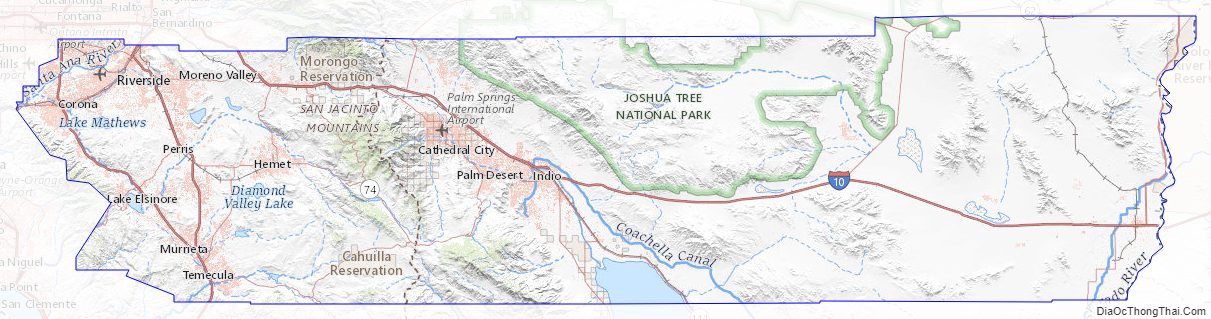
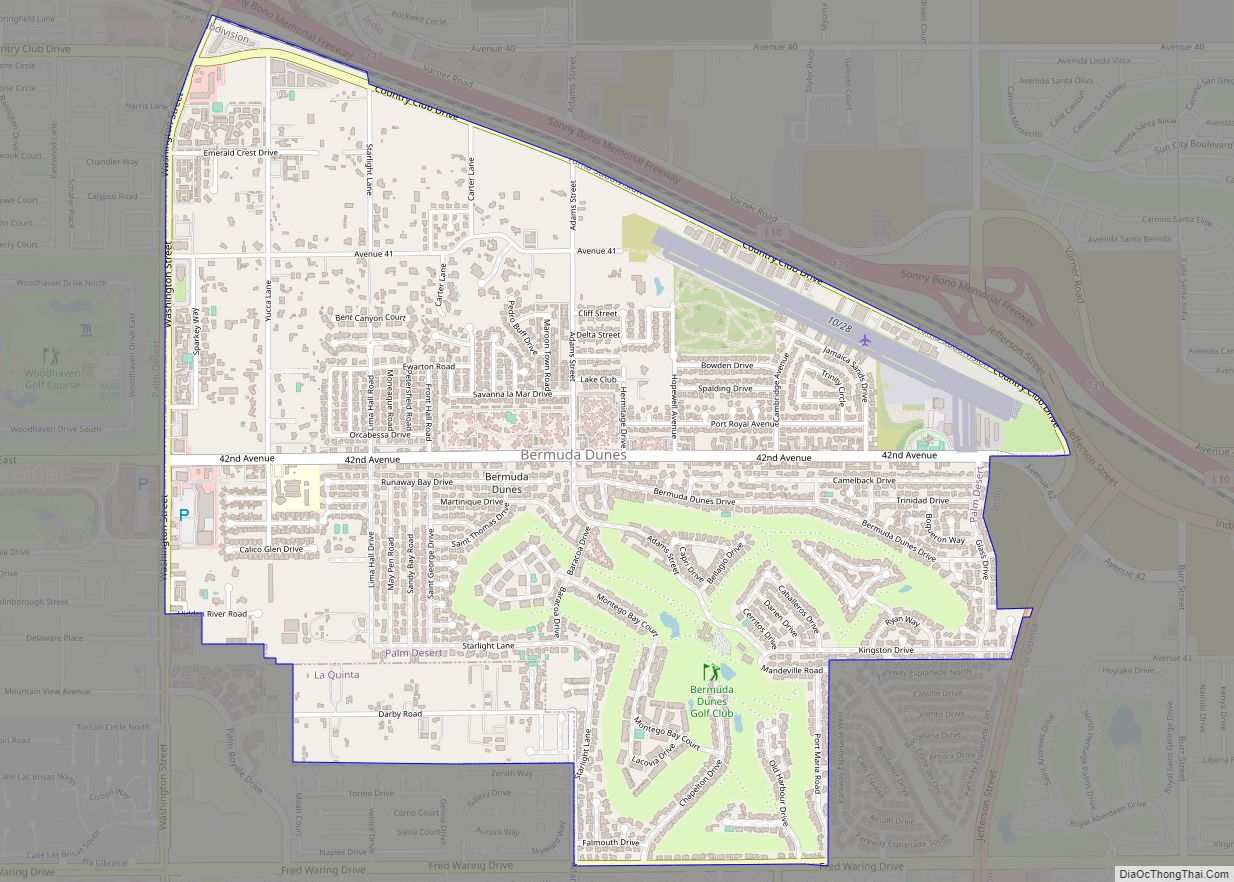
Roughly rectangular, Riverside County covers 7,208 square miles (18,670 km) in Southern California, spanning from the greater Los Angeles area to the Arizona border. Geographically, the county is mostly desert in the central and eastern portions, but has a Mediterranean climate in the western portion. Most of Joshua Tree National Park is located in the county. The resort cities of Palm Springs, Palm Desert, Indian Wells, La Quinta, Rancho Mirage, and Desert Hot Springs are all located in the Coachella Valley region of central Riverside County.
Between 2007 and 2011, large numbers of Los Angeles-area workers moved to the county to take advantage of more affordable housing. Along with neighboring San Bernardino County, it was one of the fastest-growing regions in the state prior to the recent changes in the regional economy. In addition, smaller, but significant, numbers of people have been moving into southwest Riverside County from the San Diego metropolitan area. The cities of Temecula and Murrieta accounted for 20% of the increase in population of the county between 2000 and 2007.
| Name: | Riverside County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 06-065 |
| State: | California |
| Founded: | 1893 |
| Named for: | The City of Riverside, and the city’s location beside the Santa Ana River |
| Seat: | Riverside |
| Largest city: | Riverside |
| Total Area: | 7,303 sq mi (18,910 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7,206 sq mi (18,660 km²) |
| Total Population: | 2,418,185 |
| Population Density: | 336/sq mi (130/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−8 (Pacific Time Zone) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) |
| Website: | www.CountyOfRiverside.us |
Riverside County location map. Where is Riverside County?
History
Indigenous
The Indigenous peoples of the valleys, mountains and deserts of what is now Riverside County are the Serrano, the Payómkawichum, the Mohave, the Cupeno, the Chemehuevi, the Cahuilla, and the Tongva. The Aguanga and Temecula Basins, Elsinore Trough and eastern Santa Ana Mountains are the traditional homelands of the Payómkawichum. The inland valleys in the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains and the desert of the Salton Sink are the traditional homelands of the Cahuilla.
Spanish era
The first European settlement in the county was a Mission San Luis Rey de Francia estancia or farm at the Luiseño village of Temescal. In 1819, the Mission granted Leandro Serrano permission to occupy the land for the purpose of grazing and farming, and Serrano established Rancho Temescal. Serrano was mayordomo of San Antonio de Pala Asistencia for the Mission of San Luis Rey.
Mexican era
With the signing of the Treaty of Cordoba in 1821, Mexico gained its independence from Spain, but the San Gabriel Mission near what is now Los Angeles, California, continued to expand, and established Rancho San Gorgonio in 1824. The ranch was to be one of the Mission’s principle rancherias, and the most distant, and it occupied most of today’s San Gorgonio Pass area.
Following the Mexican secularization act of 1833 by the First Mexican Republic, a series of rancho land grants were made throughout the state. In the Riverside County this included; Rancho Jurupa in 1838, El Rincon in 1839, Rancho San Jacinto Viejo in 1842, Rancho San Jacinto y San Gorgonio in 1843, Ranchos La Laguna, Pauba, Temecula in 1844, Ranchos Little Temecula, Potreros de San Juan Capistrano in 1845, Ranchos San Jacinto Sobrante, La Sierra (Sepulveda), La Sierra (Yorba), Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Nuevo y Potrero in 1846.
New Mexican colonists founded the town of La Placita on the east side of the Santa Ana River at the northern extremity of what is now the city of Riverside in 1843.
American era
When the initial 27 California counties were established in 1850, the area today known as Riverside County was divided between Los Angeles County and San Diego County. In 1853, the eastern part of Los Angeles County was used to create San Bernardino County. Between 1891 and 1893, several proposals and legislative attempts were put forth to form new counties in Southern California. These proposals included one for a Pomona County and one for a San Jacinto County. None of the proposals were adopted until a measure to create Riverside County was signed by Governor Henry H. Markham on March 11, 1893.
The new county was created from parts of San Bernardino County and San Diego County. On May 2, 1893, seventy percent of voters approved the formation of Riverside County. Voters chose the city of Riverside as the county seat, also by a large margin. Riverside County was officially formed on May 9, 1893, when the Board of Commissioners filed the final canvass of the votes.
The county is also the location of the March Air Reserve Base, one of the oldest airfields continuously operated by the United States military. Established as the Alessandro Flying Training Field in February 1918, it was one of thirty-two U.S. Army Air Service training camps established after the United States entry into World War I in April 1917. The airfield was renamed March Field the following month for 2d Lieutenant Peyton C. March, Jr., the recently deceased son of the then-Army Chief of Staff, General Peyton C. March, who was killed in an air crash in Texas just fifteen days after being commissioned. March Field remained an active Army Air Service, then U.S. Army Air Corps installation throughout the interwar period, later becoming a major installation of the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II. Renamed March Air Force Base in 1947 following the establishment of the U.S. Air Force, it was a major Strategic Air Command (SAC) installation throughout the Cold War. In 1996, it was transferred to the Air Force Reserve Command and gained its current name as a major base for the Air Force Reserve and the California Air National Guard.
Riverside county was a major focal point of the Civil Rights Movements in the US, especially the African-American sections of Riverside and heavily Mexican-American communities of the Coachella Valley visited by Cesar Chavez of the farm labor union struggle.
Riverside county has also been a focus of modern Native American Gaming enterprises. In the early 1980s, the county government attempted to shut down small bingo halls operated by the Morongo Band of Cahuilla Mission Indians and the Cabazon Band of Mission Indians. The tribes joined forces and fought the county all the way to the U.S. Supreme Court, which ruled in the tribes’ favor on February 25, 1987. In turn, Congress enacted the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act in 1988 to establish a legal framework for the relationship between Indian gaming and state governments. Naturally, both tribes now operate large casinos in the county: the Morongo Casino, Resort & Spa and the Fantasy Springs Resort Casino adjacent to Spotlight 29 Casino.
The county’s population surpassed one million people in 1990 (year-round, would be 1980 with seasonal residents) when the current trend of high population growth as a major real estate destination began in the 1970s. Once strictly a place for long-distance commuters to L.A. and later Orange County, the county and city of Riverside started becoming more of a place to establish new or relocated offices, corporations and finance centers in the late 1990s and 2000s. More light industry, manufacturing and truck distribution centers became major regional employers in the county.
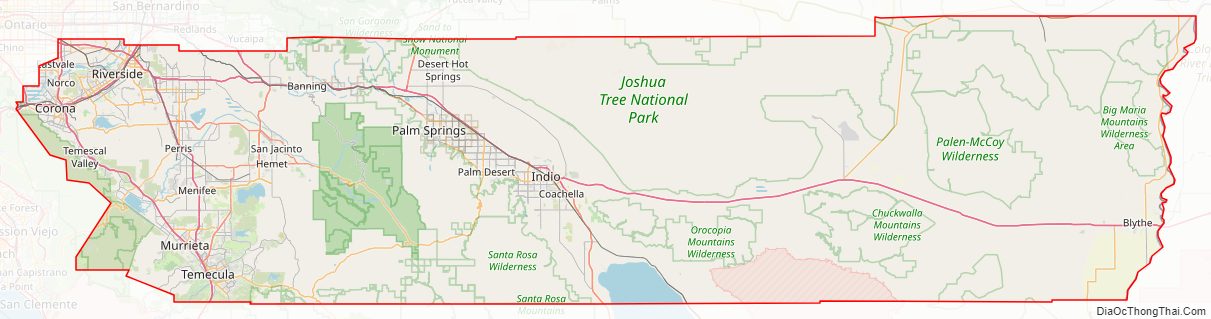
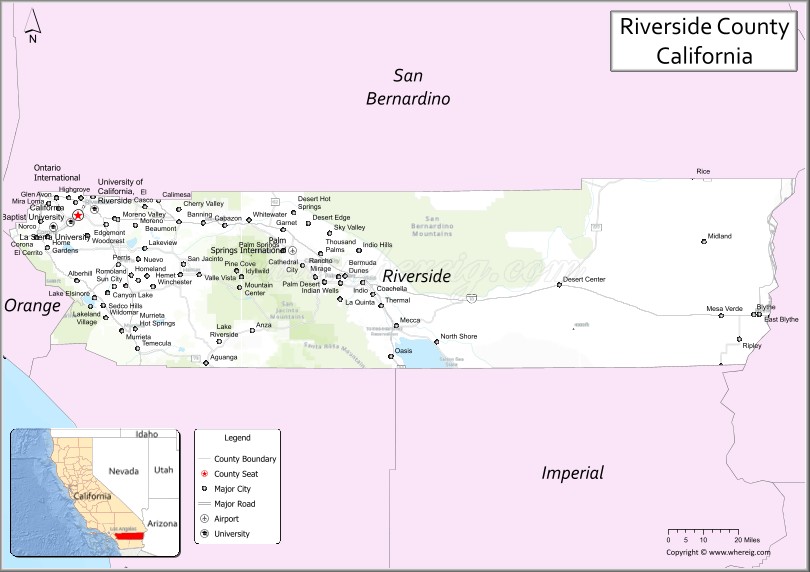
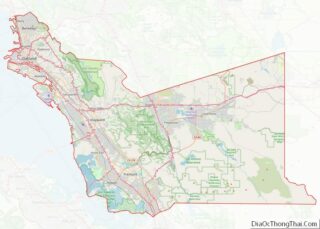
Riverside County Road Map
Geography
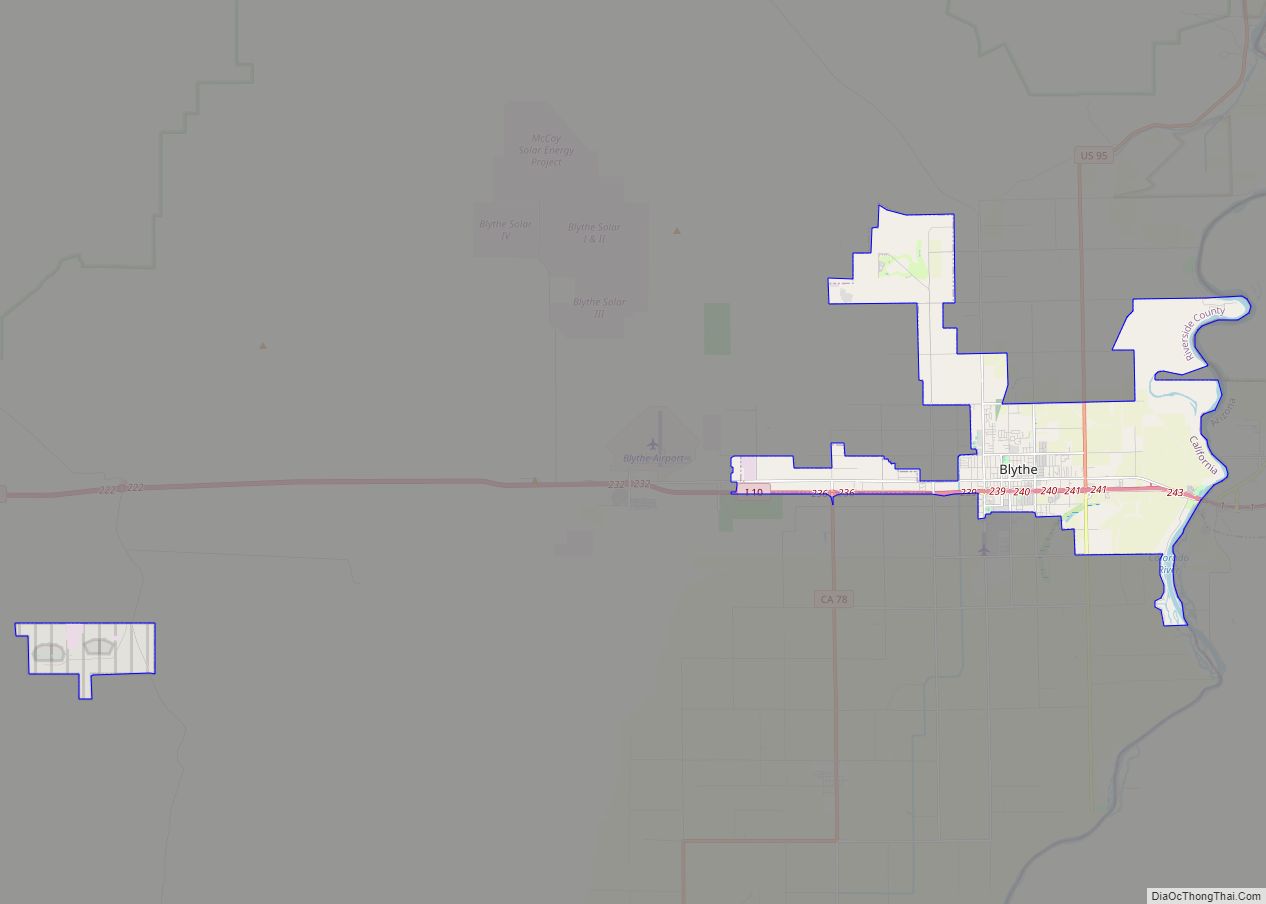
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 7,303 square miles (18,910 km), of which 7,206 square miles (18,660 km) is land and 97 square miles (250 km) (1.3%) is water. It is the fourth-largest county in California by area. At roughly 180 miles (290 km) wide in the east–west dimension, the area of the county is massive. Riverside County, California is roughly the size of the State of New Jersey in total area. County government documents frequently cite the Colorado River town of Blythe as being a “three-hour drive” from the county seat, Riverside. Some view the areas west of San Gorgonio Pass as the Inland Empire portion of the county and the eastern part as either the Mojave Desert or Colorado Desert portion. There are probably at least three geomorphic provinces: the Inland Empire western portion, the Santa Rosa Mountains communities such as Reinhardt Canyon, and the desert region. Other possible subdivisions include tribal lands, the Colorado River communities, and the Salton Sea.
Flora and fauna
There is a diversity of flora and fauna within Riverside County. Vegetative plant associations feature many desert flora, but there are also forested areas within the county. The California endemic Blue oak, Quercus douglasii is at the southernmost part of its range in Riverside County.
National protected areas
- Cleveland National Forest (part)
- Coachella Valley National Wildlife Refuge
- Dos Palmas Preserve
- Joshua Tree National Park (part)
- San Bernardino National Forest (part)
- Sand to Snow National Monument (part)
- Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument
There are 19 official wilderness areas in Riverside County that are part of the National Wilderness Preservation System. Some are integral parts of the above protected areas, most (11 of the 19) are managed solely by the Bureau of Land Management, and some share management between the BLM and the relevant other agencies. Some extend into neighboring counties:
- Agua Tibia Wilderness (part)
- Beauty Mountain Wilderness
- Big Maria Mountains Wilderness
- Cahuilla Mountain Wilderness
- Chuckwalla Mountains Wilderness
- Joshua Tree Wilderness (part)
- Little Chuckwalla Mountains Wilderness (part)
- Mecca Hills Wilderness
- Orocopia Mountains Wilderness
- Palen/McCoy Wilderness
- Palo Verde Mountains Wilderness (part)
- Pinto Mountains Wilderness
- Rice Valley Wilderness
- Riverside Mountains Wilderness
- San Gorgonio Wilderness (part)
- San Jacinto Wilderness
- San Mateo Canyon Wilderness (part)
- Santa Rosa Wilderness
- South Fork San Jacinto Wilderness
State parks
- California Citrus State Historic Park
- Lake Perris State Recreation Area
- Mount San Jacinto State Park
County parks and trails
- Hurkey Creek Park
- Idyllwild Park
- Indio Hills Palms
- Jensen Alvarado Ranch
- Lake Cahuilla Recreation Area
- Lake Skinner Recreation Area
- McCall Memorial Equestrian Park
- Santa Rosa Plateau