Waipahu (Hawaiian pronunciation: [vɐjˈpɐhu]) is a former sugarcane plantation town and now census-designated place (CDP) located in the ʻEwa District on the island of Oʻahu in the City & County of Honolulu, Hawaiʻi, United States. As of the 2020 census, the CDP population was 43,485. The U.S. postal code for Waipahu is 96797.
| Name: | Waipahu CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Hawaii |
| County: | Honolulu County |
| Elevation: | 62 ft (19 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.80 sq mi (7.25 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.68 sq mi (6.94 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.12 sq mi (0.31 km²) |
| Total Population: | 43,485 |
| Population Density: | 16,237.86/sq mi (6,269.45/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 96797 |
| Area code: | 808 |
| FIPS code: | 1579700 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0364878 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Waipahu location map. Where is Waipahu CDP?
History
Waipahu is the name of an artesian spring. In Hawaiian, Waipahu is derived from wai, meaning water, and pahū, meaning “burst or explode”; combined, Waipahu means “water forced up (as out of a spring)”. The early Native Hawaiians took pleasure in the cool and clear water gushing from the ground and named this spring Waipahu. Before the Western civilization set foot in Hawaii, the Hawaiians considered Waipahu to be the capital of Oahu. Royalty in the Kingdom of Hawaii would often gather and enjoy the fresh water from the spring Waipahu.
In 1897, Oahu Sugar Company was incorporated, and its board of directors located the sugar mill in Waipahu. It had 943 field workers. There were 44 Hawaiians, including 10 minors; 57 Portuguese; 443 Japanese, 408 of them contract laborers; and 399 Chinese, 374 of whom were contract laborers. The company’s managers from 1897 to 1940 were August Ahrens (1897–1904), E.K. Bull (1904–1919), J.B. Thomson (1919–1923), E.W. Greene (1923–1937), and Hans L’Orange (1937–1956).
In the early days of the plantation, each worker was assigned a number inscribed on a metal disc about the size of a silver dollar. The numbers 1 through 899 identified Japanese alien; 900 through 1400 were Japanese who were American citizens or Hawaii-born. The 2000 and 2100 series were Portuguese laborers, 2200 Spanish, 2300 Hawaiian, 2400 Puerto Rican, 3000 Chinese or Korean, 4000 and 5000 Filipino. The company imported laborers from many different countries including the Philippines, Japan, China, Portugal, and Norway. Very few laborers working for the Oahu Sugar Co. were Hawaiian. The majority of the company’s first laborers were either Japanese or Chinese. Each ethnic group was broken up into different camps. This division was said to have been the result of different cultures and language barriers.
Plantation workers lived by what was called The Plantation System. Field workers received an average monthly salary of $12.50. However, Filipino immigrants were paid less than all of the other laborers because they were the cheapest to import. The Filipinos, on average, made less than $10.00 a month. The Chinese generally were paid the most with a monthly average of $15.00.
In 1932 the Oahu Sugar Co. opened a continuation school, and allowed a half-day off from work once a week for workers to attend. Those who weren’t available during the day could also attend evening courses. This was to give them a chance to better their knowledge for a better job.
During the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) planes fired at the sugar mill in Waipahu, killing a civilian and injuring seven others.
Amfac acquired the company in 1961. Oahu Sugar Company shut down plantation operations after the 1995 harvest.
In 1923, the Oahu Sugar Company field also served as the community center which featured band concerts, sporting events, and carnivals. Later, the athletic field was renamed Hans L’Orange Field. Today, the park is primarily used for baseball, and is the home field of Hawaii Pacific University’s men’s baseball team, the Sea Warriors. It was the home field of the Hawaii Winter Baseball teams the North Shore Honu and West Oahu CaneFires until 2008.
In 1973, the City and County of Honolulu and the State of Hawai’i purchased 40 acres (160,000 m) opposite the Waipahu sugar mill to establish the Waipahu Cultural and Garden Park. The park is known today as the Hawai’i Plantation Village. Hawai’i Plantation Village is a living history museum located in Waipahu.
In 1997, the Governor of Hawaii, Benjamin J. Cayetano, proclaimed the months of June 1997 through November 1997 to be Waipahu Centennial Celebration Months. Many activities and events were held to celebrate the Waipahu Centennial.
Waipahu is the home to the 2008 Little League World Series champions from Waipi’o Little League. They defeated Matamoros, Mexico 12–3 in the final game on August 24, 2008. On August 28, 2010, that same team won the U.S. championship of the Little League World Series, defeating the team from Pearland, Texas, but lost to Edogawa Minami LL of Tokyo on August 29, 2010, in the international championship.
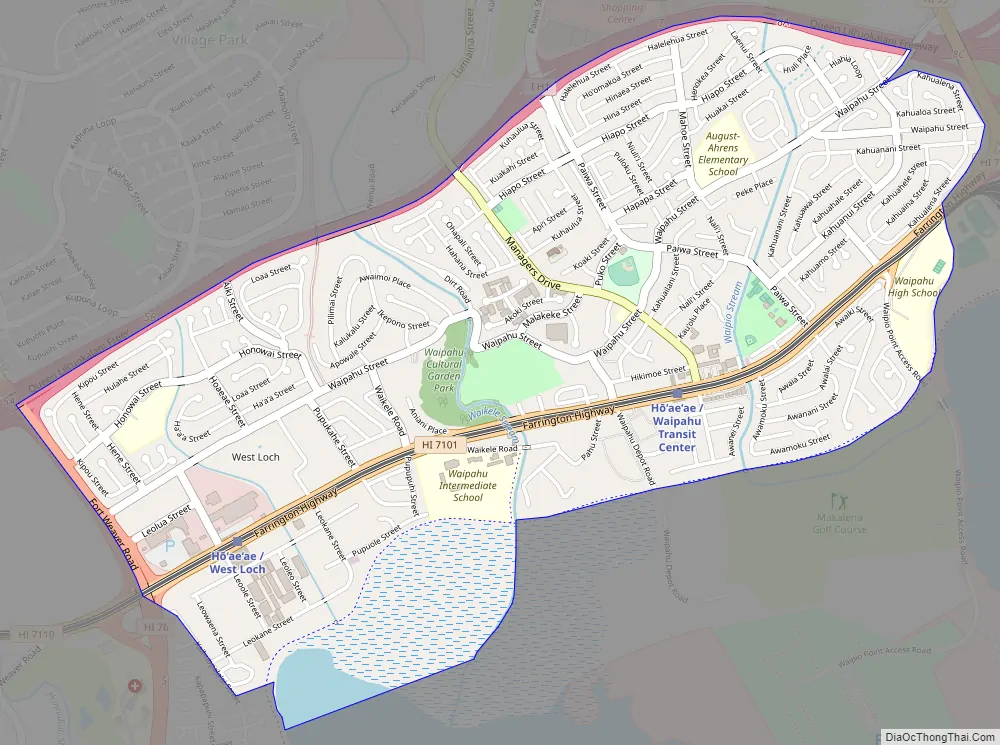
Waipahu Road Map
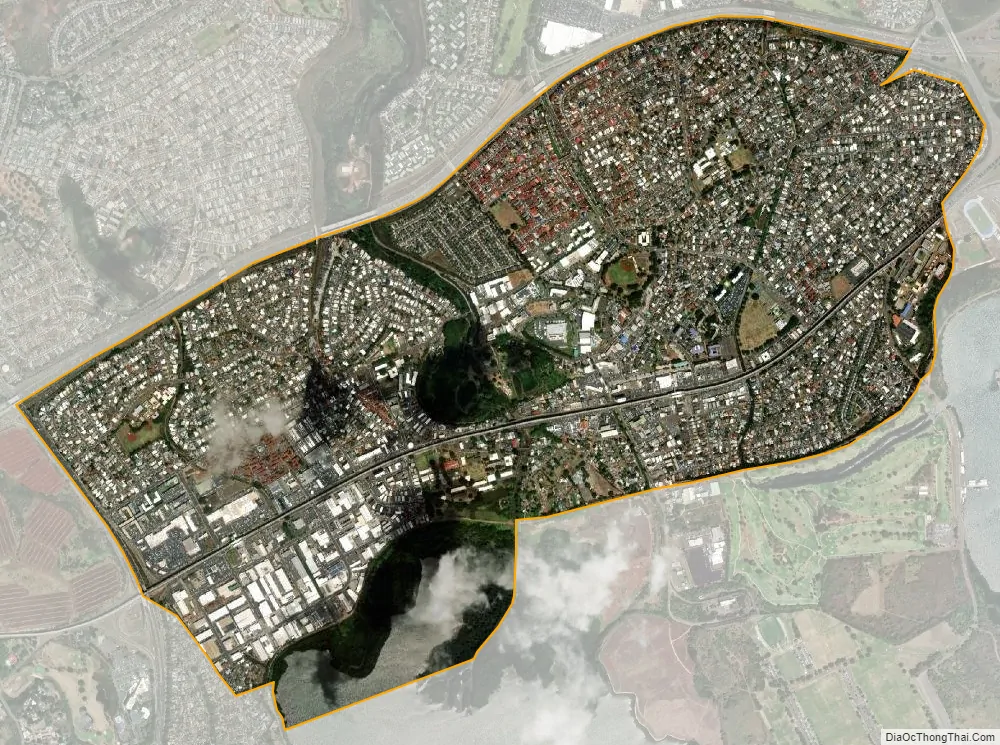
Waipahu city Satellite Map
Geography
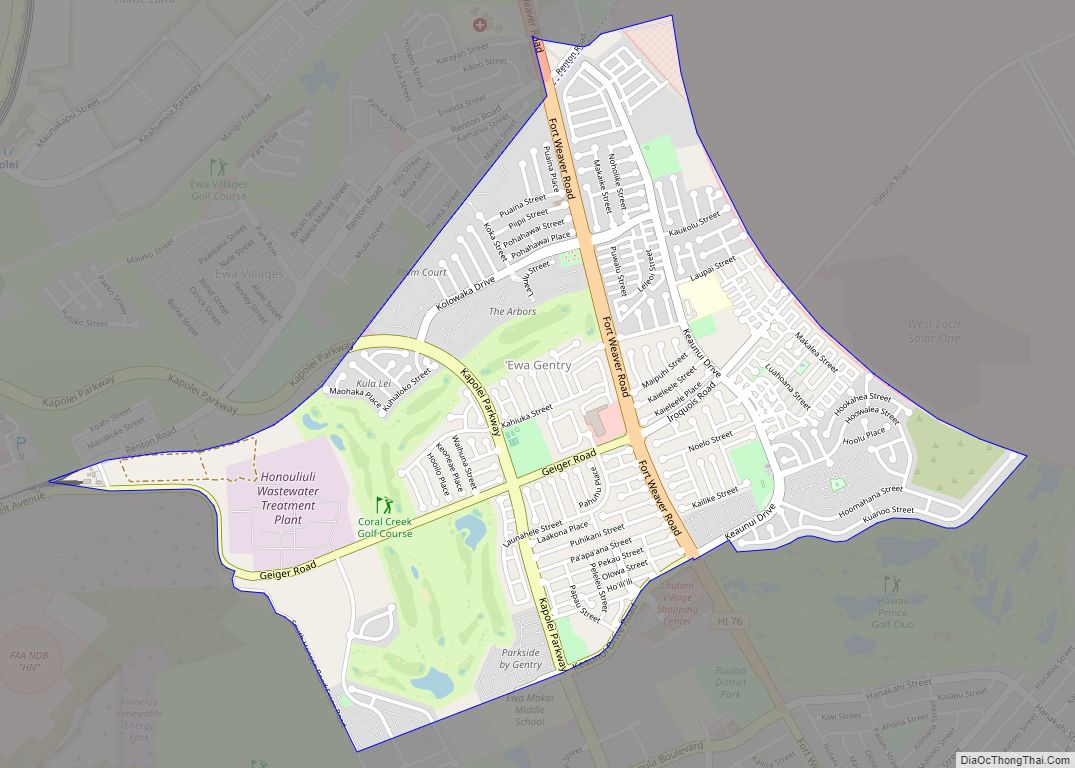
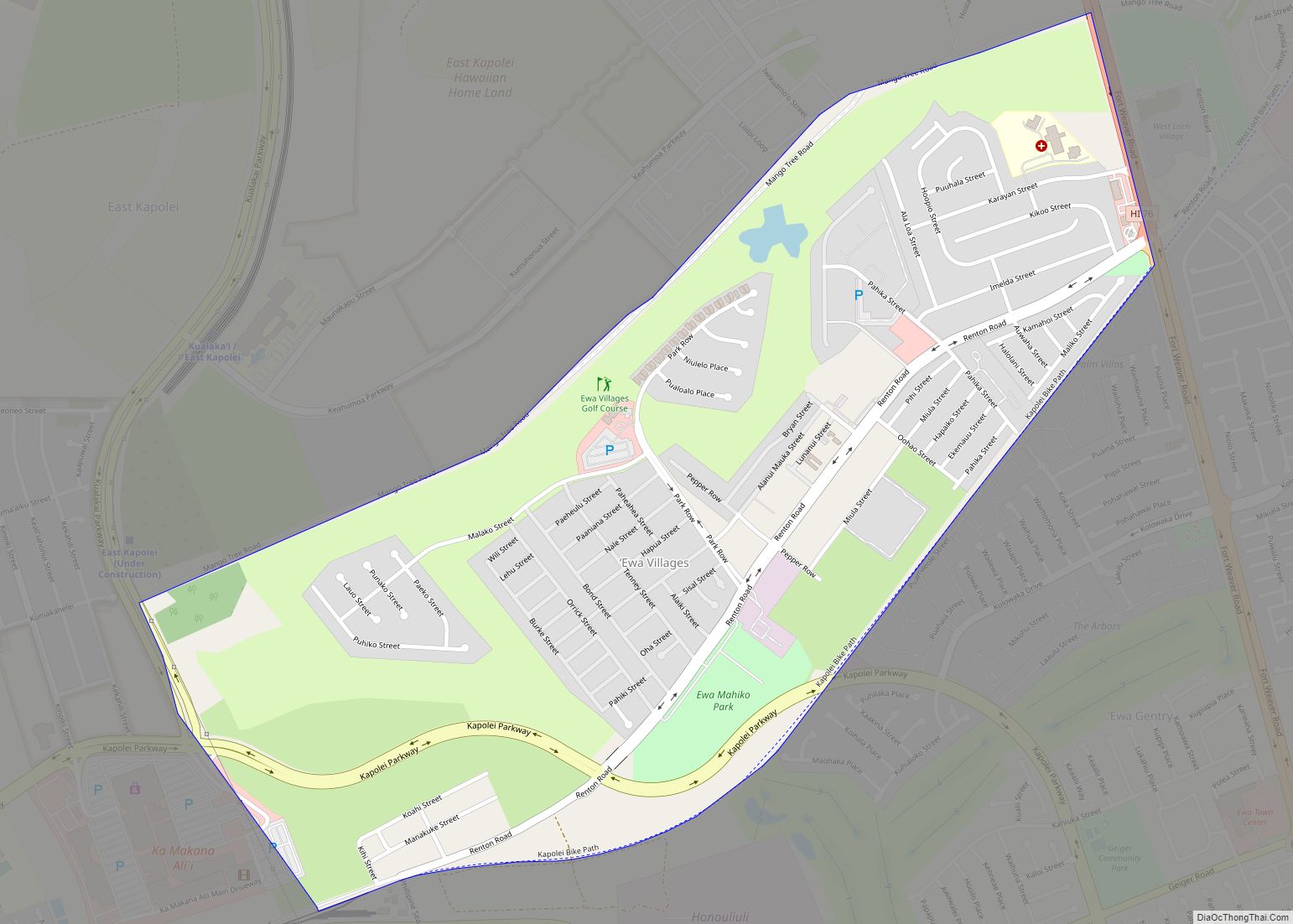
Waipahu is located along the northern shore of both Middle Loch and West Loch of Pearl Harbor. Both Interstate H-1 and Farrington Highway (Hawaii Route 90) run east–west through the length of Waipahu. The town of Waipahu spans across three ahupuaʻa (historic Native Hawaiian land division): Waipiʻo, Waikele, and Hōʻaeʻae. It is common for neighborhoods to be named after the ahupuaʻa in which it’s located. The neighboring areas of Waipio, Village Park, Royal Kunia and Waikele use Waipahu as their postal city, and are often considered to be part of Waipahu.
There are several streams that run through Waipahu, including Waikele Stream and Kapakahi Stream. Waikele Stream runs along the Hawaii Plantation Village and down into Pouhala Marsh Wildlife Sanctuary, which is habitat for several endangered bird species that are endemic to Hawaii. There is roughly 140 feet of elevation change between the north side of Waipahu along H-1 and sea level.
Waikele is located across the H1 freeway north of Waipahu. Waikele consists of newer subdivisions and an upscale outlet shopping center and world-famous golf course. To the west via either roadway can be reached Makakilo and Kapolei, with the Leeward coast beyond. To the east lie Pearl City and the H-2 interchange to Waipiʻo. At the western end of Waipahu is Kunia Road (State Rte. 750) which leads to the Waipahu newer growth areas of Royal Kunia and Village Park north of H-1, and eventually on up across the central plain to Kunia and Schofield Barracks, Wheeler Army Airfield, and Wahiawā. Kunia Road becomes Fort Weaver Road (State Rte. 76) south of Farrington Highway, and goes south through Honouliuli and ʻEwa Villages to ʻEwa Beach.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 2.8 square miles (7.2 km), all of it land.
See also
Map of Hawaii State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming