Travis County is located in south central Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,290,188. It is the fifth-most populous county in Texas. Its county seat is Austin, the capital of Texas. The county was established in 1840 and is named in honor of William Barret Travis, the commander of the Republic of Texas forces at the Battle of the Alamo. Travis County is part of the Austin–Round Rock–Georgetown Metropolitan Statistical Area. It is located along the Balcones Fault, the boundary between the Edwards Plateau to the west and the Blackland Prairie to the east.
| Name: | Travis County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 48-453 |
| State: | Texas |
| Founded: | 1840 |
| Named for: | William B. Travis |
| Seat: | Austin |
| Largest city: | Austin |
| Total Area: | 1,023 sq mi (2,650 km²) |
| Land Area: | 990 sq mi (2,600 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,290,188 |
| Time zone: | UTC−6 (Central) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Website: | traviscountytx.gov |
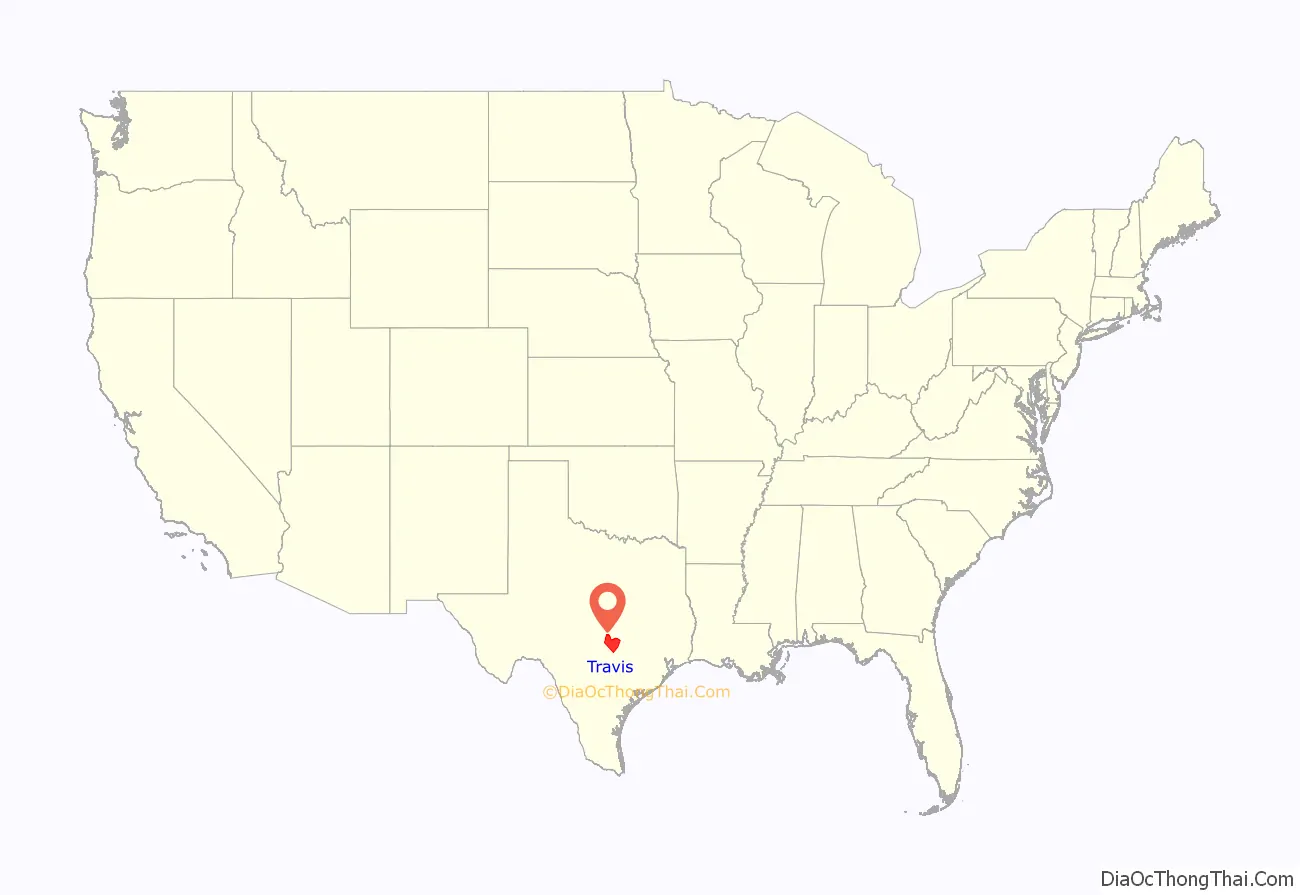
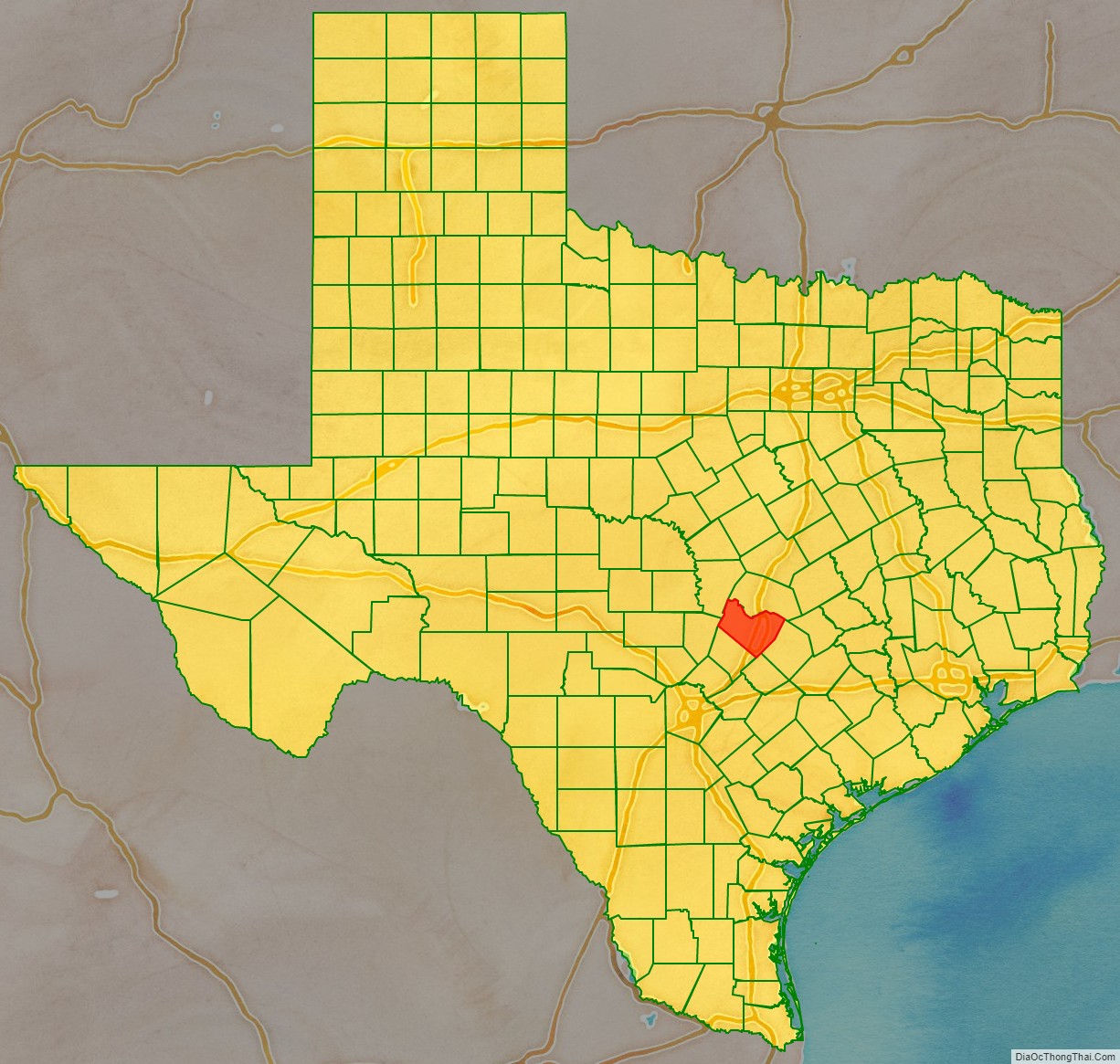
Travis County location map. Where is Travis County?
History
Pre-Columbian and colonial periods
Evidence of habitation of the Balcones Escarpment region of Texas can be traced to at least 11,000 years ago. Two of the oldest Paleolithic archeological sites in Texas, the Levi Rock Shelter and Smith Rock Shelter, are in southwest and southeast Travis County, respectively. Several hundred years before European settlers arrived, a variety of nomadic Native American tribes inhabited the area. These indigenous peoples fished and hunted along the creeks, including present-day Barton Springs, which proved to be a reliable campsite. At the time of the first permanent settlement of the area, the Tonkawa tribe was the most common, with the Comanches and Lipan Apaches also frequenting the area.
The region (along with all of modern Texas) was claimed by the Spanish Empire in the 1600s, but at the time no attempt was made to settle the area (or even to fully explore it). In 1691 Domingo Terán de los Ríos made an inspection tour through East Texas that likely took him through Travis Country. The first European settlers in the area were a group of Spanish friars who arrived from East Texas in July 1730. They established three temporary missions, La Purísima Concepción, San Francisco de los Neches and San José de los Nazonis, on a site by the Colorado River near Barton Springs. The friars found conditions undesirable and relocated to the San Antonio River within a year of their arrival.
Mexican period
In 1821 Mexico won its independence from Spain, and the new government enacted laws encouraging colonists to settle the Texas frontier by granting them land and reduced taxation. Over the next decade, thousands of foreign immigrants (primarily from the United States) moved into Texas; in particular, American empresario Stephen F. Austin established one of his colonies near what is now Bastrop, Texas (in future Travis County) in 1827. Josiah and Mathias Wilbarger, Reuben Hornsby, Jacob M. Harrell, and John F. Webber were early settlers who moved into the area in the early 1830s.
Republican period
In 1836 Texas declared and won its independence from Mexico, forming a new Republic of Texas. After Texas Vice President Mirabeau B. Lamar visited central Texas during a buffalo-hunting expedition between 1837 and 1838, he proposed that the republic’s capital (then located in Houston) be relocated to a site on the north bank of the Colorado River. In 1839 the site was officially chosen as the republic’s new capital and given the name Waterloo, Texas; shortly thereafter the city’s name was changed to Austin in honor of Stephen F. Austin. A new county was also established the following year, of which Austin would be the seat; the county was named Travis County, after William B. Travis. Though the Republic’s capital moved briefly back to Houston during the events surrounding the Texas Archive War, by 1845 Austin was again the capital, and it became the capital of the new State of Texas when Texas was annexed by the United States later that year.
Civil War and beyond
In 1861 Travis County was one of the few Texas counties to vote against secession from the Union. Since the majority of the state did favor secession, Travis County then became a part of the Confederacy for the duration of the Civil War. After the Confederacy’s defeat, Texas was fully readmitted to the Union in 1870.
From the end of the Civil War to the early twenty-first century, Travis County has experienced steady, rapid population growth (averaging more than a 36% increase every decade from 1870 to 2010), driven largely by the growth of Austin and its suburbs; it is now the fifth most populous county in Texas, after Harris (Houston), Dallas, Tarrant (Fort Worth) and Bexar (San Antonio) counties.
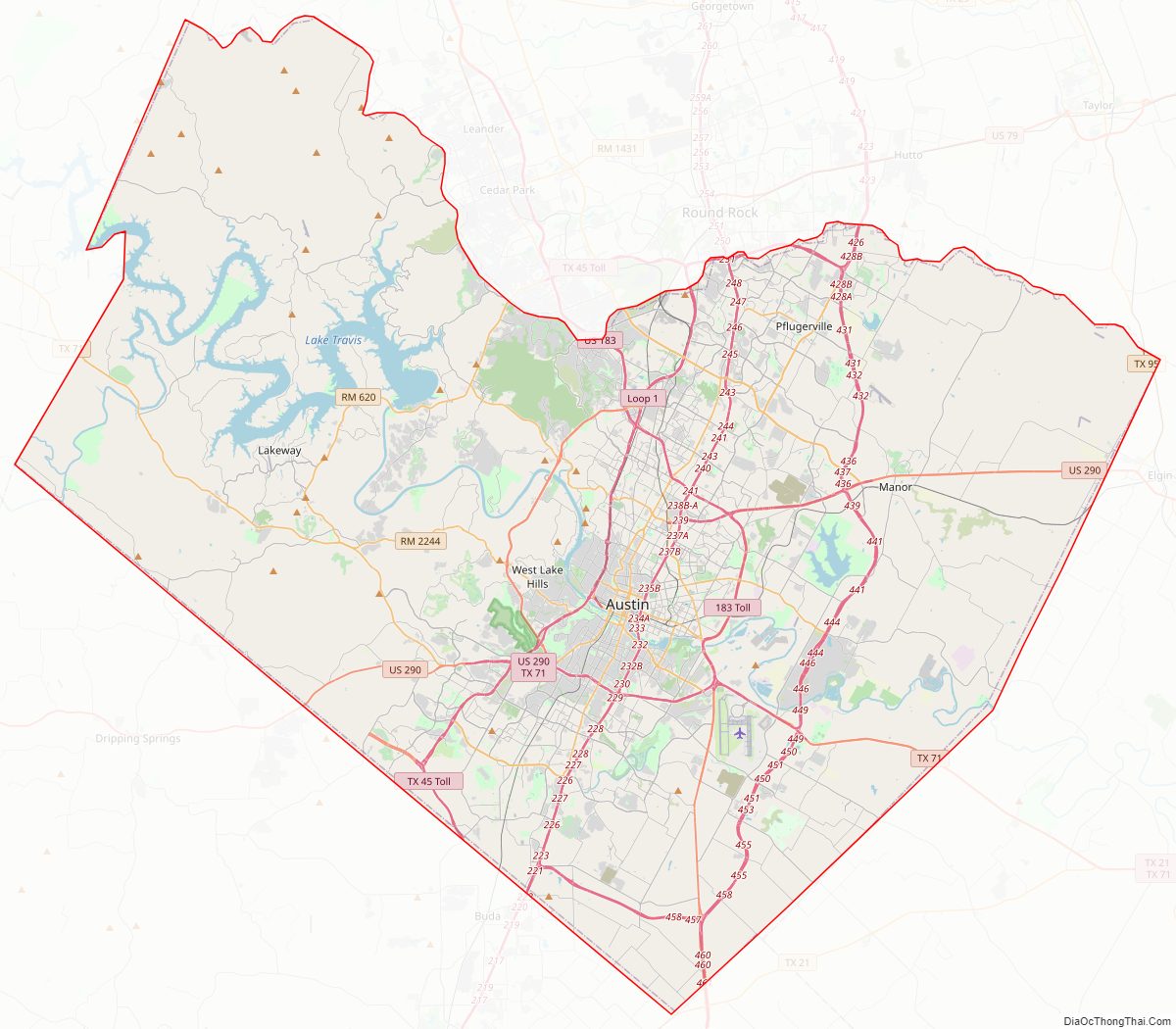
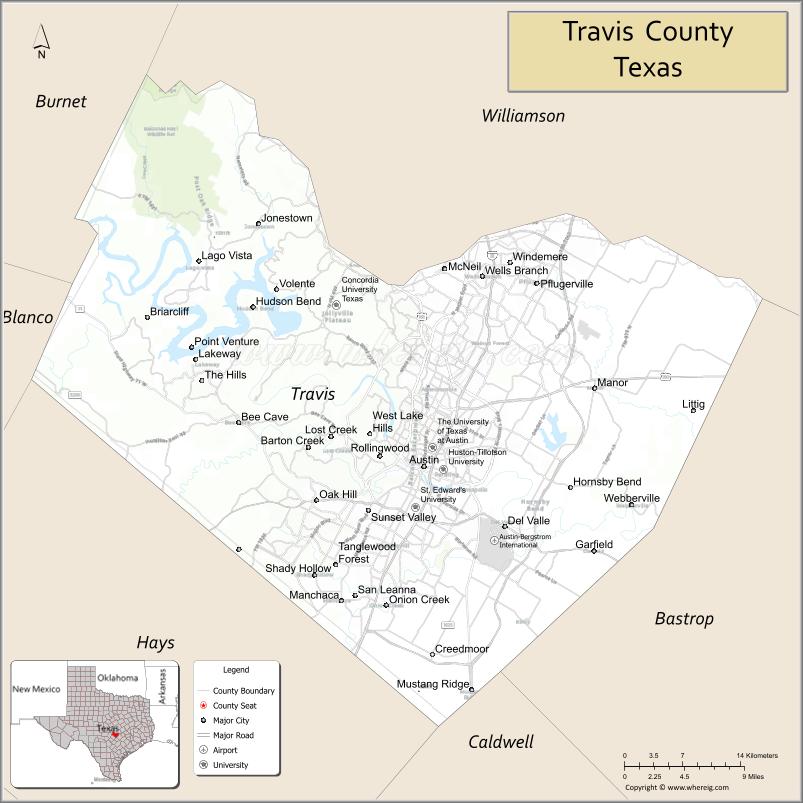
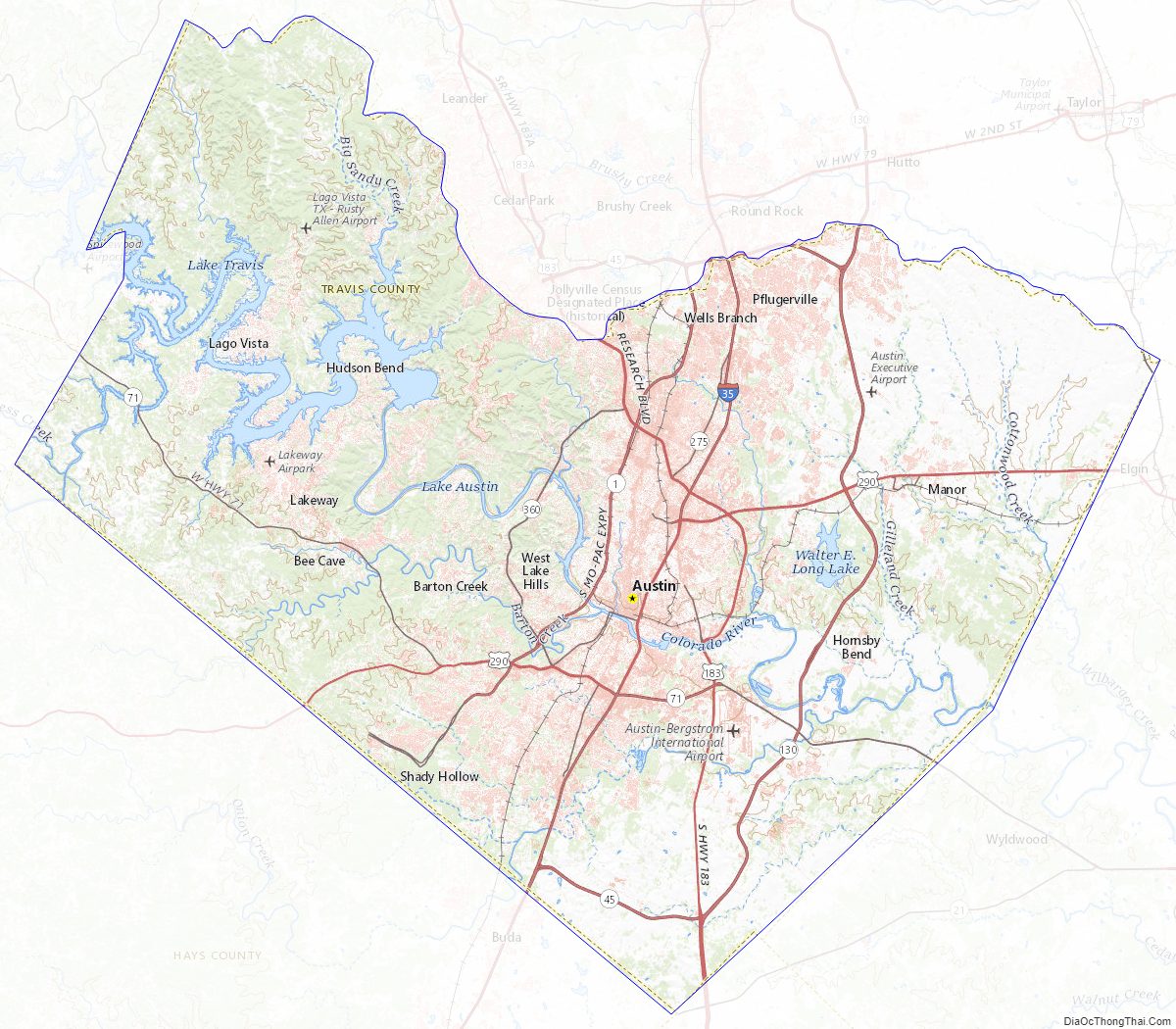
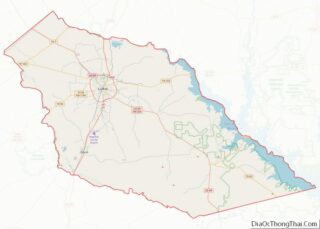
Travis County Road Map
Geography
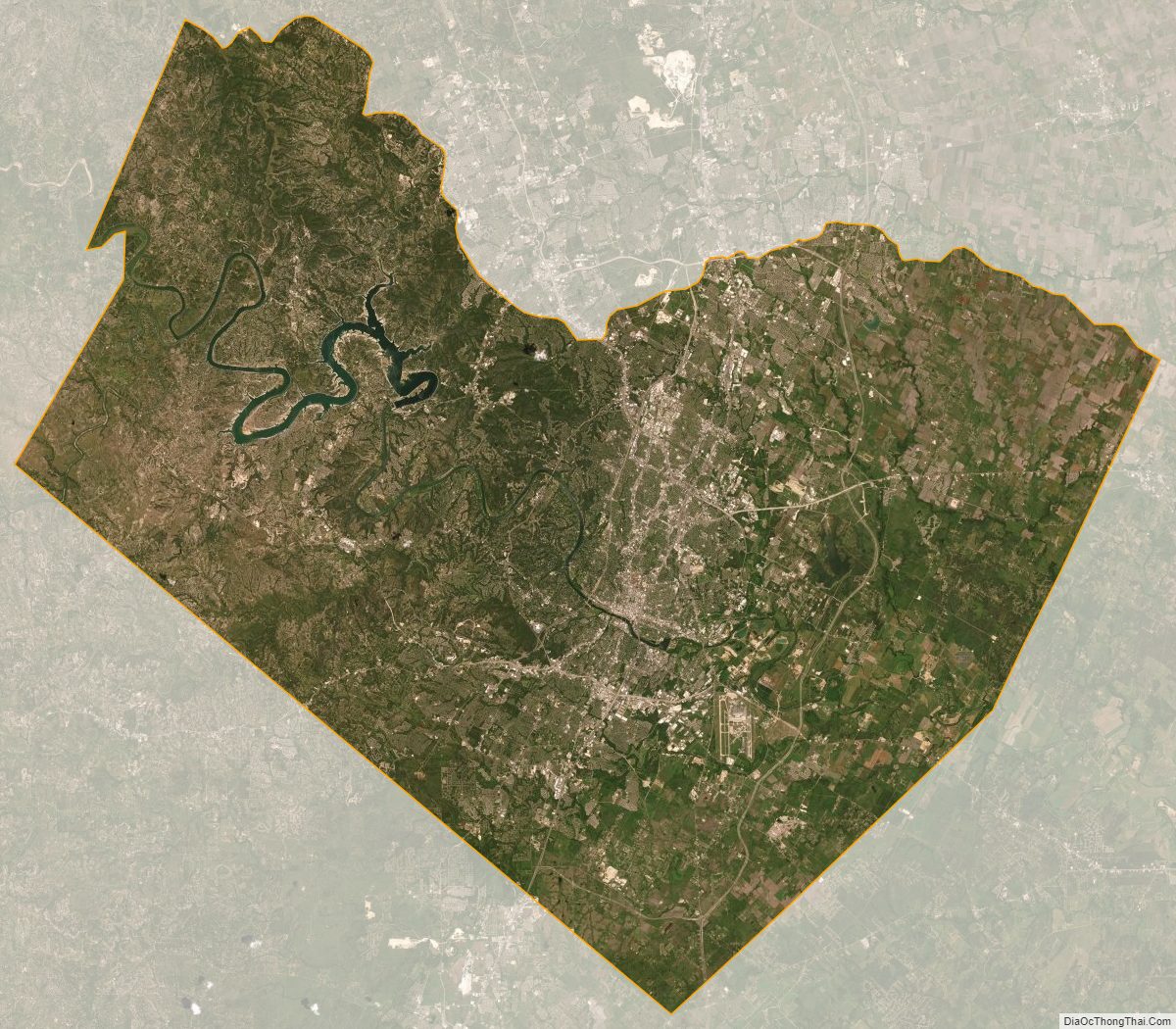
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,023 square miles (2,650 km), of which 990 square miles (2,600 km) is land and 33 square miles (85 km) (3.2%) is water. Travis County is located in the southern part of central Texas, between San Antonio and Dallas–Fort Worth. The county’s geographical center lies two miles northwest of downtown Austin at 30°18′ north latitude and 97°45′ west longitude.
Travis County straddles the Balcones Fault, the boundary between the Edwards Plateau to the west and the Texas Coastal Plain to the east. The western part of the county is characterized by the karst topography of the Texas Hill Country, while the eastern part exhibits the fertile plains and farmlands of the Blackland Prairie. The Colorado River meanders through the county from west to east, forming a series of man-made lakes (Lake Travis, Lake Austin, and Lady Bird Lake).
Springs
The limestone karst geology of the western and southwestern parts of Travis County gives rise to numerous caverns and springs, some of which have provided shelter and water for humans in the region for thousands of years. Notable springs in the county include Barton Springs, Deep Eddy and Hamilton Pool.
Major highways
Travis County is crossed by Interstate Highway 35, US Highways 183 and 290, and Texas Highway 71. IH-35 leads northward to Waco and Dallas–Fort Worth and southward to San Antonio. US-183 leads northward through Cedar Park to Lampasas and southward to Lockhart. US-290 leads westward to Fredericksburg and eastward to Houston. TX-71 leads westward to Marble Falls and eastward to Bastrop.
Other major highways within the county include Texas Highway Loop 1 (the “Mopac Expressway”), which runs from north to south through the center of the county, and Texas Highway 45, which forms parts of an incomplete highway loop around Austin. Texas Highway 130 (constructed as an alternative to IH-35 for long-distance traffic wishing to avoid Austin and San Antonio) also runs from north to south through the sparsely populated eastern part of the county.
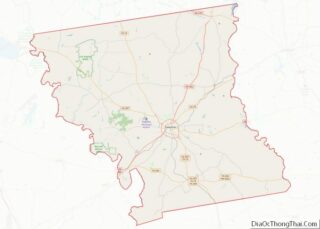
Adjacent counties
- Williamson County (north)
- Bastrop County (east)
- Caldwell County (south)
- Hays County (southwest)
- Blanco County (west)
- Burnet County (northwest)
Protected areas
- Balcones Canyonlands National Wildlife Refuge (part)