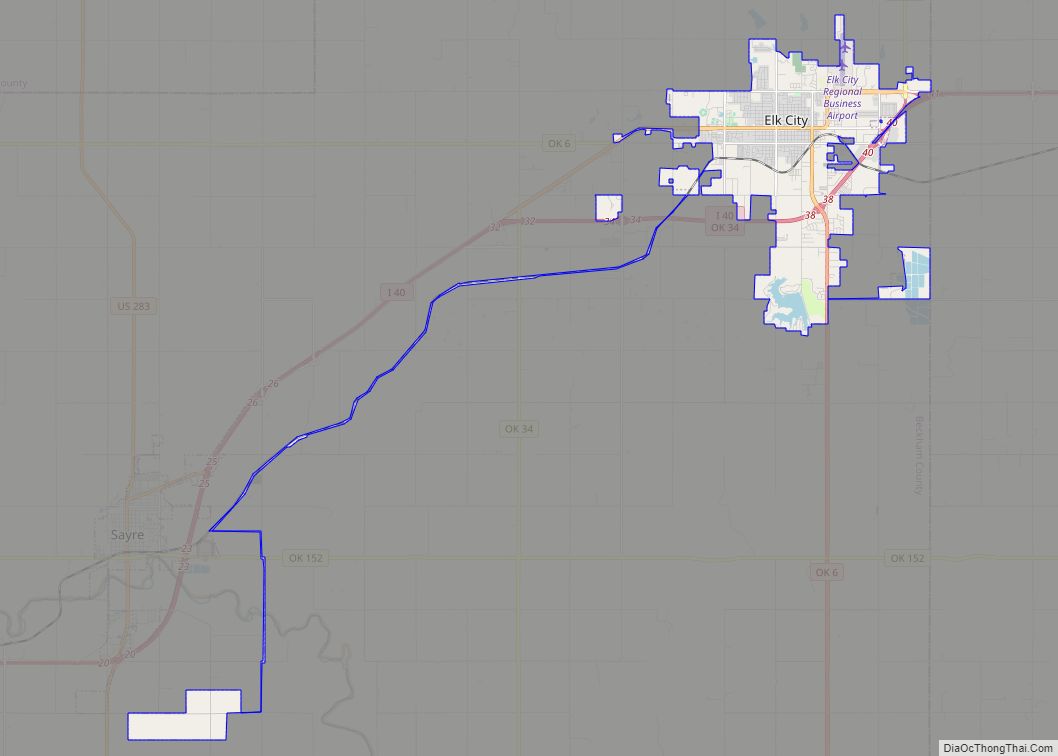
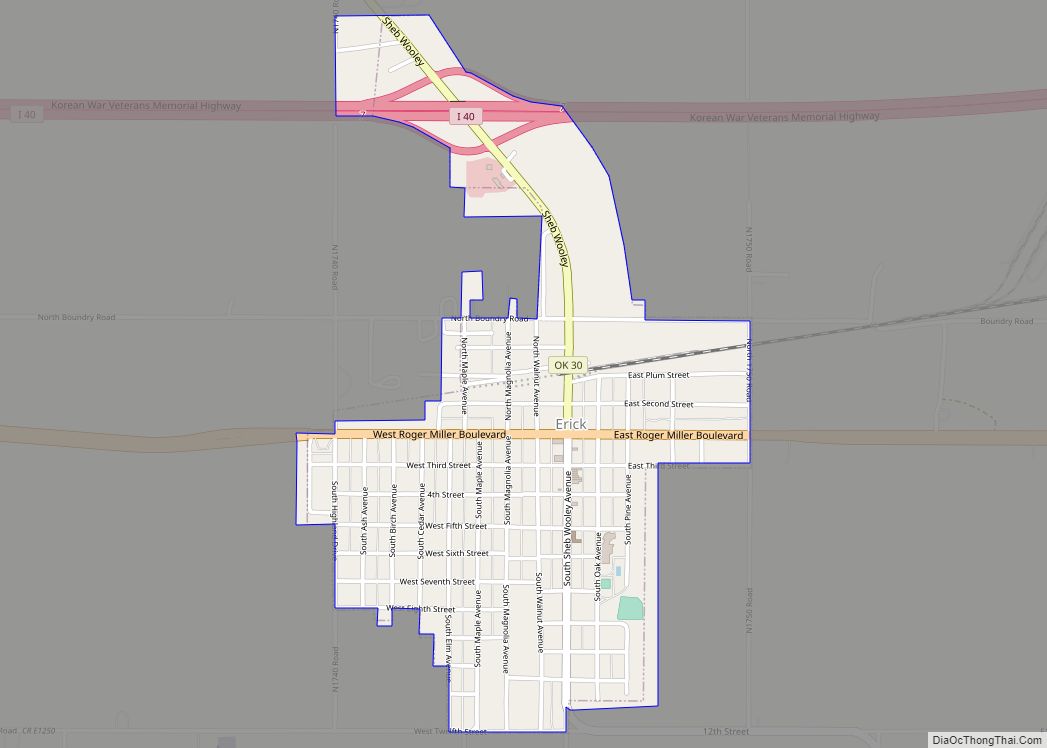
Erick (/ˈɪərɪk/ EER-ik) is a city in Beckham County, Oklahoma, United States. It is located 15 miles (24 km) west of Sayre, the county seat, and 6 miles (9.7 km) east of the Oklahoma-Texas border. The population was 1,052 at the 2010 census.
A post office, originally named Dennis, was established to serve the local community on November 8, 1900. This community developed along the Choctaw, Oklahoma and Gulf Railroad line (later the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railway), built in 1902. On November 16, 1901, the name was changed to honor Beeks Erick, the townsite developer and president of the Choctaw Townsite and Improvement Company, and the town incorporated that year.
| Name: | Erick city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Oklahoma |
| County: | Beckham County |
| Elevation: | 2,064 ft (629 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.94 sq mi (2.45 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.94 sq mi (2.45 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,000 |
| Population Density: | 1,059.32/sq mi (408.88/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 73645 |
| Area code: | 580 |
| FIPS code: | 4024200 |
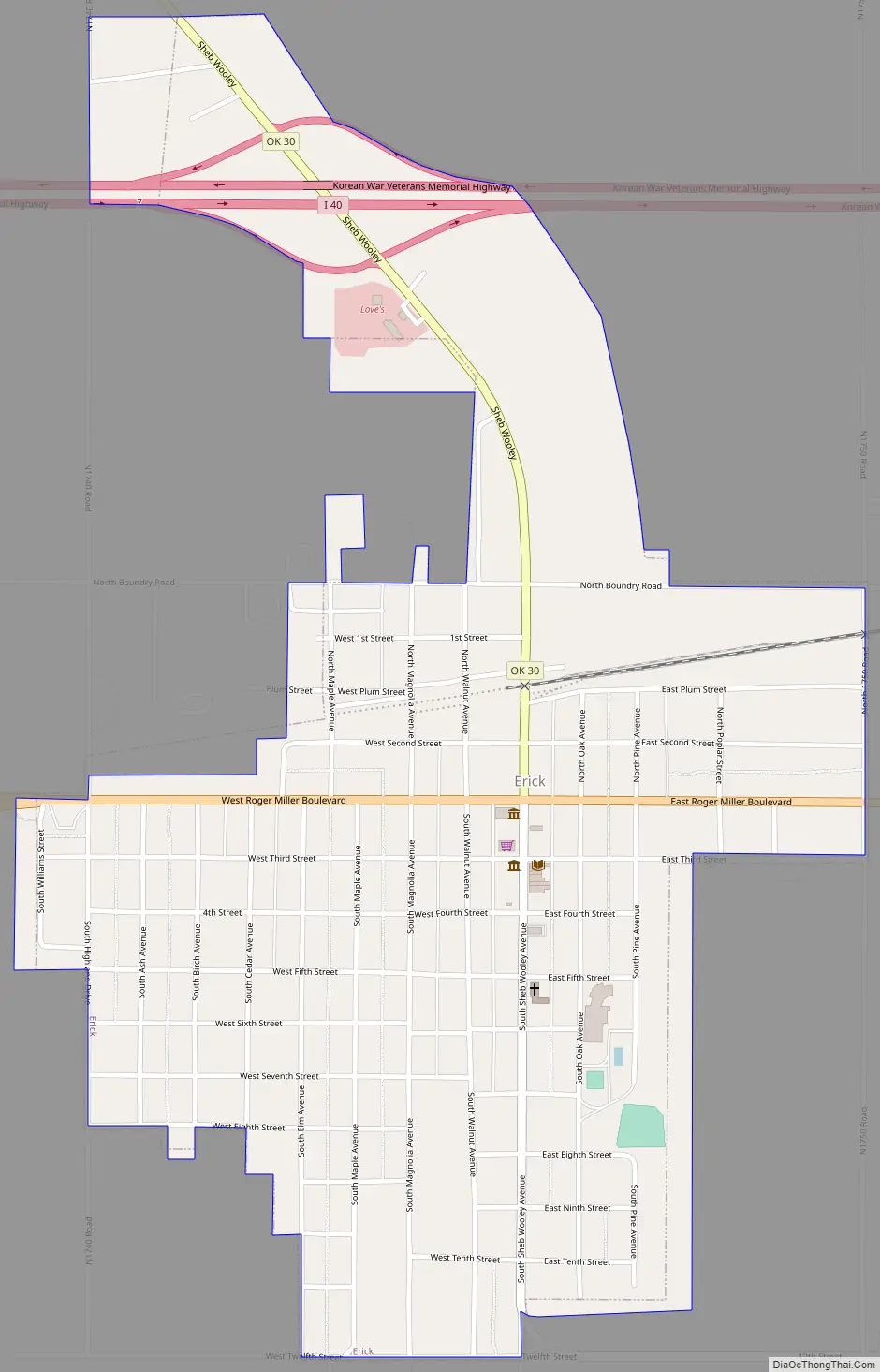
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Erick location map. Where is Erick city?
History
Erick was established in 1901 as an agricultural community on what would become the edge of the Dust Bowl during the Great Depression of the 1930s. It was located on the National Old Trails Road, one of the predecessors to the 1926 numbered US Highway system. Large segments of that road became part of U.S. Route 66.
At statehood in 1907, the population was reported as 686. In June of 1908, Erick competed with Sayre for becoming the county seat, and only lost by a small margin in the election. By 1909, Erick had become a busy community. In that year, it could boast of having 13 general stores, 2 hardware stores, multiple cotton gins and blacksmiths, a livery, a harness shop, a lumber store, five meat markets, several grocery stores, a bakery, and a confectionary, two banks and two weekly newspapers (the Beckham County Democrat and the Erick Altruist. Baptists, Christian, Methodists and Presbyterians had organized churches. By the 1910 U.S. census, population had grown to 915, increasing to 971 in the 1920 census, and reaching a peak population of 2,231 in 1930 due to a brief oil boom. The city economy was bolstered by six cotton gins, a high-density cotton compress, and an ice plant. But in 1940 the census reported 1,591 residents.
The city prospered briefly in the era between WWI and WWII, when natural gas deposits were found in the area. On July 14, 1930 the Frederick (Maryland) Post published, “Reports received here by Sheriff W.K McLemore, Wheeler County, said negroes were driven out of Erick Oklahoma last night and from Texola, Oklahoma today by a mob seeking reprisal for the death of Mrs. Harry Vaughn, wife of a farmer in a nearby county in Texas, who was beaten to death Friday by a Negro.” In a separate incident in 1933, Bonnie Parker and Clyde Barrow (better known as Bonnie and Clyde) kidnapped law enforcement officers from the Wellington, Texas area, drove them to a point near Erick, and left them tied to a tree with barbed wire cut from a fence. The officers freed themselves, but the trail of the criminals had gone cold.
Steinbeck’s Grapes of Wrath, published in 1939, was poorly received locally. According to Erick city clerk Nyla Tennery, “I can remember plainly when the book came out my parents and other people who stayed here were just real upset. That book gave all Missouri, Arkansas and Oklahoma people a shiftless, bad name, like that was the only kind of people who were here.”
U.S. Route 66
Early motor courts began to appear by 1940, with the DeLuxe Courts being the first local Route 66 lodging to appear in the AAA Directory of Motor Courts and Cottages. While civilian motorcar travel was greatly curtailed due to wartime rationing, by 1946 guidebooks listed the Erick Court and trailer park, the Elms Garage, cafés and filling stations.
Erick prospered in the post-war heyday of Route 66, with various roadside businesses catering to motorists. Guidebooks promoted the tiny city as “the first town you encounter, going west, which has a true ‘western’ look with its wide, sun-baked streets, frequent horsemen, occasional sidewalk awnings and similar touches.”
The four lanes of Route 66 from Sayre, Oklahoma to Erick were the last Oklahoma section of US 66 to be bypassed by I-40, in 1975.
Many of the original Route 66 business are now gone or have been converted to other uses.
World War II navy veteran Cal Rogers opened Cal’s Country Cooking on US 66 in May 1946, relocating to a new log cabin restaurant on an Interstate 40 exit in October 1979 after the Interstate bypassed traffic away from the old road. The family sold the business and antiques in a 1999 auction; the building is now a steak house.
The West Winds Motel, originally built with individual carport garages and promoted in its heyday with neon signage of bucking broncos, still stands but is no longer open to visitors despite attempts to restore the property.
Efforts to put “Historic Route 66” back onto maps as a tourist attraction date to the late 1980s, with the first Route 66 Association established three years after the last section of original highway (in Williams, Arizona) was bypassed by Interstate highway in 1984. Various local businesses and attractions cater to seasonal tourists attempting to find what remains of the old road.
The former City Meat Market building is now the Sandhills Curiosity Shop, one of the many Route 66 stops on Pixar’s research trips for 2006 animated film Cars. Its owners Harley and Annabelle Russell, who bill themselves as the “Mediocre Music Makers”, served as model for the country hillbilly accent used by Larry the Cable Guy’s character Mater in the film.
The 3000 square foot Roger Miller Museum was a museum opened at the corner of US 66 (Roger Miller Boulevard) and Oklahoma 30 (Sheb Wooley Avenue) in 2004 in a former 1929 café and drugstore building. It closed permanently on December 23, 2017. The space is now home to the 100th Meridian Museum.
Country musicians
Erick was home to two of Country music’s more idiosyncratic performers. Sheb Wooley, the actor, songwriter, and singer who recorded the saga of the “one-eyed one-horned flying purple people eater” was born there in 1921. Roger Miller, country superstar and author of “King of the Road,” “Dang Me,” “You Can’t Rollerskate in a Buffalo Herd,” and many others, was born in Fort Worth, Texas, but grew up in Erick from the age of three. When asked by an interviewer where Erick was near, Miller wryly replied, “It’s close to extinction.” Herbert Mayfield, one of the Mayfield Brothers of West Texas, was born in Erick but moved to Dimmitt, Texas, when he was ten years of age.
Erick Road Map
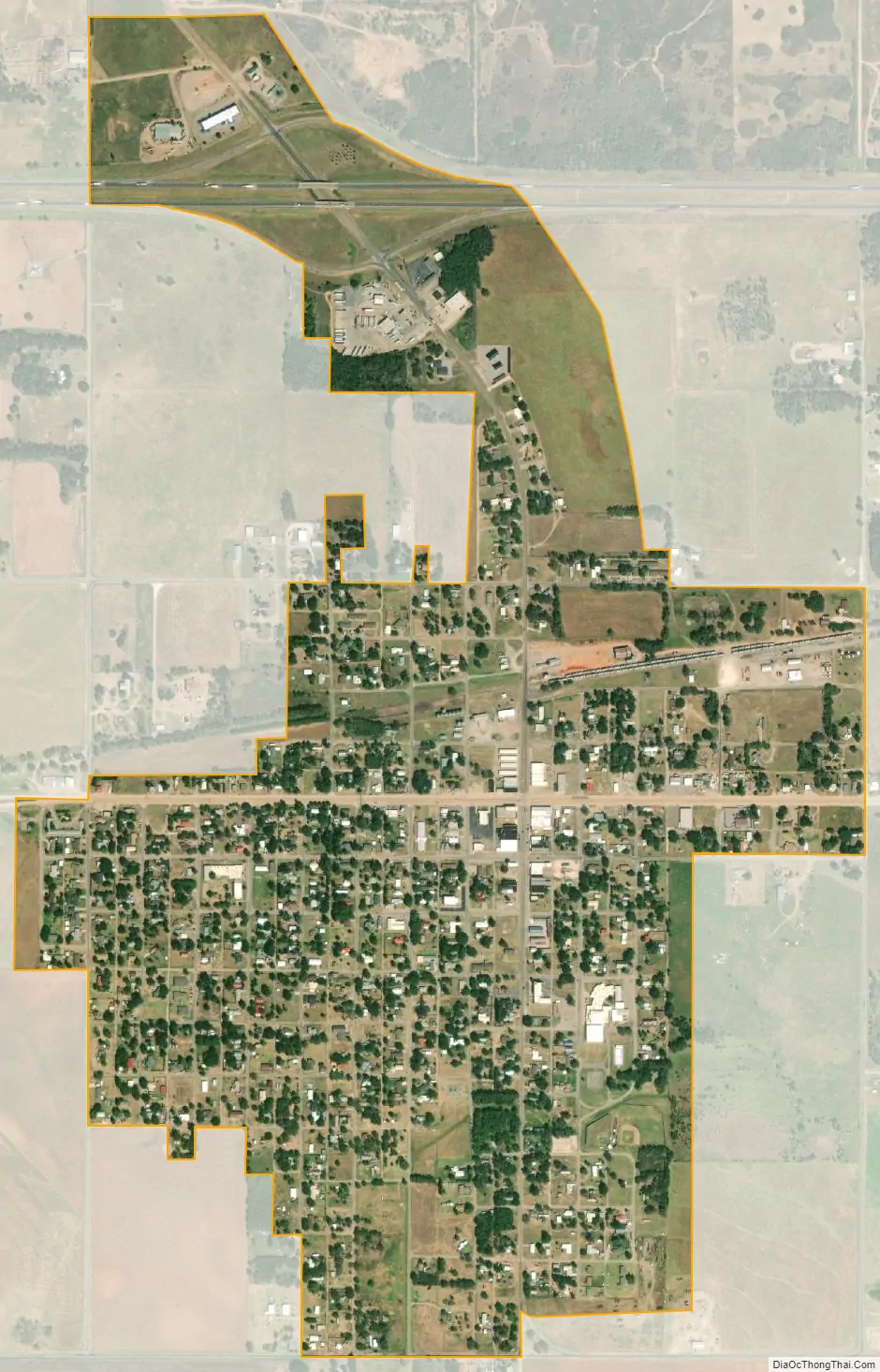
Erick city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 1.0 square mile (2.6 km), all land.
Erick is located just south of I-40 and is on the historic US Route 66 (which is signed as a business route from Interstate 40). The town is also served by State Highway 30. Erick is the second-closest Oklahoma settlement to the Texas border on US 66 or I-40 (Texola is at the border, seven miles to the west).
It is still a railroad town, being an end point on the route of Farmrail.
See also
Map of Oklahoma State and its subdivision:- Adair
- Alfalfa
- Atoka
- Beaver
- Beckham
- Blaine
- Bryan
- Caddo
- Canadian
- Carter
- Cherokee
- Choctaw
- Cimarron
- Cleveland
- Coal
- Comanche
- Cotton
- Craig
- Creek
- Custer
- Delaware
- Dewey
- Ellis
- Garfield
- Garvin
- Grady
- Grant
- Greer
- Harmon
- Harper
- Haskell
- Hughes
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnston
- Kay
- Kingfisher
- Kiowa
- Latimer
- Le Flore
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Love
- Major
- Marshall
- Mayes
- McClain
- McCurtain
- McIntosh
- Murray
- Muskogee
- Noble
- Nowata
- Okfuskee
- Oklahoma
- Okmulgee
- Osage
- Ottawa
- Pawnee
- Payne
- Pittsburg
- Pontotoc
- Pottawatomie
- Pushmataha
- Roger Mills
- Rogers
- Seminole
- Sequoyah
- Stephens
- Texas
- Tillman
- Tulsa
- Wagoner
- Washington
- Washita
- Woods
- Woodward
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming