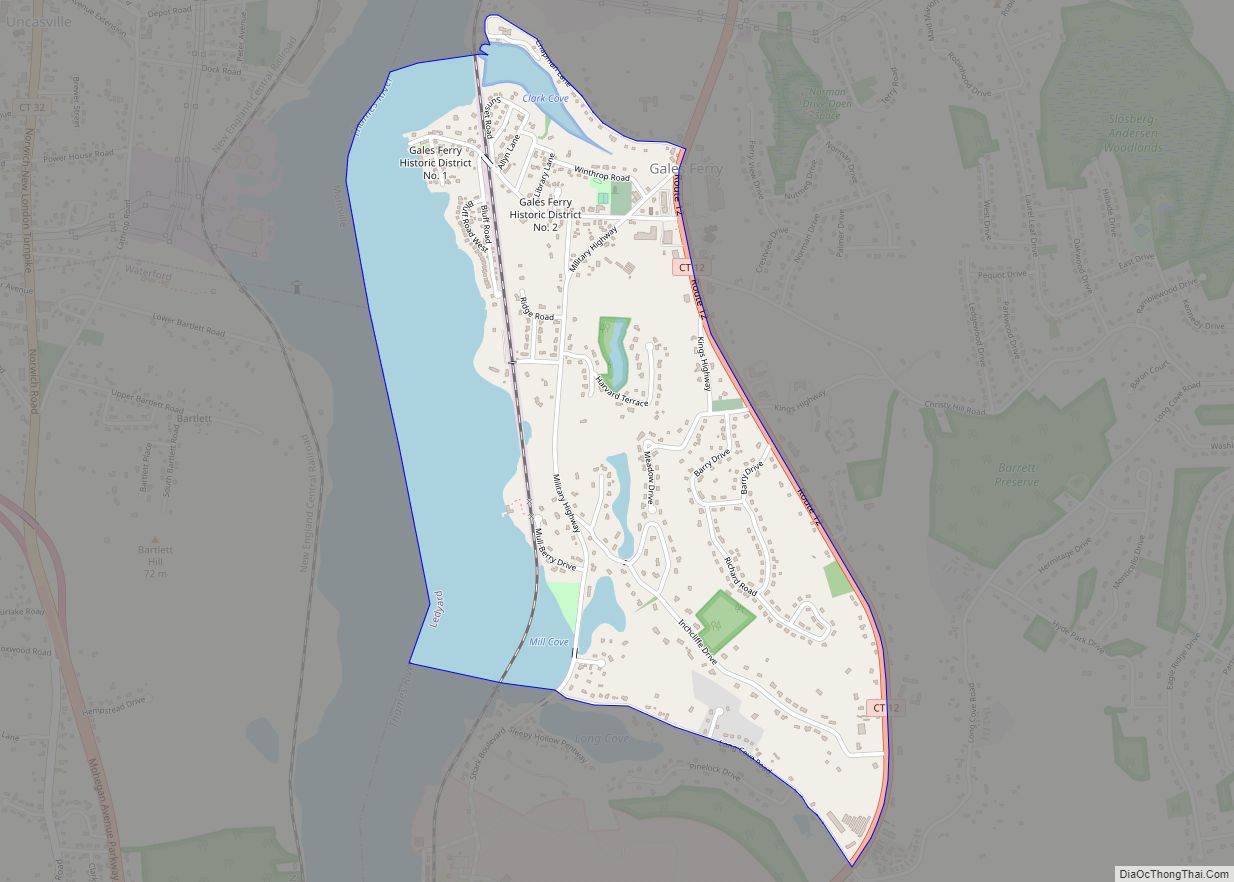
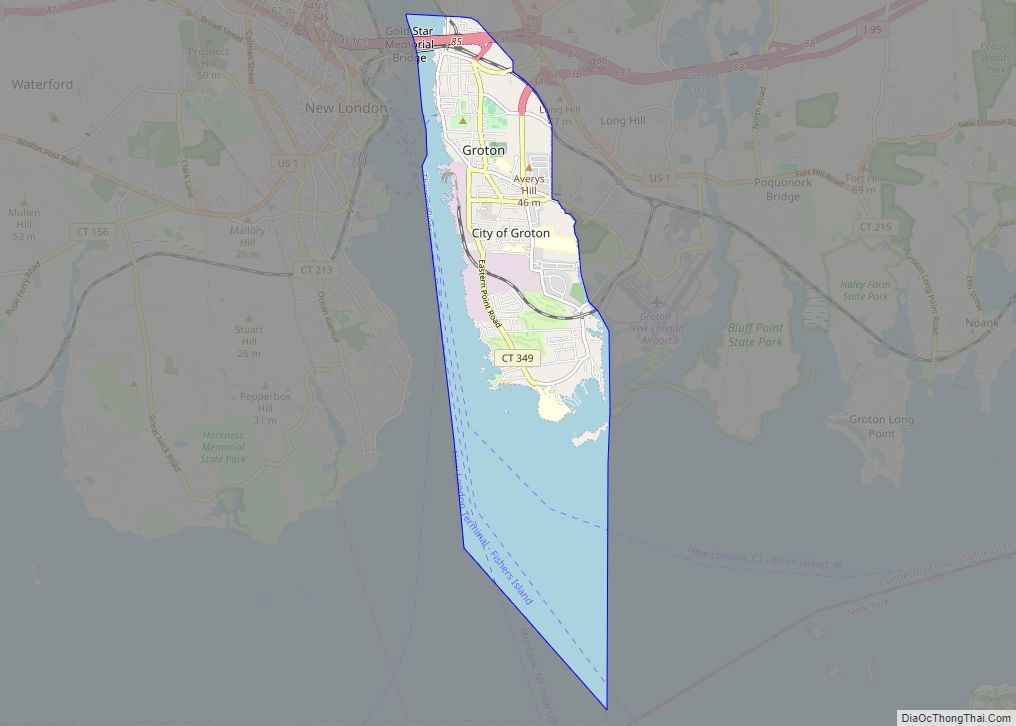
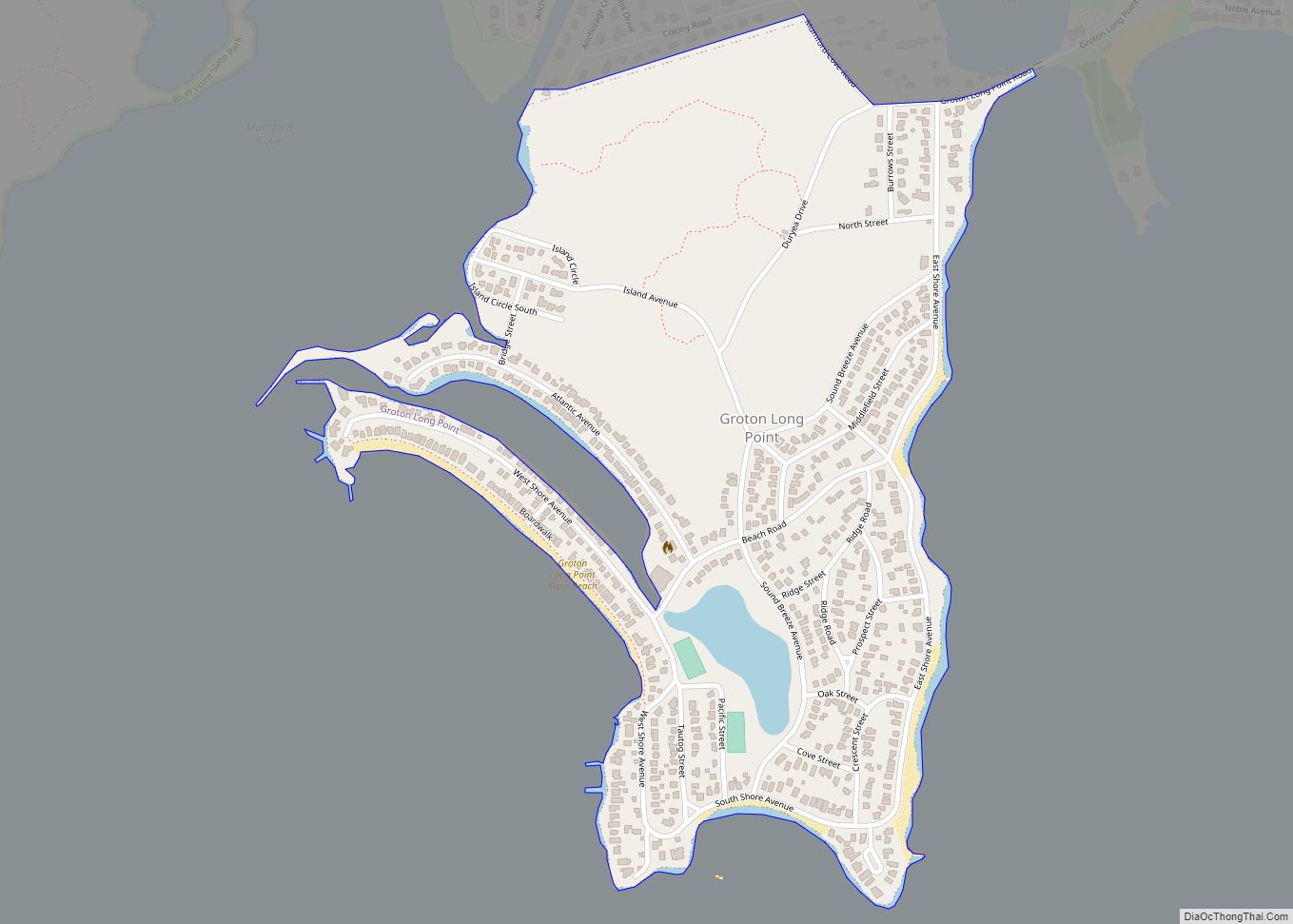
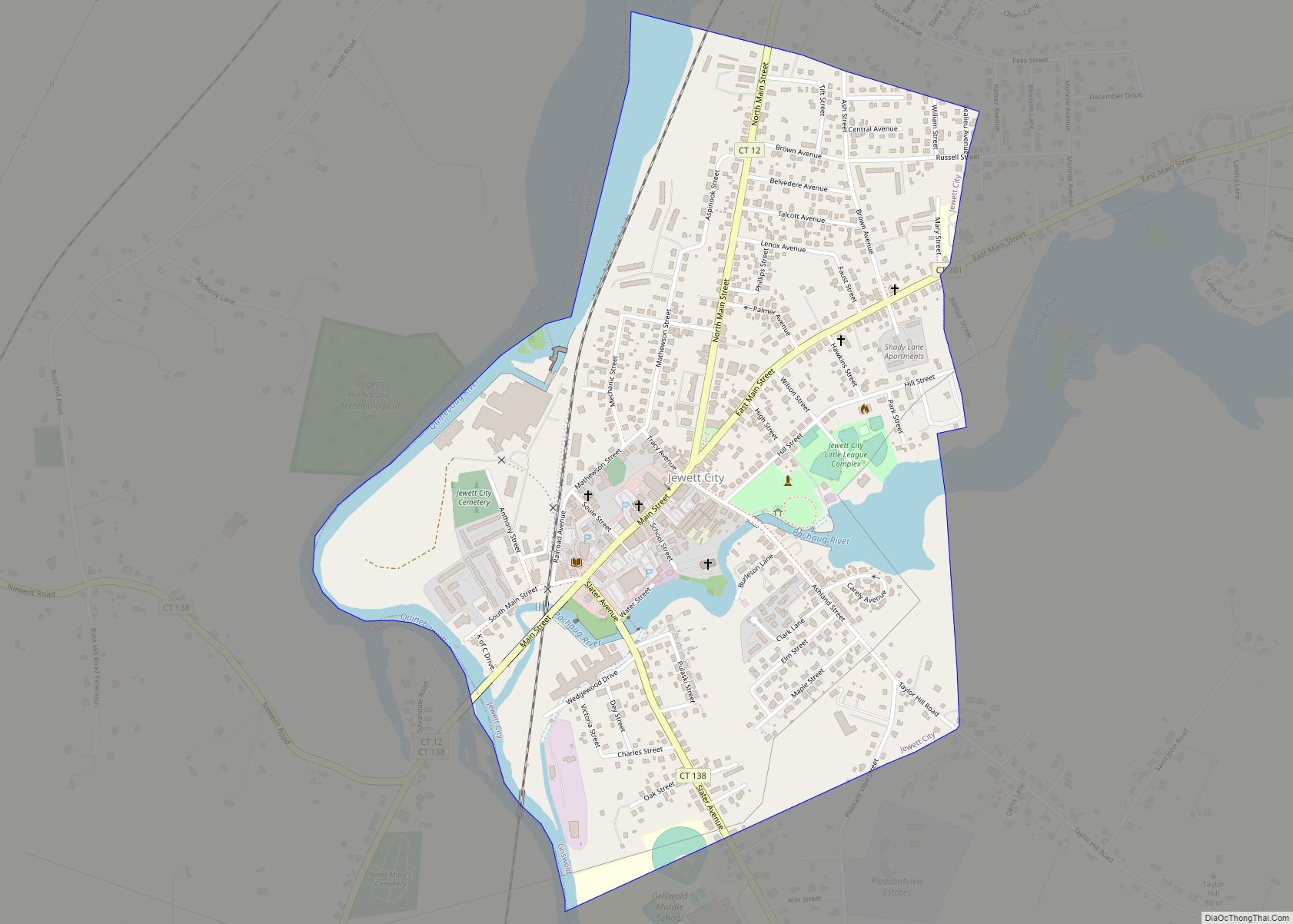
The town of Stonington is located in New London County, Connecticut, United States. Located in the state’s southeastern corner, it includes the borough of Stonington, the villages of Pawcatuck, Lords Point, and Wequetequock, and the eastern halves of the villages of Mystic and Old Mystic (the other halves being in the town of Groton). The town is part of the Southeastern Connecticut Planning Region. The population of the town was 18,335 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Stonington borough |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 21 |
| LSAD Description: | borough (suffix) |
| State: | Connecticut |
| County: | New London County |
| Elevation: | 75 ft (23 m) |
| Total Area: | 48.98 sq mi (126.85 km²) |
| Land Area: | 38.66 sq mi (100.12 km²) |
| Water Area: | 10.32 sq mi (26.72 km²) |
| Total Population: | 18,335 |
| Population Density: | 370/sq mi (140/km²) |
| Area code: | 860/959 |
| FIPS code: | 0973700 |
| Website: | www.stonington-ct.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Stonington location map. Where is Stonington borough?
History
The first European colonists established a trading house in the Pawcatuck section of town in 1649. The present territory of Stonington was part of lands that had belonged to the Pequot people, who referred to the areas making up Stonington as Pawcatuck (Stony Brook to the Pawcatuck River) and Mistack (Mystic River to Stony Brook). It was named “Souther Towne” or Southerton by Massachusetts in 1658, and officially became part of Connecticut in 1662 when Connecticut received its royal charter. Southerton was renamed “Mistick” in 1665, and finally named Stonington in 1666, meaning “stony town”. Thomas Miner, Walter Palmer, William Chesebrough, and Thomas Stanton were the founders. The town of North Stonington was set off as a parish from Stonington in 1724 and incorporated as a town in 1807.
Stonington first prospered in the 1790s when its harbor was home to a fleet engaged in the profitable seal hunting trade in which seals were hunted on islands off the Chilean and Patagonian coasts, and their skins were sold as fur in China.
Stonington repulsed two British naval bombardments. One was a desultory bombardment during the American Revolution by Sir James Wallace in the frigate HMS Rose on August 30, 1775. The other was a more damaging three-day affair between August 9 and 12, 1814 during the War of 1812. British vessels HMS Ramillies, HMS Pactolus, HMS Dispatch, and HMS Terror under the command of Sir Thomas Hardy appeared offshore on August 9. The British demanded immediate surrender, but Stonington’s citizens replied with a note that stated, “We shall defend the place to the last extremity; should it be destroyed, we shall perish in its ruins.” For three days, the Royal Navy pounded the town, but the only fatality was that of an elderly woman who was already mortally ill. The British sailed off on August 12 after suffering many dead and wounded. The battle was notable for the British utilizing stinkpots, a Chinese weapon, during the bombardment. American poet Philip Freneau wrote (in part):
A memorial in Cannon Square at the center of town serves as a memorial to the 1814 attack. The memorial consists of two 18-pounder cannon which held off the British fleet, plus a granite obelisk.
A sealing fleet consisting of 6 Stonington ships, under the command of Benjamin Pendleton, sailed during the 1820–21 season. The fleet was composed of Pendleton’s Frederick, the Hersilia captained by James P. Sheffield, the Hero captained by Nathaniel Brown Palmer, the Free Gift captained by Thomas Dunbar, the Express captained by Ephraim Williams, and the Essex captained by Josiah C. Chester. The fleet operated from Deception Island, and Palmer reported sighting Palmer Land on 16 Nov. 1820.
The Stonington Harbor Light is a low stone building erected in 1840. In the 19th century, Stonington supported a small fishing, whaling, and sealing fleet, with some direct trade with the West Indies—enough in volume for it to be made a port of entry in 1842. The small granite Customs House faces Main Street just north of Cannon Square.
The New London and Stonington Railroad Company was incorporated on July 29, 1852. The Groton and Stonington Street Railway was a trolley line created in 1904 to serve the Stonington area. The trolley was dismantled and replaced by buses in 1928.
In recent decades, Stonington has experienced a large influx of new home owners using historic Stonington Borough houses as second homes. The town has undergone a widespread reconditioning of these homes since the mid-1990s, when an altercation over property rights attracted substantial news coverage about Stonington’s revitalization.
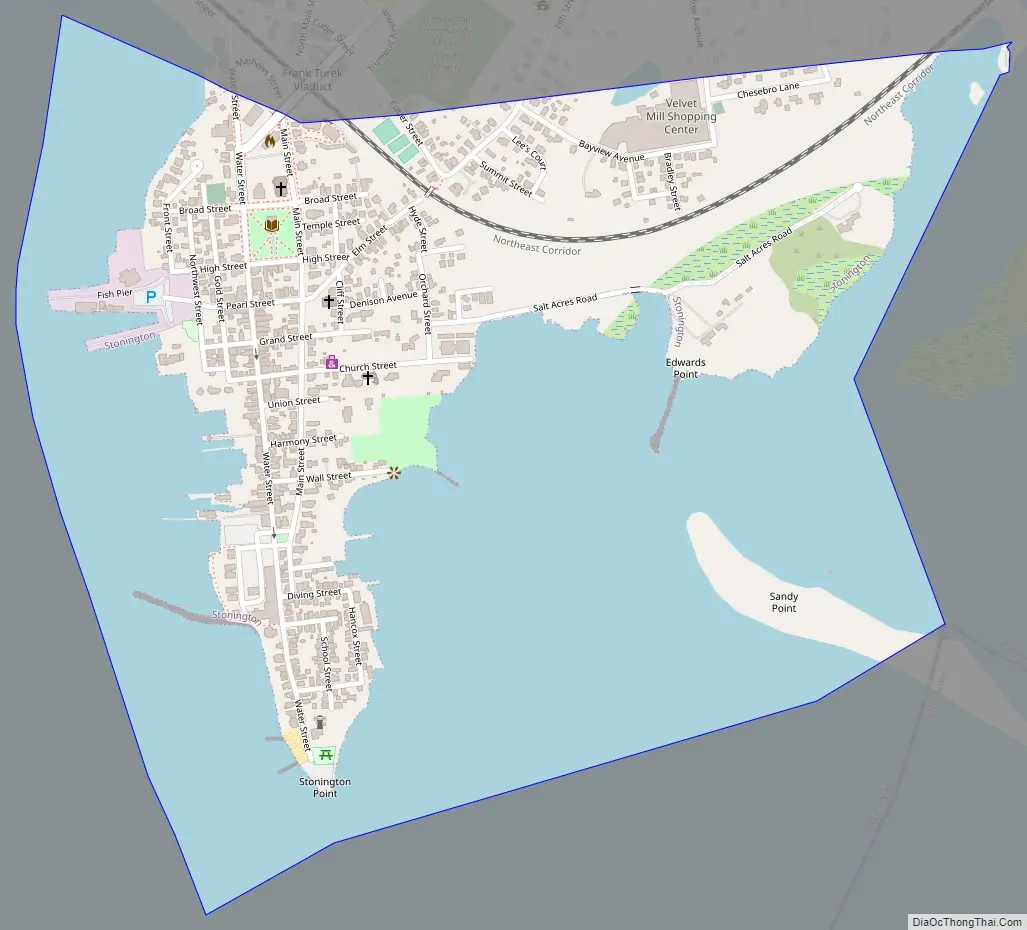
Stonington Road Map
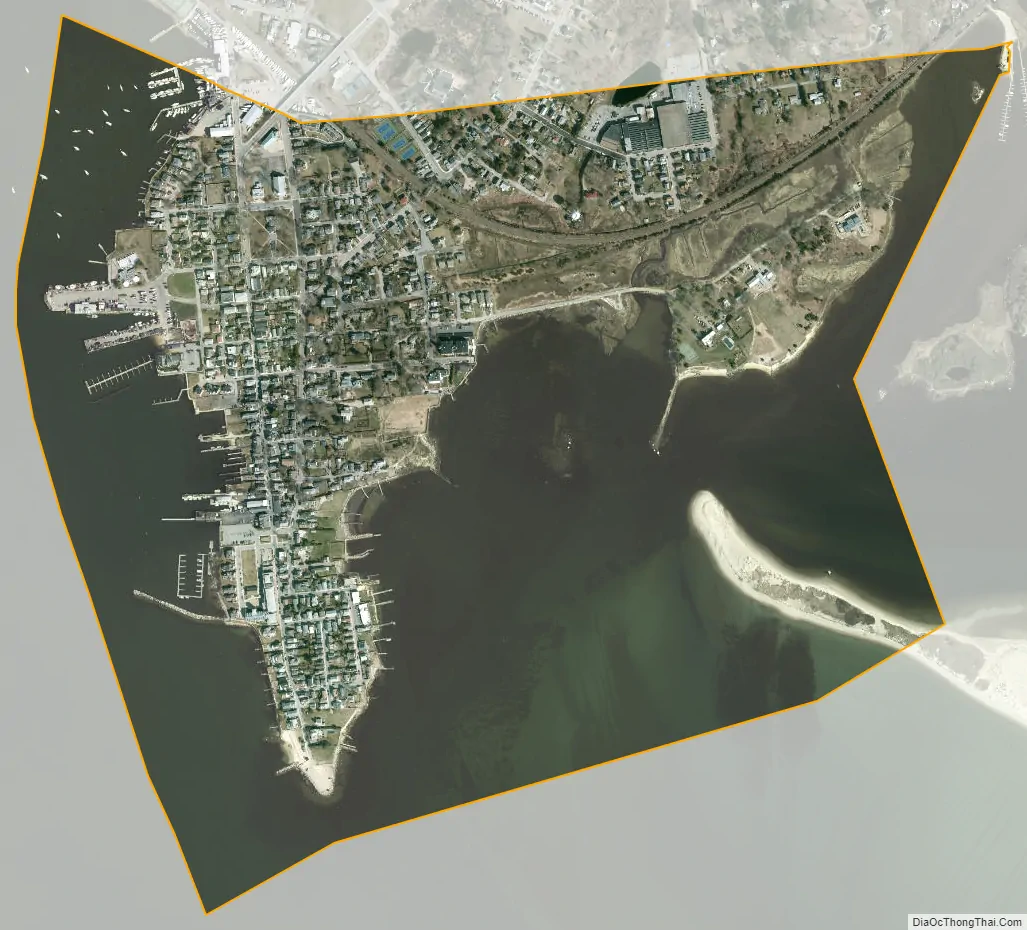
Stonington city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 50.0 sq mi (129.6 km), of which 38.7 sq mi (100.2 km) is land and 11.4 sq mi (29.4 km) (or 22.68%), is water.
In the waters off Stonington, the states of New York, Connecticut, and Rhode Island come together at a single point.
Principal communities
- Lords Point (06378)
- Mystic (06355) (partly in the town of Groton)
- Enders Island, Greenmanville, Mason’s Island, Pequotsepos, Quiambaug, Seaport Heights
- Old Mystic (06372) (mostly in the town of Groton)
- Quaketaug Hill, Wolf Neck
- Pawcatuck (06379)
- Anguilla, Anguilla Acres, Blueberry Hill, Brookside, Castle Hill, Clarksville, Downerville, Hinckley Hill, Lower Pawcatuck, Oak Hill Gardens, Solomonville, Stillmanville, The Highlands, Berry Hill, Wequetequock Hill
- Stonington Borough (06378)
- Wequetequock (06379)
Other minor communities include Deans Mill, Grand View Park, Greenhaven, Ledward Island, Ram Island, Road Church District, and Wamphassuc Point.
Climate
Stonington has a humid continental climate (Dfa/Dfb) and is located in hardiness zones 6b/7a.
See also
Map of Connecticut State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming