Stamford (/ˈstæmfərd/) is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, 34 miles (55 kilometers) outside of New York City. It is the largest city in the Western Connecticut Planning Region, and Connecticut’s second-most populous city, behind Bridgeport. With a population of 135,470, Stamford passed Hartford and New Haven in population as of the 2020 census. It is in the Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk-Danbury metropolitan statistical area, which is part of the New York City metropolitan area (specifically, the New York–Newark, NY–NJ–CT–PA Combined Statistical Area).
As of 2023, Stamford is home to eight Fortune 500 companies and numerous divisions of large corporations. This gives it the largest financial district in the New York metropolitan region outside New York City and one of the nation’s largest concentrations of corporations. Dominant sectors of Stamford’s economy include financial services, tourism, information technology, healthcare, telecommunications, transportation, and retail. Its metropolitan division is home to colleges and universities including UConn Stamford and Norwalk Community College.
| Name: | Stamford city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Connecticut |
| County: | Fairfield County |
| Elevation: | 23 ft (7 m) |
| Land Area: | 37.62 sq mi (97.43 km²) |
| Water Area: | 14.41 sq mi (37.33 km²) |
| Population Density: | 3,601.0/sq mi (1,390.4/km²) |
| Area code: | 203/475 |
| FIPS code: | 0973000 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0211129 |
| Website: | www.stamfordct.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Stamford location map. Where is Stamford city?
History
Stamford was known as Rippowam by the Siwanoy Native American inhabitants of the region, and the very first European settlers in the area also called it that. The present name is after the town of Stamford, Lincolnshire, England. The deed to Stamford was signed on July 1, 1640, between Captain Turner of the New Haven Colony and Chief Ponus. By the 18th century, one of the town’s primary industries was merchandising by water, which was possible due to Stamford’s proximity to New York.
In 1692, Stamford was home to a less famous witch trial than the well-known Salem witch trials, which also occurred in 1692. The accusations were less fanatical and on a smaller scale, but they also grew to prominence through gossip and hysterics.
New Canaan officially separated from Stamford when it incorporated as a town in 1801, followed by Darien in 1820.
Starting in the late 19th century, New York residents built summer homes on the shoreline, and some moved to Stamford permanently and started commuting to Manhattan by train. Stamford incorporated as a city in 1893.
In 1950, the U.S. Census Bureau reported the city’s population as 94.6% white and 5.2% black.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Stamford’s commercial real estate boomed as corporations relocated from New York City to peripheral areas. A massive urban redevelopment campaign during that time resulted in a downtown with many tall office buildings. The F.D. Rich Company was the city-designated urban renewal developer of the downtown area in an ongoing, contentious project beginning in the 1960s and continuing through the 1970s. The company put up what was the city’s tallest structure, One Landmark Square, at 21 floors high, and the GTE building (now One Stamford Forum), along with the Marriott Hotel, the Stamford Town Center and many other downtown office buildings. One Landmark Square has since been dwarfed by the new 34-story Park Tower Stamford condominium tower, and again by the Atlantic Station development, another Rich Company project in partnership with Cappelli Enterprises. Over the years, other developers have joined in building up the downtown, a process that continued through the 1980s and 1990s and into the new century.
Since 2008, an 80-acre (32-hectare) mixed-use redevelopment project for Stamford’s Harbor Point neighborhood has added additional growth south of downtown. The redevelopment plan included six million square feet (560,000 m) of new residential, retail, office and hotel space, and a marina. In July 2012, roughly 900 of the projected 4,000 Harbor Point residential units had been constructed. New restaurants and recreational activities have come up in the Harbor Point area, which is considered New Stamford. From 2008 to 2017, the city issued permits for 4,341 housing units.
During the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S., many New Yorkers relocated to Stamford and its metropolitan area.
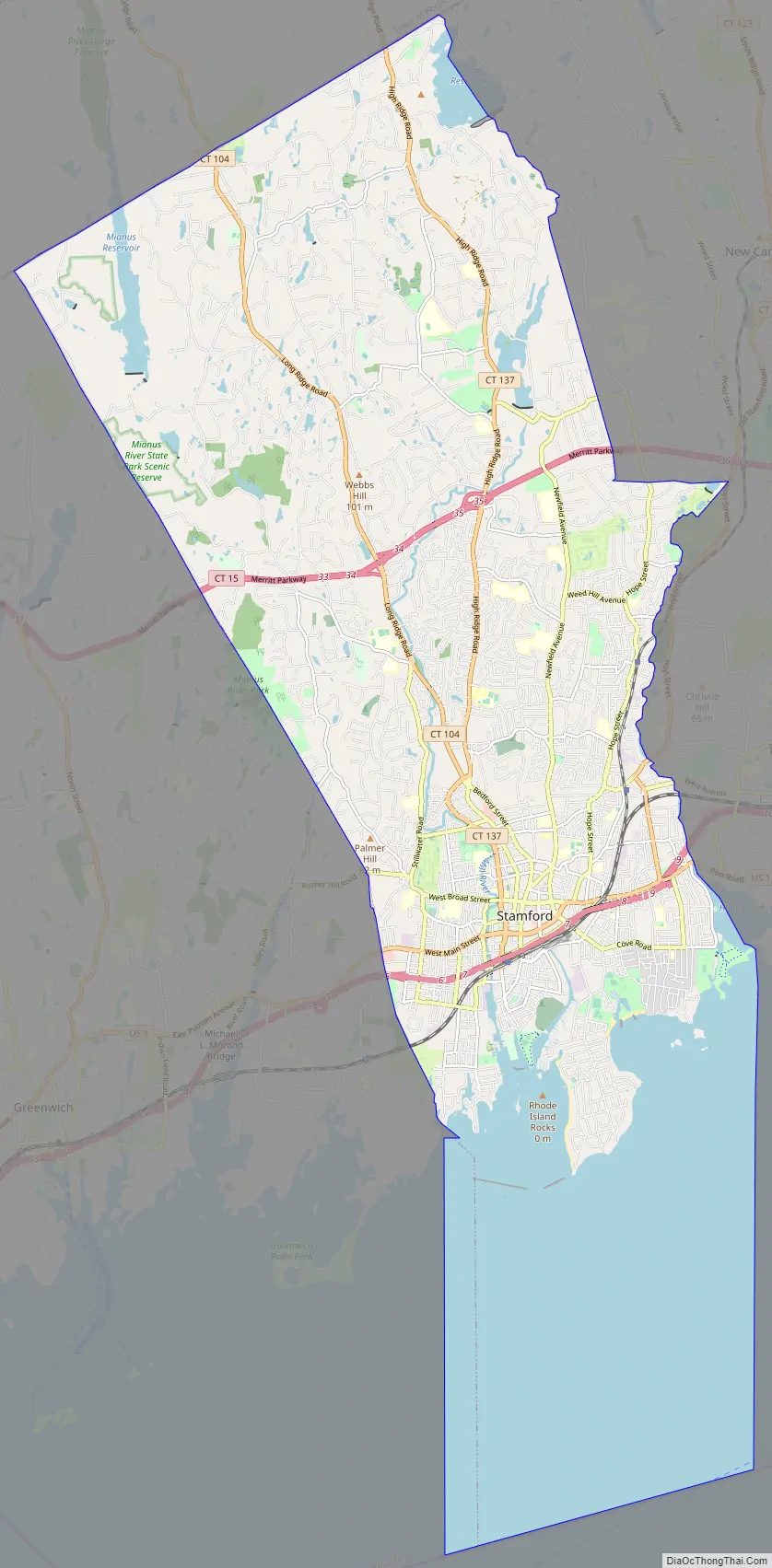
Stamford Road Map
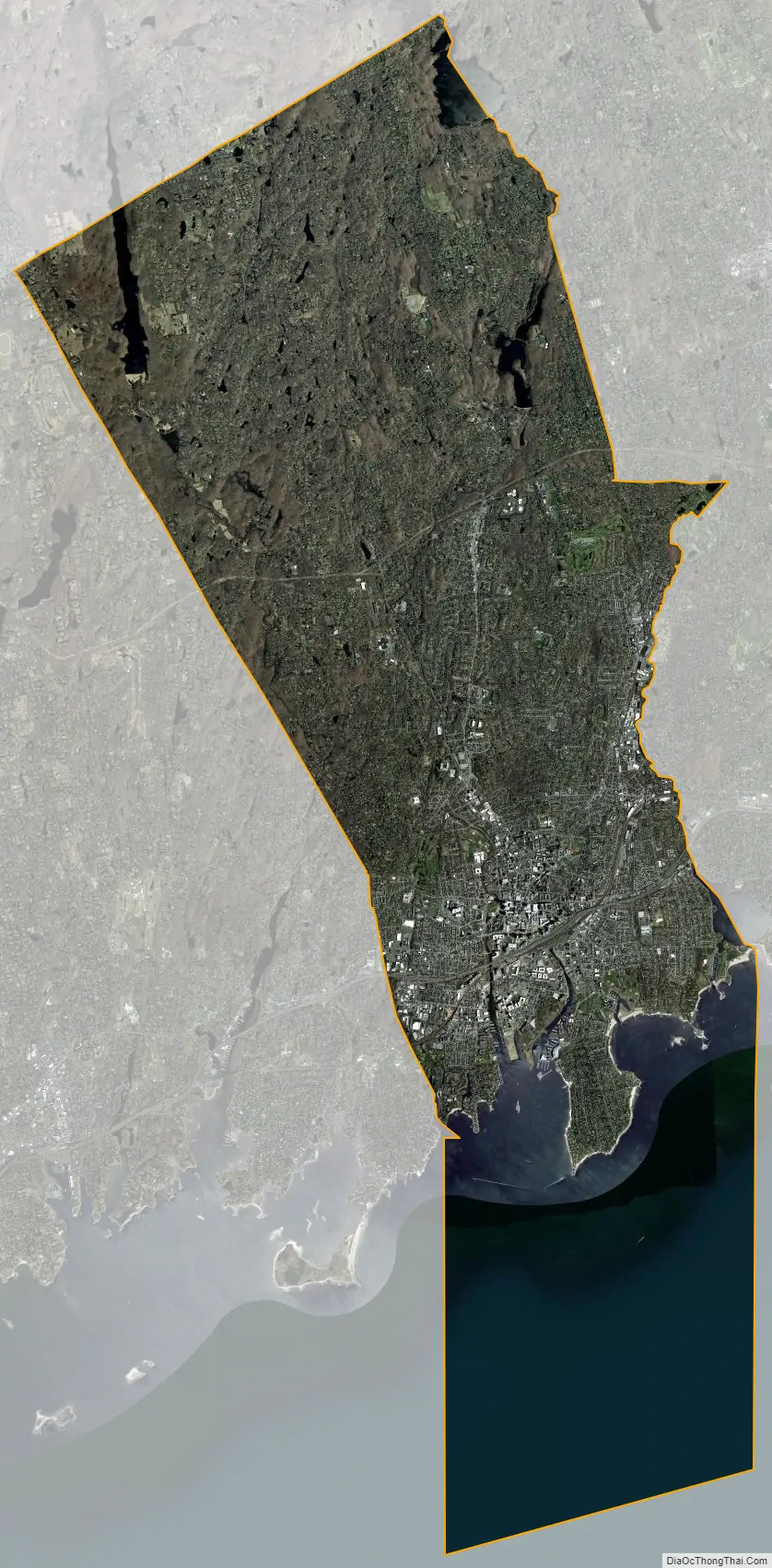
Stamford city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the city has an area of 52.09 square miles (134.9 km), of which 37.62 square miles (97.4 km) is land and 14.41 square miles (37.3 km) is water. Stamford is the state’s largest city by area. The population density was 3,101.9 inhabitants per square mile (1,197.7/km) in 2010. The city is halfway between Manhattan and New Haven at approximately 38 miles (60 kilometers) from each; it is 79 miles (127 kilometers) from the state capital of Hartford.
Stamford is near the southwestern point of Connecticut, on Long Island Sound; it is part of the Gold Coast. Stamford comprises approximately 45 distinct neighborhoods and villages, and two historic districts, including Cove, East Side, Downtown, North Stamford, Glenbrook, West Side, Turn of River, Waterside, Springdale, Belltown, Ridgeway, Newfield, South End, Westover, Shippan, Roxbury, and Palmers Hill.
North of the Merritt Parkway is considered the North Stamford section of the city, encompassing its largest land mass though it is the least densely populated. North Stamford functionally and legally acts as one municipality with the city of Stamford. Stamford borders Pound Ridge, New York to the north, the Long Island Sound to the south, Greenwich to the west, Darien to the east, and New Canaan to the northeast.
The city has islands in Long Island Sound: Cove Island, Grass Island, Greenway Island, Jack Island, and Cuties Island (also known as Vincent Island). Cove Island is a prominent beach and recreation area. It lies approximately 9 miles (14 kilometers) from Norwalk.
Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, Stamford has a temperate climate (Cfa), with long, hot summers, and cool to cold winters, with precipitation spread fairly evenly throughout the year. Like the rest of coastal Connecticut, it lies in the broad transition zone between the colder continental climates of the northern U.S. and southern Canada to the north, and the warmer temperate and subtropical climates of the middle and south Atlantic states to the south.
The warm/hot season in Stamford is from mid-April through early November. Late day thundershowers are common in the hottest months (June, July, August, September), despite the mostly sunny skies. The cool/cold season is from late November though mid-March. Winter weather is far more variable than summer weather along the Connecticut coast, ranging from sunny days with higher temperatures to cold and blustery conditions with occasional snow. As on much of the Connecticut coast and nearby Long Island, some of the winter precipitation is rain or a mix and rain and wet snow. Stamford averages about 30 inches (75 cm) of snow annually, compared to inland areas like Hartford and Albany that average 45–60 inches (110–150 cm).
Although infrequent, tropical cyclones (hurricanes/tropical storms) have struck Connecticut and the Stamford metropolitan area. Hurricane landfalls have occurred along the Connecticut coast in 1903, 1938, 1944, 1954 (Carol), 1960 (Donna), Hurricane Gloria in 1985, and Hurricane Sandy in 2012.
Stamford lies in USDA garden zone 7a. It averages about 90 days annually with freeze. Coastal Connecticut is the broad transition zone where so-called “subtropical indicator” plants and other broadleaf evergreens can be cultivated. As such, Southern Magnolias, Needle Palms, Windmill palm, Loblolly Pines, and Crape Myrtles are grown in private and public gardens. As in much of coastal Connecticut, Long Island, and coastal New Jersey, the growing season is rather long in Stamford, averaging 210 days from April 8 to November 5 according to the National Weather Service in Bridgeport.
See also
Map of Connecticut State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming