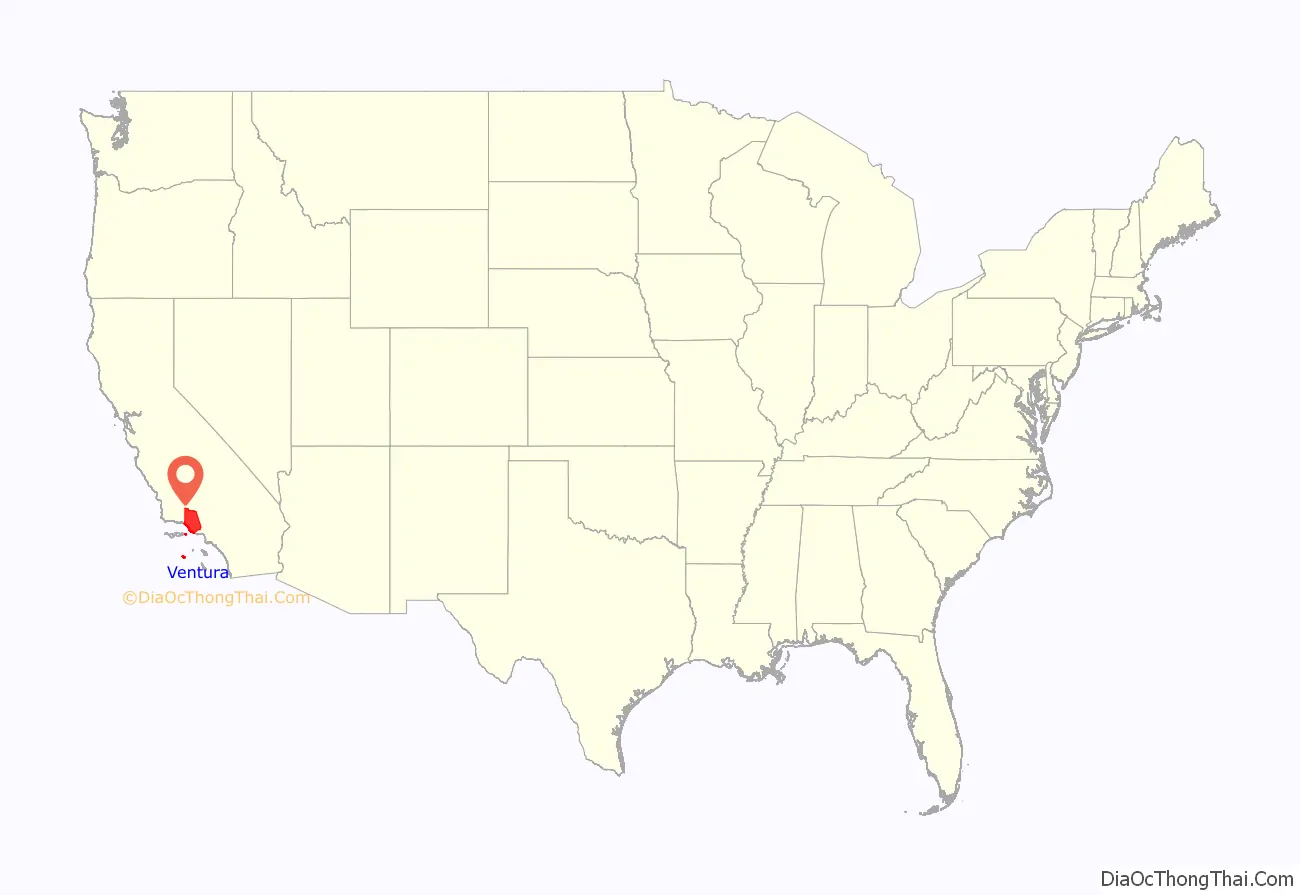
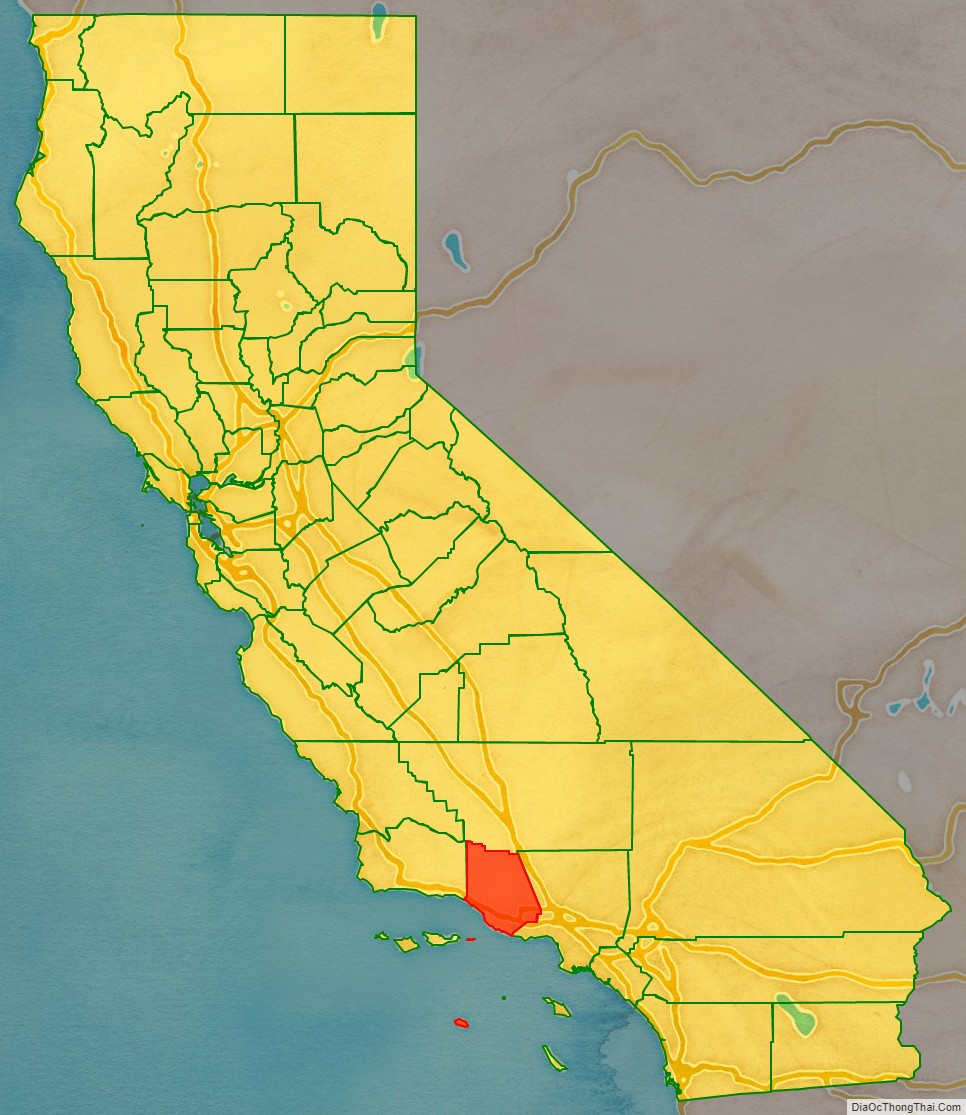
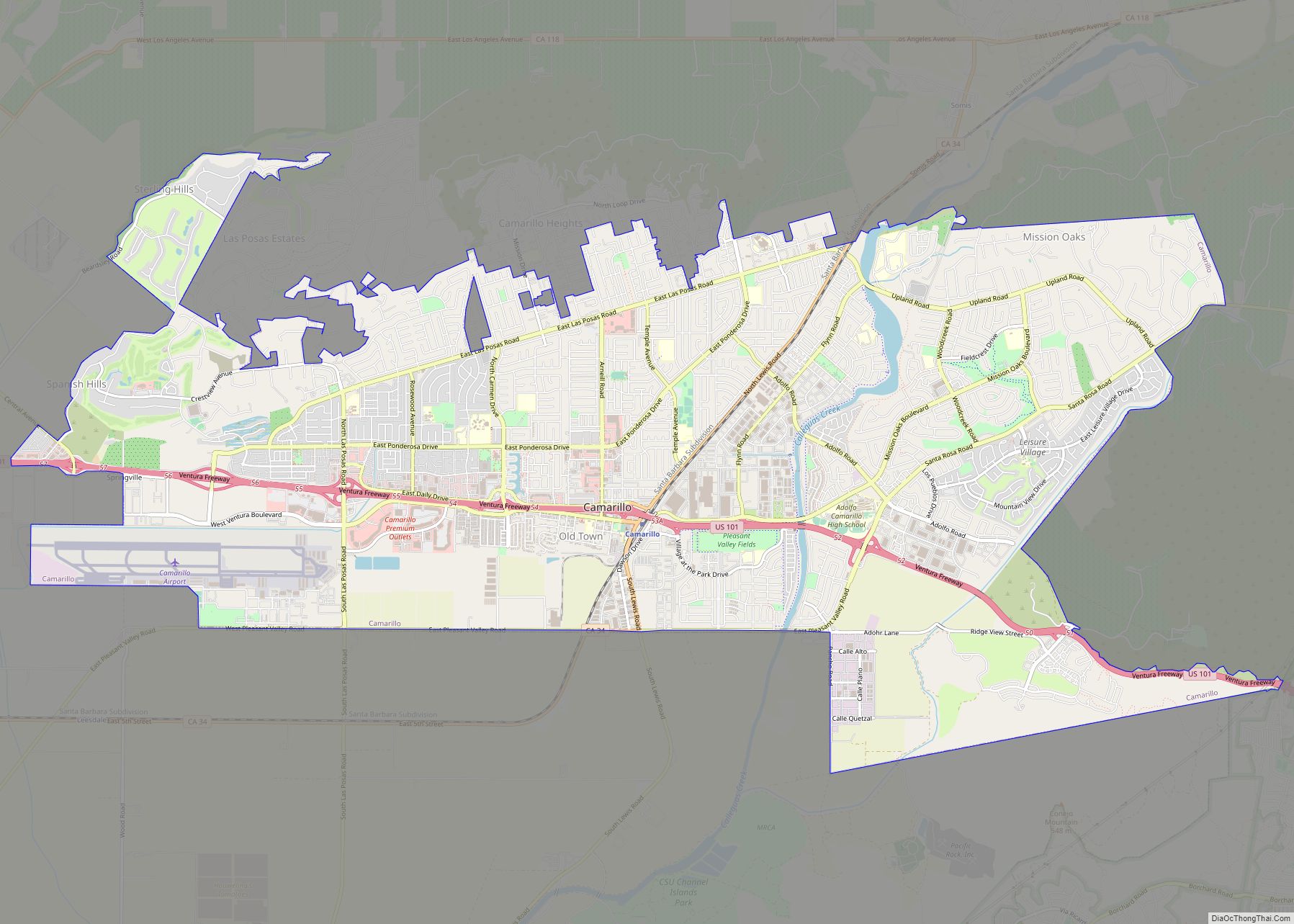
Ventura County (/vɛnˈtʊərə/ (listen)) is a county in the southern part of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 843,843. The largest city is Oxnard, and the county seat is the city of Ventura.
Ventura County comprises the Oxnard–Thousand Oaks–Ventura, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of the Greater Los Angeles area (Los Angeles-Long Beach, CA Combined Statistical Area). It is also considered the southernmost county along the California Central Coast.
Two of the Channel Islands are part of the county: Anacapa Island, which is the most visited island in Channel Islands National Park, and San Nicolas Island.
| Name: | Ventura County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 06-111 |
| State: | California |
| Founded: | 1872 |
| Named for: | Mission San Buenaventura, which was named after Saint Bonaventure |
| Seat: | Ventura |
| Largest city: | Oxnard (population) Thousand Oaks (area) |
| Total Area: | 2,208 sq mi (5,720 km²) |
| Land Area: | 1,843 sq mi (4,770 km²) |
| Total Population: | 843,843 |
| Population Density: | 458/sq mi (177/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−8 (Pacific Time Zone) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) |
| Website: | www.countyofventura.org |
Ventura County location map. Where is Ventura County?
History
Pre-colonial period
Ventura County was historically inhabited by the Chumash people, who also settled much of Santa Barbara and San Luis Obispo Counties, with their presence dating back 10,000–12,000 years. The Chumash were hunter-gatherers, fishermen, and also traders with the Mojave, Yokuts, and Tongva Indians. The Chumash are also known for their rock paintings and for their great basketry. Chumash Indian Museum in Thousand Oaks has several reconstructed Chumash houses (‘apa) and there are several Chumash pictographs in the county, including the Burro Flats Painted Cave in Simi Valley. The plank canoe, called a tomol in Chumash, was important to their way of life. Canoe launching points on the mainland for trade with the Chumash of the Channel Islands were located at the mouth of the Ventura River, Mugu Lagoon and Point Hueneme. This has led to speculations among archeologists of whether the Chumash could have had a pre-historic contact with Polynesians. According to diachronic linguistics, certain words such as tomolo’o (canoe) could be related to Polynesian languages. The dialect of the Chumash language that was spoken in Ventura County was Ventureño.
Several place names in the county has originated from Chumash, including Ojai, which means moon, and Simi Valley, which originates from the word Shimiyi and refers to the stringy, thread-like clouds that typify the region. Others include Point Mugu from the word Muwu (meaning “beach”), Saticoy from the word Sa’aqtiko’y (meaning “sheltered for the wind”), and Sespe Creek from the word S’eqp’e (meaning “kneecap”).
Spanish period
In October 1542, the expedition led by Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo anchored in an inlet near Point Mugu; its members were the first Europeans to arrive in the area that would become Ventura County.
Active occupation of California by Spain began in 1769. Gaspar de Portolà led a military expedition by land from San Diego to Monterey, passing through Ventura County in August of that year. A priest with the expedition, Father Juan Crespí, kept a journal of the trip and noted that the area was ideal for a mission to be established and it was a “good site to which nothing is lacking”. Also on this expedition was Father Junípero Serra, who later founded a mission on this site.
On March 31, 1782, the Mission San Buenaventura was founded by Father Serra. It is named after Saint Bonaventure, one of the early intellectual founders of the Franciscan order. The town that grew up around the mission was originally named San Buenaventura (and retains the name officially), it has been known as Ventura since 1891.
In the 1790s, the Spanish Governor of California began granting land concessions to Spanish Californians who were often retiring soldiers. These concessions were known as ranchos and consisted of thousands of acres of land that were used primarily as ranch land for livestock. In Ventura County, Rancho Simi was granted in 1795 and Rancho El Conejo in 1802. Fernando Tico was granted Ojai and part of Ventura by Gov. Alvarado.
Mexican period
In 1822, California was notified of Mexico’s independence from Spain and the Governor of California, the Junta, the military in Monterey and the priests and neophytes at Mission San Buenaventura swore allegiance to Mexico on April 11, 1822. California land that had been vested in the King of Spain was now owned by the nation of Mexico.
By the 1830s, Mission San Buenaventura was in a decline with fewer neophytes joining the mission. The number of cattle owned by the mission dropped from first to fifteenth ranking in the California Missions. The missions were secularized by the Mexican government in 1834. The Mexican governors began granting land rights to Mexican Californians, often retiring soldiers. By 1846, there were 19 rancho grants in Ventura County. In 1836, Mission San Buenaventura was transferred from the Church to a secular administrator. The natives who had been working at the mission gradually left to work on the ranchos. By 1839, only 300 Indians were left at the Mission and it slipped into neglect.
Several outhouses dating back to the 1800s were discovered in July 2007, at a site that had been cleared to prepare for development. The area proved to be a treasure trove for archaeologists who braved the lingering smell in the dirt to uncover artifacts that showed heavy utilization by mission inhabitants, Indians, early settlers and Spanish and Mexican soldiers.
American period
The Mexican–American War began in 1846 but its effect was not felt in Ventura County until 1847. In January of that year, Captain John C. Frémont led the California Battalion into San Buenaventura to find that the Europeans had fled, leaving only the Indians in the Mission. Fremont and the Battalion continued south to sign the Treaty of Cahuenga with General Andrés Pico. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo formally transferred California to the United States in 1848.
By 1849, a constitution had been adopted for the California territory. The new Legislature met and divided the pending state into 27 counties. At the time, the area that would become Ventura County was the southern part of Santa Barbara County.
The 1860s brought many changes to the area. A drought caused many of the ranchos to experience financial difficulties and most were divided, sub-divided and sold. Large sections of land were bought by eastern capitalists based on favorable reports of petroleum deposits. A United States Post Office was opened at Mission San Buenaventura in 1861. On April 1, 1866, the town of San Buenaventura was incorporated, becoming the first officially recognized town in what would become Ventura County.
On January 1, 1873, Ventura County was officially split from Santa Barbara County, bringing a flurry of change. That same year, a courthouse and wharf were built in San Buenaventura. A bank was opened and the first public library was created. The school system grew, with the first high school opening in 1890.
Other towns were starting in the county. A plan for Hueneme (later Port Hueneme) was recorded in 1874, and Santa Paula‘s plan was recorded in 1875. The community of Nordhoff (later renamed Ojai) was started in 1874. Bardsdale, Fillmore, Piru, and Montalvo were established in 1887. 1892 saw Simi (later Simi Valley), Somis, Saticoy, and Moorpark. Oxnard was a latecomer, not being established until 1898.
The Southern Pacific Railroad laid tracks through San Buenaventura in 1887. For convenience in printing their timetables, Southern Pacific shortened San Buenaventura to Ventura. The Post Office soon followed suit. While the city remains officially known as San Buenaventura, it is more commonly referred to as Ventura. The rail line to Northern California originally went through Saugus, Fillmore and Santa Paula, providing a boom to those communities along the line. In 1905, Tunnel #26 was completed between Chatsworth and Corriganville near Simi Valley, shortening the rail route. At a length of 7,369 feet (2,246 m), Tunnel #26 was the longest tunnel ever constructed in its day. This tunnel joined to the railroad spur coming the other direction from Montalvo through Camarillo, Moorpark and Simi Valley, making the contemporary main line used today. One stop along the way, at a 90-degree turn, was at a sugar beet processing factory. The factory bore the name of its absentee owners, the Oxnard Brothers. A small community of farm and factory workers grew near the train stop. That community, now bearing the name of the factory shortened to the one word train stop Oxnard, has become the largest city in Ventura County.
Oil has been known in Ventura County since before the arrival of the Europeans, as the native Chumash people used tar from natural seeps as a sealant and waterproofing for baskets and canoes. In the 1860s, several attempts were made to harvest the petroleum products under Ventura County but none were financially successful, and the oil speculators eventually changed from oil to land development. In 1913, oil exploration began in earnest, with Ralph Lloyd obtaining the financial support of veteran oil man Joseph B. Dabney. Their first well, named “Lloyd No. 1”, was started on January 20, 1914. The well struck oil at 2,558 feet (780 m) but was destroyed when it went wild. Other wells met a similar fate, until 1916, when a deal was struck with the Shell Oil Company. 1916 was the year that the large South Mountain Oil Field was discovered; other deals followed with General Petroleum in 1917 and Associated Oil Company in 1920. At its peak, the largest oil field in the county, the Ventura Avenue oilfield, discovered in 1919 in the hills north of Ventura, was producing 90,000 barrels (14,000 m) of oil a day, with annual production of over 1.5 million barrels. More oil fields came online in the 1920s and 1930s, with the Rincon field, the second largest, in 1927, and the adjacent San Miguelito in 1931.
In the early hours of the morning of March 12–13, 1928, the St. Francis Dam collapsed, sending nearly 12,500 million U.S. gallons (47 gigaliters) of water rushing through the Santa Clarita Valley killing as many as 600 people, destroying 1,240 homes and flooding 7,900 acres (32 km) of land, devastating farm fields and orchards. This was the single largest disaster to strike Ventura County and the second largest, in terms of lives lost, in the state.
Modern period
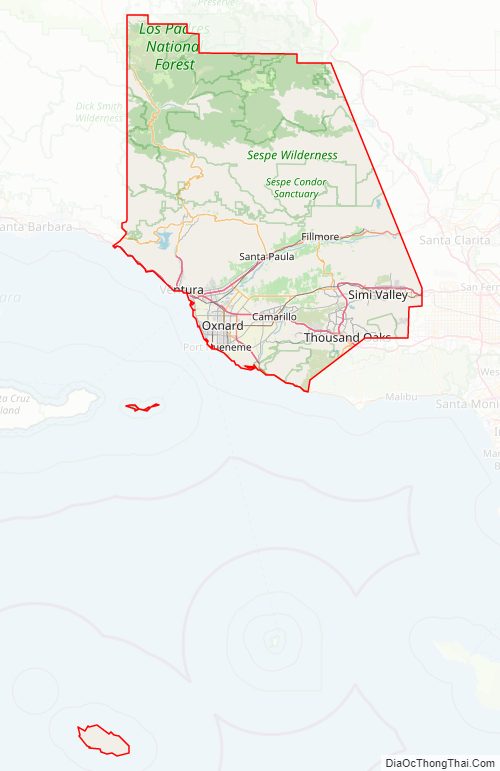
Ventura County can be separated into two major parts, East County and West County, which are divided by the Conejo Grade. East County consists of all cities east of the Conejo Grade. Geographically East County is the end of the Santa Monica Mountains, in which the Conejo Valley is located, and where there is a considerable increase in elevation. Communities which are considered to be in the East County are Thousand Oaks, Newbury Park, Lake Sherwood, Hidden Valley, Santa Rosa Valley, part of Westlake Village, Oak Park, Moorpark, and Simi Valley. A majority of these communities are in the Conejo Valley.
West County, which is everything west of the Conejo Grade, consists of communities such as Camarillo, Oxnard, Somis, Point Mugu, Port Hueneme, Ventura, Ojai, Santa Paula, and Fillmore. West County consists of some of the first developed cities in the county. The largest beach communities are located in West County on the coastline of the Channel Islands Harbor.
Starting in the mid-20th century, there was a large growth in population in the East County, moving from the San Fernando Valley in Los Angeles and out into the Conejo and Simi Valleys. Part of the Conejo Valley is situated in Los Angeles County. This part consists of Calabasas, Hidden Hills, Agoura Hills, Agoura, and Westlake Village. The other half of the Conejo Valley, which belongs to Ventura County, consists of Lake Sherwood, Hidden Valley, Oak Park, Thousand Oaks, and Newbury Park, which was formerly an unincorporated area that is now the most westerly part of Thousand Oaks. Many working-class people migrated to this area during the 1960s and 1970s out of East and Central Los Angeles. As a result, there was a large growth in population into the Conejo Valley and into Ventura County through the U.S. Route 101 corridor. Making the U.S. 101 a full freeway in the 1960s, and the expansions that followed, helped make commuting to Los Angeles easier and opened the way for development westward. The communities that have seen the most substantial development are Calabasas, Hidden Hills, Agoura Hills, Westlake Village, Thousand Oaks, and Newbury Park. The neighboring East County area of Simi Valley saw its already considerable population of nearly 60,000 inhabitants in 1970 grow to over 100,000 over the following two decades.
Development moved farther down the U.S. 101 corridor and sent population rising in West County cities as well. The largest population growth there has been in Camarillo, Oxnard, and Ventura. Development in the East County and along the US 101 corridor is rare today, because most of these cities, such as Thousand Oaks and Simi Valley, are approaching build-out. Although the area still has plenty of open space and land, almost all of it is in greenbelts between the cities. Because of this, its private low-key location, its country feel, and its proximity to Los Angeles, the Conejo Valley area has become a very attractive place to live. Like most areas of Ventura County, it once had relatively inexpensive real estate, but prices have risen sharply. For example, real estate in Newbury Park has increased in price by more than 250% in the last 10 years.
The Thomas Fire was a massive wildfire that affected Ventura and Santa Barbara Counties, and one of multiple wildfires that ignited in Southern California in December 2017. It burned approximately 281,893 acres (440 sq mi; 114,078 ha), becoming the largest wildfire in modern California history, before it was fully contained on January 12, 2018.
The Thomas Fire destroyed at least 1,063 structures, while damaging 280 others; and the fire caused over $2.176 billion (2018 USD) in damages, including more than $204.5 million in suppression costs, becoming the seventh-most destructive wildfire in state history. The agriculture industry suffered at least $171 million in losses due to the Thomas Fire. Southern California Edison paid the county over $11 million in claims related to damages and costs since its equipment was likely associated with one ignition point of the fire near Santa Paula.
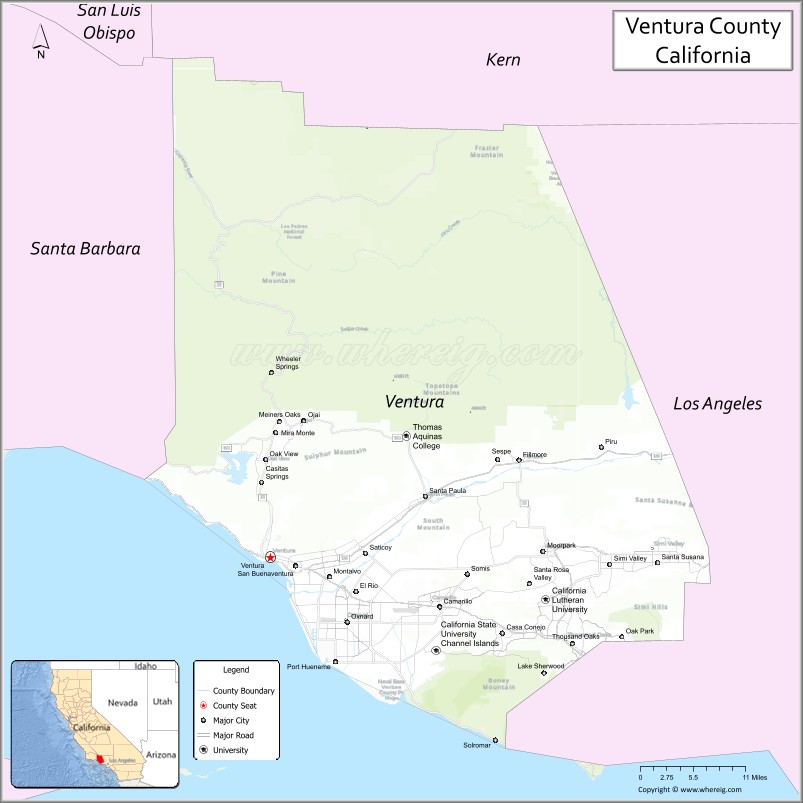
Ventura County Road Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 2,208 square miles (5,720 km), of which 1,843 square miles (4,770 km) is land and 365 square miles (950 km) (16.5%) is water.
Parts of the county are on the Oxnard Plain which includes the cities of Oxnard, Camarillo, Port Hueneme and much of Ventura. Other cities and communities lie in the intermountain valleys of the Transverse Range. The Santa Clara River Valley is the most prominent valley, while other valleys include Conejo Valley, Simi Valley, Santa Rosa Valley, Tierra Rejada Valley and Las Posas Valley. Other parts of the county are on small coastal mountains, such as the Santa Ynez Mountains, Simi Hills, Santa Monica Mountains and the Piru Mountains. Most of the population of Ventura County lives in the southern portion of the county. The major population centers are the Oxnard Plain and the Simi and Conejo Valleys. In local media, the county is usually split between the eastern portion, generally associated with the San Fernando Valley, and the western portion, often referred to as “Oxnard-Ventura”. To the east is Los Angeles County.
Because the total amount of precipitation is small, conserving water and obtaining water from additional sources outside of Ventura County are vital concerns. The climate, though mostly mild and dry, varies because of the variations in topography through for instance differences in elevation and physical geography. The Santa Clara River is the principal waterway. Lake Casitas, an artificial reservoir, is the largest body of water.
The highest peaks in the county include Mount Pinos (8831′, 2697 m), Frazier Mountain (8017′, 2444 m), and Reyes Peak (7525′, 2294 m) in the Transverse Ranges. The uplands are well-timbered with coniferous forests, and receive plentiful snow in the winter. Mount Pinos is sacred to the Chumash Indians. It is known to them as Iwihinmu, and was considered to be the center of the universe; being the highest peak in the vicinity, it has unimpeded views in three directions.
The USDA Economic Research Service rated Ventura County the most desirable county to live in the 48 contiguous states, using six metrics of climate (“mild, sunny winters, temperate summers, low humidity”), topographic variation, and access to water, “that reflect environmental qualities most people prefer.”
Physical geography
There are 555,953 acres (224,986 ha) outside of national forest land in Ventura County, which means that 53 percent of the county’s total area is made up of national forest. Of the land outside of national forest land, approximately 59 percent is agricultural and 17.5 percent urban. North of Highway 126, the county is mountainous and mostly uninhabited, and contains some of the most unspoiled, rugged and inaccessible wilderness remaining in southern California. Most of this land is in the Los Padres National Forest, and includes the Chumash Wilderness in the northernmost portion, adjacent to Kern County, as well as the large Sespe Wilderness and portions of both the Dick Smith Wilderness and Matilija Wilderness (both of these protected areas straddle the line with Santa Barbara County). All of the wilderness areas are within the jurisdiction of Los Padres National Forest.
The coastal plain was formed by the deposition of sediments from the Santa Clara River and from the streams of the Calleguas-Conejo drainage system. It has a mean elevation of fifty feet (15 m), but at points south of the Santa Clara River, the elevation is as much as 150 feet (46 m), and at points north of the river, as much as 300 feet (91 m). The coastal plain is generally known as the Oxnard Plain with the part that centers on Camarillo lying east of the Revelon Slough is called Pleasant Valley. Most of the arable land in the county is found on the coastal plain. Small coastal mountains rim Ventura County on its landward side. They range in elevation from 50 feet (15 m) along the coast south of the coastal plain, to about 3,100 feet (940 m) in the Santa Monica Mountains. The Santa Ynez Mountains, the Topatopa Mountains, and the Piru Mountains make up the northern boundary of the coastal plain, the Santa Susana Mountains are alongside the eastern boundary of the county, and the Simi Hills and the Santa Monica Mountains are along the southern border with Los Angeles County. South Mountain and Oak Ridge are low and long mountains that separate Santa Clara Valley from the Las Posas Valley and Simi Valley. The Camarillo Hills and the Las Posas Hills extend from Camarillo to Simi Valley and separate the Las Posas-Simi area from the Santa Rosa Valley and Tierra Rejada Valley.
The intermountain valley of the Santa Clara River is the most prominent valley in the county and trends east–southwest. The Santa Clara River drains an area of 1,605 square miles (4,160 km) and flows from its headwaters in Los Angeles to where it empties into the Pacific. Its principal tributaries are Piru Creek, Santa Paula Creek, and Sespe Creek. The valley of the Ventura River is a narrow valley north of Ventura. Ojai Valley is connected to the Ventura River Valley by San Antonio Creek. The small Upper Ojai Valley, east of Ojai Valley and 300 to 500 feet (91 to 152 m) higher, drains to the Ventura River on the west and to Santa Paula Creek on the east. Ojai and Upper Ojai Valleys are surrounded by mountains and are rich agricultural areas. The Ventura River flows south and drains an area of 226 square miles (590 km). Over South Mountain and Oak Ridge, south of the Santa Clara River, are Las Posas Valley and Simi Valley. Las Posas Valley extends eastward from the Oxnard Plain almost to Simi Valley, which is in the east end of Ventura County. The city of Simi Valley is bounded on the east by the Santa Susana Mountains and on the south by the Simi Hills. To the south, over the Camarillo- and Las Posas Hills, are Santa Rosa- and Tierra Rejada Valleys, which extend from Camarillo eastward for ten miles (16 km). In the hills south of Santa Rosa Valley is the broad Conejo Valley. Santa Rosa Valley, Conejo Valley, Simi Valley, and Tierra Rejada Valley are drained by Calleguas Creek and its principal tributary, Conejo Creek. These creeks originate in the Santa Susana and Santa Monica Mountains.
The county’s diverse 43-mile (69 km) coastline features a variety of terrain. There are many State beaches: Emma Wood, San Buenaventura, McGrath, and Mandalay State Beach. Other beaches include Channel Islands Beach, Solimar Beach, Oxnard Beach Park, and Silver Strand Beach. While Point Mugu State Park is known for its steep coastal terrain with little beach access, nearby County Line Beach in the south coast community of Solromar is part of the fabled Malibu coastline. Ventura County has plenty of other surf spots along the coast including the notable surf spot, Rincon Point, on the Santa Barbara County-line.
The Channel Islands in Ventura County are Anacapa and San Nicholas Islands.
Climate
Ventura County has a considerable range in climate because of differences in topography between one part of the county and another. Rainfall is limited in summer and crops have to be irrigated. The average annual temperature is near 60 °F at low elevations near the ocean, in the 50s over most of the northern two-thirds of the county, and less than 45 °F in the Topatopa Mountains. The annual range in temperature is between 70 °F and 80 °F on the Coastal Plain and as much as 100 °F in the interior. For July, the average maximum temperature is between 70 °F and 80 °F on the Coastal Plain but exceeds 90 °F in the upper part of the Ventura- and Cuyama River Valleys. For January, the average minimum temperature is near 40 °F on the coast but in the lower 30s and upper 20s in the northern parts of Ventura County. No temperature data are available for the highest point in the county, Mount Pinos. The length of the growing season ranges more than 300 days near the coast to less than 175 days in the coldest part in northern Ventura County. In both the northern and southern ends of the county, the annual precipitation totals between ten and fifteen inches. In the Topatopa Mountains, the annual total is more than thirty-three inches. The drier parts of the county get less than five inches of rain annually, and the higher and wetter parts get more than 60 inches annually. Measureable amounts of rainfall in Ventura County are reported on thirty to thirty-five days annually, and half an inch or more on six to twelve days annually. In the northern parts of Ventura County, snowfall averages five inches or more per year, and along the northern border and Mount Pinos, more than twenty inches.
Automobile emissions account for most of the air pollution. Other sources include chemical plants, gasoline stations, paint and cleaning products.
Adjacent counties
- Santa Barbara County, California — west
- Kern County, California — north
- Los Angeles County, California — east
National protected areas
- Angeles National Forest (part)
- Channel Islands National Park (part)
- Hopper Mountain National Wildlife Refuge
- Los Padres National Forest (part)
- Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area (part)
- Dick Smith Wilderness (part)
Rivers
Rivers in Ventura County include:
- Los Sauces Creek
- Madrianio Creek
- Padre Juan Canyon
- Ventura River
- Manuel Canyon
- Cañada Larga
- Cañada de Alisos
- Coyote Creek
- Lake Casitas
- Laguna Creek
- Willow Creek
- Santa Ana Creek
- Roble-Casitas Canal
- Poplin Creek
- Deep Cat Lake
- East Fork Coyote Creek
- West Fork Coyote Creek
- Lake Casitas
- Matilija Creek
- Rattlesnake Creek
- Lime Creek
- Murietta Creek
- Middle Fork Matilija Creek
- Upper North Fork Matilija Creek
- North Fork Matilija Creek (This and Matilija Creek