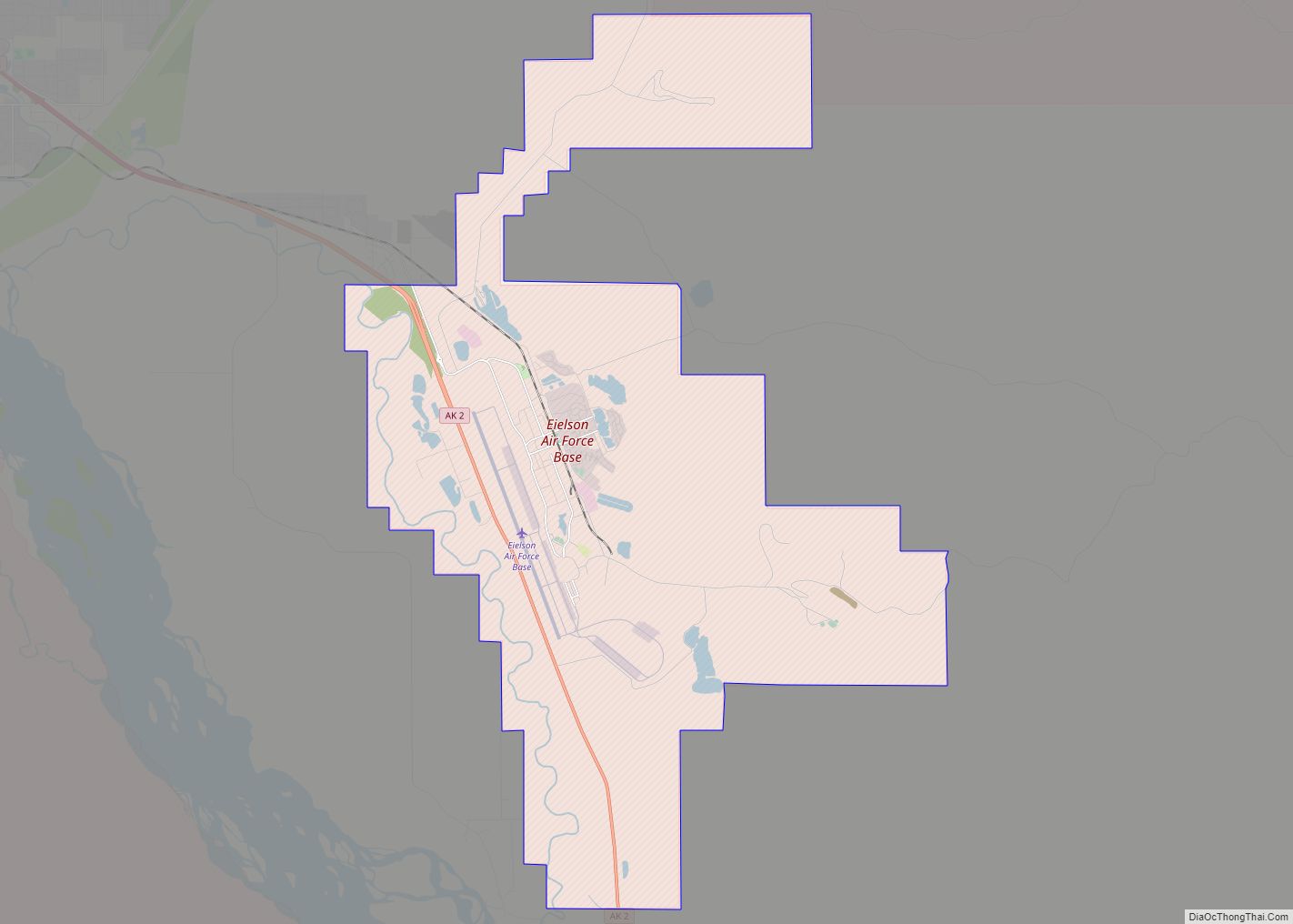
Eielson Air Force Base (IATA: EIL, ICAO: PAEI, FAA LID: EIL) is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located approximately 26 miles (42 km) southeast of Fairbanks, Alaska, and just southeast of Moose Creek, Alaska. It was established in 1943 as Mile 26 Satellite Field and redesignated Eielson Air Force Base on 13 January 1948. It has been a Superfund site since 1989. Eielson AFB was named in honor of polar pilot Carl Ben Eielson.
Its host unit is the 354th Fighter Wing (354 FW) assigned to the Eleventh Air Force of the Pacific Air Forces. The 354 FW’s primary mission is to support RED FLAG-Alaska, a series of Pacific Air Forces commander–directed field training exercises for U.S. Forces, joint offensive counter-air, interdiction, close-air support, and large force employment training in a simulated combat environment. These exercises are conducted on the Joint Pacific Alaskan Range Complex (JPARC) with air operations flown out of Eielson and its sister installation, Elmendorf Air Force Base.
Eielson projects to have 54 Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II combat aircraft assigned to the installation, of which the first two aircraft arrived on 21 April 2020. The last of the aircraft arrived in April 2022. The planes come with an estimated 3,500 personnel, to include airmen and their families as well as civilian personnel. The F-35 program increases the number of military personnel at Eielson by approximately 50%, which is a significant change for a base once on the brink of closure.
| Name: | Eielson AFB CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Fairbanks North Star Borough |
| Elevation: | 167 metres (548 ft) |
| FIPS code: | 0221370 |
| Website: | www.eielson.af.mil |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
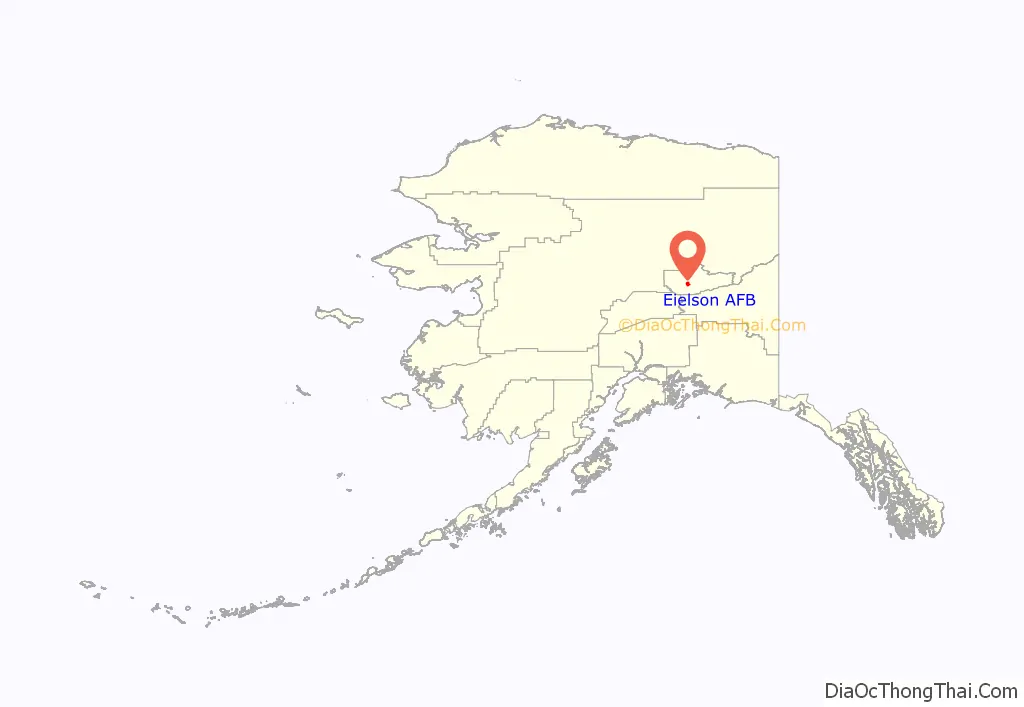
Eielson AFB location map. Where is Eielson AFB CDP?
History
World War II
On 7 June 1943, the Western Defense Command ordered construction of a new airfield near present-day Fort Wainwright, then a United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) airfield named after Major Arthur K. Ladd. Because of its hazard-free approaches and relatively flat terrain, surveyor reports indicated a site a little more than 25 miles southeast of Ladd Army Airfield to be the best in the vicinity for military aviation. The field became known as “Mile 26” because of its proximity to a United States Army Signal Corps telegraph station and a Richardson Highway milepost marker using the same designation.
A month later, contractors and civilian crews from Ladd Field started laying out the new airfield. Actual construction began on 25 August 1943. Crews built two parallel runways, 165 feet (50 m) across and 6,625 feet (2,019 m) long. Other facilities included an operations building, housing for 108 officer and 330 enlisted personnel, and a ten-bed dispensary. The garrison and airfield totaled about 600 acres (2.4 km). Completed on 17 October 1944, the 14-month project cost about eight-million dollars.
Operational uses of Mile 26 were few. Ladd Field served as the debarkation point for the Alaska-Siberia Ferry Route of the Lend-Lease program and was the hub of activity. Lend-lease aircraft would occasionally land at Mile 26, but there are no records indicating any lend-lease aircraft used the airfield to depart for the Soviet Union. Mile 26 closed when the war ended.
Cold War
The base reopened in September 1946, once again as a satellite of Ladd Field. The first USAAF operational unit assigned to Eielson was the 57th Fighter Group, equipped successively with P-38 Lightnings, P/F-51 Mustangs, F-80 Shooting Stars, and F-94 Starfire aircraft. The 57th FG was inactivated on 13 April 1953. On 1 December 1947 Strategic Air Command B-29 Superfortress bombers arrived at Mile 26 Field with the deployment of the 97th Bombardment Wing, Very Heavy, from Smoky Hill Air Force Base, Kansas. The wing reported to Fifteenth Air Force, Strategic Air Command (SAC), although the Yukon Sector of the Alaskan Air Command controlled its operations. At the end of the Alaskan deployment the wing returned to Kansas on 12 March 1948.
A year later Eielson moved from under the shadow of Ladd Field when the Alaskan Air Command assumed organizational control. Also in the fall of 1947, Colonel Jerome B. McCauley assumed duties as commander. The primary missions of Mile 26 were to support Arctic training for USAF tactical and strategic units, as well as defend the base itself.
Headquarters USAF General Order 2, dated 13 January 1948, redesignated Mile 26 as Eielson Air Force Base. It was named for Carl Ben Eielson, an Alaska aviation pioneer who was killed, along with his mechanic Earl Borland, in the crash of their Hamilton H-45 aircraft in 1929. Eielson and Borland were attempting a rescue flight to an icebound ship in the Bering Sea when they were killed. On 1 April 1948, the Eielson Air Force Base Wing (Base Complement) was formed. The host-unit subsequently would be dubbed the Eielson Air force Base Bomb Wing, and finally, in January 1949, the 5010th Wing. Colonel John L. Nedwed, the third commander of the base since it fell under Alaskan Air Command fifteen months before, became the first to head the 5010th.
For the next 34 years, the 5010th (alternately known as the Wing, Composite Wing, Air Base Wing, and lastly, Combat Support Group) served as host-unit at Eielson. Construction boomed at Eielson during the 1950s. Many of the facilities used today were built at that time, including Amber Hall, the Thunderdome, Base Exchange, Gymnasium, Theater, some of the schools, and many of the dormitories.
The 720th Fighter-Bomber Squadron, equipped with F-86 Sabres, was deployed to Eielson during 1954–55. The 720th was a part of the 450th Fighter-Bomber Wing stationed at Foster Air Force Base, Texas. The 720th was replaced by the 455th Fighter-Bomber Squadron (323d FBW), stationed at Bunker Hill Air Force Base, Indiana.
The Air Defense Command deployed interceptors to Eielson during the 1960s. Det. 3, 317th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron from Elmendorf Air Force Base deployed F-102 Delta Daggers and F-106 Delta Darts to the base between 1960 and 1969.
During the height of the Cuban Missile Crisis of October 1962, Eielson-based Lockheed U-2 pilot Charles Maultsby was allegedly blinded by the aurora borealis while collecting radiation from Soviet nuclear weapons tests over the North Pole and accidentally strayed 300 miles (480 km) into Soviet airspace, into Chukotka. Soviet MiG interceptors were sent to intercept the plane before he was escorted back to U.S. territory by nuclear-armed F-102 interceptors.
The Cold War saw the use of Eielson’s expansive reservation as a maneuver area for the U.S. Army. The 1960s 171st Infantry Brigade (Separate) and 172nd Infantry Brigade (Separate) both trained here, both on a regular and extensive basis, not to mention units of the Alaska National Guard. Later in the 70s mid 80s the 172nd Infantry Brigade (the 171st Infantry Brigade was inactivated on 13 November 1972), followed by the 6th Infantry Division when the 172nd Infantry Brigade itself was deactivated on 15 April 1986 (it was reactivated in Alaska on 17 April 1998, and inactivated in Iraq on 14 December 2006)
Today the 1st Brigade 25th Infantry Division and the 4th Brigade 25th Infantry Division can be found training there. Several important large scale winter field problems have been conducted here over the years as well, seeing large numbers of U.S. Army ground combat units from the Contiguous United States lower 48 states, U.S. Marine Corps units, and Canadian Armed Forces troops.
375th/58th Strategic Weather Squadron
The 375th Weather Reconnaissance Squadron, from the 308th Bombardment Group at Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma, arrived at Eielson on 5 March 1949. The 308th flew WB-29 Superfortresses. The unit was redesignated the 58th Strategic Weather Squadron on 21 February 1951 as part of the 303d Bombardment Wing at Davis-Monthan Air Force Base, Arizona.
The 58th Weather Squadron remained at Eielson until 8 August 1958.
6th Strategic Wing
In July 1960, the Strategic Air Command (SAC) stationed the 4157th Combat Support Group (later Strategic Wing) at Eielson. The 6th Strategic Wing (6 SW) replaced the 4157 SW on 25 March 1967, relocating from Walker Air Force Base, New Mexico after its closure.
The 6th SW flew RC–135 strategic reconnaissance missions with an assigned squadron, and, with KC–135 Stratotankers deployed to Eielson from SAC, Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC), and the Air National Guard (ANG), conducted Alaska Tanker Task Force (ATTF) missions to support reconnaissance and numerous exercises for the USAF and U.S. Navy.
The 6th SW remained at Eielson AFB until 1992.
343d Composite Wing
A new chapter for the base began 1 October 1981 when the 343d Composite Wing replaced the 5010th as Eielson’s host unit. Flying squadrons assigned to the new wing included the 25th Tactical Air Support Squadron (TASS) and the 18th Fighter Squadron (18 FS). The 25 TASS, at Eielson since 1971, flew O-2 Skymaster and OV-10 Bronco aircraft until its inactivation in 1989; the newly assigned 18 FS operated A-10 Thunderbolt IIs until it converted to F-16 Fighting Falcons in 1991.
In 1984, the 343d Composite Wing was redesignated a Tactical Fighter Wing. Seven years later, in 1991, it was redesignated as the 343d Wing. Also that year, the 343d gained a second flying unit, the 11th Tactical Air Support Squadron (11 TASS), which flew OA-10 aircraft.
354th Fighter Wing
On 20 August 1993, the 354 FW replaced the 343d Wing. No personnel or equipment were affected by the change. Prior to its shutdown, the 343d was the oldest surviving air combat unit in Alaska with a lineage dating back to the Aleutian Campaign. The 18 FS, whose history also dated back to World War II, remained active, but the 355 FS replaced the 11th TASS.
Another change involved the 3rd Fighter Training Squadron, which was replaced by the 353rd Fighter Squadron (later redesignated as a Combat Training Squadron).
Within the first year of its arrival the 354 FW hosted an Arctic combat search and rescue exercise between the United States, Canada, and Russia. Ironically, these were the same countries that took part in the search and recovery efforts that followed the fatal crash of Carl Ben Eielson and his mechanic, Earl Borland, in 1930 as they were attempting to fly relief supplies to the Nanuk.
The 343d FW 3d Fighter Training Squadron was replaced by the 353d Fighter Training Squadron from the 354th FW. The 3d Fighter Training Squadron had its origins with the 3d Tactical Fighter Squadron at Korat Royal Thai Air Force Base, Thailand, being formed in March 1973. The 3d TFS received its A-7D Corsair II aircraft from the then deployed 353d Tactical Fighter Squadron of the 354th Tactical Fighter Wing, deployed to Korat from Myrtle Beach Air Force Base, South Carolina.
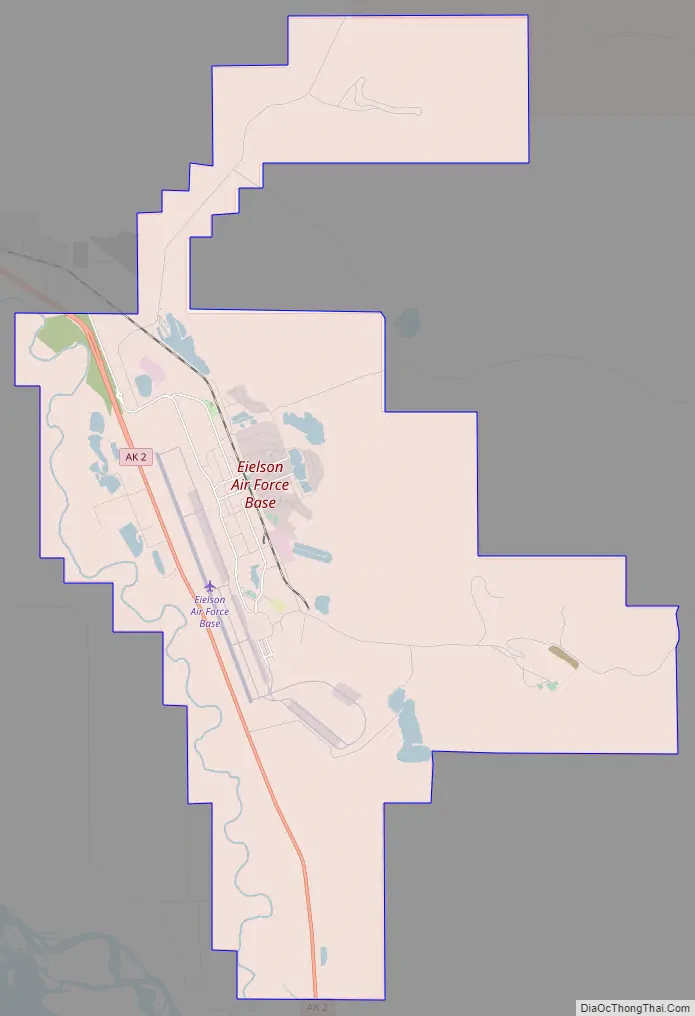
Eielson AFB Road Map
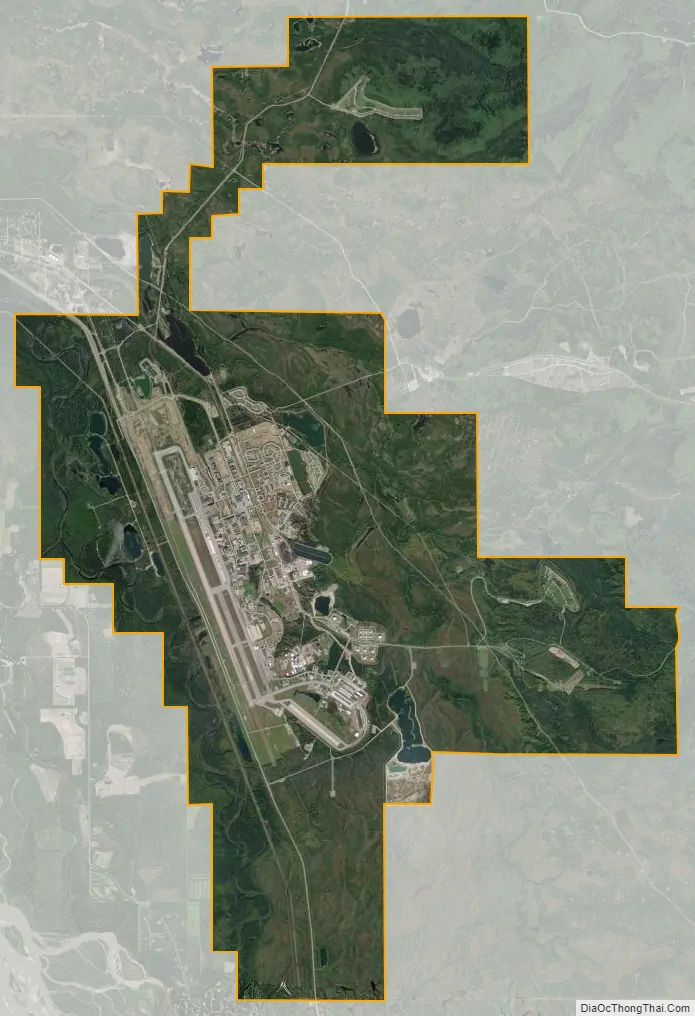
Eielson AFB city Satellite Map
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming