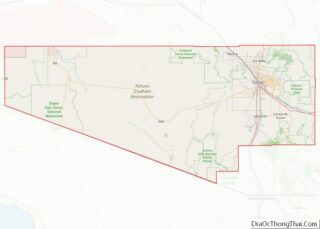
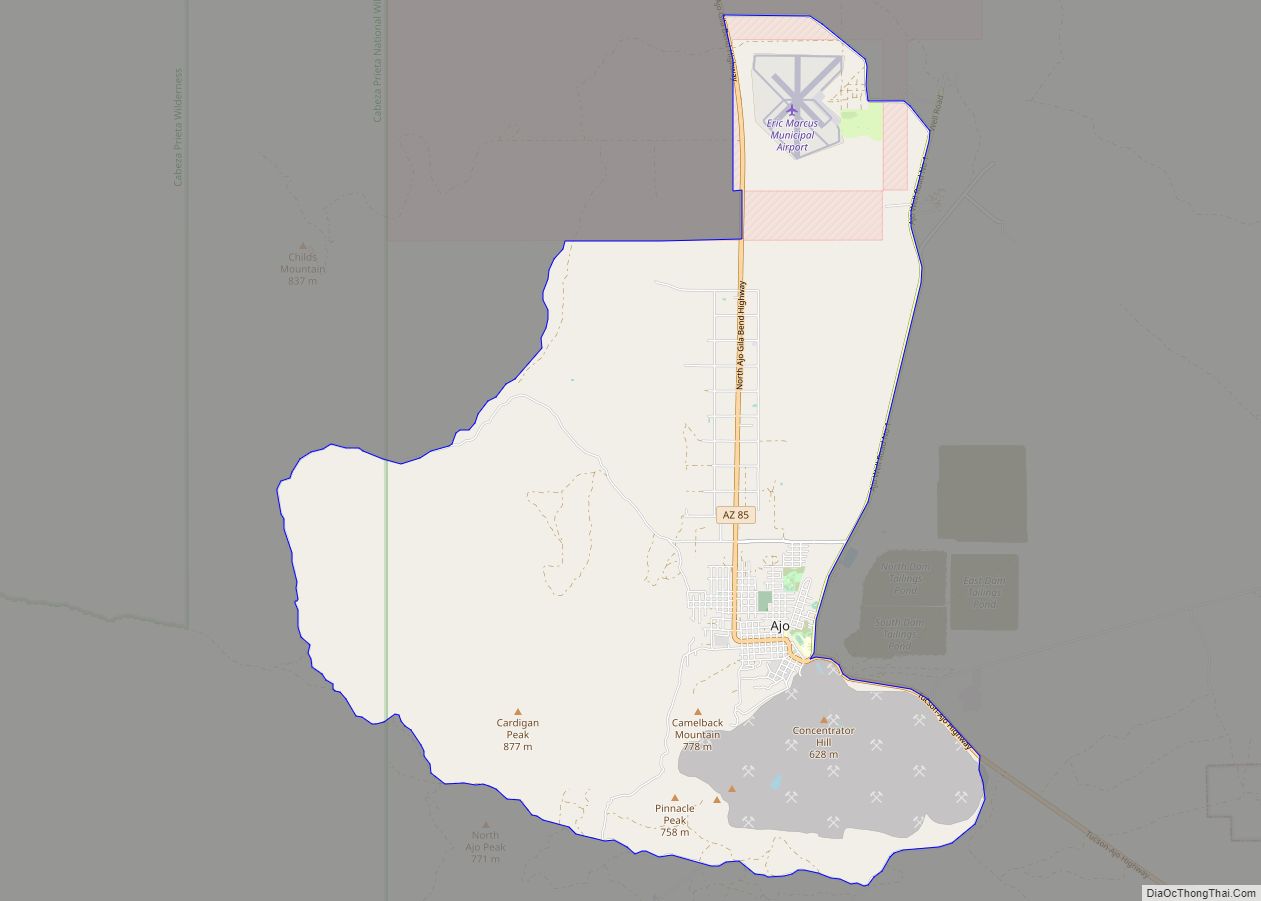
Ajo (/ˈɑːhoʊ/ AH-hoh) is an unincorporated community in Pima County, Arizona, United States. It is the closest community to Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument. The population was 3,304 at the 2010 census. Ajo is located on State Route 85 just 43 miles (69 km) from the Mexican border.
| Name: | Ajo CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Arizona |
| County: | Pima County |
| Elevation: | 1,759 ft (536 m) |
| Total Area: | 33.33 sq mi (86.32 km²) |
| Land Area: | 33.33 sq mi (86.32 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 3,039 |
| Population Density: | 91.19/sq mi (35.21/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 85321 |
| Area code: | 520 |
| FIPS code: | 0400870 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0000538 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Ajo location map. Where is Ajo CDP?
History
Ajo is the Spanish word for garlic (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈaxo]). The Spanish may have named the place using the familiar word in place of the similar-sounding O’odham word for paint (oʼoho). The Tohono O’odham people obtained red paint pigments from the area.
Native Americans, Spaniards, and Americans have all extracted mineral wealth from Ajo’s abundant ore deposits. In the early nineteenth century, there was a Spanish mine nicknamed “Old Bat Hole” that was abandoned due to Indian raids. Tom Childs, Sr., found the deserted mine complete with a 60-foot (18 m) shaft, mesquite ladders, and rawhide buckets in 1847. He did not stay long at that time, because he was on his way to the silver mines near Magdalena de Kino, Sonora.
Thirty-five years later, Childs and his son returned with a friend and started developing the abandoned mine.
High-grade native copper made Ajo the first copper mine in Arizona. Soon the Arizona Mining & Trading company, formed by Peter R. Brady, a friend of Childs, worked the rich surface ores, shipping loads around Cape Horn for smelting in Swansea, Wales, in the mid-1880s. The mine closed when a ship sank off the coast of Patagonia. Long supply lines and the lack of water discouraged large mining companies
With the advent of new recovery methods for low-grade ore, Ajo boomed. In 1911, Col. John Campbell Greenway, a Rough Rider and star Yale athlete, bought the New Cornelia mine from John Boddie. He became general manager of the Calumet and the Arizona mining company and expanded it on a grand scale. The Tucson, Cornelia and Gila Bend Railroad was built from Gila Bend to serve the mining industry and was in service from 1916 to 1985. In 1921, Phelps Dodge, the nation’s largest copper company, bought New Cornelia and the mine became the New Cornelia Branch of Phelps Dodge, managed by Michael Curley. For several decades more than 1,000 employees worked for Phelps Dodge in the open pit mine. In 1983 union-affiliated mine employees went on strike. The mine continued with non-union labor for a short while before stopping production in 1985.
The town was originally segregated, with neighborhoods called Indian Village and Mexican Town for the non-white residents. Ajo is home to many retired people, Border Patrol agents, and young families.
During the construction of a new border wall in 2019–2020, many workers lived in the RV parks, hotels and rental houses.
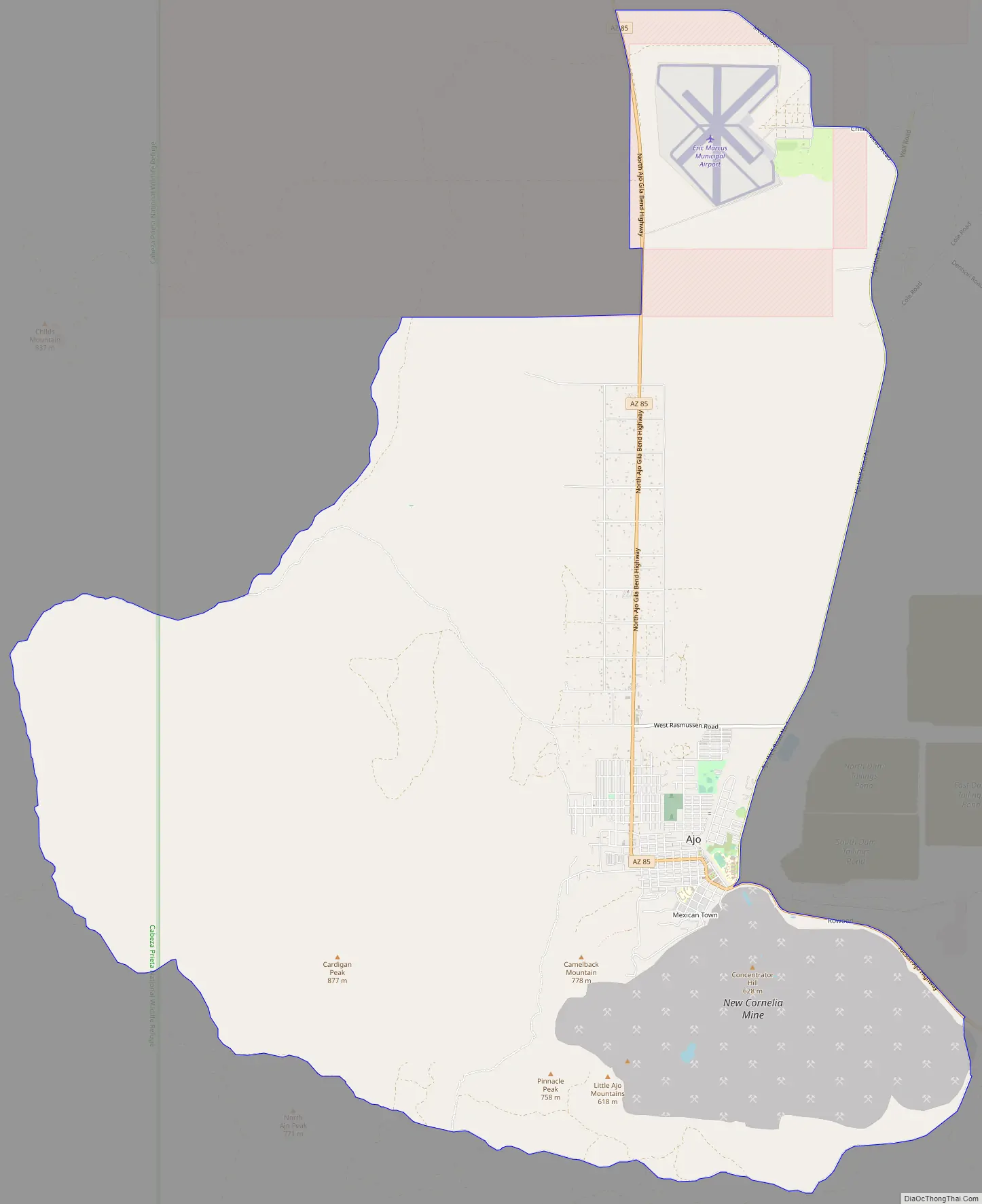
Ajo Road Map
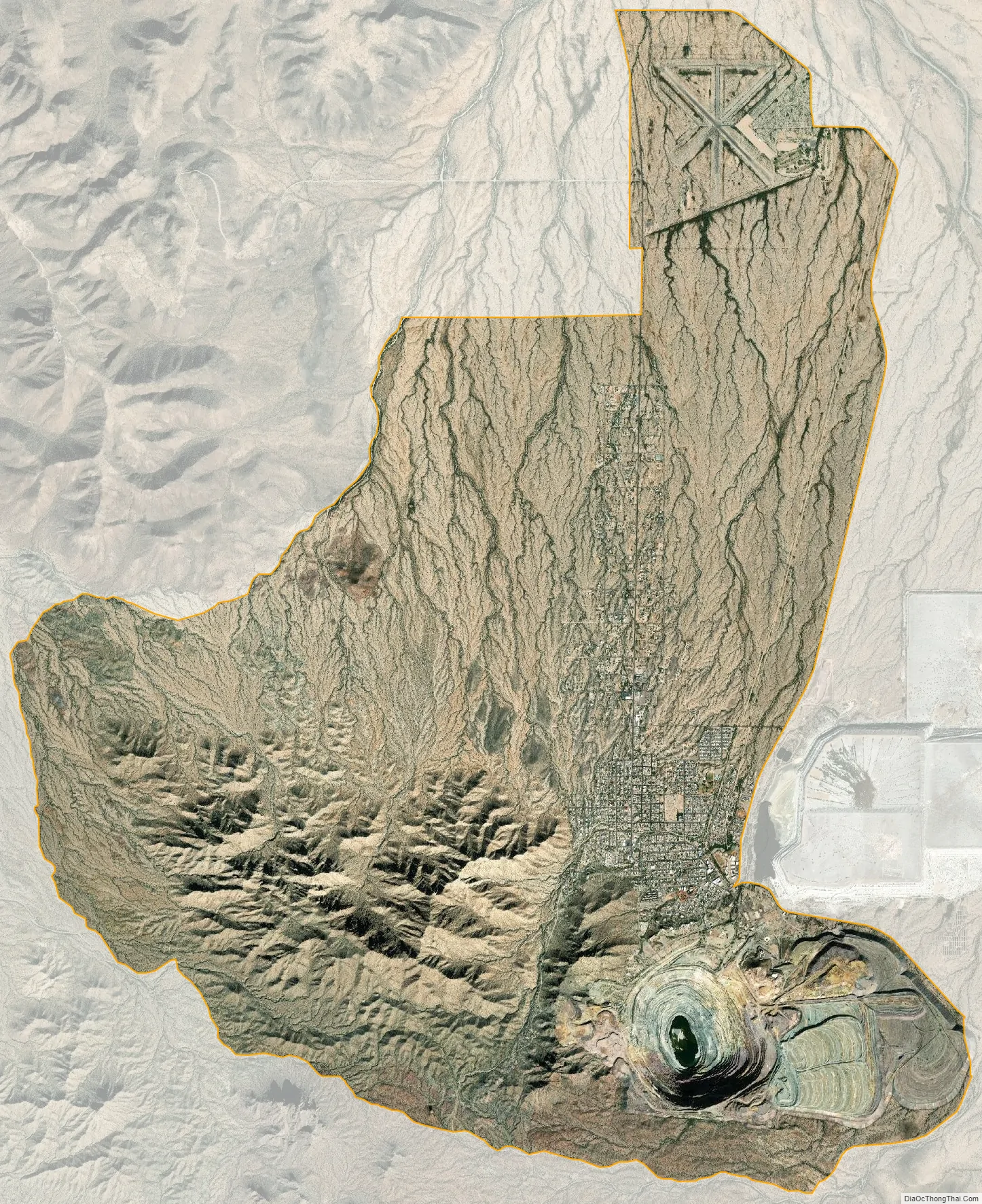
Ajo city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the census-designated place has a total area of 28.1 square miles (72.8 km), all land. The census definition of the area was created by the Census Bureau for statistical purposes and may not precisely correspond to local understanding of the area with the same name. Ajo is located in the Little Ajo Mountains.
Plants of the Sonoran Desert thrive around Ajo, including saguaros and ocotillos. The Ajo lily or desert lily, an onion-like plant, also grows in the area.
The mineral ajoite was first found at the New Cornelia Mine, Ajo. The rare mineral papagoite was also first described in the New Cornelia mine.
Climate
This area has a large amount of sunshine year round due to its stable descending air and high pressure. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Ajo has a hot desert climate, abbreviated BWh on climate maps. Rainfall is very low except during occasional monsoonal or frontal incursions, and is especially minimal between April and June. Since 1914 the wettest calendar year has been 1946 with 15.33 inches (389 mm) – including a record daily fall of 4.15 inches (105 mm) on 18 September – and the driest 1928 with 3.33 inches (85 mm). Temperatures are very hot from April to October and mild to warm from November to March, with extremes ranging from 17 °F (−8 °C) on 22 January 1937 during that month’s record Western cold wave, to 117 °F (47 °C) on 31 July 1995.
See also
Map of Arizona State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming