Los Angeles County, officially the County of Los Angeles (Spanish: Condado de Los Ángeles), and sometimes abbreviated as L.A. County, is the most populous county in the United States, with 9,861,224 residents estimated in 2022. Its population is greater than that of 40 individual U.S. states. Comprising 88 incorporated cities and many unincorporated areas within a total area of 4,083 square miles (10,570 km), it is home to more than a quarter of Californians and is one of the most ethnically diverse U.S. counties. The county’s seat, Los Angeles, is the second most populous city in the United States, with about 3.9 million residents.
| Name: | Los Angeles County |
|---|---|
| FIPS code: | 06-037 |
| State: | California |
| Founded: | 1850 |
| Seat: | Los Angeles |
| Largest city: | Los Angeles |
| Total Area: | 4,751 sq mi (12,310 km²) |
| Land Area: | 4,058 sq mi (10,510 km²) |
| Total Population: | 9,861,224 |
| Population Density: | 2,430/sq mi (940/km²) |
| Time zone: | UTC−8 (Pacific Time Zone) |
| Summer Time Zone (DST): | UTC−7 (Pacific Daylight Time) |
| Website: | lacounty.gov |
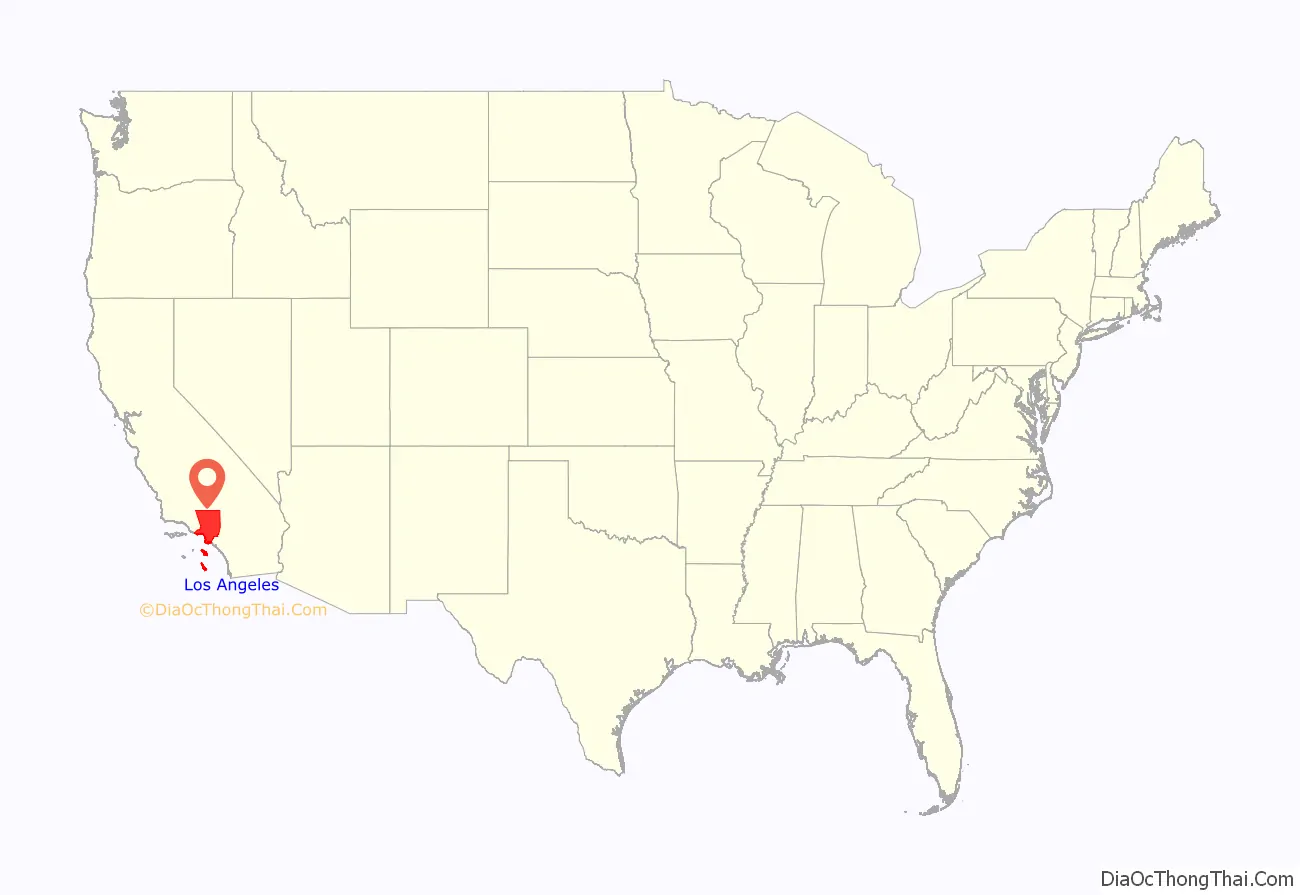
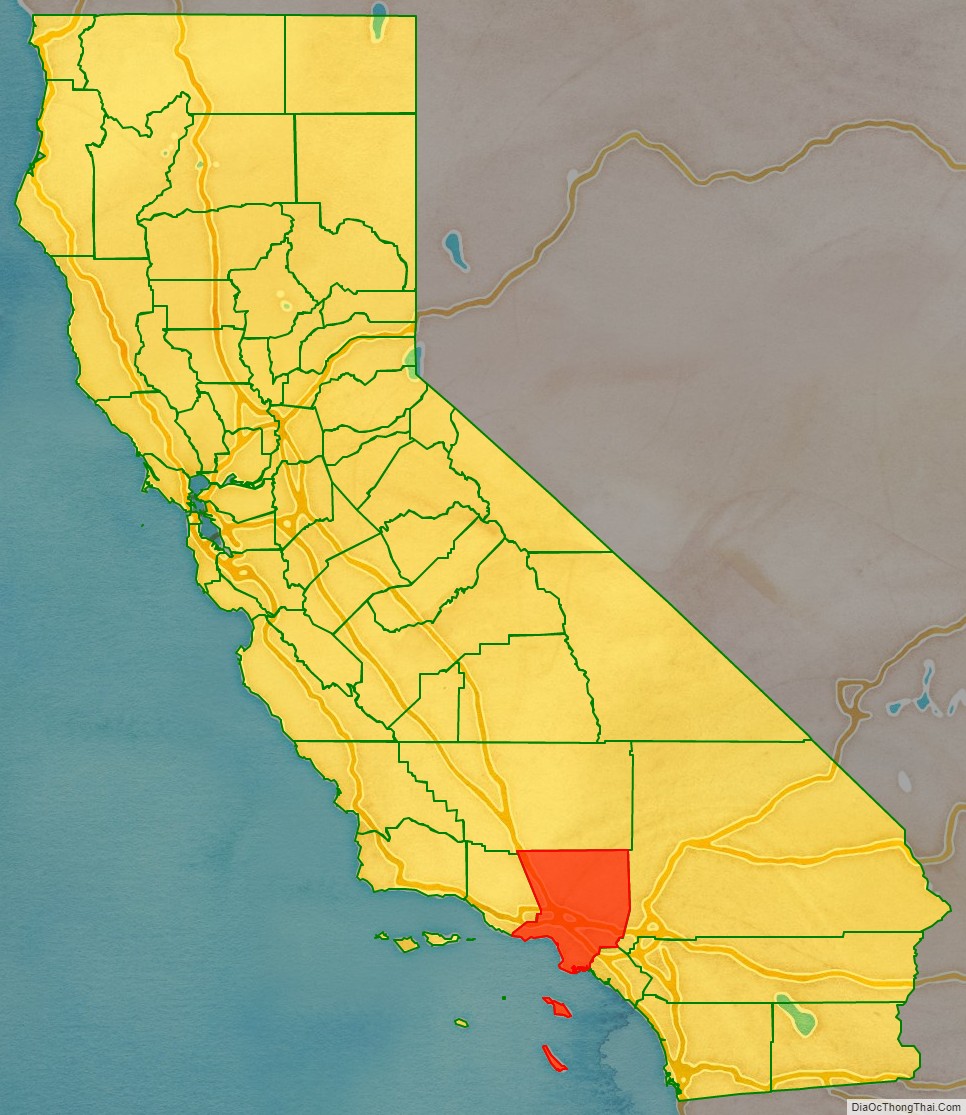
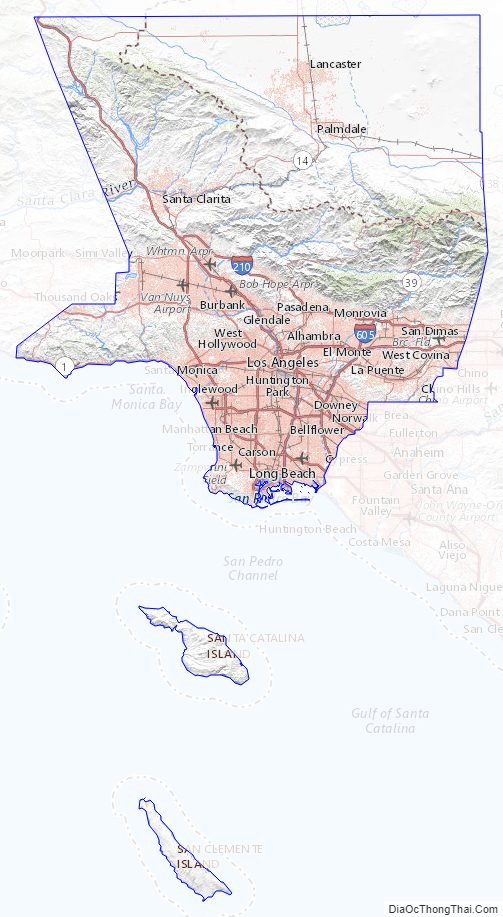
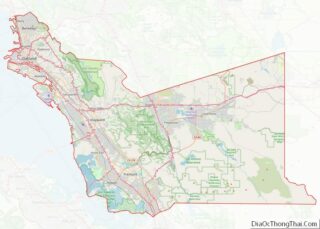
Los Angeles County location map. Where is Los Angeles County?
History
Los Angeles County is one of the original counties of California, created at the time of statehood in 1850. The county originally included parts of what are now Kern, San Bernardino, Riverside, Inyo, Tulare, Ventura, and Orange counties. In 1851 and 1852, Los Angeles County stretched from the coast to the state line of Nevada. As the population increased, sections were split off to organize San Bernardino County in 1853, Kern County in 1866, and Orange County in 1889.
Prior to the 1870s, Los Angeles County was divided into townships, many of which were amalgamations of one or more old ranchos. They were:
- Azusa – encompassed the foothill communities east of the San Gabriel River, including present-day Covina and Duarte
- El Monte – encompassed communities in the Whittier Narrows area, including present-day El Monte, La Puente, as well as Monterey Park
- Azusa and El Monte Townships – merged for the 1870 census
- City of Los Angeles – then consisting solely of its four-league Spanish land grant
- Los Angeles Township – consisted of areas surrounding the City of Los Angeles, including the San Fernando Valley and present-day West Los Angeles and East Los Angeles. Most of this area has now been annexed to the city of Los Angeles.
- Los Nietos – consisted of areas south of the Whittier Narrows and Puente Hills south to present-day Long Beach, centered on the early settlement at Los Nietos. Some of this area is now in Orange County
- San Jose – consisted of the eastern portions of the county drained by San Jose Creek, including what is now the cities of Pomona, Claremont and Walnut
- San Gabriel – consisted of the western San Gabriel Valley and foothill communities, including present-day Alhambra and Pasadena. Centered on the Mission San Gabriel
- Santa Ana – consisted of what is now northern and central Orange County, including what is now Fullerton, Huntington Beach and the City of Orange. Centered on Santa Ana).
- For the 1870 census, Anaheim district was enumerated separately
- San Juan – consisted of what is now southern Orange County. Centered on Mission San Juan Capistrano
- San Pedro – consisted of the present-day South Bay communities, Compton and western Long Beach. Centered on the wharf of San Pedro. Renamed Wilmington Township by 1870).
- Tejon – consisted of all of northern Los Angeles County and what is now southern Kern County. Centered on Fort Tejon
- When Kern County was formed, the portion of the township remaining in Los Angeles County became Soledad Township. More recently, statewide droughts in California have further strained Los Angeles County’s water security
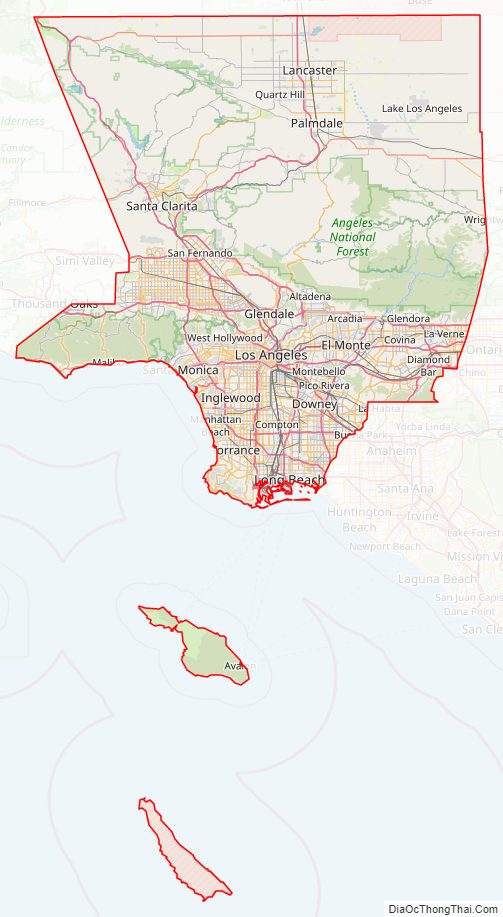
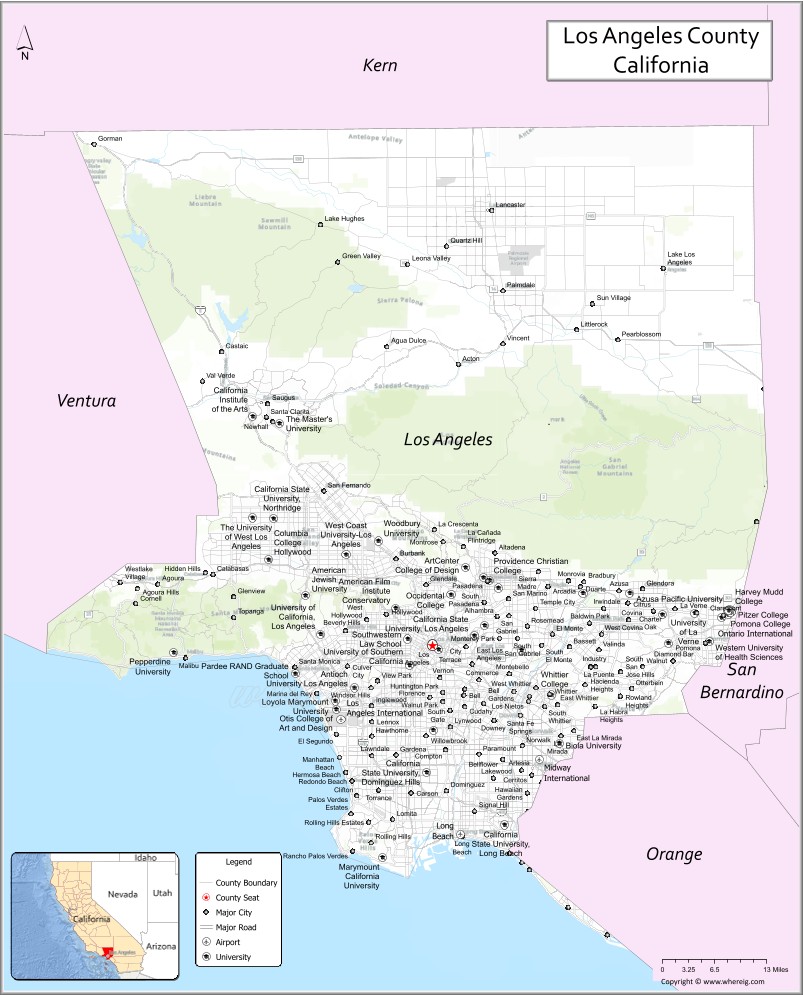
Los Angeles County Road Map
Geography
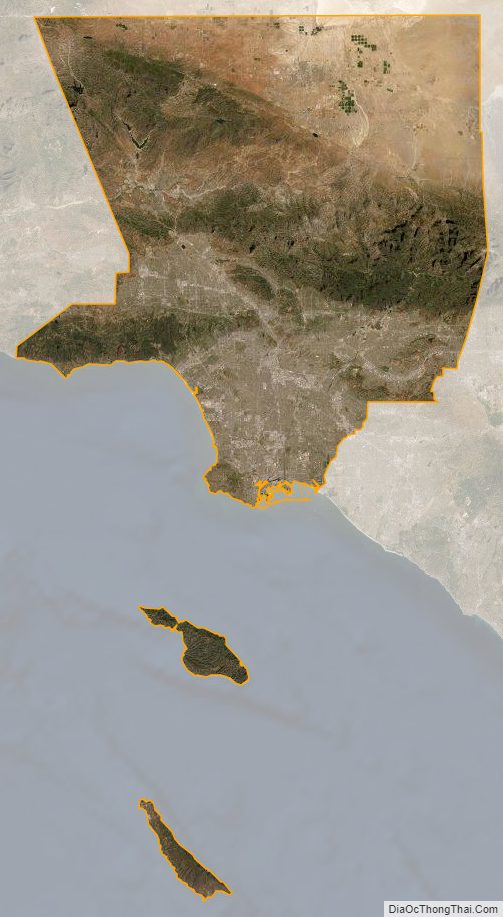
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has an area of 4,751 square miles (12,310 km), of which 4,058 square miles (10,510 km) (85%) is land and 693 square miles (1,790 km) (15%) is water. Los Angeles County borders 70 miles (110 km) of coast on the Pacific Ocean and encompasses mountain ranges, valleys, forests, islands, lakes, rivers, and desert. The Los Angeles River, Rio Hondo, Ballona Creek, the San Gabriel River and the Santa Clara River flow in Los Angeles County, while the primary mountain ranges are the Santa Monica Mountains and the San Gabriel Mountains. The western extent of the Mojave Desert begins in the Antelope Valley, in the northeastern part of the county.
Most of the population of Los Angeles County resides in the south and southwest, with major population centers in the Los Angeles Basin, San Fernando Valley, and San Gabriel Valley. Other population centers are found in the Santa Clarita Valley, Pomona Valley, Crescenta Valley and Antelope Valley.
The county is divided west-to-east by the San Gabriel Mountains, which are part of the Transverse Ranges of southern California, and are contained mostly within the Angeles National Forest. Most of the county’s highest peaks are in the San Gabriel Mountains, including Mount San Antonio 10,068 feet (3,069 m) at the Los Angeles-San Bernardino county lines, Mount Baden-Powell 9,399 feet (2,865 m), Mount Burnham 8,997 feet (2,742 m) and Mount Wilson 5,710 feet (1,740 m). Several lower mountains are in the northern, western, and southwestern parts of the county, including the San Emigdio Mountains, the southernmost part of Tehachapi Mountains and the Sierra Pelona Mountains.
Los Angeles County includes San Clemente Island and Santa Catalina Island, which are part of the Channel Islands archipelago off the Pacific Coast.
Lakes and reservoirs
- Bouquet Reservoir
- Castaic Lake
- Crystal Lake
- Elizabeth Lake
- Holiday Lake
- Hollywood Reservoir
- Hughes Lake
- Jackson Lake
- Las Virgenes Reservoir
- Malibou Lake
- Morris Reservoir
- Munz Lakes
- Lake Palmdale
- Puddingstone Reservoir
- Pyramid Lake
- Quail Lake
- Silver Lake Reservoir
- Stone Canyon Reservoir
- Tweedy Lake
- Westlake in City of Westlake Village
- Lake Lindero
Major divisions of the county
- East: Eastside, San Gabriel Valley, portions of the Pomona Valley
- West: Westside, Beach Cities
- South: South Bay, South Los Angeles, Palos Verdes Peninsula, Gateway Cities, Los Angeles Harbor Region
- North: San Fernando Valley, Crescenta Valley, portions of the Conejo Valley, portions of the Antelope Valley and Santa Clarita Valley
- Central: Downtown Los Angeles, Mid-Wilshire, Northeast Los Angeles
National protected areas
- Angeles National Forest (part)
- Los Padres National Forest (part)
- Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area (part)