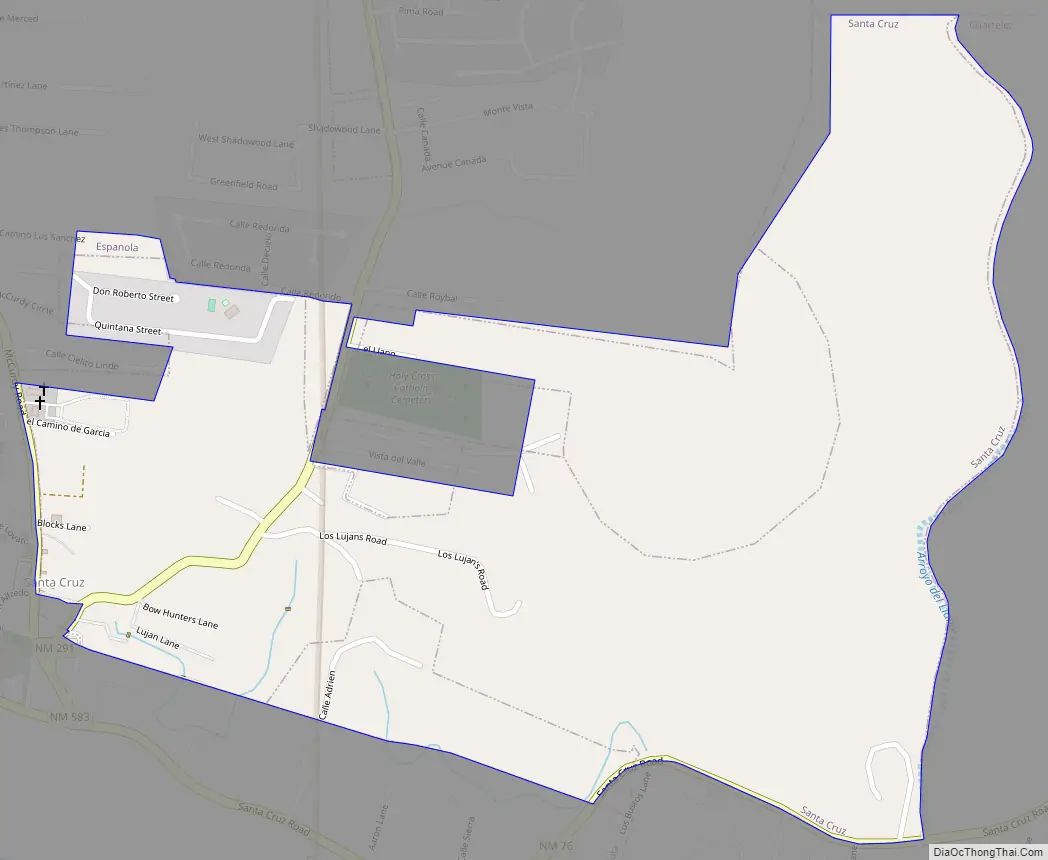
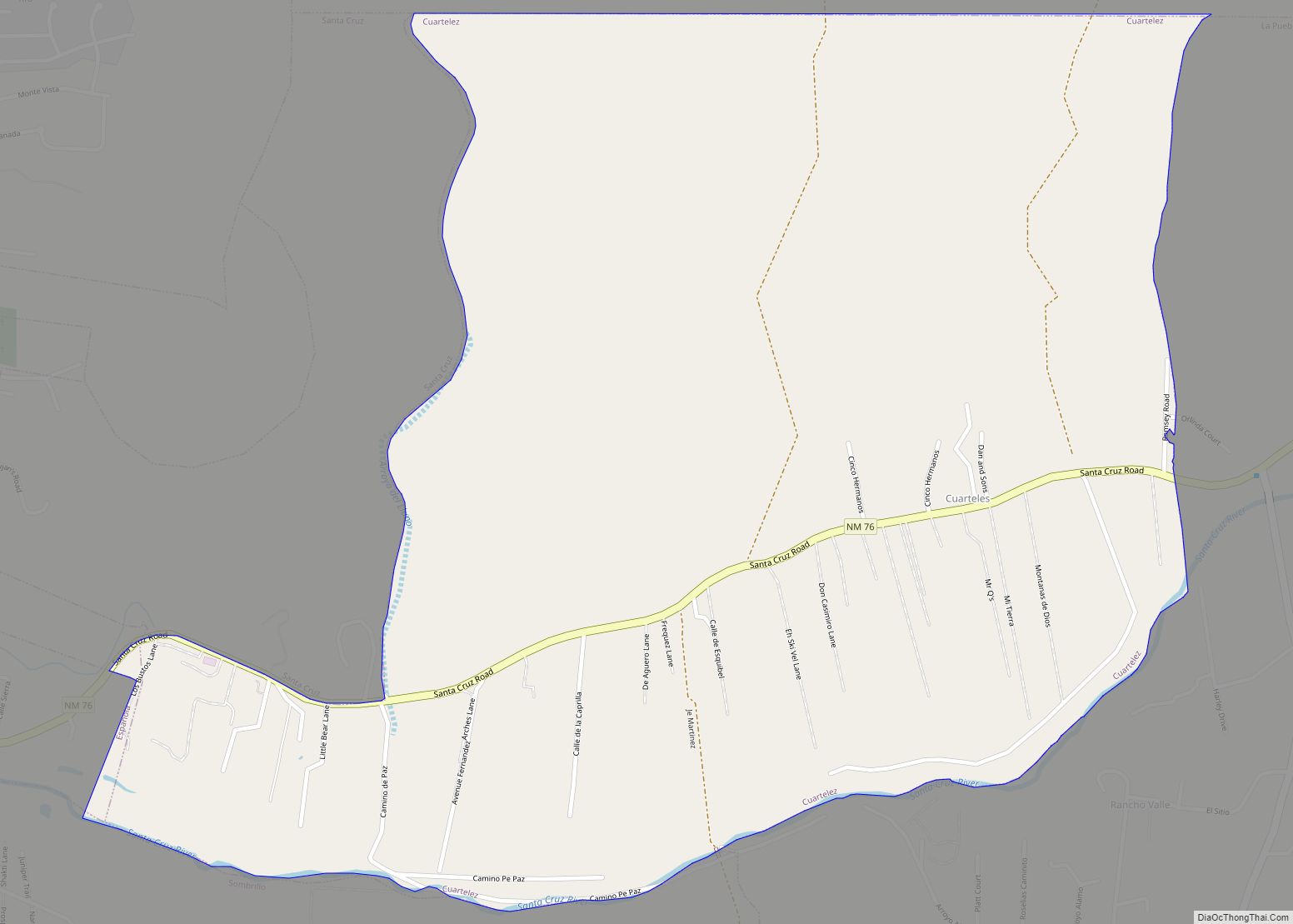
Santa Cruz is a census-designated place (CDP) in Santa Fe County, New Mexico, United States. It is part of the Santa Fe, New Mexico Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 423 at the 2000 census.
| Name: | Santa Cruz CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | New Mexico |
| County: | Santa Fe County |
| Founded: | 1695-04-21 |
| Elevation: | 5,663 ft (1,726 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.62 sq mi (1.61 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.62 sq mi (1.61 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 416 |
| Population Density: | 669.89/sq mi (258.83/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 87567 |
| Area code: | 505 |
| FIPS code: | 3570460 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0928814 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Santa Cruz location map. Where is Santa Cruz CDP?
History
Overview
The area that was later to be occupied by the village of Santa Cruz de la Cañada is located 25 miles northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, and a half-mile east of Española, New Mexico, at 5,655 feet AMSL, and UTM NAD 83, Z-13S, 404927E, 3983643N in the valley of the Santa Cruz River half-mile from its confluence with the Rio Grande. Upon arrival of Spanish conquistadores in 1540, the Santa Cruz area was inhabited by Tewa speakers (descendants of “Ancestral Puebloans,” formerly referred to as “Anasazi”), and after Vargas’ “reconquests” (of the Pueblo Revolt) of 1692 and 1696, by southern Tewa (or Tano) who had been relocated from the Galisteo Basin, 45 miles south, as a result of Vargas’ Spanish repopulation efforts on behalf of the Spanish Crown. Among the best reference materials for this history is: “The Pueblo Indian Revolt of 1696 and the Franciscan Missions in New Mexico” by J. Manuel Espinosa (1991).
Colonial period
The nearby, and unsuccessful, Spanish colony at San Gabriel established by the explorer Juan de Oñate at Ohkay Owingeh in 1598 produced Spanish haciendas and ranchos in the vicinity. During the Pueblo Revolt of 1680, Hispanic settlers were forced to leave the area. In 1695, following the Reconquest of 1692-1694 and the second Pueblo Revolt in 1696, Governor and Captain General of New Mexico, Don Diego de Vargas reestablished the Hispanic settlement. It was established as a new Spanish villa for those that had arrived from Mexico City as settlers and participants in the military campaigns during the reconquest. It was named Villa Nueva de Santa Cruz de los Españoles Mejicanos del Rey Nuestro Señor Carlos Segundo (The New Town of the Holy Cross of Mexican Spaniards under the King Our Lord Charles II). It later shortened simply to Santa Cruz de la Cañada (la Cañada translates as “a small river or creek valley”).
The new Hispanic community was the second villa established by the Spanish in New Mexico and was one of only three established during the colonial period, the first being Santa Fe and the last, Albuquerque. The area surrounding Santa Cruz de la Cañada was described during this period as containing many copious fruit orchards irrigated by the Santa Cruz River and its tributaries.
The original population of Tano Pueblo Natives in the area were at first grouped by Diego de Vargas into two pueblos with the same names (San Lazaro and San Cristobal) as previously established in this Galisteo Basin, but were relocated from the area by the end of the 17th century, following the second Pueblo Revolt. Many of the Tewa People left the area to join the Hopi people and became the Hopi-Tewas at First Mesa.
The existing Santa Cruz Catholic Church building in the Holy Cross Parish was originally constructed between 1733 and 1748 to replace a structure that was reported to be in danger of collapsing and beyond repair, although the Archdiocese of Santa Fe archives do not have a record either that Santa Cruz was a parish or that there was a church building existing at that time. The first baptism in the community was recorded on September 15, 1710. Artwork in the church has been contributed by well known local Santeros. The church is currently maintained by the Sons of the Holy Family and is open to tourists and visitors Monday through Friday.
Mexican period
Throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth century, frontier settlement at Santa Cruz de la Cañada had produced a rustic and self-reliant population. With news of Mexican independence in 1821, the town was hardly affected with the exception of the new government’s laws and office appointments. Trade with the United States had been forbidden under the former Spanish government, but now enterprising Anglo-Americans began pouring down the Santa Fe Trail, bringing a new prosperity to the region
The Revolt of 1837 was centered in Santa Cruz de la Cañada. In 1835, Mexico’s new autocratic and unpopular provincial governor, Albino Pérez, was met on his arrival in Santa Fe with suspicion and opposition, on the basis of rumors of aggressive new tax collections. Following his defeat in Texas, President Antonio López de Santa Anna, with his “Siete Leyes,” was moving toward government centralization, an increased ability to tax, and eventually to military dictatorship.
When Pérez had Juan José Esquibel, the alcalde (mayor) of Santa Cruz, jailed in 1837, influential members of the community raised a militia. Pérez led a force in response which was defeated by the rebels at Black Mesa near San Ildefonso Pueblo before he reached Santa Cruz. The rebels beheaded Pérez and killed some of his government officials, then appointed genizaro José González as new governor. Later, utilizing the support of Anglo merchants in Santa Fe, New Mexico native Manuel Armijo defeated of the rebels at Puertocito Pojoaque, east of Santa Cruz de la Cañada.
Territorial period
The arrival of the American Army under Stephen W. Kearny in 1846 ended the twenty-five years of Mexican rule in New Mexico. In January 1847, however, rebellious forces murdered the first U.S. assigned Governor, Charles Bent, at his home in Taos, beginning the Taos Revolt. Occupying forces in Santa Fe quickly moved an army north under Colonel Sterling Price to stop the rebellion. Colonel Price’s troops first met armed resistance at Santa Cruz against a poorly armed and trained force of rebels which they subdued with cannon. The skirmish would become known as the Battle of Cañada.
Statehood through present
Santa Cruz has continued to maintain much of its traditions and history especially through the Catholic Church. The mission church, built after the first fell into disrepair in the early eighteenth century, remains active and vibrant with a large and dedicated congregation. The arrival of the railroad in the 1880s brought the growth of a new town named Española. The growth of the new city eventually encompassed the old Spanish community and has largely concealed it. Once considered the second most important settlement in New Mexico, the town is now masked by its popular tourist neighbors Taos and Santa Fe.
Santa Cruz Road Map
Santa Cruz city Satellite Map
Geography
Santa Cruz is located at 35°59′37″N 106°2′31″W / 35.99361°N 106.04194°W / 35.99361; -106.04194 (35.993730, -106.042015).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 0.7 square mile (1.8 km), all land.
See also
Map of New Mexico State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming