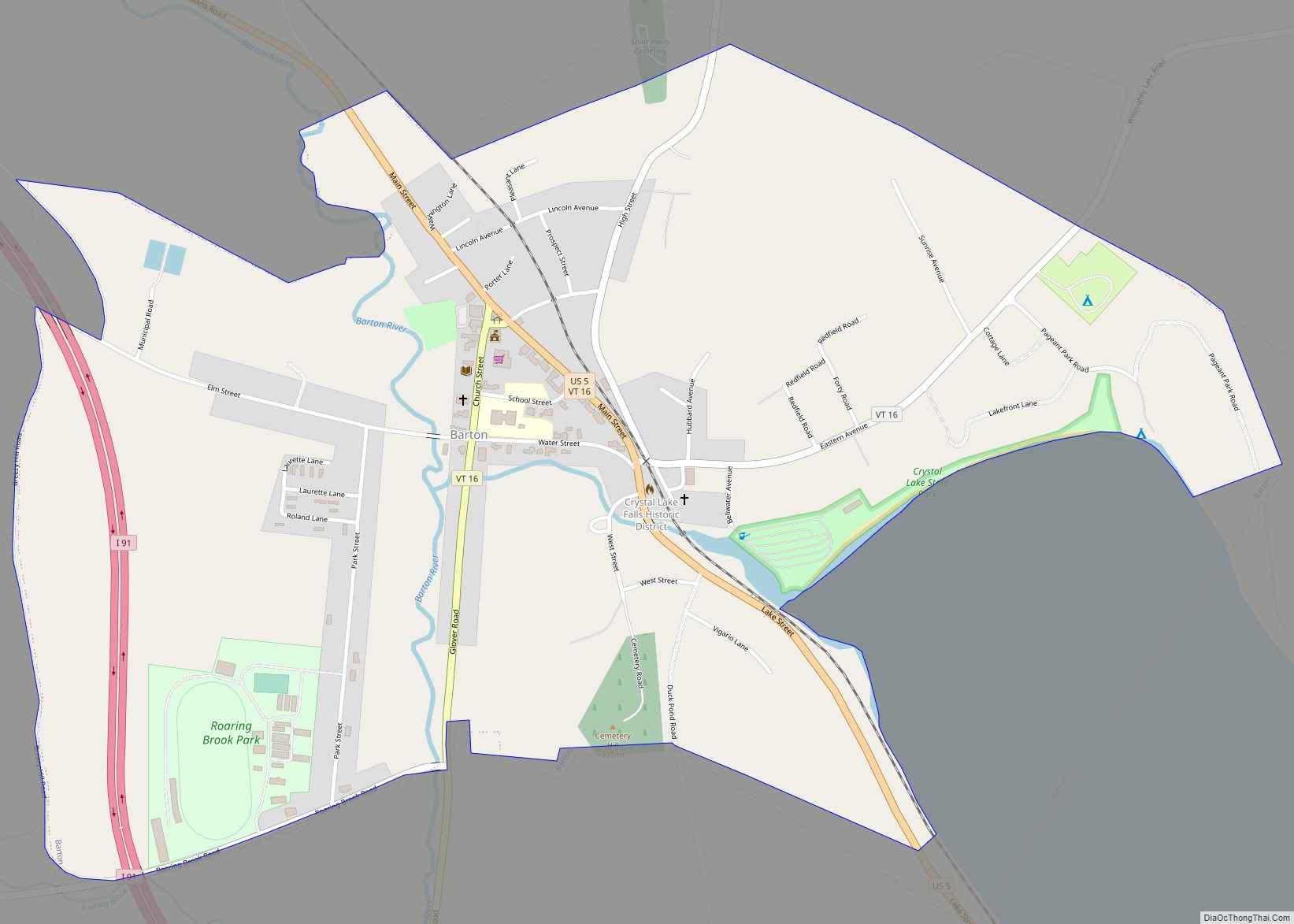
Barton is a town in Orleans County, Vermont, United States. The population was 2,872 at the 2020 census. The town includes two incorporated villages, Barton and Orleans. Approximately a quarter of the town’s population lives in each of the villages, and approximately half lives outside the villages. Only four other towns in the state contain two incorporated villages.
The Nulhegan Abenaki Tribe, a state-recognized tribe, is headquartered here.
| Name: | Barton village |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 47 |
| LSAD Description: | village (suffix) |
| State: | Vermont |
| County: | Orleans County |
| Elevation: | 931 ft (353 m) |
| Total Area: | 44.9 sq mi (116.3 km²) |
| Land Area: | 43.7 sq mi (113.1 km²) |
| Water Area: | 1.3 sq mi (3.3 km²) |
| Total Population: | 2,872 |
| Population Density: | 66/sq mi (25.4/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 05822, 05839, 05875 |
| Area code: | 802 |
| FIPS code: | 5003475 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1462037 |
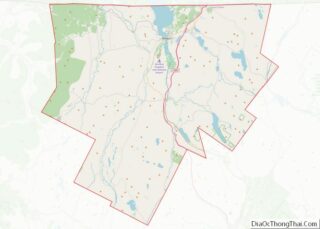
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Barton location map. Where is Barton village?
History
The Abenaki and their ancestors had been in this area for 12,000 years. They were part of the large Wabanaki confederacy of related Algonguian-speaking peoples that extended into what is now Canada. In 2011 and 2012 the state of Vermont officially recognized four Abenaki tribes. The Nulhegan Abenaki Tribe has its headquarters in Barton.
Early European traders and colonists were French. Anglo-Americans began to enter the area later in the 18th century. Both groups pushed the Abenaki aside when they wanted the land, and the natives suffered high mortality due to new infectious diseases.
France and England continued their European competition in North America, including in wars of the early 18th century. There was frequent raiding by each group of colonists and their Native American allies between their settlements, leading to a brisk trade in ransomed captives.
The French and Indian War was the North American front of the Seven Years’ War later in the century. In the latter warfare, Rogers’ Rangers attacked Saint-Francis, Quebec in 1759, but were forced to retreat. They came through this area, splitting their forces before reaching Barton. One group followed the Barton River south to the falls at the outlet of Crystal Lake, where they caught fish to eat. They continued south over the summit into the Passumpsic River Valley.
After the American Revolutionary War and independence, Barton was chartered on October 20, 1789. The land was granted in lieu of pay to 60 Revolutionary War veterans, mainly from Rhode Island. They included Admiral John Paul Jones, General William Barton after whom the town was named, and Ira Allen. Prior to formal chartering, the town had been known as “Providence.”
From 1791 to 1793 Timothy Hinman built what is now called the Hinman Settler Road, linking Barton south to Greensboro and north through Brownington to Derby and Canada. The early Anglo-American settlers of Barton found wigwams, in a decayed condition, quite numerous in the vicinity of the outlet of Barton pond. They realized that this had been a favorite camping ground of the Abenaki. They noted that Foosah, an Abenaki, said that he had killed 27 moose, besides large numbers of beaver and otter, near this pond in the winter of 1783–1784.
On June 6, 1810, the body of water known today as Runaway Pond flooded the Barton River Valley, resulting in widespread destruction. Its effects can still be seen today. In 1824, voters decided to fund education for all children, establishing public schools. A private academy started operating in 1852 with 107 students. This was the forerunner of Barton Academy.
Railroad construction reached Barton in 1858. The first train arrived in 1863. As each new railroad terminus was built, the stagecoaches used them as well. The stage ran north from Barton, from what is now the junction of State Road 58 and US 5, to connect with the Hinman Settler Road. It came from Glover and ran up Barton Hill, over what is now Maple Hill Road, and on to what is now the Orleans Country Club; from there it went to Brownington.
Fred Kimball opposed slavery and became an agent on the Underground Railroad before the Civil War, assisting refugee slaves from the South to reach freedom in Vermont or pass into Canada. Some of the refugees wanted to get as far as possible from slave catchers, who became more aggressive as bounties were increased after the 1850 Fugitive Slave Act.
Some 182 men from the town volunteered to fight in the Civil War. By 1863, enthusiasm for the war had waned, and Congress passed legislation to start a draft of soldiers. Individuals were allowed to buy their way out of the draft for $300, a steep sum for many men at the time, or find a substitute, usually paying a bounty of $100. Barton’s quota was 14. Of the 14 men originally drafted, seven bought their way out, and six obtained a substitute. One served.
The town had a total of seven granite quarries, which were a mainstay of the economy. Around 1900, a granite quarry was located on the east side of Crystal Lake. Steamboats carried stone by barges across the lake. In winter, barges were slid across on the ice.
In 1907 excavation for the new Barton Academy revealed an Abenaki burying ground. There is no record of what happened to the artifacts that were discovered in the graves.
Increasing steadily, Barton’s population reached a peak of 3,506 people in 1920. In 1921, the town put on a large pageant celebrating its 125th anniversary. A professional choreographer and playwright was hired. 300 townspeople performed, and they were watched by 4,500 paying spectators, a record audience for the county at the time. The investment of $1,000 was recouped. The festival area was afterwards known as Pageant Park, which is now owned by the Barton village.
Following the outbreak of World War II, the Portland Pipeline company built a crude oil pipeline to Montreal, Canada from Portland, Maine in 1941. It wanted to avoid the risk of U-Boat attacks that resulted from shipping by sea. In 2005, the portion of the line that passes through Barton town was evaluated and taxed at $2,277,000.
The last one-room schools stopped operation in the late 1950s. In 1964, a candlepin bowling alley was opened. Up to ten community leagues used the facility. It closed in 2000 after some legal problems.
In 1967, the school districts found that their high schools, Barton Academy and Orleans High School, were too small to accommodate current needs. They converted them to elementary school use and built a new facility, Lake Region Union High School.
On February 14, 2016, the temperature dropped to −20 °F (−29 °C). The high for the day was −18 °F (−28 °C). There had been insufficient snow to insulate homes against the cold, and a life-threatening emergency developed after electric power failed. It was off for 12 hours, jeopardizing the lives of many residents, particularly the elderly, among those who depended on electrical fired furnaces. Exterior electrical generators could not be started due to the cold. Plumbing froze and burst in many houses.
South Barton
The unincorporated village of South Barton, sometimes called Kimball Station, no longer exists. It was located near the Wheeler Mountain Road south of Crystal Lake on present-day Route 5.
In 1858, Barton (and Orleans County) obtained a triangular piece of land from Sheffield which included all of May Pond, the entire area south of Crystal Lake, and the village of South Barton. In 1861, the village of South Barton had its own post office, and, in 1874, its own railroad depot. In the early 1930s, 30 students attended its one-room schoolhouse.
Its main industry was logging. The village foundered because it lacked electric power, which the other two villages in town had aggressively pursued getting installed. South Barton tried to rely on steam power, but by the early 1940s, the village was no longer viable. Its post office closed in 1947. Three industries operated successively in the same location: the Orleans and Caledonia Steam Mill Company, Willoughby Wood and Lumber Company, and US Bobbin and Shuttle Company. Eventually the relocation of the latter to New York state took enough jobs that remaining residents left the village.
Barton Road Map
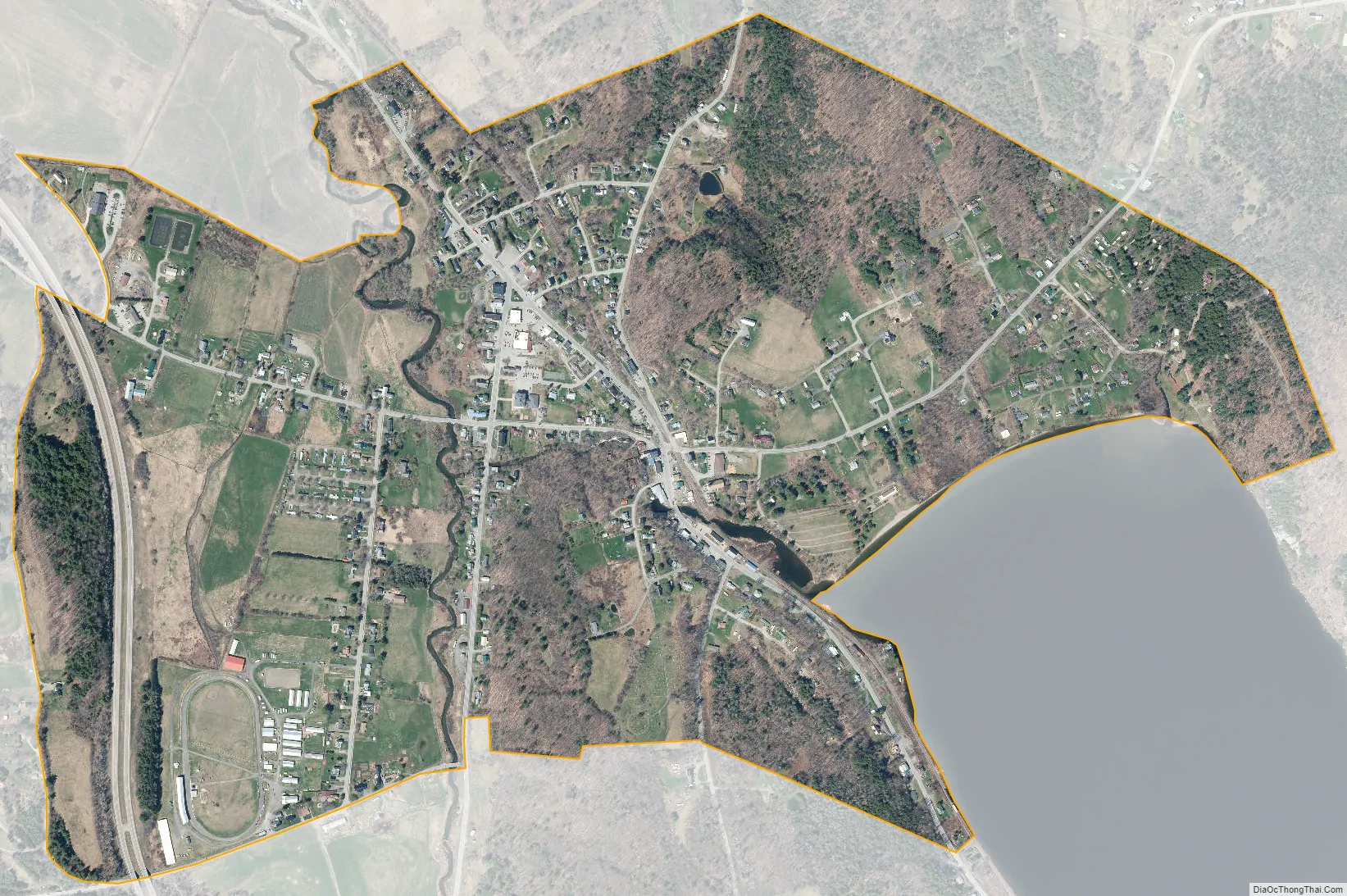
Barton city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 44.9 square miles (116.3 km), of which 43.7 square miles (113.1 km) is land and 1.3 square miles (3.3 km) (2.81%) is water. Barton averages 931 feet (284 m) above sea level (ASL).
The principal rock is calciferous mica schist. About two miles (3 km) from the Irasburg line, and parallel with it, there is a narrow vein of hornblende schist the whole length of the town. In the eastern corner, covering an area of several square miles, the rocks are a mixture of granite, syenite, and protogine. Iron has been found in small quantities, and some traces of gold.
The highest peak in Barton is Barton Mountain – 2,235 feet (681 m) ASL. May Hill is 2,007 feet (612 m) high.
Rivers include the Barton, and Willoughby; Hogtrough Brook, Lord Brook, Annis Brook, May Pond Brook, Willoughby Brook, and Roaring Brook. Each spring, the migrating rainbow trout swim up the Willoughby River to spawn in Lake Willoughby.
Crystal Lake State Park is located in Barton.
See also
Map of Vermont State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming