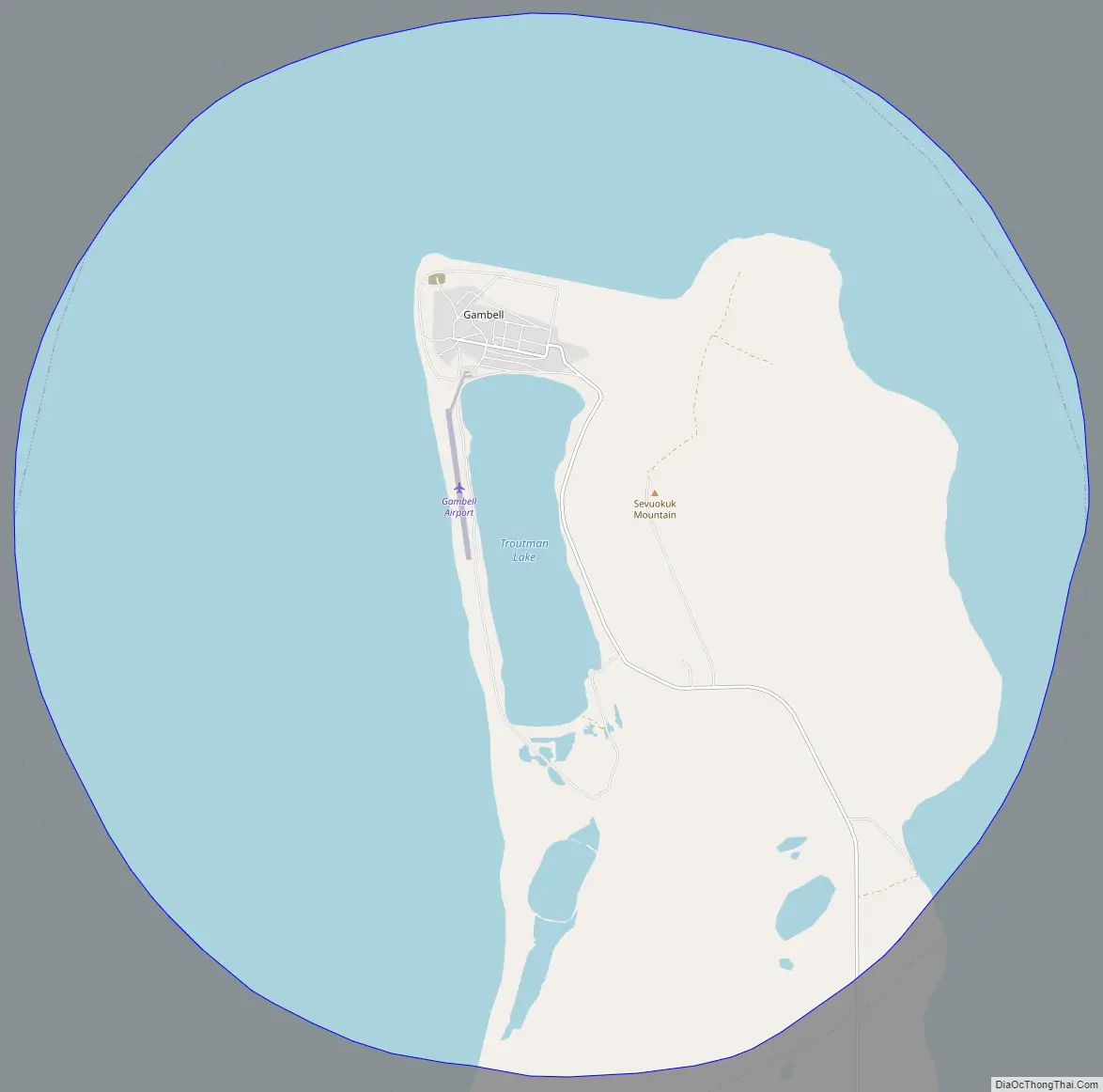
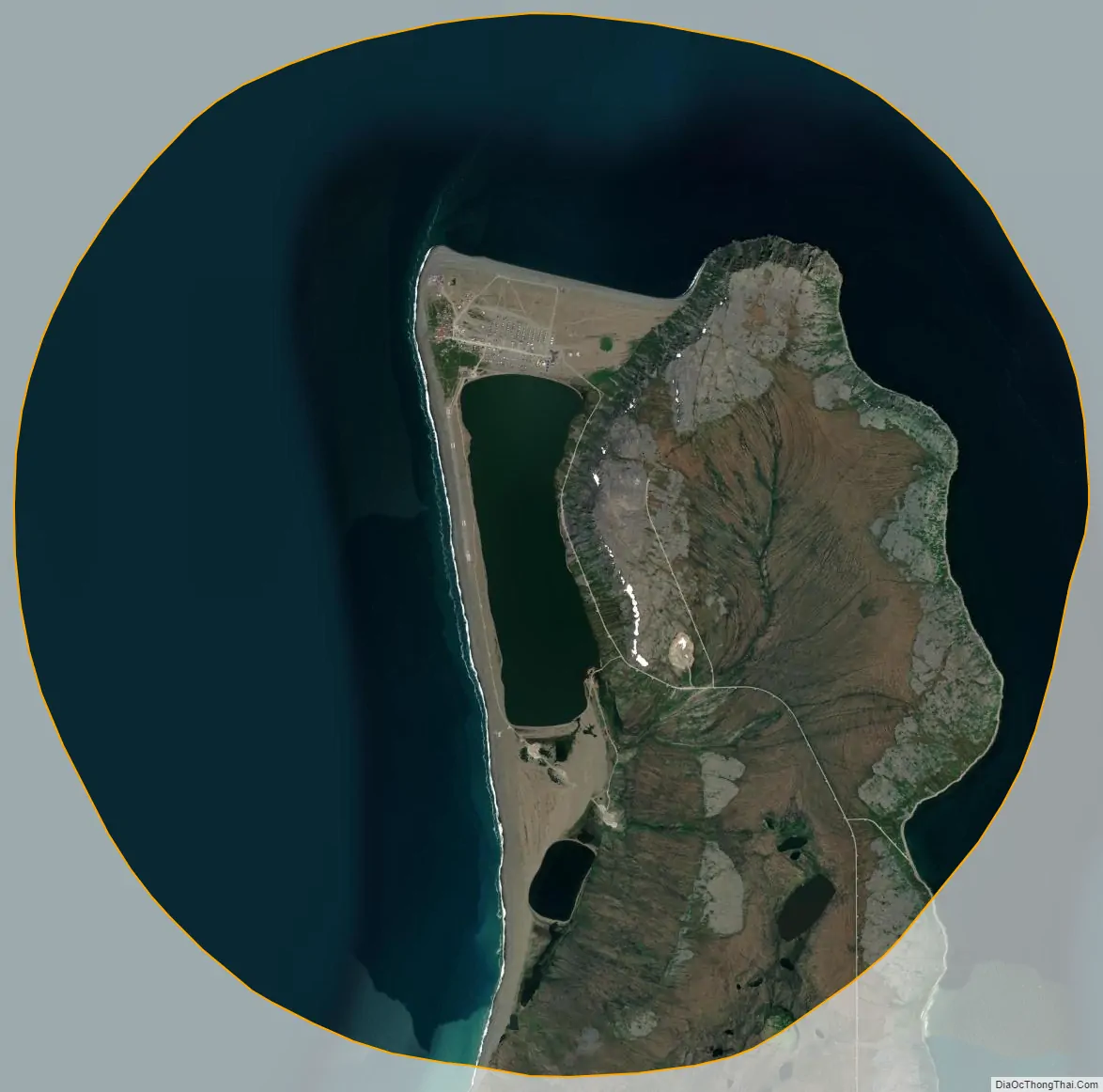
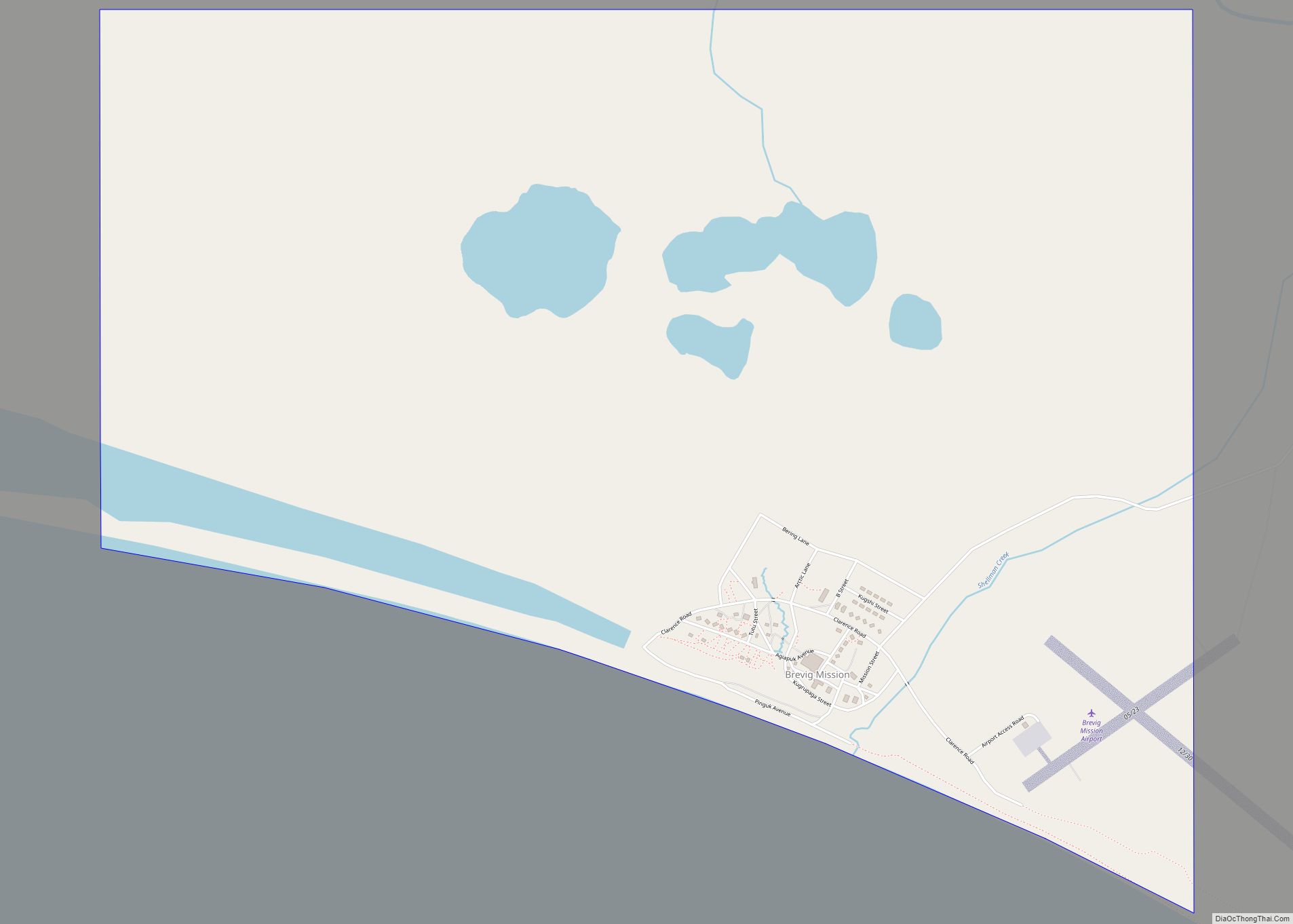
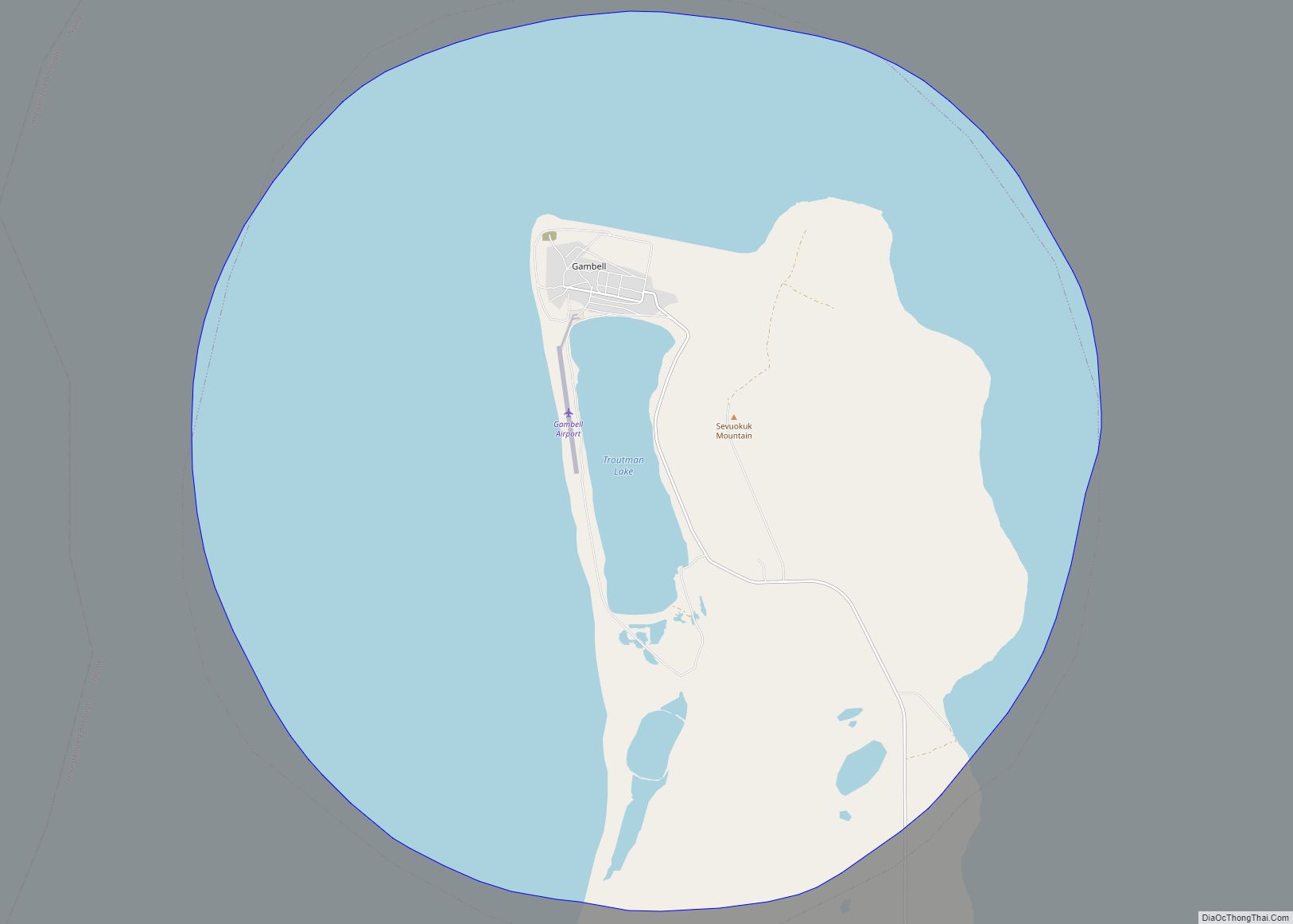
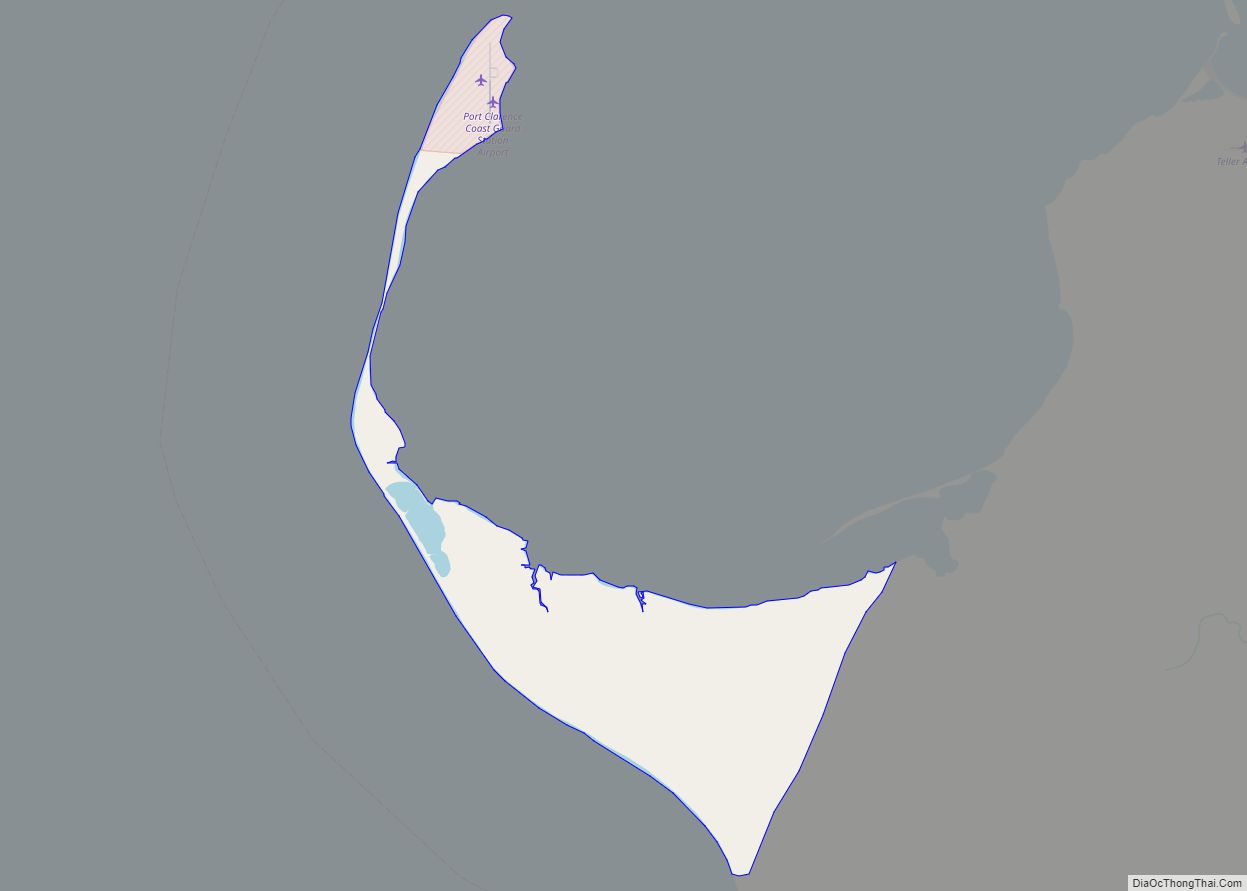
Gambell (GAM-bull) (Central Siberian Yupik: Sivuqaq, Russian: Гамбелл) is a city in the Nome Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Located on St. Lawrence Island, it had a population of 681 at the 2010 census, up from 649 in 2000.
| Name: | Gambell city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Nome Census Area |
| Incorporated: | December 12, 1963 |
| Elevation: | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Total Area: | 28.42 sq mi (73.61 km²) |
| Land Area: | 10.51 sq mi (27.21 km²) |
| Water Area: | 17.91 sq mi (46.40 km²) |
| Total Population: | 681 |
| Population Density: | 60.92/sq mi (23.52/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99742 |
| Area code: | 907 |
| FIPS code: | 0227640 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1402463 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Gambell location map. Where is Gambell city?
History
Sivuqaq is the Yupik language name for St. Lawrence Island and for Gambell. It has also been called Chibuchack and Sevuokok.
St. Lawrence Island has been inhabited sporadically for the past 2,000 years by both Alaskan Yup’ik and Siberian Yupik people. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the island had a population of about 4,000.
Between 1878 and 1880 a famine decimated the island’s population. Many who did not starve left. The remaining population of St. Lawrence Island was nearly all Siberian Yupik.
In 1887, the Reformed Episcopal Church of America opened a mission on St. Lawrence Island. That year, a carpenter, lumber and tools were left at Sivuqaq by a ship. The carpenter worked with local Yupik to build a wood building, the first they had ever seen. When the building was finished, the carpenter left the keys to the door with a local chief and departed. Since the carpenter had not spoken Siberian Yupik, the residents did not know the purpose of the building.
The Reformed Episcopal Church had not been able to find missionaries willing to live on St. Lawrence Island, so the building built for the mission was left unoccupied. In 1890, the building was acquired by Sheldon Jackson. He spoke to the Reverend Vene and Nellie Gambell, of Wapello, Iowa, about moving to St. Lawrence Island. Gambell was hired as a schoolteacher and the Gambells came to the island in 1894. They had a daughter in 1897. Nellie Gambell became ill and the Gambells spent the winter of 1897–1898 in the United States, where Nellie was hospitalized. In the spring of 1898, on the return journey to St. Lawrence Island, their ship sank in a storm and 37 people on it drowned, including the Gambells and their daughter. After their death, Sivuqaq was renamed in the Gambells’ honor.
On June 22, 1955, during the Cold War, a US Navy P2V Neptune with a crew of 11 was attacked by two Soviet fighters in international waters over the Bering Straits between Siberia and Alaska, and crashed near Gambell, where the crew was rescued (3 wounded by Soviet fire; 4 injured in crash.) The Soviet government, in response to a US diplomatic protest, was unusually conciliatory, stating:
The Soviet military was under strict orders to “avoid any action beyond the limits of the Soviet state frontiers.”
The Soviet government “expressed regret in regard to the incident”, adding that “taking into account… conditions which do not exclude the possibility of a mistake from one side or the other,” it was willing to compensate the US for 50% of damages sustained—the first such offer ever made by the Soviets for any Cold War shootdown incident. The US government said it was satisfied with the Soviet expression of regret and the offer of partial compensation, although it said that the Soviet statement fell short of what the available information indicated.
Gambell and Savoonga received joint title to most of St. Lawrence Island under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971.
The An-24 incident at Gambell, Alaska occurred on February 27, 1974, when a Soviet Antonov An-24LR “Toros” (CCCP-47195) ice reconnaissance aircraft landed at Gambell.
On August 30, 1975, Wien Air Alaska Flight 99 crashed when trying to land in Gambell. 10 of the 32 passengers and crew on board were killed.
In October 2022, two Russian citizens arrived by small boat and sought political asylum, saying they wanted to avoid compulsory military service. It was an unusual and dangerous trip; Alaska Governor Mike Dunleavy said he did not expect a continual stream of other arrivals. US Senator for Alaska Lisa Murkowski later revealed that the two refugees were members of a group indigenous to Siberia.
Gambell Road Map
Gambell city Satellite Map
Geography
Gambell is on the northwest cape of St. Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea, 325 km (202 mi) southwest of Nome. It is 58 km (36 mi) from the Chukchi Peninsula in the Russian Far East.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has an area of 30.4 square miles (79 km), of which 10.9 square miles (28 km) is land and 19.5 square miles (51 km) (64.10%) is water.
The town is served by Gambell Airport.
Climate
Owing to the influence of the cold Bering Sea, Gambell has a polar climate (Köppen ET). Its hottest month averages cooler than 50 °F or 10 °C. The climate features long, frigid and snowy winters alongside short cool summers. The cold sea creates pronounced seasonal lag, sufficient that April averages colder than December and May colder than October.
Compared to most northern hemisphere polar climates, Gambell is relatively moderate, featuring only discontinuous permafrost and despite the freezing of the Bering Sea less frigid winters than typical for Asia and North America at similar latitudes. As an example, Iqaluit on the other side of North America averages 9.8 °F or 5.4 °C colder over the year at a similar latitude, and Arviat on northern Hudson Bay 12 °F or 6.7 °C colder despite being two degrees further south.
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming