Wasilla (Dena’ina: Benteh) is a city in Matanuska-Susitna Borough, United States and the fourth-largest city in Alaska. It is located on the northern point of Cook Inlet in the Matanuska-Susitna Valley of the southcentral part of the state. The city’s population was 9,054 at the 2020 census, up from 7,831 in 2010. Wasilla is the largest city in the borough and a part of the Anchorage metropolitan area, which had an estimated population of 398,328 in 2020.
Established at the intersection of the Alaska Railroad and Old Carle Wagon Road, the city prospered at the expense of the nearby mining town of Knik. Historically entrepreneurial, the economic base shifted in the 1970s from small-scale agriculture and recreation to support for workers employed in Anchorage or on Alaska’s North Slope oilfields and related infrastructure. The George Parks Highway turned the town into a commuter suburb of Anchorage.
Wasilla gained international attention when Sarah Palin, who served as Mayor of Wasilla before her election as Governor of Alaska, was chosen by John McCain as his running mate for Vice President of the United States in the 2008 United States presidential election.
Wasilla is named after Chief Wasilla, a local Dena’ina chief. “Wasilla” is the anglicized spelling of the chief’s Russian-given name, Васи́лий Vasilij, which corresponds to the English name Basil.
| Name: | Wasilla city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Matanuska-Susitna Borough |
| Incorporated: | February 26, 1974 |
| Elevation: | 341 ft (104 m) |
| Total Area: | 13.13 sq mi (34.01 km²) |
| Land Area: | 12.40 sq mi (32.10 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.73 sq mi (1.90 km²) |
| Total Population: | 9,054 |
| Population Density: | 730.40/sq mi (282.01/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99629, 99654, 99687 |
| Area code: | 907 |
| FIPS code: | 0283080 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1411788 |
| Website: | cityofwasilla.gov |
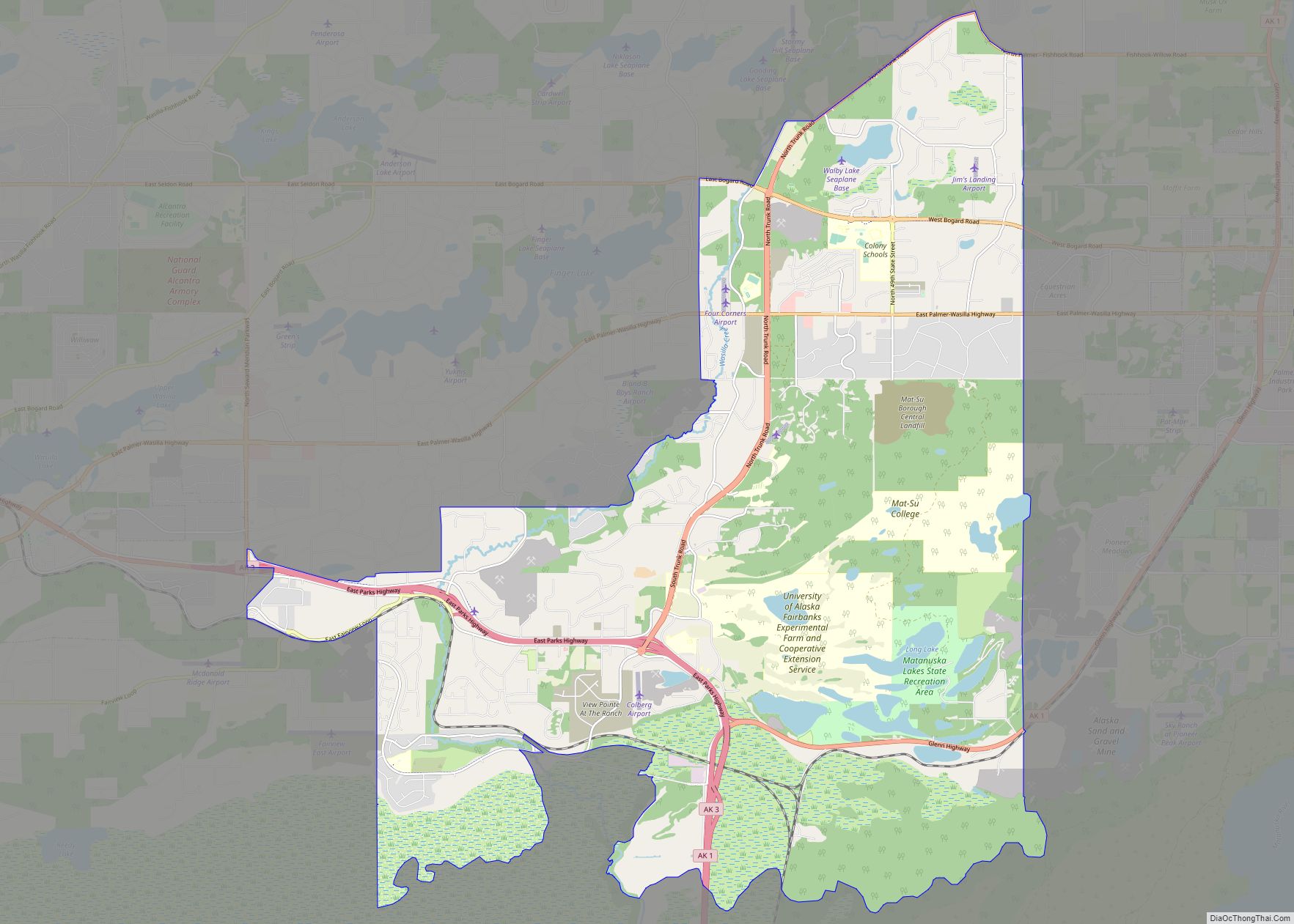
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
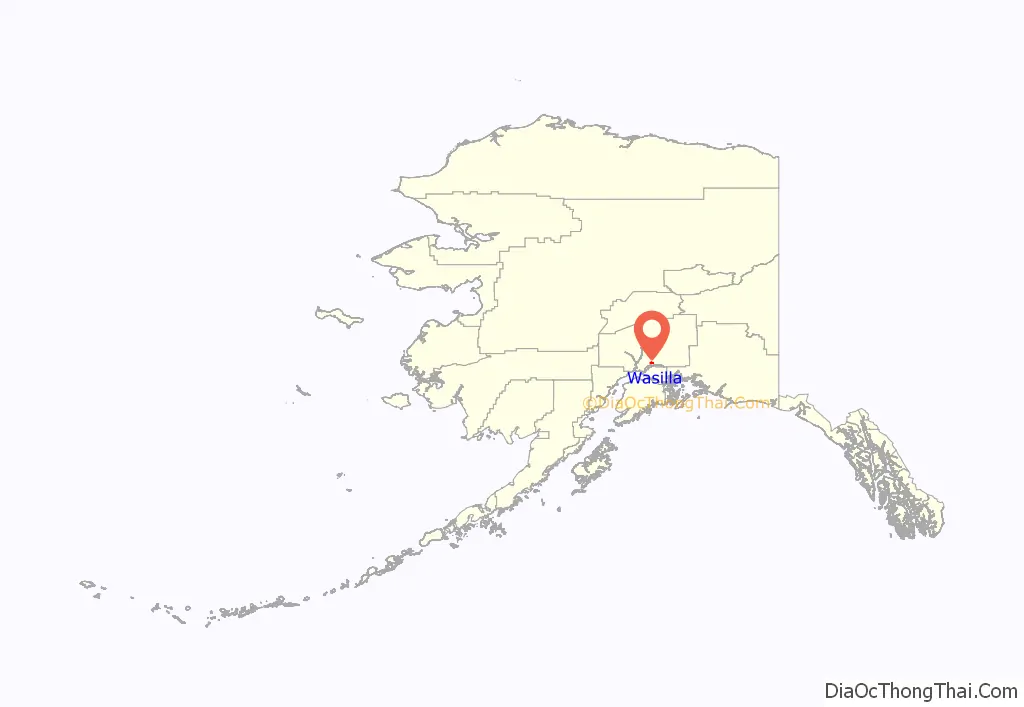
Wasilla location map. Where is Wasilla city?
History
Glacial ice sheets covered most of the northern hemisphere during the last glacial period, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, until they disappeared between 10,000 and about 7,000 years ago. Early humans moved through the area and left evidence of their passage. The Matanuska-Susitna valley was eventually settled by the Dena’ina Alaska natives who utilized the fertile lands and fishing opportunities of Cook Inlet. The Dena’ina are one of the eleven sub-groups comprising the indigenous Athabaskan groups extending down Canada’s western coast. The area around downtown Wasilla was known to the Dena’ina as Benteh, which translates as “among the lakes”. Near the mouth of the Matanuska River, the town of Knik was settled about 1880. In 1900, the Willow Creek Mining District was established to the north and Knik thrived as a mining settlement.
In 1917, the U.S. government planned the Alaska Railroad to intersect the Carle Wagon Road (present Wasilla-Fishhook Road) which connected Knik and the mines. Local businesses and residents rushed to buy land nearby, and Knik declined. Wasilla Station was named for the nearby Wasilla Creek. Local miners used the name “Wassila Creek”, referring to Wassila, a chief of the Dena’ina. There are two sources cited for the name, one being derived from a Dena’ina word meaning “breath of air” while another stating Dena’ina derived it from the Russian name Васи́лий Vasilij. As Knik declined into a ghost town, Wasilla served early fur trappers and miners working the gold fields at Cache Creek and Willow Creek. More than 200 farm families from the Upper Midwest were moved into the Matanuska and Susitna valleys in 1935 as part of a U.S. government program to start a new farming community to counteract this trend; their linguistic influence is still audible in the region.
The area was a supply base for gold mines near Hatcher Pass through World War II. Until construction of the George Parks Highway around 1970, nearby Palmer was the leading city in the Matanuska Valley. Wasilla was at the end of the Palmer-Wasilla highway and the road to Big Lake provided access to land west of Wasilla. The Parks Highway put Wasilla at mile 40–42 of what became the major highway and railroad transportation corridor linking Southcentral Alaska to Interior Alaska. As a result, population growth and community development shifted from the Palmer area to Wasilla and the surrounding area. Wasilla was incorporated as a city in 1974. All non-borough municipalities throughout Alaska are designated cities.
In 1994, a statewide initiative to move Alaska’s capital to Wasilla was defeated by a vote of about 116,000 to 96,000. About that time, the Matanuska Valley began to recover from an economic collapse, beginning a sustained boom that involved dramatic population growth, increased local employment, and a boom in residential and commercial real estate development. The local real estate market slowed in 2006. In 2008, suburban growth and dwindling snow forced organizers of the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race to bypass Wasilla permanently, due to a warming climate. The race had its start in Wasilla from 1973 to 2002, the year when reduced snow cover forced a “temporary” change to Willow.
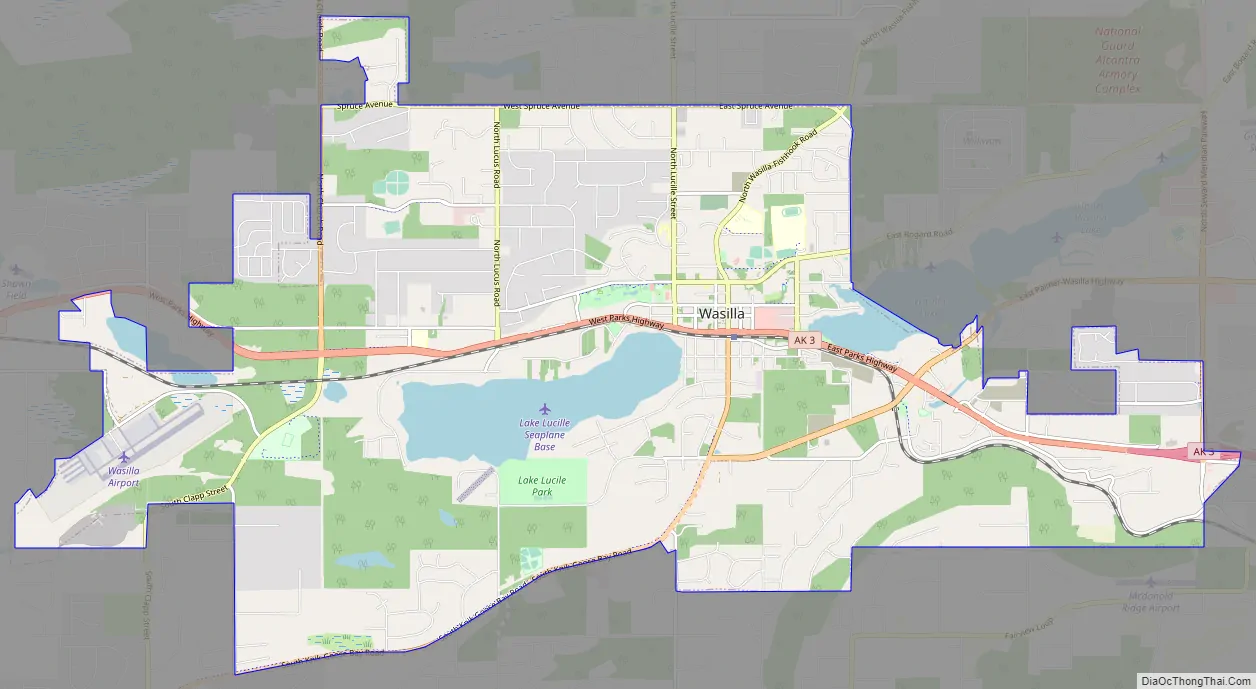
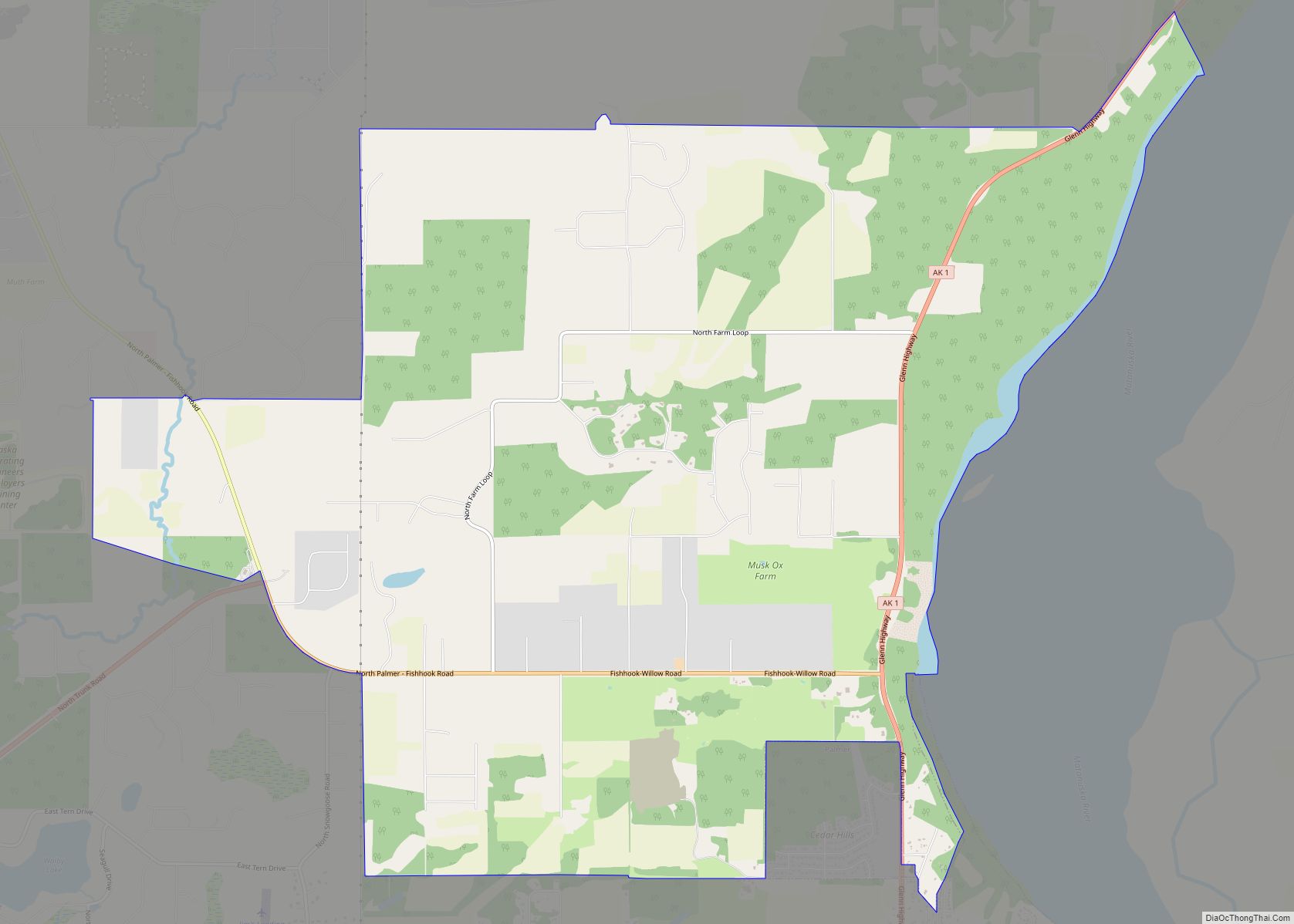
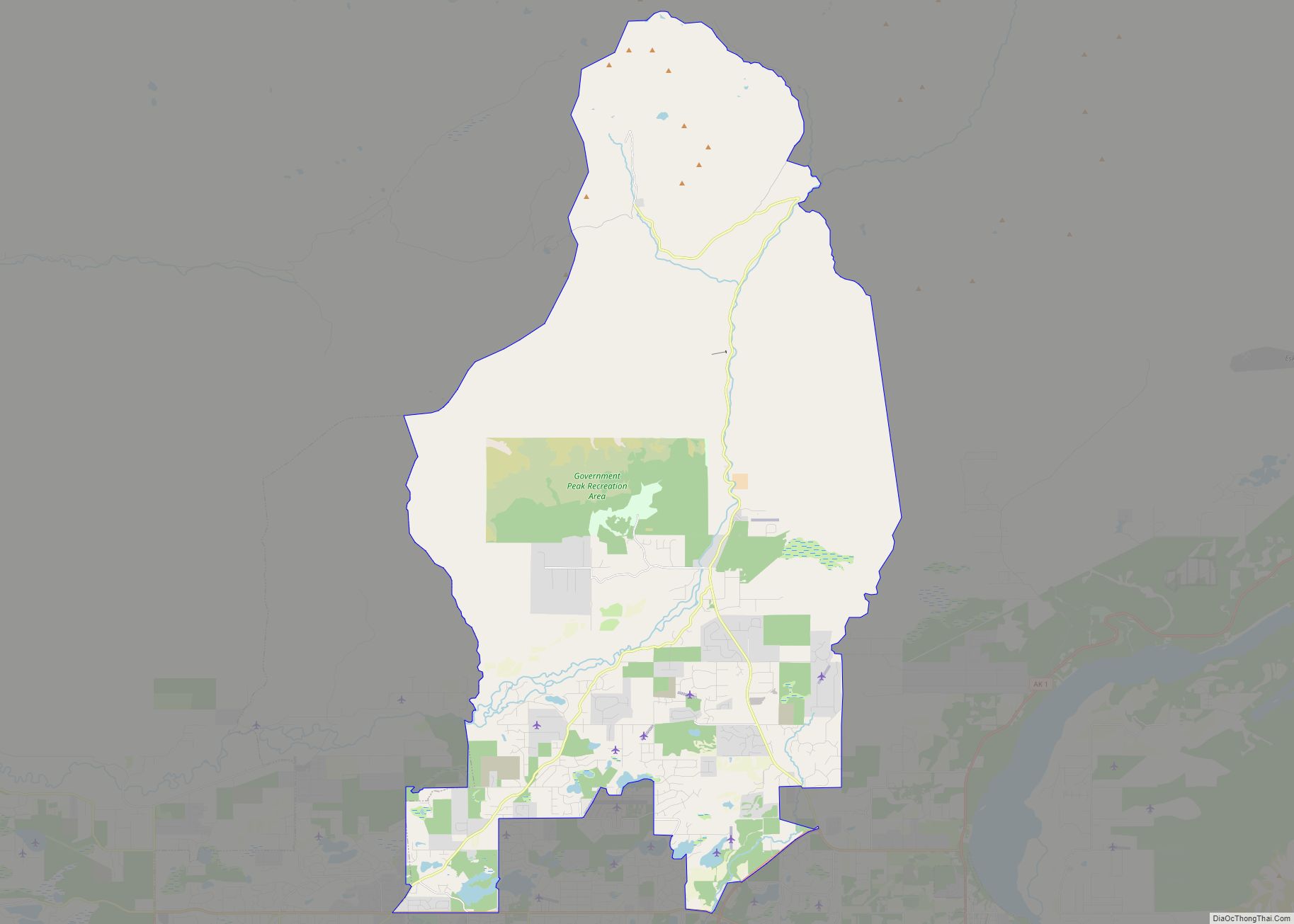
Wasilla Road Map
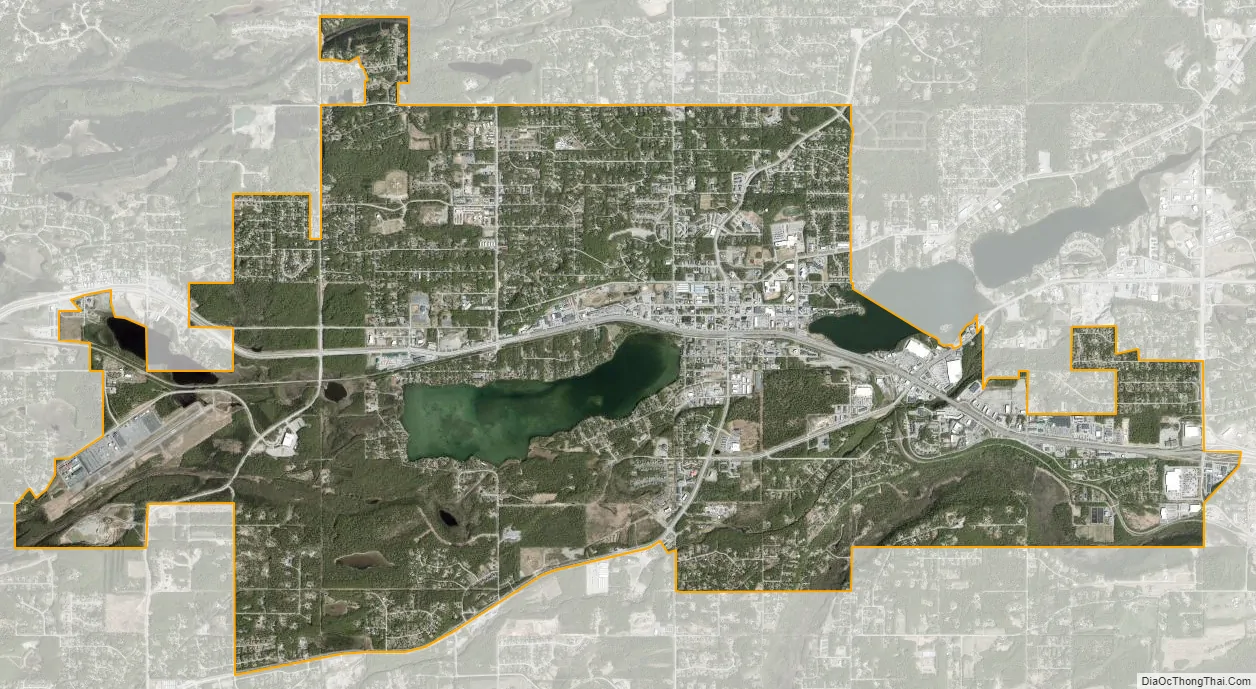
Wasilla city Satellite Map
Geography
Wasilla is located at 61°34′54″N 149°27′9″W / 61.58167°N 149.45250°W / 61.58167; -149.45250 (61.581732, −149.452539).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has an area of 12.4 square miles (32.2 km). 11.7 square miles (30.4 km) of it is land and 0.7 square miles (1.8 km) of it (5.64%) is water.
Located near Wasilla Lake and Lake Lucille, Wasilla is one of two towns in the Matanuska Valley. The community surrounds Mi. 39–46 of the George Parks Highway, roughly 43 mi (69 km) by highway northeast of Anchorage. Nearly one third of the people of Wasilla drive the 40-minute commute to work in Anchorage every day. Six miles to the southeast is Mount POW/MIA.
Climate
Wasilla has a climate similar to that of Anchorage, classified as a subarctic climate (Dfc) by Köppen-Geiger climate classification, although with slightly warmer daytime maxima and colder nighttime minima due to its inland location. On average, over the course of the entire year, there are 30–31 days of sub-0 °F (−17.8 °C) lows, 37–38 days of 70 °F (21.1 °C)+ highs, and 1.4 days of 80 °F (26.7 °C)+ highs. The average annual precipitation is 17 inches (430 mm), with 52 inches (1.32 m) of snowfall.
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming