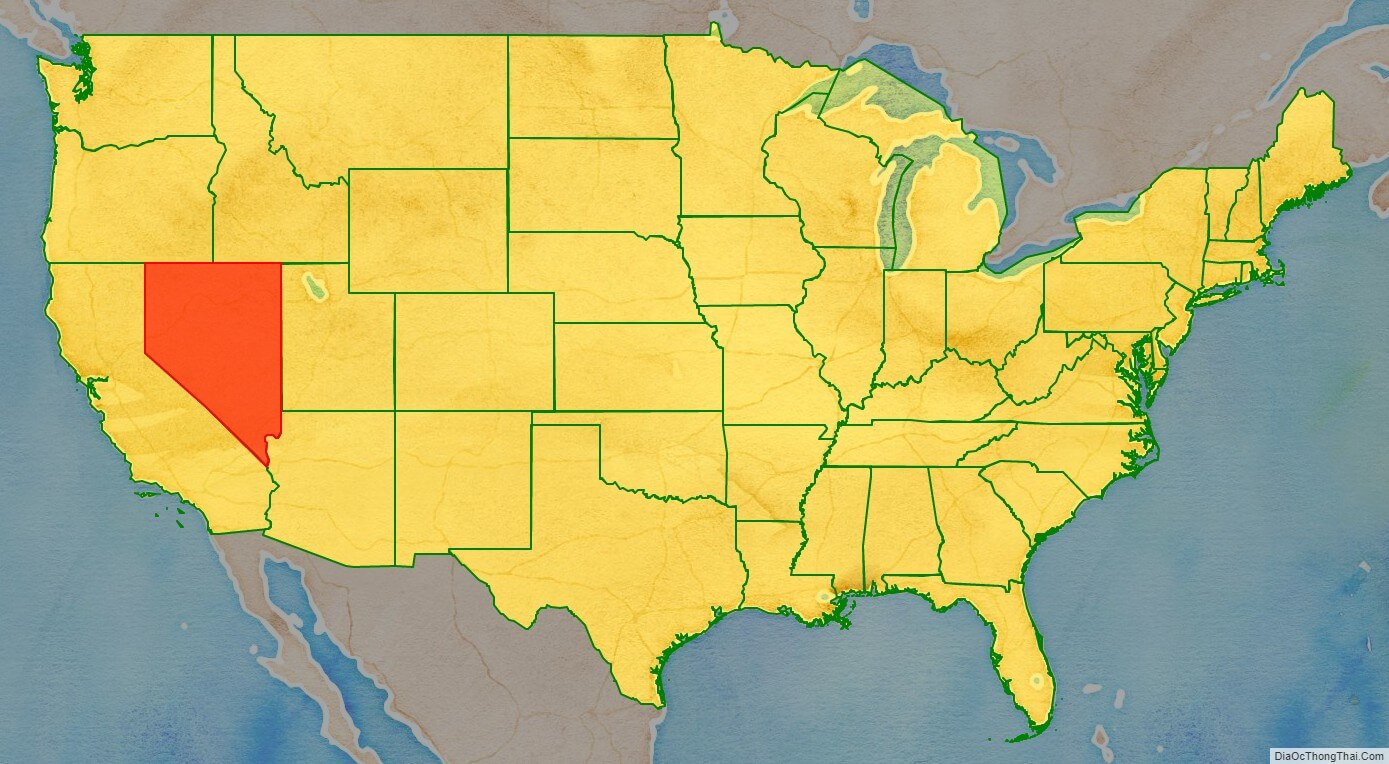
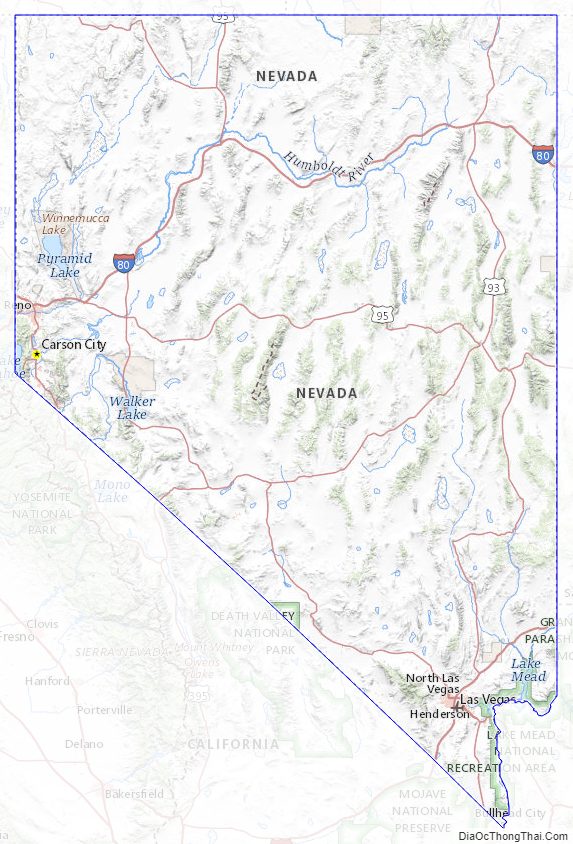
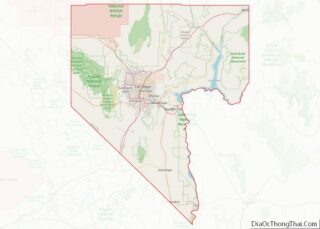
Nevada (/nəˈvædə/ nə-VAD-ə; Spanish: [neˈβaða]) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the 9th-least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada’s people live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state’s four largest incorporated cities. Nevada’s capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state.
Nevada is officially known as the “Silver State” because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the “Battle Born State” because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words “Battle Born” also appear on its state flag); due to a presidency held by Abraham Lincoln, the Union benefited immensely from the support of newly awarded statehood by the infusion of the monetary support of nearly $400 million in silver ore generated at the time by the Comstock Lode. It is also known as the “Sagebrush State”, for the native plant of the same name; and as the “Sage-hen State”. The name means “snowy” in Spanish, referring to Nevada’s small overlap with the Sierra Nevada mountain range; however, the rest of Nevada is largely desert and semi-arid, much of it within the Great Basin. Areas south of the Great Basin are within the Mojave Desert, while Lake Tahoe and the Sierra Nevada lie on the western edge. About 86% of the state’s land is managed by various jurisdictions of the U.S. federal government, both civilian and military.
American Indians of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes inhabit what is now Nevada. The first Europeans to explore the region were Spanish. They called the region Nevada (snowy) because of the snow which covered the mountains in winter, similar to the Sierra Nevada in Spain. The area formed part of Alta California’s territory within the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which gained independence as Mexico in 1821. The United States annexed the area in 1848 after its victory in the Mexican–American War, and it was incorporated as part of Utah Territory in 1850. The discovery of silver at the Comstock Lode in 1859 led to a population boom that became an impetus to the creation of Nevada Territory out of western Utah Territory in 1861. Nevada became the 36th state on October 31, 1864, as the second of two states added to the Union during the Civil War (the first being West Virginia).
Nevada is known for its libertarian laws. In 1940, with a population of just over 110,000 people, Nevada was by far the least-populated state, with less than half the population of the next least-populous state, Wyoming. However, legalized gambling and lenient marriage and divorce laws transformed Nevada into a major tourist destination in the 20th century. Nevada is the only U.S. state where prostitution is legal, though it is illegal in its most populated regions – Clark County (Las Vegas), Washoe County (Reno) and Carson City (which, as an independent city, is not within the boundaries of any county). The tourism industry remains Nevada’s largest employer, with mining continuing as a substantial sector of the economy: Nevada is the fourth-largest producer of gold in the world. Nevada is the driest state, and over time, and influenced by climate change, droughts in Nevada have been increasing in frequency and severity, putting a further strain on Nevada’s water security.
| Before statehood: | Nevada Territory, Utah Territory, Arizona Territory |
|---|---|
| Admitted to the Union: | October 31, 1864 (36th) |
| Capital: | Carson City |
| Largest city: | Las Vegas |
| Largest metro and urban areas: | Las Vegas Valley |
| Elevation: | 5,500 ft (1,680 m) |
| Total Area: | 110,577 sq mi (286,382 km) |
| Area Rank: | 7th |
| Total Population: | 3,104,614 |
| Population Rank: | 32nd |
| Population Density: | 26.8/sq mi (10.3/km) |
| Population Density Rank: | 42nd |
| Median Household Income: | $60,365 |
| Income Rank: | 24th |
| Demonym(s): | Nevadan |
| USPS abbreviation: | NV |
| ISO 3166 code: | US-NV |
| Website: | www.nv.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Nevada location map. Where is Nevada state?
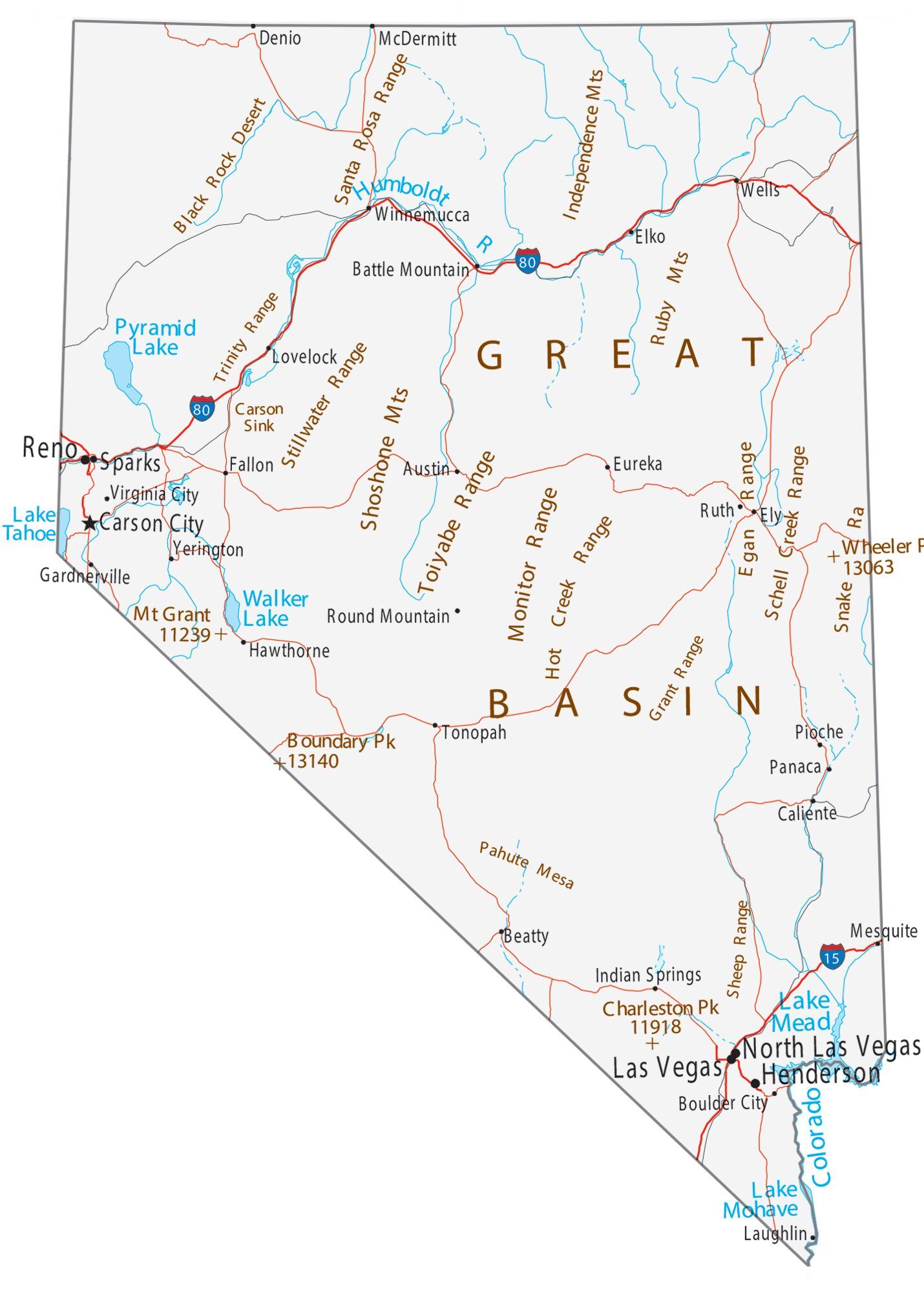
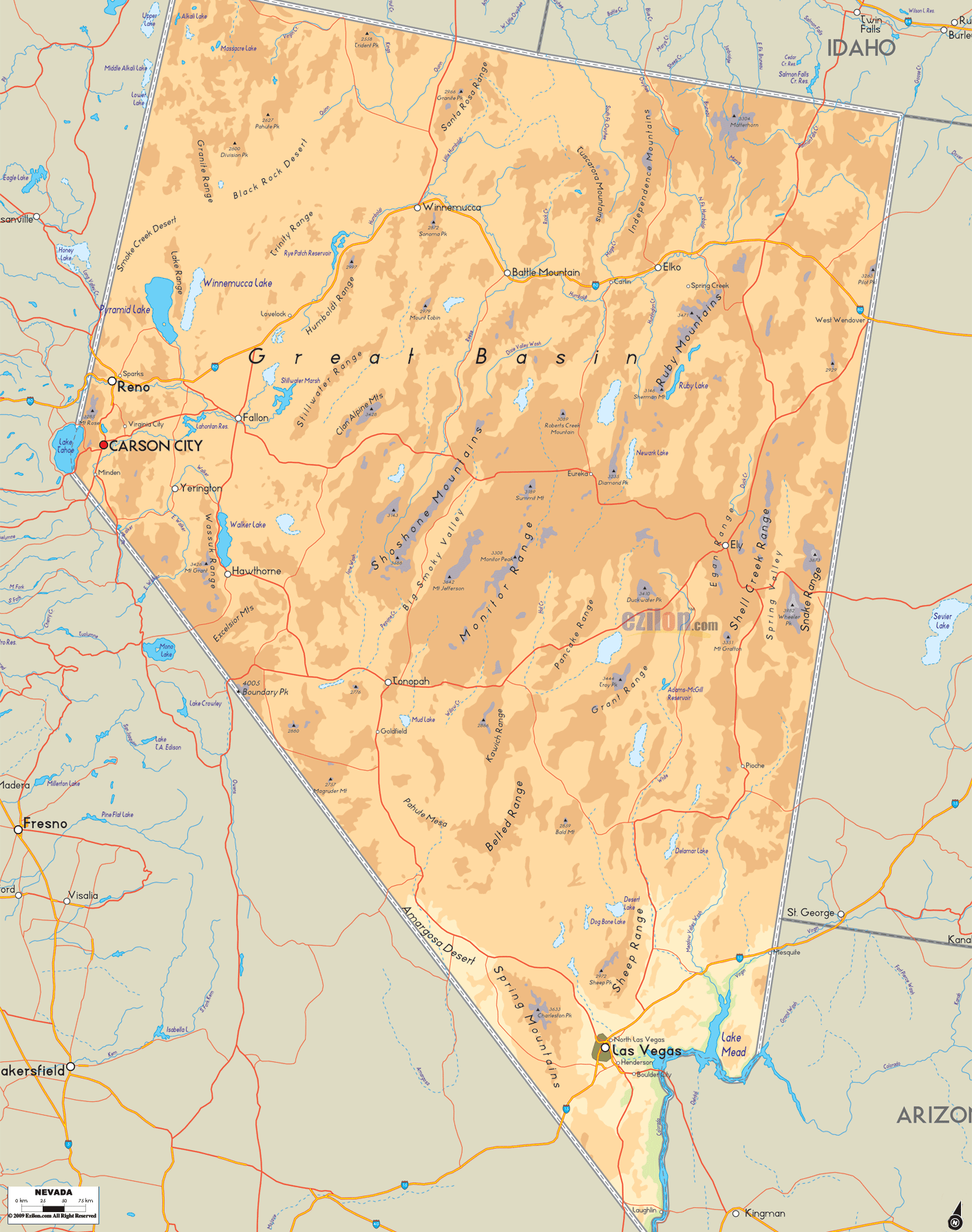
Nevada Road Map
Nevada Map – Roads & Cities
Nevada Street Map
History
Native American history
Before the arrival of Europeans, the earliest inhabitants were Native American tribes including the Goshute, the Southern Paiute people, the Mohave people, and the Wašišiw (Washoe people).
Before 1861
Francisco Garcés was the first European in the area. Nevada was annexed as a part of the Spanish Empire in the northwestern territory of New Spain. Administratively, the area of Nevada was part of the Commandancy General of the Provincias Internas in the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Nevada became a part of Alta California (Upper California) province in 1804 when the Californias were split. With the Mexican War of Independence won in 1821, the province of Alta California became a territory (state) of Mexico, with a small population. Jedediah Smith entered the Las Vegas Valley in 1827, and Peter Skene Ogden traveled the Humboldt River in 1828. When the Mormons created the State of Deseret in 1847, they laid claim to all of Nevada within the Great Basin and the Colorado watershed. They also founded the first white settlement in what is now Nevada, Mormon Station (modern-day Genoa), in 1851. In June 1855, William Bringhurst and 29 fellow Mormon missionaries from Utah arrived at a site just northeast of downtown Las Vegas and built a 150-foot square adobe fort, the first permanent structure erected in the valley, which remained under the control of Salt Lake City until the winter of 1858–1859.
As a result of the Mexican–American War and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Mexico permanently lost Alta California in 1848. The new areas acquired by the United States continued to be administered as territories. As part of the Mexican Cession (1848) and the subsequent California Gold Rush that used Emigrant Trails through the area, the state’s area evolved first as part of the Utah Territory, then the Nevada Territory (March 2, 1861; named for the Sierra Nevada).
The first discovery of a major U.S. deposit of silver ore occurred in Comstock Lode under Virginia City, Nevada, in 1859.
Separation from Utah Territory
On March 2, 1861, the Nevada Territory separated from the Utah Territory and adopted its current name, shortened from The Sierra Nevada (Spanish for “snow-covered mountain range”). The 1861 southern boundary is commemorated by Nevada Historical Markers 57 and 58 in Lincoln and Nye counties.
Statehood (1864)
Eight days before the presidential election of 1864, Nevada became the 36th state in the Union, despite lacking the minimum 60,000 residents that Congress typically required a potential state to have in order to become a state. (At the time, Nevada’s population was little more than 10,000.) Governor Nye was frustrated that previous attempts to send the constitution via overland mail and by sea had failed by October 24, so on October 26 the full text was sent by telegraph at a cost of $4,303.27 – the most costly telegraph on file at the time for a single dispatch, equivalent to $74,556.44 in 2021. Finally, the response from Washington came on October 31, 1864: “the pain is over, the child is born, Nevada this day was admitted into the Union”. Statehood was rushed to the date of October 31 to help ensure Abraham Lincoln’s reelection on November 8 and post-Civil War Republican dominance in Congress, as Nevada’s mining-based economy tied it to the more industrialized Union. As it turned out, however, Lincoln and the Republicans won the election handily and did not need Nevada’s help.
Nevada is one of only two states to significantly expand its borders after admission to the Union, with the other being Missouri, which acquired additional territory in 1837 due to the Platte Purchase. In 1866 another part of the western Utah Territory was added to Nevada in the eastern part of the state, setting the current eastern boundary. Nevada achieved its current southern boundaries on January 18, 1867, when it absorbed the portion of Pah-Ute County in the Arizona Territory west of the Colorado River, essentially all of present-day Nevada south of the 37th parallel. The transfer was prompted by the discovery of gold in the area, and officials thought Nevada would be better able to oversee the expected population boom. This area includes most of what is now Clark County and the Las Vegas metropolitan area.
Mining shaped Nevada’s economy for many years (see Silver mining in Nevada). When Mark Twain lived in Nevada during the period described in Roughing It, mining had led to an industry of speculation and immense wealth. Both mining and population temporarily declined in the late 19th century. However, the rich silver strike at Tonopah in 1900, followed by strikes in Goldfield and Rhyolite, created a second mining boom in Nevada and Nevada’s population.
Unregulated gambling was commonplace in the early Nevada mining towns but was outlawed in 1909 as part of a nationwide anti-gambling crusade. Because of subsequent declines in mining output and the decline of the agricultural sector during the Great Depression, Nevada again legalized gambling on March 19, 1931, with approval from the legislature. Governor Fred B. Balzar’s signature enacted the most liberal divorce laws in the country and open gambling. The reforms came just eight days after the federal government presented the $49 million construction contract for Boulder Dam (now Hoover Dam).
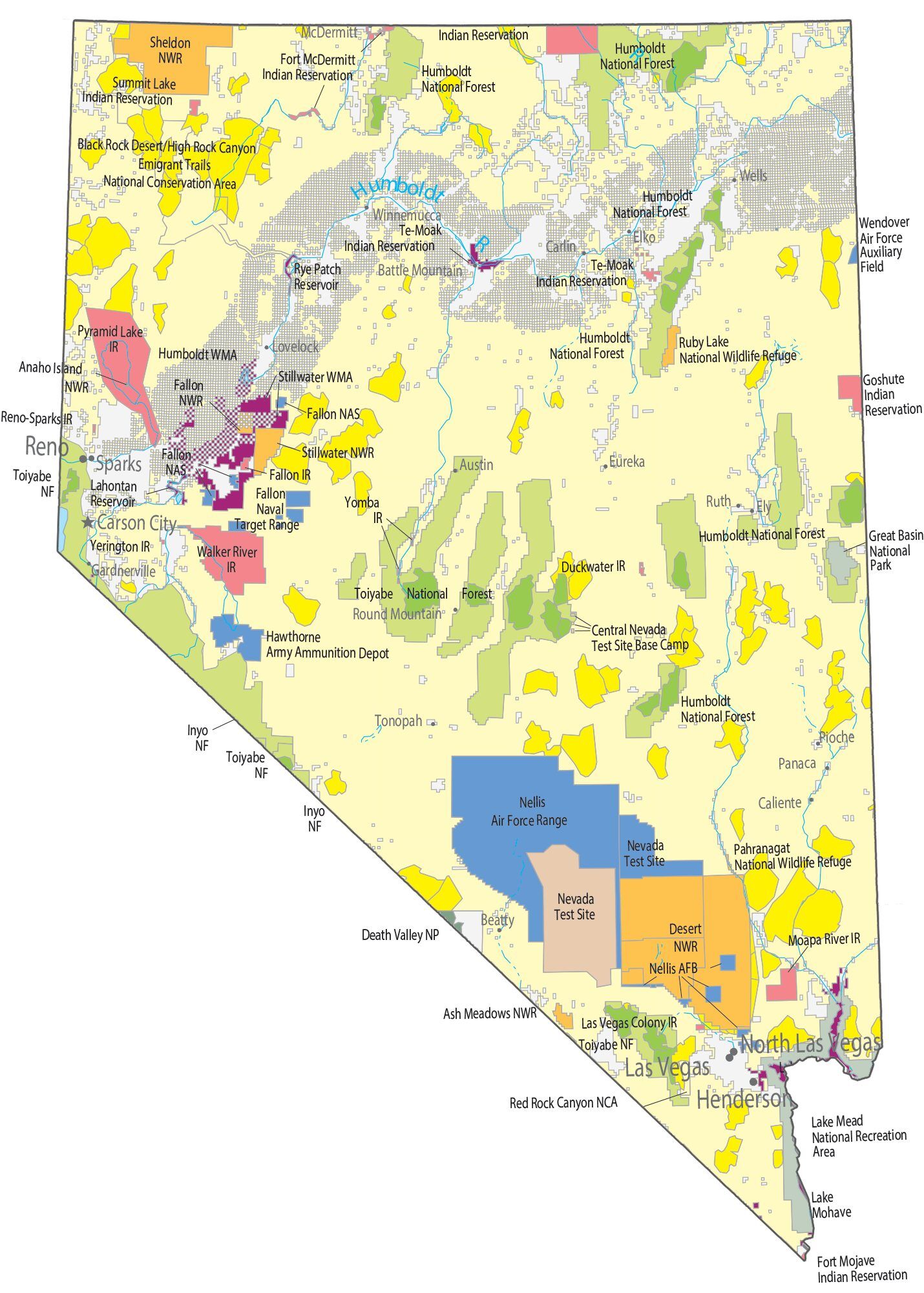
The Nevada Test Site, 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas, was founded on January 11, 1951, for the testing of nuclear weapons. The site consists of about 1,350 square miles (3,500 km) of the desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site began with a 1 kiloton of TNT (4.2 TJ) nuclear bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. The last atmospheric test was conducted on July 17, 1962, and the underground testing of weapons continued until September 23, 1992. The location is known for having the highest concentration of nuclear-detonated weapons in the U.S.
Over 80% of the state’s area is owned by the federal government. The primary reason for this is homesteads were not permitted in large enough sizes to be viable in the arid conditions that prevail throughout desert Nevada. Instead, early settlers would homestead land surrounding a water source, and then graze livestock on the adjacent public land, which is useless for agriculture without access to water (this pattern of ranching still prevails).
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Nevada on March 5, 2020. Because of concerns about coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Nevada governor Steve Sisolak declared a state of emergency on March 12, 2020. Four days later, Nevada reported its first death. On March 17, 2020, Sisolak ordered the closure of non-essential businesses in the state, to help prevent the spread of the coronavirus. Grocery stores were among the businesses considered essential, and restaurants were allowed to provide drive-thru, takeout, and delivery services. At the end of March 2020, Sisolak announced a 90-day moratorium on evictions and foreclosures for commercial and residential tenants. The moratorium would be extended several times over the next year.
Various protests were held against Sisolak’s shutdown order beginning in April 2020. Las Vegas mayor Carolyn Goodman was also critical of the shutdown and its length, urging Sisolak to reopen the state. Goodman was widely criticized after suggesting that Las Vegas become a control group to test the effectiveness of social distancing. Nevada launched the first phase of its reopening on May 9, 2020. Restaurants, retailers, outdoor malls, and hair salons were among the businesses allowed to reopen, but with precautions in place, such as limiting occupancy to 50 percent. A second phase went into effect on May 29, 2020. It allowed for the reopening of state parks and businesses such as bars, gyms, and movie theaters. Casinos began reopening on June 4, 2020.
Nevada State Map – Places and Landmarks
Nevada Political Map
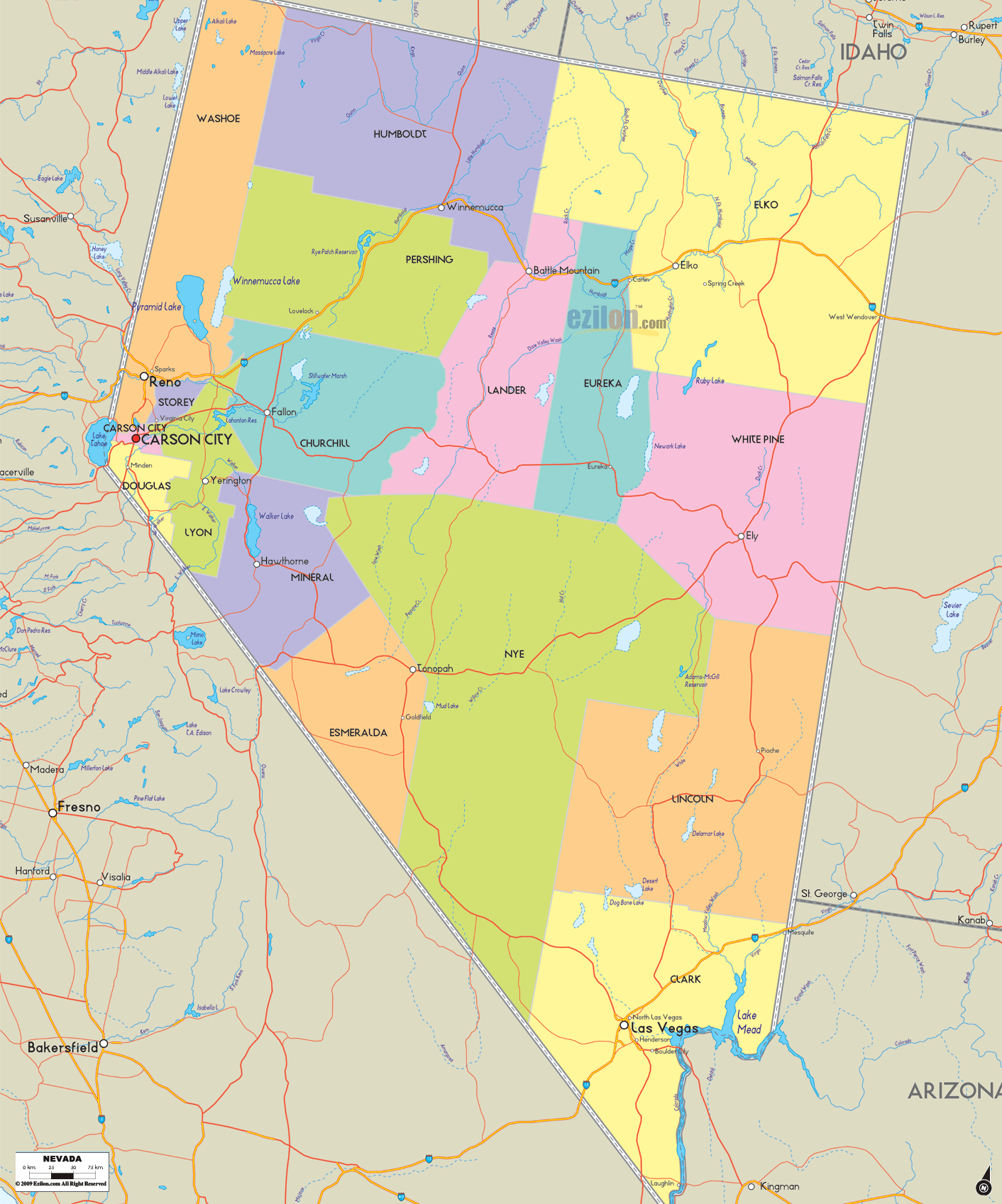
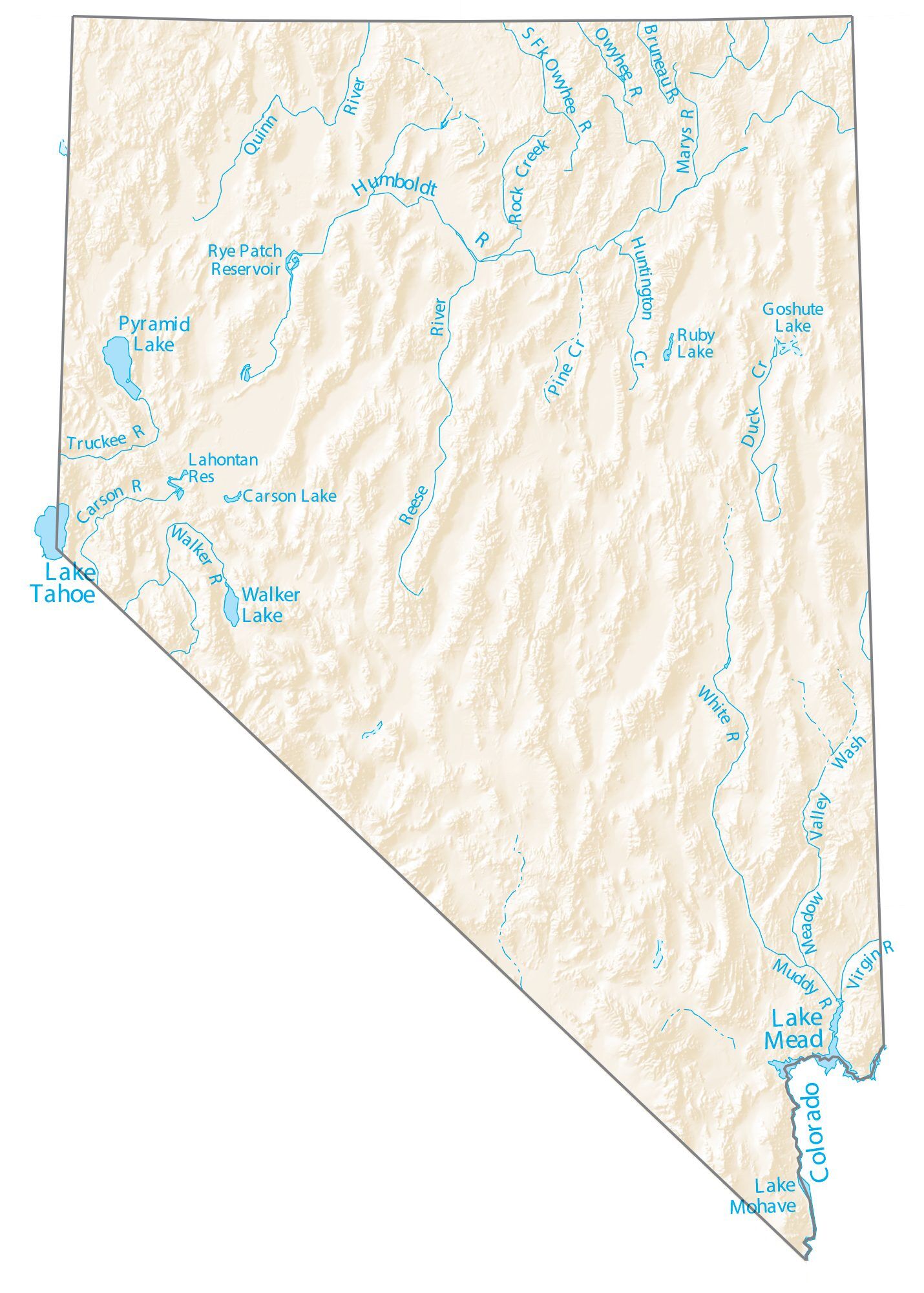
Nevada Lakes and Rivers Map
Geography
Nevada is almost entirely within the Basin and Range Province and is broken up by many north–south mountain ranges. Most of these ranges have endorheic valleys between them.
Much of the northern part of the state is within the Great Basin, a mild desert that experiences hot temperatures in the summer and cold temperatures in the winter. Occasionally, moisture from the Arizona Monsoon will cause summer thunderstorms; Pacific storms may blanket the area with snow. The state’s highest recorded temperature was 125 °F (52 °C) in Laughlin (elevation of 605 feet or 184 meters) on June 29, 1994. The coldest recorded temperature was −52 °F (−47 °C) set in San Jacinto in 1972, in the northeastern portion of the state.
The Humboldt River crosses the state from east to west across the northern part of the state, draining into the Humboldt Sink near Lovelock. Several rivers drain from the Sierra Nevada eastward, including the Walker, Truckee, and Carson rivers. All of these rivers are endorheic basins, ending in Walker Lake, Pyramid Lake, and the Carson Sink, respectively. However, not all of Nevada is within the Great Basin. Tributaries of the Snake River drain the far north, while the Colorado River, which also forms much of the boundary with Arizona, drains much of southern Nevada.
The mountain ranges, some of which have peaks above 13,000 feet (4,000 m), harbor lush forests high above desert plains, creating sky islands for endemic species. The valleys are often no lower in elevation than 3,000 feet (910 m), while some in central Nevada are above 6,000 feet (1,800 m).
The southern third of the state, where the Las Vegas area is situated, is within the Mojave Desert. The area receives less rain in the winter but is closer to the Arizona Monsoon in the summer. The terrain is also lower, mostly below 4,000 feet (1,200 m), creating conditions for hot summer days and cool to chilly winter nights.
Nevada and California have by far the longest diagonal line (in respect to the cardinal directions) as a state boundary at just over 400 miles (640 km). This line begins in Lake Tahoe nearly 4 miles (6.4 km) offshore (in the direction of the boundary), and continues to the Colorado River where the Nevada, California, and Arizona boundaries merge 12 miles (19 km) southwest of the Laughlin Bridge.
The largest mountain range in the southern portion of the state is the Spring Mountain Range, just west of Las Vegas. The state’s lowest point is along the Colorado River, south of Laughlin.
Nevada has 172 mountain summits with 2,000 feet (610 m) of prominence. Nevada ranks second, after Alaska, for the greatest number of mountains in the United States, followed by California, Montana, and Washington.
Climate
Nevada is the driest state in the United States. It is made up of mostly desert and semi-arid climate regions, and, with the exception of the Las Vegas Valley, the average summer diurnal temperature range approaches 40 °F (22 °C) in much of the state. While winters in northern Nevada are long and fairly cold, the winter season in the southern part of the state tends to be of short duration and mild. Most parts of Nevada receive scarce precipitation during the year. The most rain that falls in the state falls on the east and northeast slopes of the Sierra Nevada.
The average annual rainfall per year is about 7 inches (180 mm); the wettest parts get around 40 inches (1,000 mm). Nevada’s highest recorded temperature is 125 °F (52 °C) at Laughlin on June 29, 1994, and the lowest recorded temperature is −50 °F (−46 °C) at San Jacinto on January 8, 1937. Nevada’s 125 °F (52 °C) reading is the third highest statewide record high temperature of a U.S. state, just behind Arizona’s 128 °F (53 °C) reading and California’s 134 °F (57 °C) reading.
Flora and fauna
The vegetation of Nevada is diverse and differs by state area. Nevada contains six biotic zones: alpine, sub-alpine, ponderosa pine, pinion-juniper, sagebrush and creosotebush.
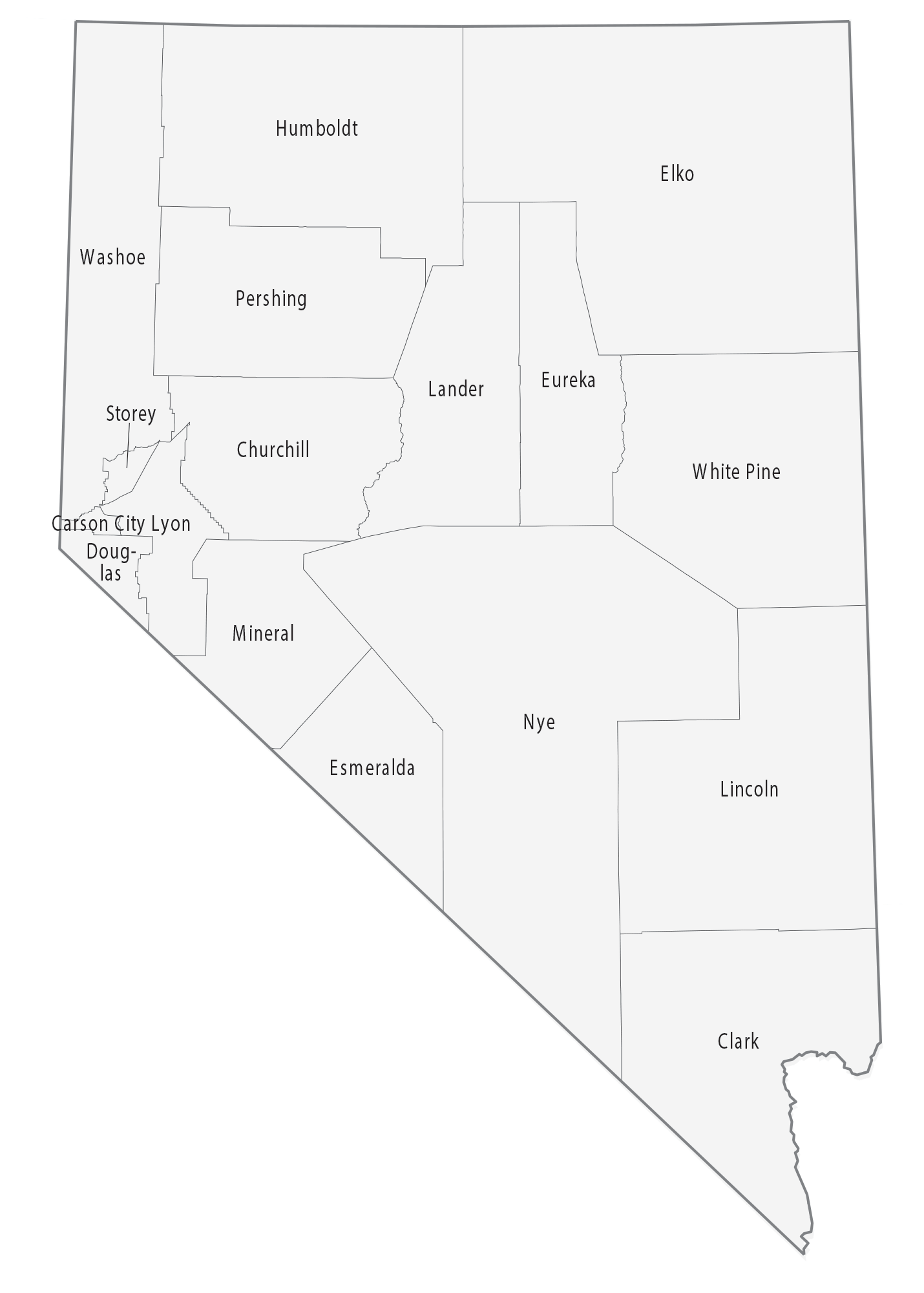
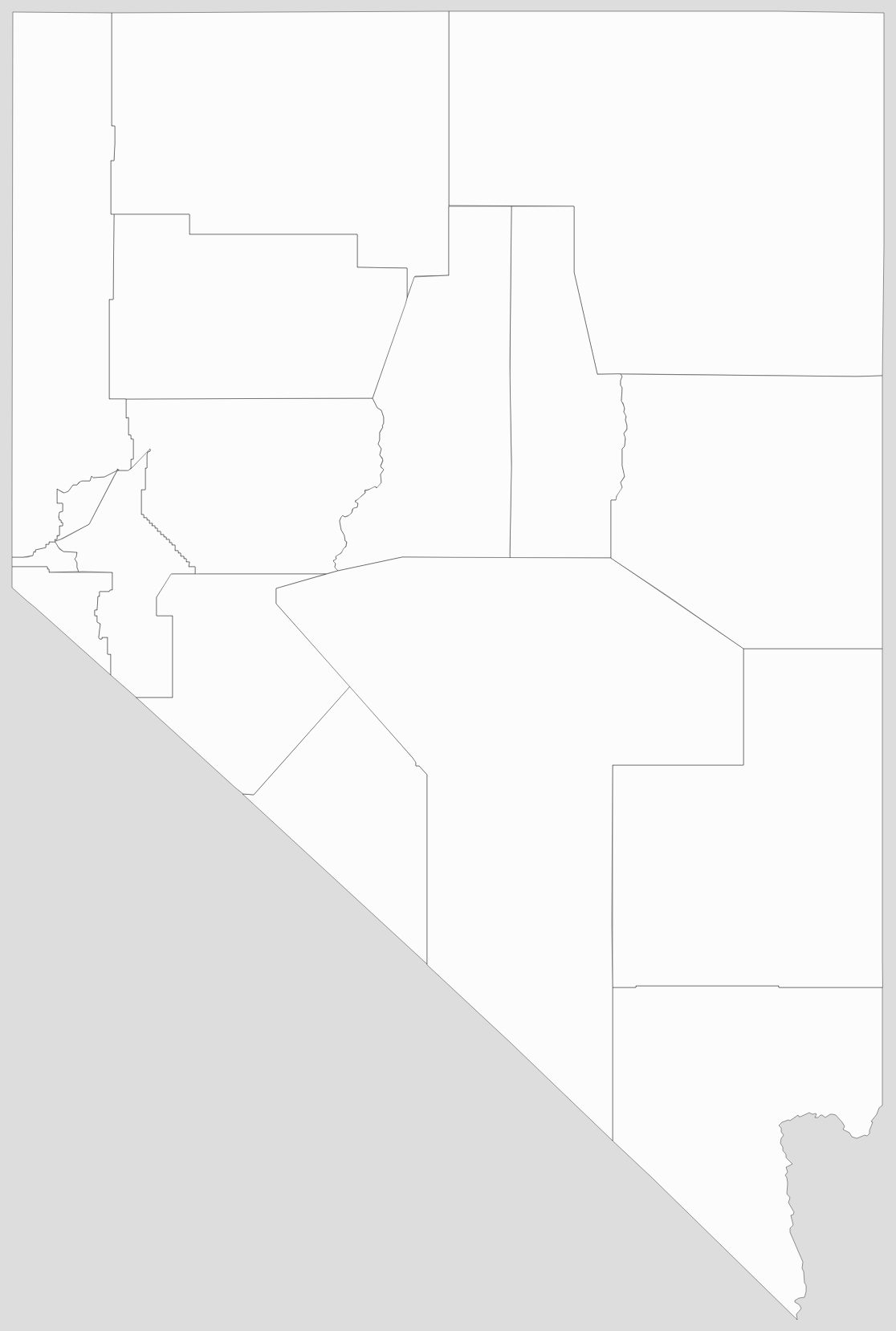
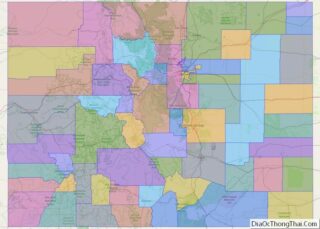
Counties
Nevada is divided into political jurisdictions designated as counties. Carson City is officially a consolidated municipality, meaning it legally functions as both a city and a county. As of 1919, there were 17 counties in the state, ranging from 146 to 18,159 square miles (380 to 47,030 km).
Lake County, one of the original nine counties formed in 1861, was renamed Roop County in 1862. Part of the county became Lassen County, California, in 1864, resolving border uncertainty. In 1883, Washoe County annexed the portion that remained in Nevada.
In 1969, Ormsby County was dissolved and the Consolidated Municipality of Carson City was created by the Legislature in its place coterminous with the old boundaries of Ormsby County.
Bullfrog County was formed in 1987 from part of Nye County. After the creation was declared unconstitutional, the county was abolished in 1989.
Humboldt County was designated as a county in 1856 by Utah Territorial Legislature and again in 1861 by the new Nevada Legislature.
Clark County is the most populous county in Nevada, accounting for nearly three-quarters of its residents. Las Vegas, Nevada’s most populous city, has been the county seat since the county was created in 1909 from a portion of Lincoln County, Nevada. Before that, it was a part of Arizona Territory. Clark County attracts numerous tourists: An estimated 44 million people visited Clark County in 2014.
Washoe County is the second-most populous county of Nevada. Its county seat is Reno. Washoe County includes the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
Lyon County is the third most populous county. It was one of the nine original counties created in 1861. It was named after Nathaniel Lyon, the first Union General to be killed in the Civil War. Its current county seat is Yerington. Its first county seat was established at Dayton on November 29, 1861.
Settlements
Nevada Physical Map
Nevada Topographic Map
Nevada Satellite Map
Others printable maps
Nevada Outline Map
Blank Nevada County Map
See also
Map of Nevada State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming