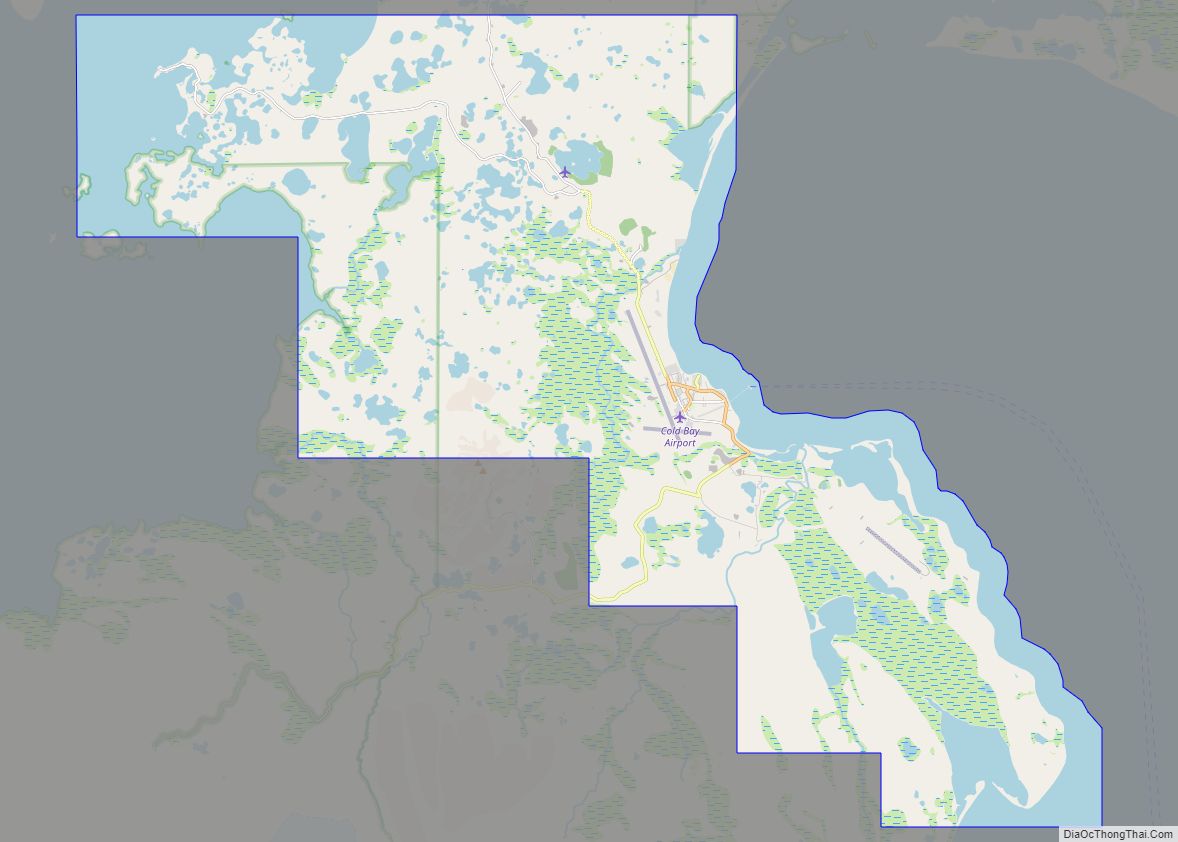
Cold Bay (Aleut: Udaamagax,; Sugpiaq: Pualu) is a city in Aleutians East Borough, Alaska, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 108, but at the 2020 census this had reduced to 50.
Cold Bay is one of the main commercial centers of the Alaska Peninsula, which extends west towards the Aleutian Islands, and is home to Cold Bay Airport.
| Name: | Cold Bay city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Aleutians East Borough |
| Incorporated: | January 1982 |
| Elevation: | 138 ft (42 m) |
| Total Area: | 68.06 sq mi (176.26 km²) |
| Land Area: | 53.41 sq mi (138.34 km²) |
| Water Area: | 14.64 sq mi (37.92 km²) |
| Total Population: | 50 |
| Population Density: | 0.94/sq mi (0.36/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99571 |
| Area code: | 907 (local prefix: 532) |
| FIPS code: | 0216530 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1418448 |
| Website: | http://www.coldbay.org/ |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
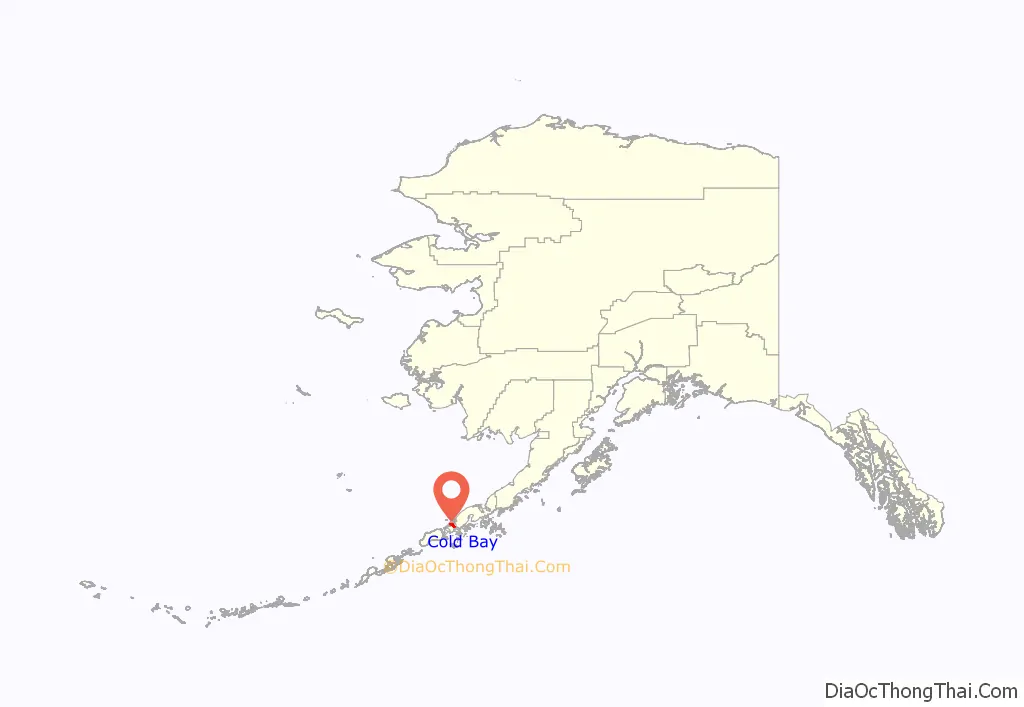
Cold Bay location map. Where is Cold Bay city?
History
There is evidence of prehistoric occupation by Aleuts and later Russian encampments. Cold Bay’s significance to American history began with the Japanese invasion of the Aleutians in World War II. General Simon Bolivar Buckner, Jr. ordered the creation of Fort Randall, an airbase on the shores of Cold Bay, in 1942 as a part of a general expansion of American assets in the Aleutians. It (along with Otter Point) served as a base for the 11th Air Force to provide protection to the only deep water port in the Aleutians at the time, Dutch Harbor.
This protection was necessary when during Yamamoto’s Midway Campaign, a diversionary attack was launched against Dutch Harbor. The initial attack was repulsed by the surprise presence of P-40s stationed here. A second larger attack with its own fighter escort the next day caused minor damage. Later, with the victory in the Pacific, the forces grew to 20,000 troops. The quonset huts used to house this massive encampment still stand around the community. It also was a base of operations for the US Navy with the seaplane tender USS Casco (AVP-12) among the ships based in Cold Bay.
In the spring and summer of 1945, Cold Bay was the site of the largest and most ambitious transfer program of World War II, Project Hula, in which the United States transferred dozens of ships and craft to the Soviet Union and trained Soviet personnel in their operation in anticipation of the Soviet Union entering the war against Japan.
In later decades, control of the airfield passed to civil authorities, who maintained it as a useful refueling and emergency landing location for great circle flights from the west coast of the United States to East Asia. A Distant Early Warning Line station established nearby was eventually decommissioned.
During the 1980s, deregulation of the airline industry under President Ronald Reagan caused many of the compelling interests supporting the need for the community to evaporate. Today, Cold Bay is still occasionally used for emergency or precautionary landings of commercial flights, and is also a hub for traffic from Anchorage and Seattle to the small communities around it.
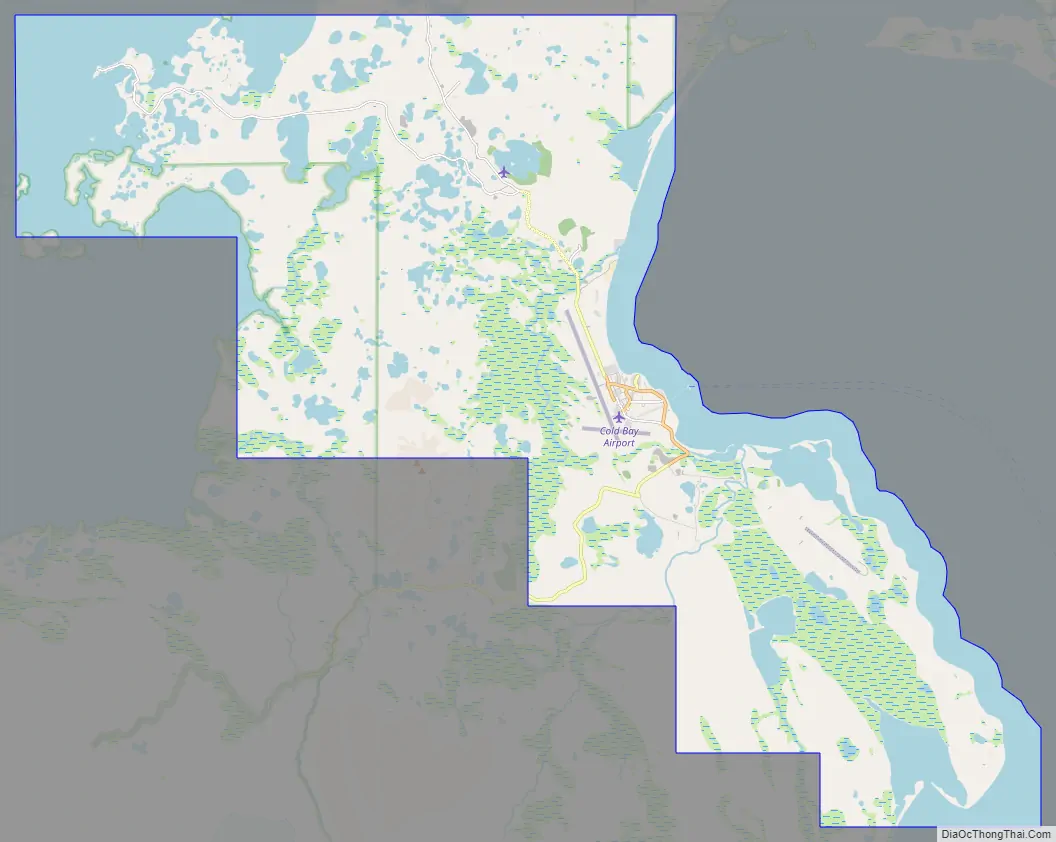
Cold Bay Road Map
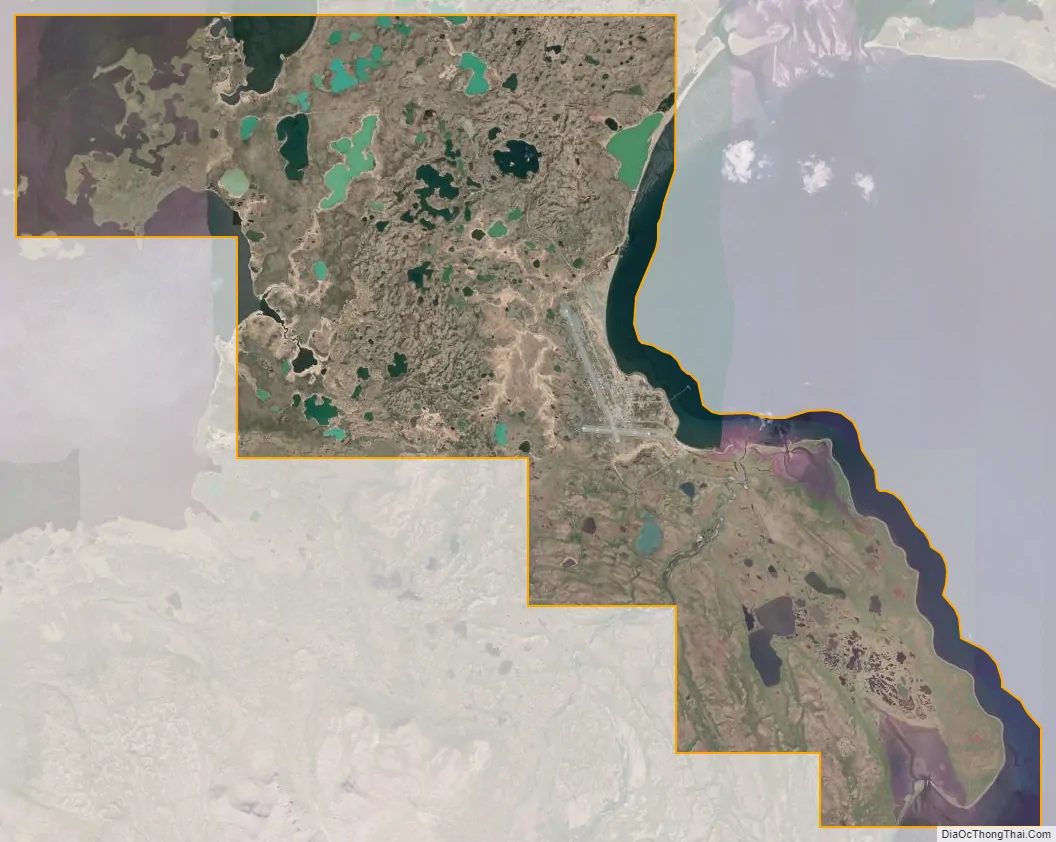
Cold Bay city Satellite Map
Geography
Cold Bay is located at 55°12′33″N 162°42′51″W / 55.20917°N 162.71417°W / 55.20917; -162.71417 (55.209038, -162.714298). It is west of Hawaii.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 70.9 square miles (184 km), of which, 54.4 square miles (141 km) of it is land and 16.6 square miles (43 km) of it (23.34%) is water.
Cold Bay holds the record for most overcast community in America.
Climate
Cold Bay has an either an ocean-moderated subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification: Dfc) if the 0 °C isotherm is used, or a subpolar oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfc) if the −3 °C (26.6 °F) isotherm is used, both of those climate being typical of southwest Alaska, though the summers are almost cool enough to qualify as a tundra (Köppen climate classification: ET). Cold Bay is considered the cloudiest place in the United States, with an average of 304 days of heavy overcast (covering over 3/4 of the sky).
Cold Bay’s recorded temperature range is between 78 °F (26 °C) and −13 °F (−25 °C). The coldest daytime maximum on record is 0 °F (−18 °C), while the annual coldest maximum between 1991 and 2020 was at 16 °F (−9 °C). With warm summer days being rare, nights remain chilly also during the warmer season. The warmest recorded overnight low is at a very modest 57 °F (14 °C) and the annual average warmest night tends to fall to 53 °F (12 °C). Many years fail to break 68 °F (20 °C) during the warmest afternoon.
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming