Sahuarita /sɑːwəˈriːtə/ is a town in Pima County, Arizona, United States. Sahuarita is located south of the Tohono O’odham Nation and abuts the north end of Green Valley, 15 miles (24 km) south of Tucson. The population was 34,134 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Sahuarita town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | Arizona |
| County: | Pima County |
| Founded: | 1911 |
| Incorporated: | 1994 |
| Elevation: | 2,703 ft (824 m) |
| Total Area: | 31.68 sq mi (82.06 km²) |
| Land Area: | 31.68 sq mi (82.06 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 34,134 |
| Population Density: | 1,077.36/sq mi (415.97/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 85629 |
| Area code: | 520 |
| FIPS code: | 0462140 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 33948 |
| Website: | http://www.sahuaritaaz.gov/ |
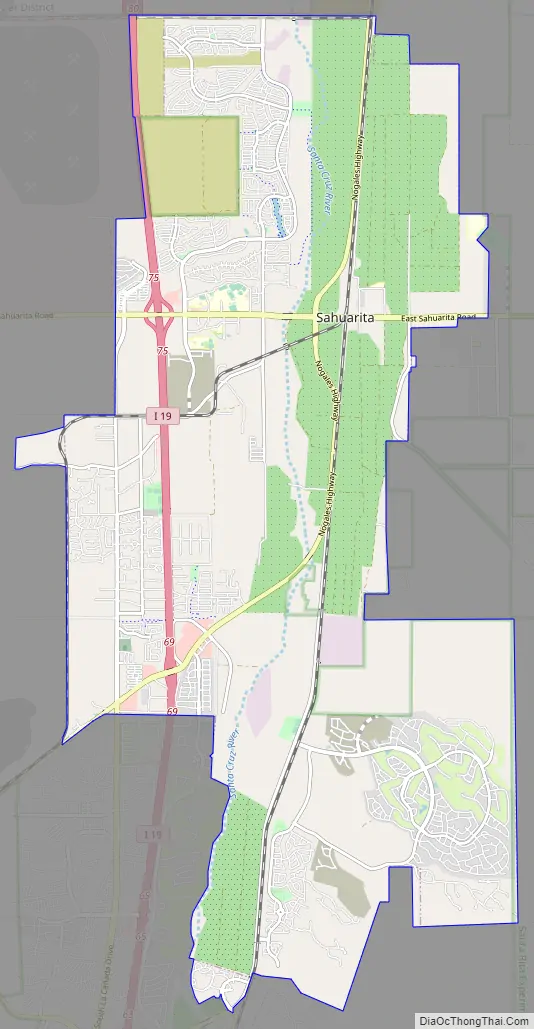
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
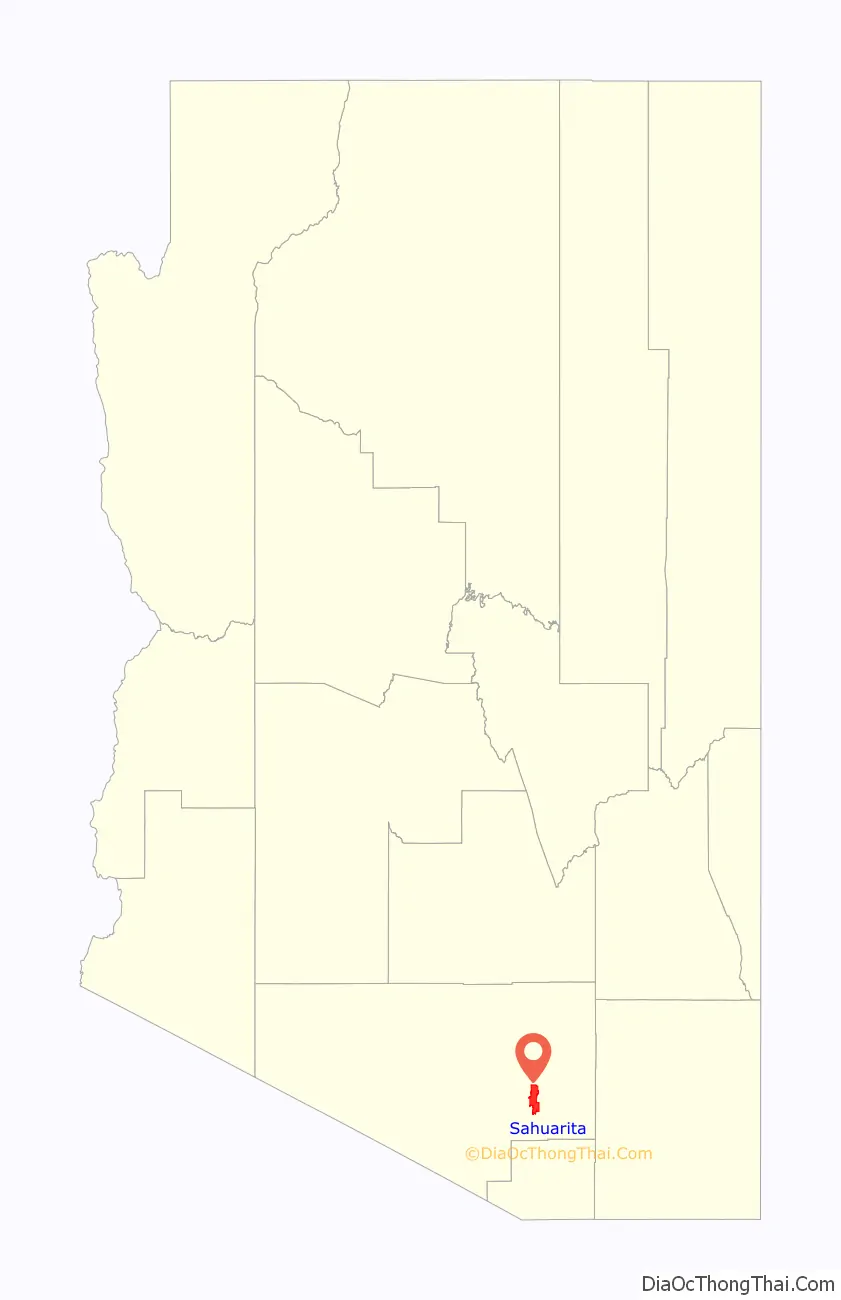
Sahuarita location map. Where is Sahuarita town?
History
Sahuarita was founded in 1911 and incorporated in 1994.
Hohokam (200–1450)
The first known human inhabitants of the Sahuarita region were the Hohokam people, which may be the ancestors of the modern day Tohono O’odham nation. The Hohokam were known for their highly innovative and extensive use of irrigation. The Hohokam were a very peaceful people, they had extensive trade routes extending to Mesoamerica, and showed many cultural influences from their southern neighbors.
Sobaipuri (1400–1900)
The Sobaipuri were possibly related to the Hohokam, and occupied the Southern portion of the Santa Cruz, with the Pima to their North and South. While Coronado passed just east of Sahuarita in 1521, it wasn’t until Eusebio Kino’s 1691 journey along the Santa Cruz River that he met the leaders of the Sobaipuri people. Kino was a true champion of the indigenous Indians, opposing forced labor in mines by Spanish overseers. Kino would later go on to found the Mission San Xavier del Bac in 1699, just north of Sahuarita. In 1775, Francisco Garcés would follow the same path, laying the groundwork for the founding of Tucson.
Spanish and Mexican control (1775–1853)
In 1775, after building a series of missions in the region, the Spanish established a fort in the Tucson region to control the Native American settlements nearby. This just north of Sahuarita, which effectively placed the region under Spanish control. Eventually a town came to be and was named Tucson. After the Mexican War of Independence in 1821, the region came under Mexican control until they sold the land to the United States as part of the Gadsden Purchase.
Incorporation into the U.S. (1854–1874)
In 1854, following the Gadsden Purchase, Sahuarita would become a part of the Territory of New Mexico, in the United States of America. In the same year, Andrew B. Gray would travel the region on behalf of the Texas Western Railroad, in order to run a preliminary survey of the region. Meanwhile, the Native American peoples of the region were being pushed onto each other’s land through American expansionism. In 1857, the Sobaipuri, who had acted as a buffer between the hostile Mexicans to the south and Apache to the north, finally collapsed under the pressure and vacated the area, generally moving westward to Papago territory. Sahuarita was part of the Confederate Arizona Territory between 1861 and 1862 before being captured by the Union and incorporated into Arizona Territory in 1863. In 1867, Fort Crittenden was created between Sonoita and Patagonia in order to support the establishment of American settlements in the Santa Cruz Valley. In 1874, the San Xavier reservation was created, now called the Tohono O’odham Reservation, and Native Americans were forcibly relocated to the reservation.
Sahuarita on the map (1870–1925)
An 1870 map of Arizona shows an “Indian Village” just north of Sahuarita. The earliest known reference to the town can be found on a German map from 1875, which labels the town “Sahuarito”. The first known US map to list the town came in 1879, by the US Department of Interior, calling the town “Saurita”. The Saurita town name would continue to be found on successive maps of 1880 and 1890. Finally, a 1925 map of “Auto Trails” (e.g. roadways) of Arizona and New Mexico lists “Continental” instead of Sahuarita. The roadway at the time was an “improved road”, one step inferior to a “paved road”, laying the route to what today is called the Old Nogales Highway.
Sahuarita Ranch (1879–1886)
In 1879 Sahuarita Ranch was created by James Kilroy Brown. Brown choose the name Sahuarita due to the preponderance of saguaros in the area. The ranch was used as a staging area between Tucson, Arivaca, and Quijotoa. A small community developed in the area named Sahuarito, while the railroad laid tracks through the area (which remain to this day) and established a station and post office. Although originally surveyed by the Texas Western Railroad, the route would soon be run by the Southern Pacific Railroad up until the late 20th century. Brown sold his ranch in 1886 which caused the region to stagnate for three decades.
During this time, the hub of Sahuarita commerce was at the intersection of Sahuarita Road and Nogales Highway, in the form of the One Stop Market and Sahuarita Bar and Grill. These 130-year-old buildings which remained intact were demolished for a road expansion in 2013.
Continental Farm (1915–present)
The Continental Farm of Sahuarita plays a central role in town history. In 1915, worried about the possibility of a German blockade of rubber imports, Bernard Baruch, Joseph Kennedy and J.P. Morgan founded the farm along the Santa Cruz River with hopes of growing guayule: plants that provide rubber. The project was abandoned after the end of World War I, and in 1922, was sold to Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands. The Queen rented the land to cotton farmers, in what would be the primary crop for the following four decades. In 1948, R. Keith Walden relocated the Farmers Investment Co. (FICO) from California to Arizona, buying the Continental Farm lands from the Queen. In 1965, over fears of a fall in demand for cotton resulting from the advent of synthetic fibers, Walden switched his crop to pecans. Today, the FICO pecan orchard is the largest in the world, with over 6,000 acres (24 km) and 106,000 trees.
World War II (1941–1945)
During World War II, Sahuarita was home to the Sahuarita Airstrip which was used to train bomber pilots for service in the war. Camp Continental, a labor camp for German prisoners of war was also located in Sahuarita. The location of the camp was around what is now Continental Ranch, West of the Nogales Highway and the Quail Crossing Boulevard intersection. It was established around November, 1944, as one of 21 “branch” POW camps established throughout the state. The population of 250 prisoners primarily worked in agriculture, tending to cotton and vegetable crops. More than one escape attempt was made by the Germans, all of which failed.
Sahuarita Bombing and Gunnery Range (1942–1978)
The United States Army Air Corps, from Davis–Monthan Air Force Base, first used this 27,046-acre (109.45 km) range in April, 1942 for practice bombing runs. The Sahuarita Flight Strip was completed in 1943, with a 5,540-foot (1,690 m) paved runway, and the bombing runs ceased shortly thereafter. The site included 12 buildings in addition to the airstrip, and four observational towers. In 1950, bomber crews operating out of Carswell AFB, Texas, restarted bombing runs on the range, which would last until 1962, with the airway strip remaining in use as an emergency landing strip thereafter. The Federal government soon released the land to the State of Arizona in 1978, who in turn leased the land to a cattle rancher. The former airstrip has been converted into a roadway that leads to “Sahuarita Park”, while the remaining land remains in use for cattle grazing.
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers is continuing its longstanding efforts of identifying remaining munitions, preventing environmental contamination, and protecting several endangered species in the area, including jaguars, spotted owls, among others. Several different types of expended ammunition rounds can be found throughout the range, most of which found are 10 to 20 mm anti-aircraft rounds. Shrapnel from the dropped ordnance also litters the range, as well as dozens of crushed olive drab ammunition boxes. Shell casings and magazine clips can also be found, along with JATO tanks and large cross targets, constructed of wood with orange reflectors for visibility from the air. The crosses were used as targets for the airmen in training. Many United States Tobacco Company tins have been found, discarded by the several different aviators who occupied the area during its military days. The actual airstrip is now used as a road leading to Sahuarita Park and the Edge Charter School, both of which were built among the remains of the older air force buildings.
Cold War
Sahuarita contains the Titan Missile Museum, built in 1963 during the height of the Cold War, which is the only Titan Missile site in the world accessible to the public. The actual Titan II missile, the most powerful nuclear missile on standby in the US, remains in the silo for visitors to see. The Sahuarita Airstrip continued to be used by the U.S. Air Force throughout most of the Cold War.
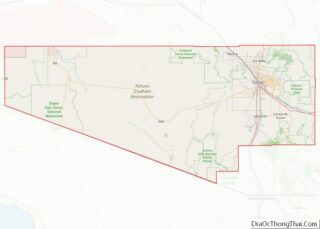
Sahuarita Road Map
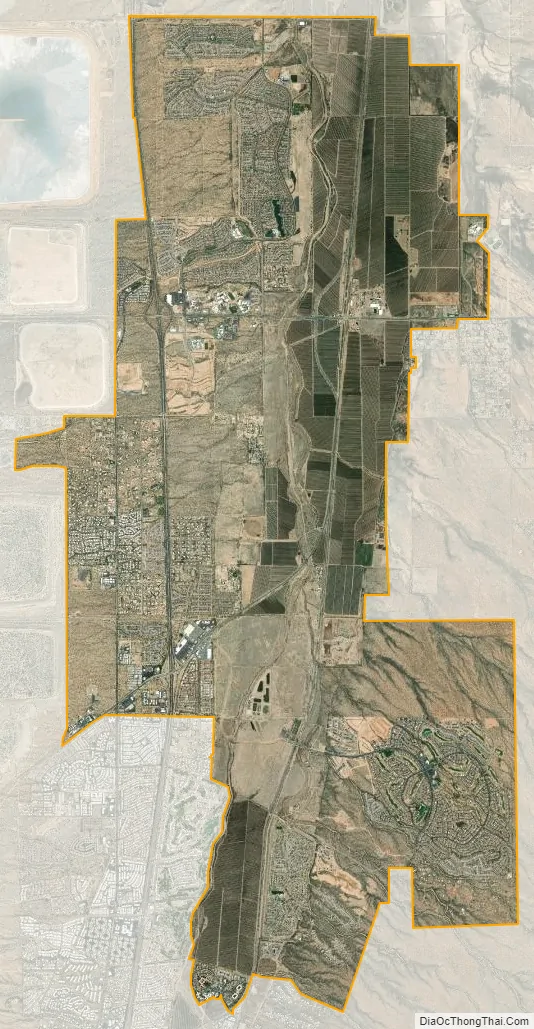
Sahuarita city Satellite Map
Geography
Sahuarita is located at 31°55′45″N 110°58′56″W / 31.92917°N 110.98222°W / 31.92917; -110.98222 (31.929245, -110.982241). According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 15.2 square miles (39.4 km), all land. Since the most recent census was taken in 2000, the town has annexed more land; its area is now approximately 30 sq mi (80 km). The Santa Cruz River (Arizona) runs through the desert town, flowing north towards Tucson, mostly during the monsoons, or extended climatic wet periods. Late 19th century and early 20th century still contained beaver in the river from Tucson, southwards. Madera Canyon, located just southeast of the town, is another important landmark, day trip site, and a birdwatching point.
Water sustainability
In the desert southwest, water sustainability is a major concern. According to a 2007 report by Pima County, 76,000 acre-feet (94,000,000 m) of water was pumped from the aquifer in the Upper Santa Cruz Valley in 2006 [in the report referred to as the Green Valley area, which includes Sahuarita], with 85 percent of that water being used for mining and agriculture. The remaining 15 percent was split between water used for golf courses and residential/commercial water use. The report explains that “The Green Valley area does not have a sustainable water supply given current groundwater pumping rates… the water table in Green Valley has been declining in past years, and is expected to decline even faster as water demands [continue to increase]…”. The report concludes that “Water supplies will become critical within the next ten years.”
The Upper Santa Cruz Valley has several “major water users”, all pumping water out of the same aquifer. None of these are owned by Pima County, the town of Sahuarita, nor Green Valley. The major water users are all private companies: ASARCO-Mission Mine, Phelps Dodge Sierrita Mine; Farmers Water Company; Sahuarita Water Company, Las Quintas Serenas Water Company, Quail Creek Water Company, Community Water Company of Green Valley, and the Green Valley Water District. The proliferation of water companies can be partially explained by the fact that the actual water in the aquifer is not owned by anyone, thus any amount of water can be pumped out, with costs limited only to drilling, pumping, distribution, etc.
Sahuarita Lake
Sahuarita Lake is an artificial lake that was completed on June 22, 2001, by Rancho Sahuarita. The lake surface area is 435,600 square feet (40,470 m), with a 1-mile (1.6 km) long perimeter and maximum depth of 10 feet (3.0 m), holding approximately 70 acre-feet (86,000 m) of water. This reflects a water amount equivalent to less than one tenth of one percent (<0.1%) of the 76,000 acre-feet (94,000,000 m) of water used by all of Sahuarita and Green Valley in 2006.
The lake is a “managed lake”, which means that natural ecological changes within the lake that do “not fit within the parameters set by man”, are cause for remedial action to return to the goals of the management plan. Air compressors located at various points under the lake continually inject air through diffusers which aids the movement of water in a process called vertical mixing. This system of continual aeration enables the circulation of all water in the lake on a daily basis, and therefore creates an ecological balance and uniform appearance. The lake also contains fish and frogs, the former of which are regularly stocked by the Arizona State Department of Game and Fish, and is an attraction to ducks and various kinds of birds.
The lake consumes water to the extent that all the water in the lake must be replenished every year. Regarding water evaporation, lake documents state that according to the USDA Water Conservation Laboratory in Phoenix, the mean annual evaporation rate for Sahuarita is 69 inches (1,800 mm) per year. This results in a mean water loss of 57.5 acre-feet (70,900 m) per year. Regarding water loss due to seepage, initial estimates indicated an annual loss of 10 acre-feet (12,000 m) of water, or 17% of total capacity per year. The J. Harlan Glenn Engineers that provided this estimate indicated that this equates to an “extremely low seepage rate”. On average, 65 gpm (gallons of water per minute) must be pumped into the lake to maintain its current level. A nearby well site that draws on the shared Upper Santa Cruz Valley aquifer is used to refill the lake. In 2006, 105.3 acre-feet (129,900 m) of water was used for the entire Sahuarita lake park, which includes water for the 5 acres (20,000 m) of grass and restroom facilities.
See also
Map of Arizona State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming