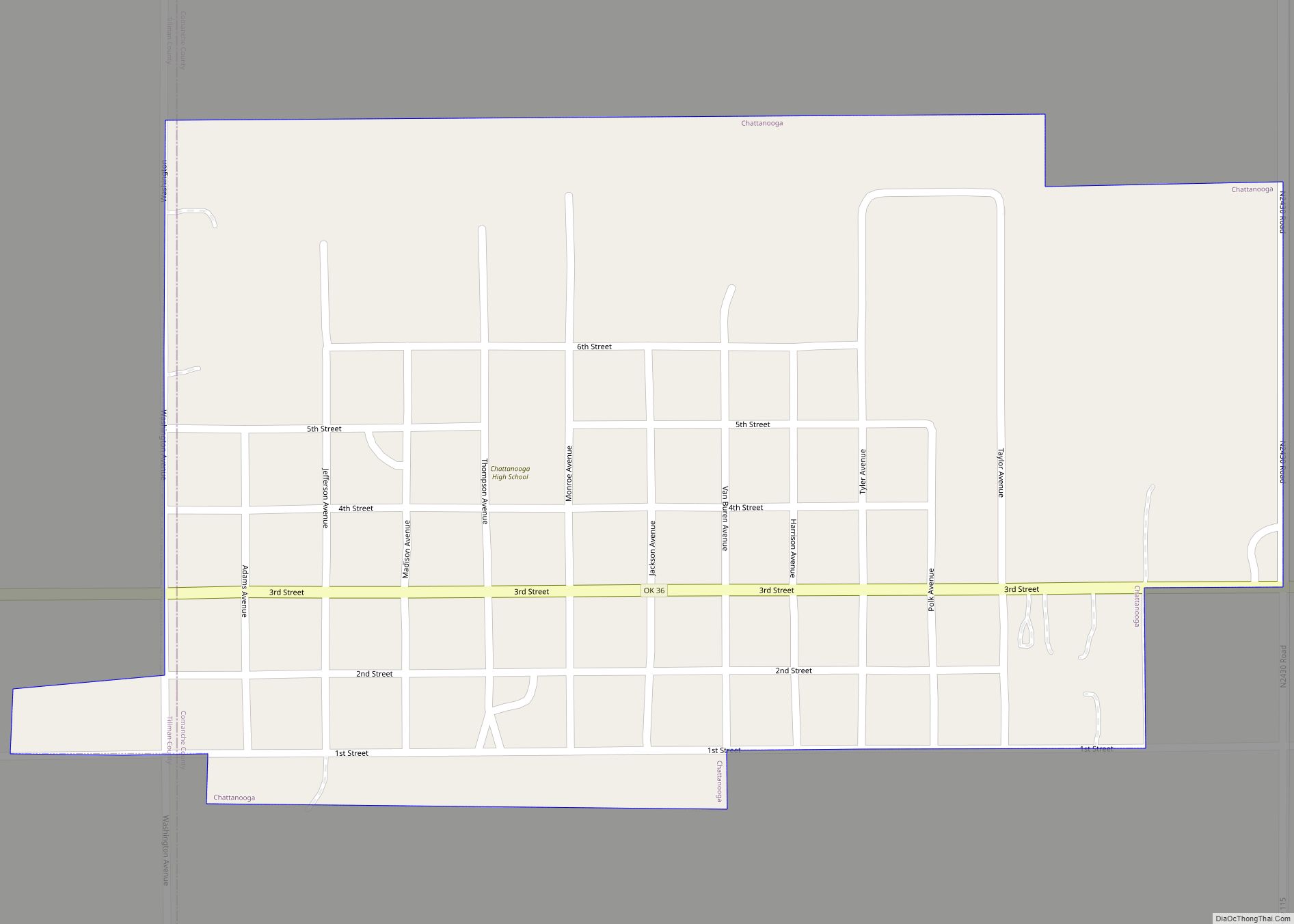
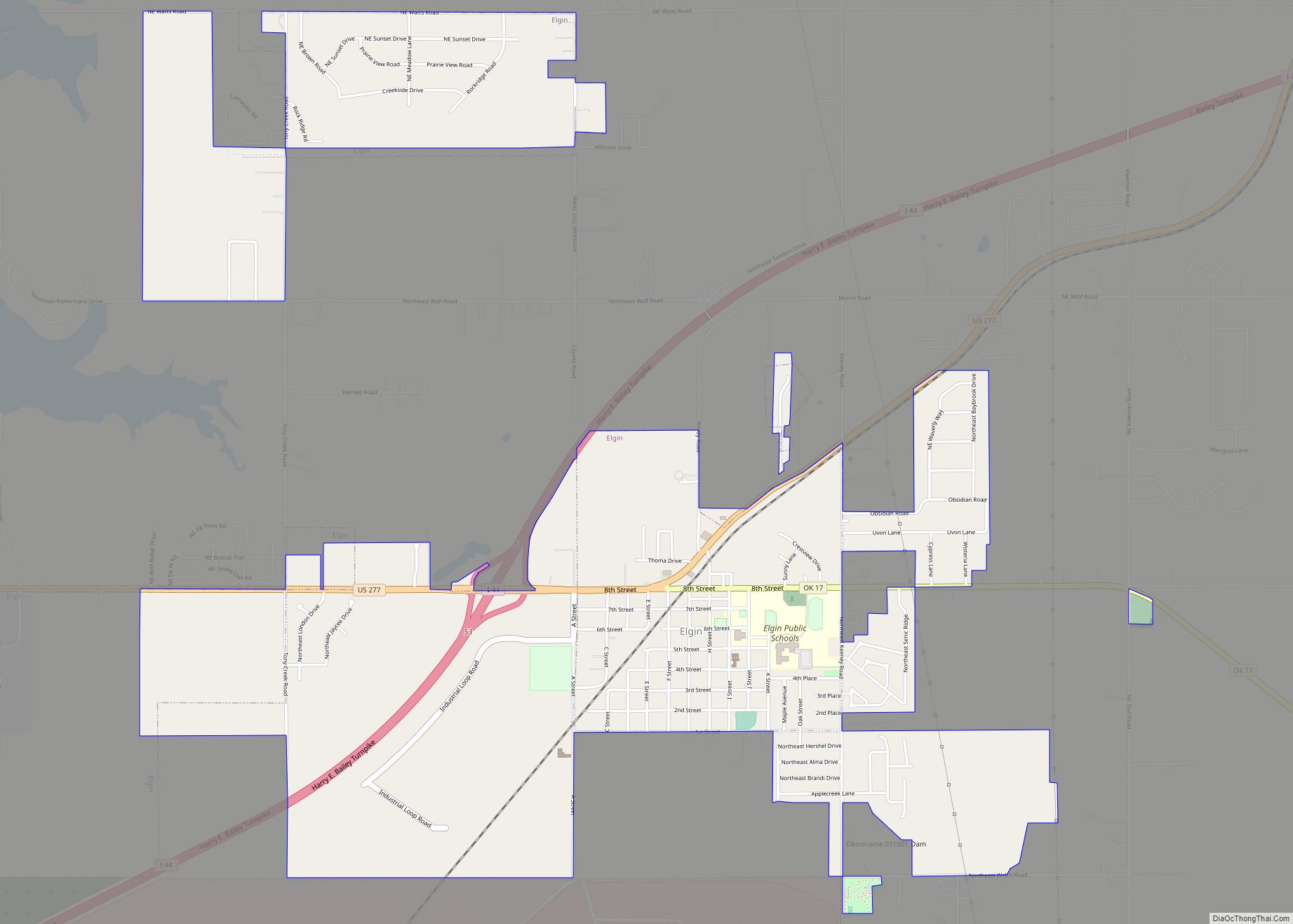
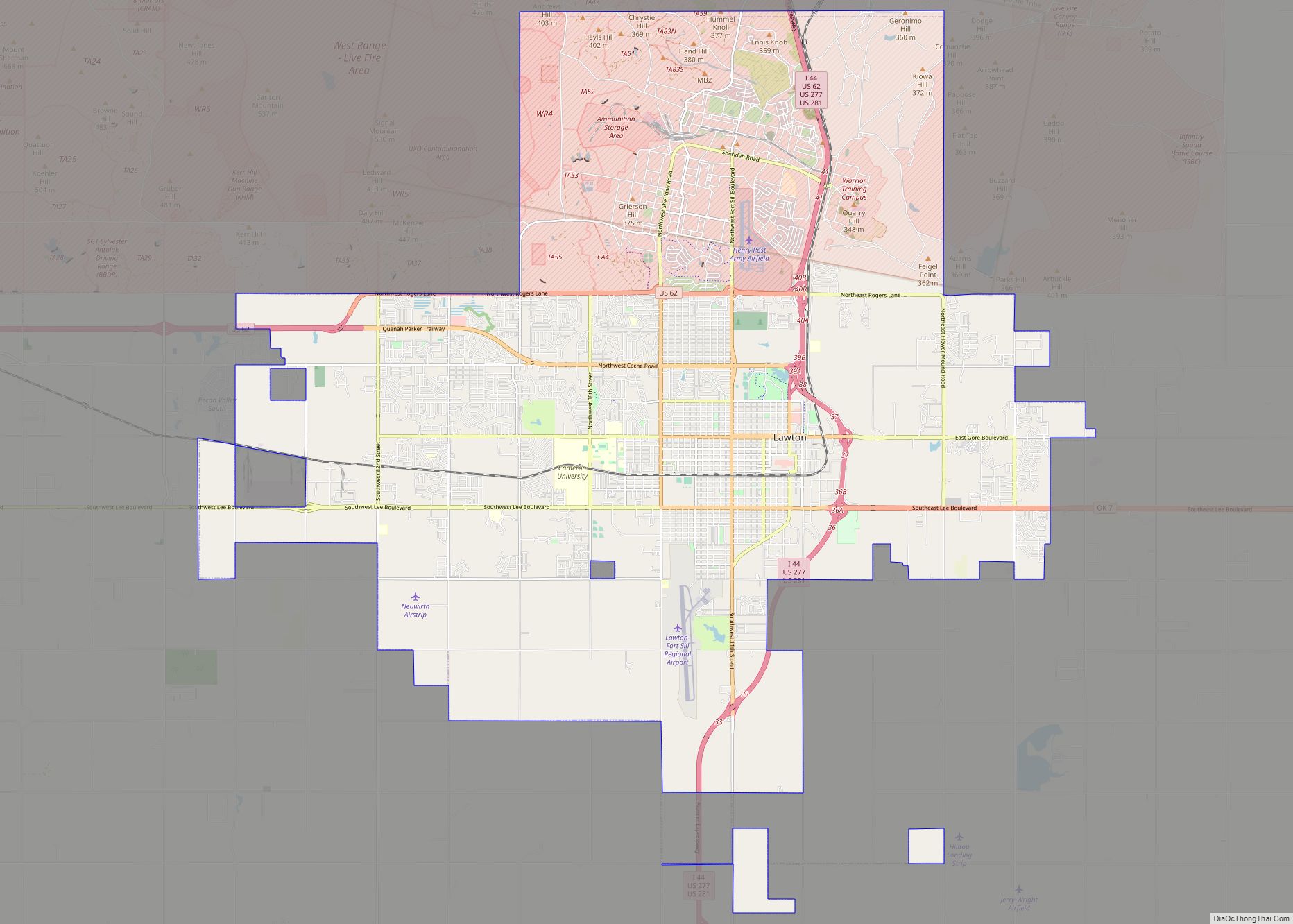
Lawton is a city in and the county seat of Comanche County, in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Located in southwestern Oklahoma, approximately 87 mi (140 km) southwest of Oklahoma City, it is the principal city of the Lawton, Oklahoma, metropolitan statistical area. According to the 2020 census, Lawton’s population was 90,381, making it the sixth-largest city in the state, and the largest in Western Oklahoma.
Developed on former reservation lands of the Kiowa, Comanche, and Apache Indians, Lawton was founded by European Americans on 6 August 1901. It was named after Major General Henry Ware Lawton, who served in the Civil War, where he earned the Medal of Honor, and was killed in action in the Philippine–American War. Lawton’s landscape is typical of the Great Plains, with flat topography and gently rolling hills, while the area north of the city is marked by the Wichita Mountains.
The city’s proximity to the Fort Sill Military Reservation, formerly the base of the Apache territory before statehood, gave Lawton economic and population stability throughout the 20th century.
Although Lawton’s economy is still largely dependent on Fort Sill, it has grown to encompass manufacturing, higher education, health care, and retail. The city has a council-manager government; the city council members are elected from single-member districts and the mayor is elected at-large. They hire a professional city manager to direct daily operations.
Interstate 44 and three major United States highways serve the city, while Lawton-Fort Sill Regional Airport connects Lawton by air. Recreation can be found at the city’s many parks, lakes, museums, and festivals. Notable residents of the city include many musical and literary artists, as well as several professional athletes.
| Name: | Lawton city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Oklahoma |
| County: | Comanche County |
| Founded: | August 6, 1901 |
| Elevation: | 1,109 ft (338 m) |
| Land Area: | 81.44 sq mi (210.92 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.03 sq mi (0.09 km²) % |
| Population Density: | 1,109.85/sq mi (428.52/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 73501–73503, 73505-73507 |
| Area code: | 580 |
| FIPS code: | 4041850 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1094539 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Lawton location map. Where is Lawton city?
History
The territory of present-day Oklahoma was long settled by ancient cultures of prehistoric American Indians, including the Clovis, 11500 BCE; Folsom, 10600 BCE; and Plainview, 10000 BCE cultures.
The valleys of the Arkansas River and Red River were the center of Caddoan Mississippian culture, which began to develop about 800 CE. The people developed more dense settlement and a complex architecture of earthwork platform mounds. Archeological evidence has shown that these people were the direct ancestors of the historic Caddoan-language peoples who inhabited the larger region, including the Caddo and the Wichita peoples.
In the 16th century, Spanish explorer Francisco Vásquez de Coronado visited in 1541, beginning European contact. Around the 1700s, two tribes from the north, the Comanche and Kiowa, migrated to the Oklahoma and Texas regions.
For most of the 18th century, the French exerted nominal control over the Oklahoma region as part of their La Louisiane, or New France. The largest French settlements were along the Gulf Coast, in New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama. The limited interaction between the Native American and European peoples was based on fur trading.
In 1803, the French sold this territory as Louisiana Purchase to the US, under President Thomas Jefferson. European Americans continued to migrate into the Southeast and across the Mississippi River into Indian territories, especially seeking territory to expand cotton cultivation, which was a lucrative commodity crop. They pressured the government to give them access to Indian lands. In 1830, under President Andrew Jackson, Congress passed the Indian Removal Act, which removed American Indian tribes from the Southeast and relocated them to Indian Territory west of the Mississippi River.
The southern part of this territory was originally assigned to the Choctaw and Chickasaw. Following the Civil War, during which most of the Southeast tribes had allied with the Confederacy, in 1867, the United States required new treaties of peace. In 1867, under the Medicine Lodge Treaty, it allotted the southwest portion of former Choctaw and Chickasaw lands to the Comanche, Kiowa, and Apache tribes. It had forced them to move out of East Texas and nearby areas of Arkansas.
Fort Sill was established in 1869 after the American Civil War and commanded by Major General Philip Sheridan. He was leading a campaign in Indian Territory to stop raids into Texas by American Indian tribes. In 1874, the Red River War broke out in the region when the Comanche, Kiowa, and Southern Cheyenne left their Indian Territory reservation. Attrition and skirmishes by the US Army finally forced the return of the tribes to Indian Territory in June 1875.
In 1891, the United States Congress appointed a commission to meet with the tribal leaders and come to an agreement allowing White settlement. Years of controversy and legal maneuvering ensued before President William McKinley issued a proclamation on 4 July 1901, that gave the federal government control over 2,000,000 acres (8,100 km) of “surplus” Indian lands that remained after allotments of communal tribal lands to individual households under the Dawes Act. Under other legislation, the United States through the Dawes Commission allotted communal lands as plots to individual households of tribal members, selling off what remained as “surplus”. These actions extinguished the tribal claims to communal lands, a condition needed for the admission of Oklahoma as a state in 1907.
After these changes, the legislature of the new state began to organize counties. Three 320-acre sites in Kiowa, Caddo and Comanche counties were selected for county seats. Lawton was designated as the Comanche County seat. The town was named for Major General Henry W. Lawton, a quartermaster at Fort Sill, who had taken part in the pursuit and capture of Comanche chief Geronimo.
The city was opened to settlement through an auction of town lots beginning on 6 August 1901, which was completed 60 days later. By 25 September 1901, the Rock Island Railroad expanded to Lawton and was soon joined by the Frisco Line. The first city elections were held 24 October 1901.
The United States’ entry into World War I accelerated development at Fort Sill and Lawton. The availability of 5 million US gallons (19,000 m) of water from Lake Lawtonka, just north of Fort Sill, was a catalyst for the War Department to establish a major cantonment named Camp Doniphan. It was active until 1922.
Similarly, the US response in World War II stimulated activity and expansion at Fort Sill and Lawton. The city’s population increased from 18,055 to 34,757 from 1940 to 1950. By the 1960s, it had reached 61,697.
In the postwar period, Lawton underwent tremendous growth during the late 1940s and 1950s, leading city officials to seek additional water sources to supplement existing water from Lake Lawtonka. In the late 1950s, the city purchased large parcels of land along East Cache Creek in northern Comanche County for the construction of a dam and human-made lake, built in 1959 on the creek just north of U.S. 277 west of Elgin. Lake Ellsworth, named for a former Lawton mayor, soft-drink bottler C.R. Ellsworth, was dedicated in the early 1960s. It offered additional water resources, but also recreational opportunities and flood control along Cache Creek.
In 1966, the Lawton City Council annexed several square miles of land on the city’s east, northeast, west, and northwest borders, expanding east beyond the East Cache Creek area and west to 82nd Street. On 1 March 1964, the north section of the H. E. Bailey Turnpike was completed, connecting Lawton directly to Oklahoma City, the capital. The south section of the turnpike leading to the Texas border was completed on April 23, 1964.
Urban-renewal efforts in the 1970s transformed downtown Lawton. A number of buildings dating to the city’s founding were demolished to build an enclosed shopping mall, which was believed to provide a suburban attraction for shoppers.
On June 23, 1998, the city expanded when Lawton annexed neighboring Fort Sill. The Base Realignment and Closure of 2005 resulted in reassignment of people from other bases and consolidation of some military activities at Fort Sill, increasing the number of people assigned there and its scope of activities. Lawton expects a continuing benefit if population and economic growth over the course of the next 20 years.
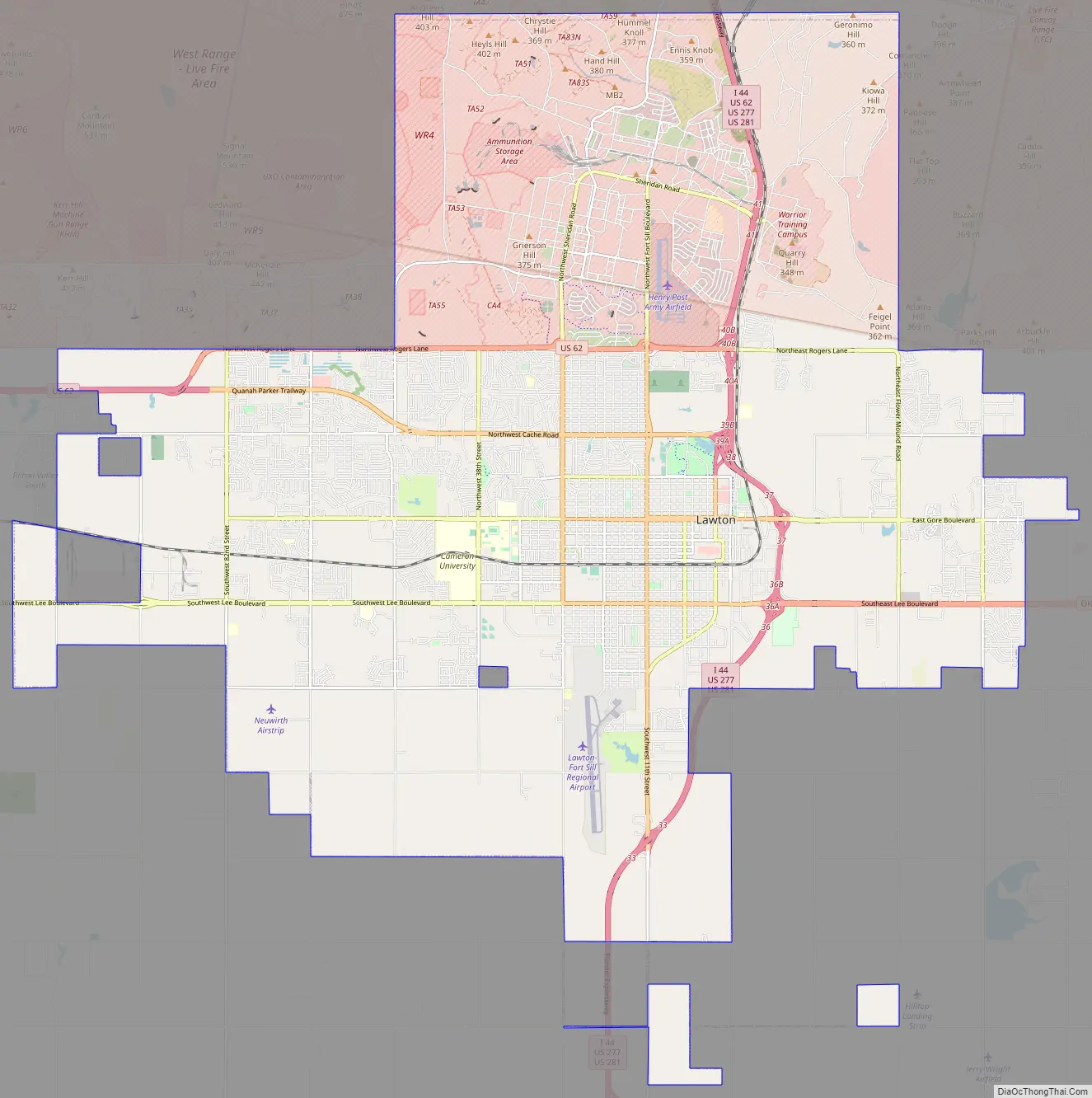
Lawton Road Map
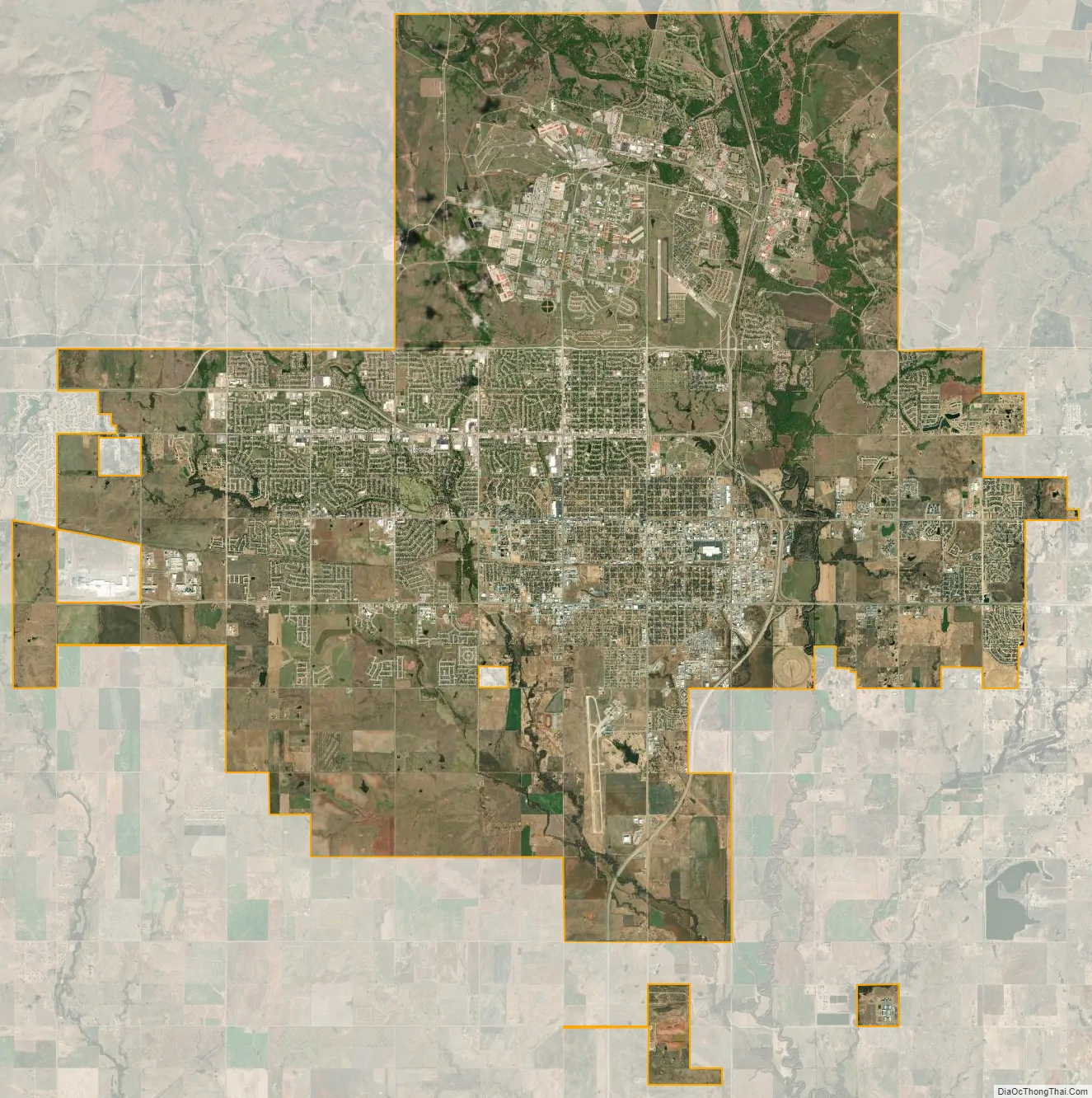
Lawton city Satellite Map
Geography
Lawton is the fifth-largest city in Oklahoma, located at 34°36′16″N 98°23′45″W / 34.60444°N 98.39583°W / 34.60444; -98.39583 (34.604444 N, 98.395833 W). The city has a total area of 75.1 sq mi (195 km), all land. Lawton is located about 84 mi (135 km) southwest of Oklahoma City. Other surrounding cities include Wichita Falls about 47 mi (76 km) to the south, Duncan about 33 mi (53 km) to the east, and Altus about 56 mi (90 km) to the west.
Lawton lies in an area typical of the Great Plains, with prairie, few trees, and flat topography with gently rolling hills. The region north of the city consists of the Wichita Mountains, including Mount Scott and Mount Pinchot, the area’s highest peaks. The area consists mostly of Permian Post Oak Conglomerate limestone on the northern sections of the city.
In the south sections of the city, Permian Garber sandstone is commonly found with some Hennessey Group shale. Area creeks including East Cache Creek contain deposits of Quaternary alluvium. To the northwest, the Wichita Mountains consist primarily of Wichita Granite Group from the Cambrian period.
Climate
Lawton lies in a dry subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa), with frequent variations in weather daily, except during the constantly hot and dry summer. Frequent strong winds, usually from the south or south-southeast during the summer, help to lessen the hotter weather. Northerly winds during the winter can occasionally intensify cold periods.
The average mean temperature for southwest Oklahoma is 61.9 °F (16.6 °C). The summers can be mildly hot; Lawton averages 21 days with temperatures 100 °F (37.8 °C) and above. The winters are typically mild, though periods of extreme cold can occur. Lawton averages eight days that fail to rise above freezing. The city receives about 31.6 inches (800 mm) of precipitation and less than 3 in (80 mm) of snow annually.
Lawton is located squarely in the area known as Tornado Alley and is prone to severe weather from late April through early June. Most notably, an F4 tornado in 1957, and an F3 tornado in 1979 struck the southern region of the city.
See also
Map of Oklahoma State and its subdivision:- Adair
- Alfalfa
- Atoka
- Beaver
- Beckham
- Blaine
- Bryan
- Caddo
- Canadian
- Carter
- Cherokee
- Choctaw
- Cimarron
- Cleveland
- Coal
- Comanche
- Cotton
- Craig
- Creek
- Custer
- Delaware
- Dewey
- Ellis
- Garfield
- Garvin
- Grady
- Grant
- Greer
- Harmon
- Harper
- Haskell
- Hughes
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnston
- Kay
- Kingfisher
- Kiowa
- Latimer
- Le Flore
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Love
- Major
- Marshall
- Mayes
- McClain
- McCurtain
- McIntosh
- Murray
- Muskogee
- Noble
- Nowata
- Okfuskee
- Oklahoma
- Okmulgee
- Osage
- Ottawa
- Pawnee
- Payne
- Pittsburg
- Pontotoc
- Pottawatomie
- Pushmataha
- Roger Mills
- Rogers
- Seminole
- Sequoyah
- Stephens
- Texas
- Tillman
- Tulsa
- Wagoner
- Washington
- Washita
- Woods
- Woodward
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming