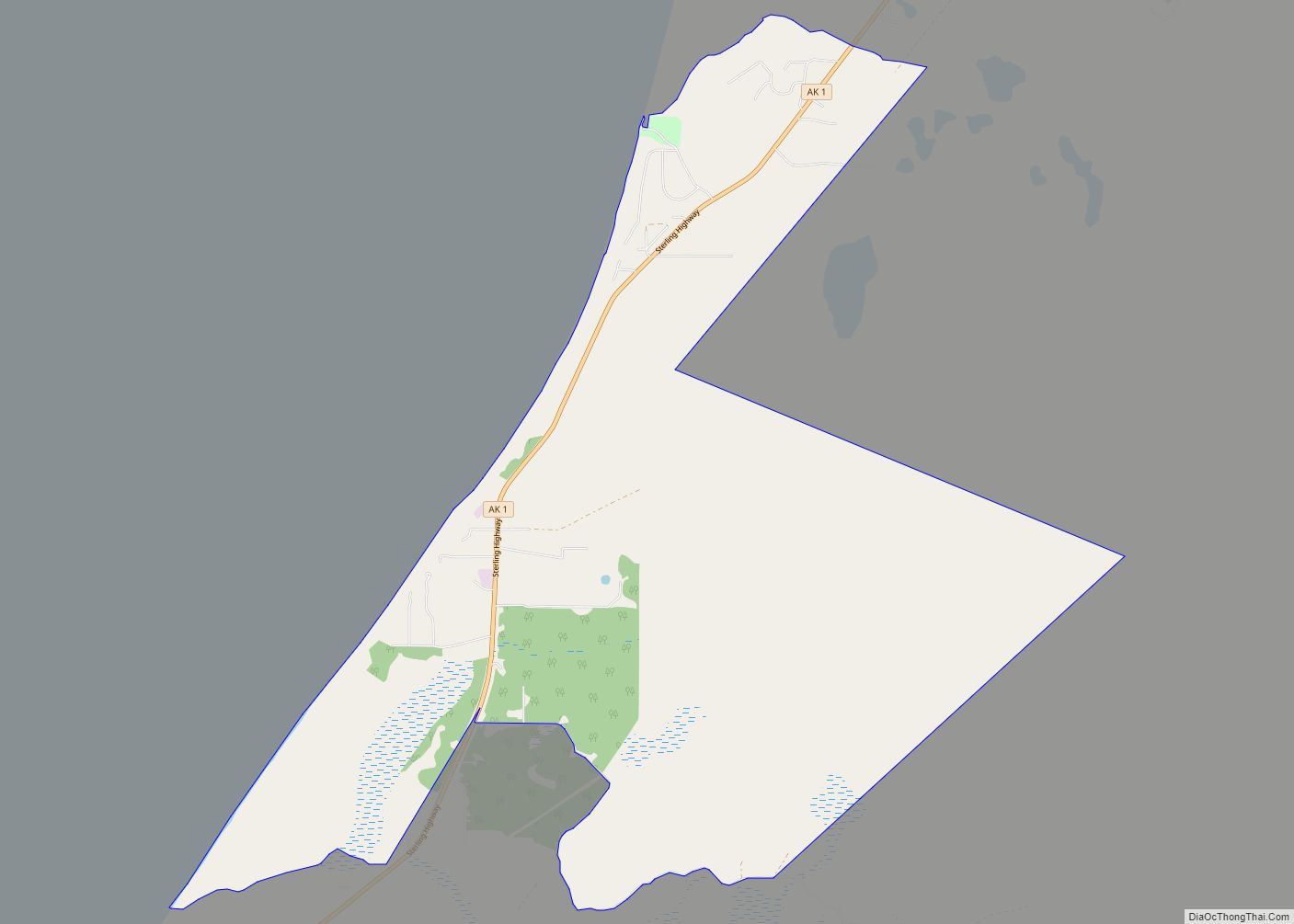
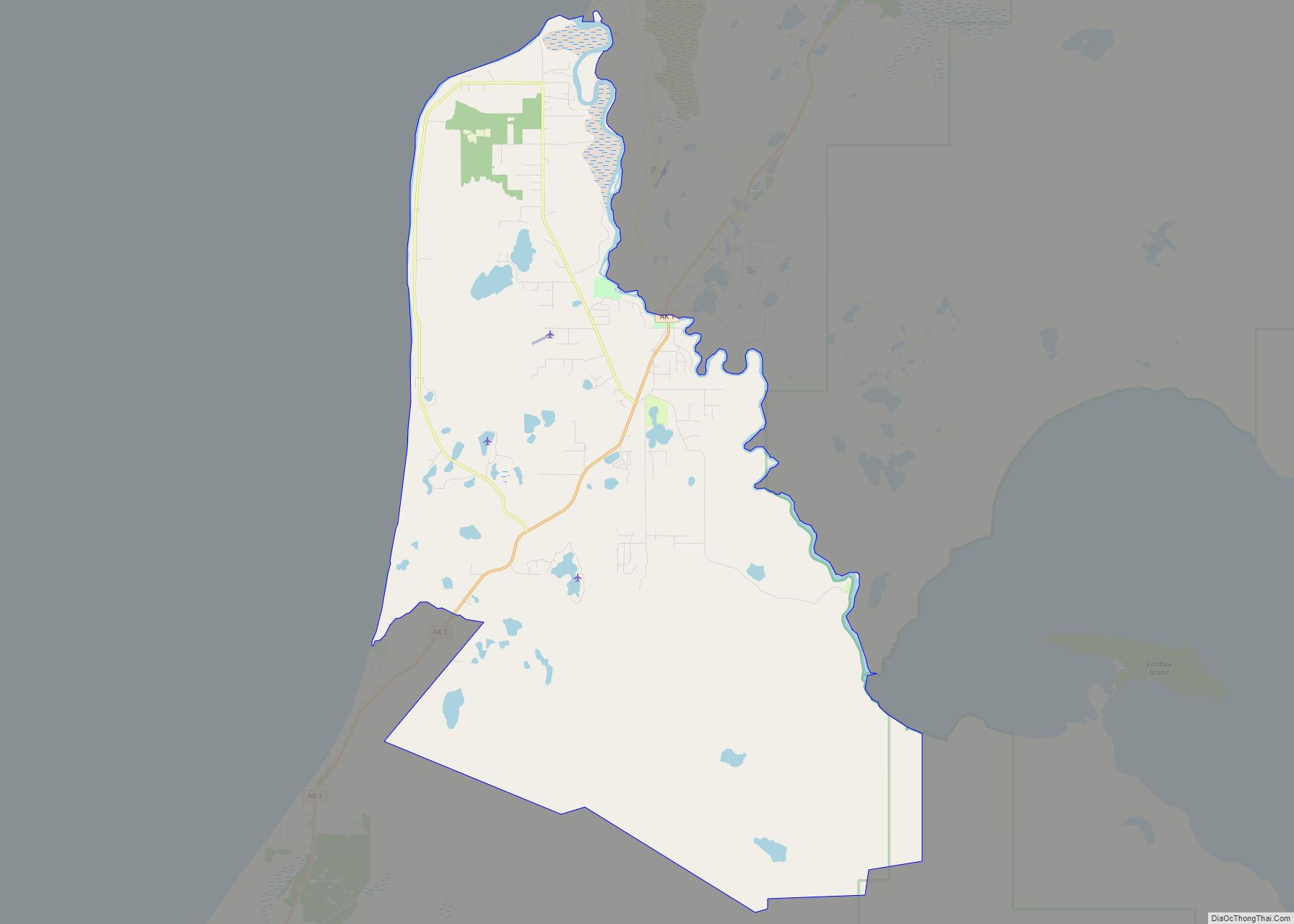
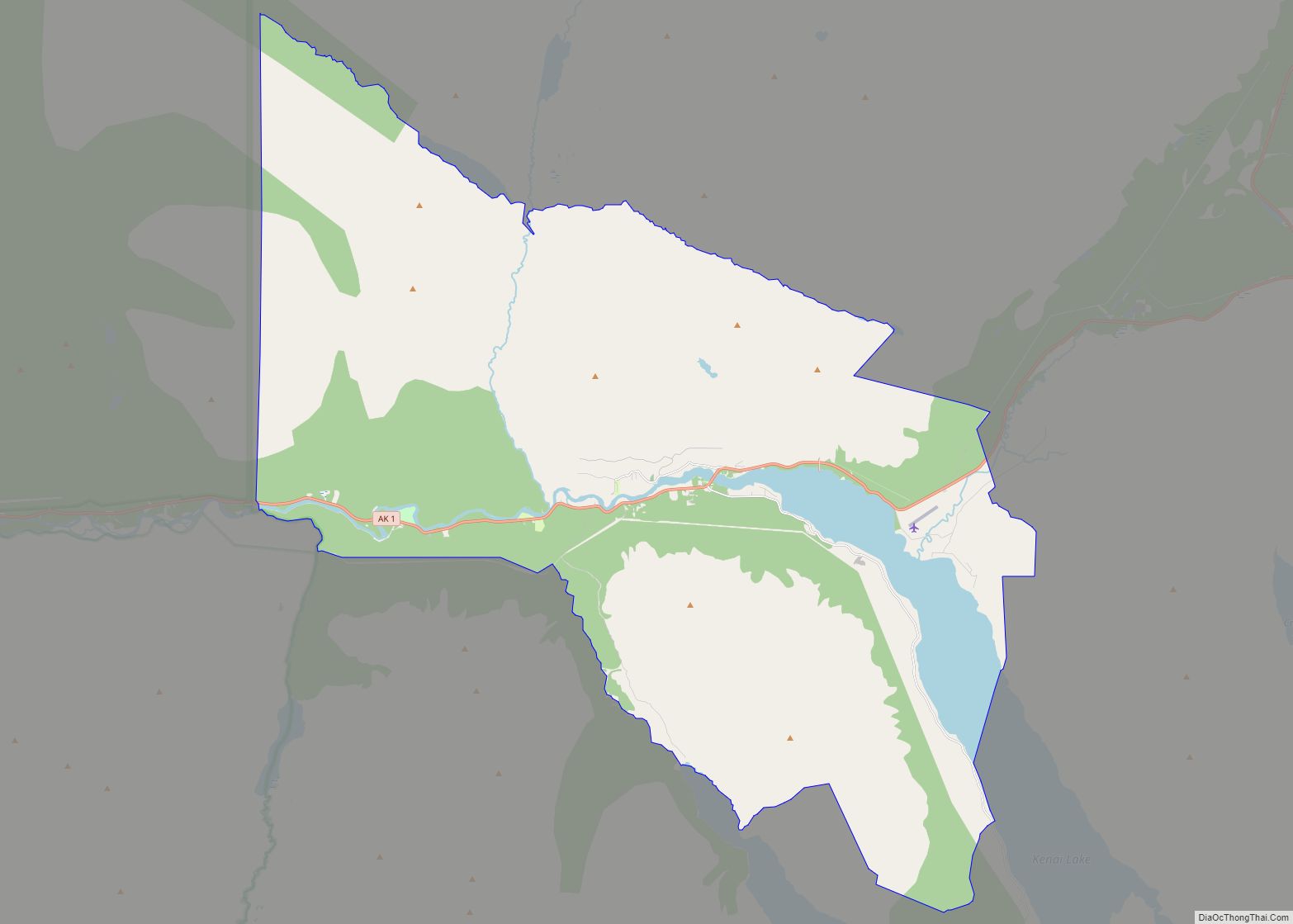
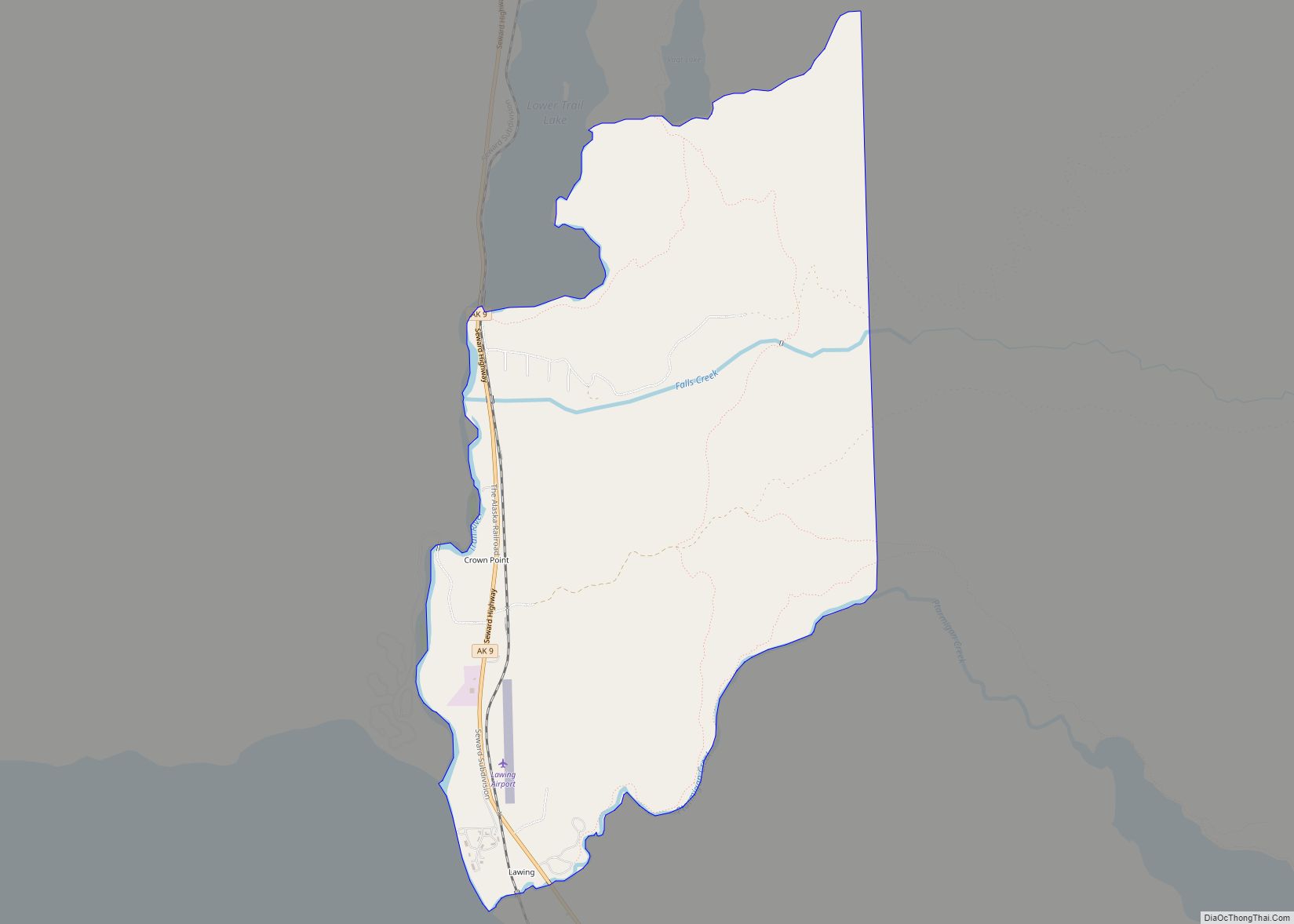
| Name: | Homer city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Kenai Peninsula Borough |
| Incorporated: | March 31, 1964 |
| Elevation: | 95 ft (29 m) |
| Total Area: | 25.25 sq mi (65.41 km²) |
| Land Area: | 13.79 sq mi (35.71 km²) |
| Water Area: | 11.47 sq mi (29.70 km²) |
| Total Population: | 5,522 |
| Population Density: | 400.52/sq mi (154.64/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99603 |
| Area code: | 907 |
| FIPS code: | 0233140 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1413141 |
| Website: | www.ci.homer.ak.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
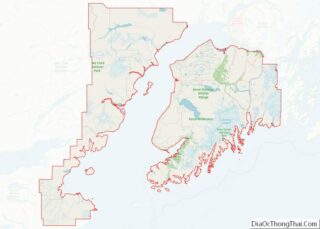
Homer location map. Where is Homer city?
History
Tiller digs indicate that early Alutiiq people probably camped in the Homer area, although their villages were on the far side of Kachemak Bay.
Coal was discovered in the area in the 1890s. The Cook Inlet Coal Fields Company built a town, dock, coal mine, and railroad at Homer. Coalmining in the area continued until World War II. It is estimated that 400 million tons of coal deposits are still present in the area.
Homer was named for Homer Pennock, a goldmining company promoter, who arrived in 1896 on the Homer Spit and built living quarters for his crew of 50 men. However, goldmining was never profitable in the area.
Another earlier settlement, Miller’s Landing, was named after a Charles Miller, who homesteaded in the area around 1915. According to local historian Janet Klein, he was an employee of the Alaska Railroad and had wintered company horses on the beach grasses on the Homer Spit. He built a landing site in a small bight in Kachemak Bay, where supply barges from Seldovia could land and offload their cargos. Miller’s landing was legally considered a census-designated place separate from Homer until it was annexed in 2002, but has always been locally considered part of Homer.
Halibut and salmon sport fishing, along with tourism and commercial fishing are the dominant industries. Homer co-hosted the 2006 Arctic Winter Games. The Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge and the Kachemak Bay Research Reserve co-host a visitor center with interpretive displays known as the Alaska Islands and Ocean Visitor Center, and a cultural and historical museum there is called the Pratt Museum.
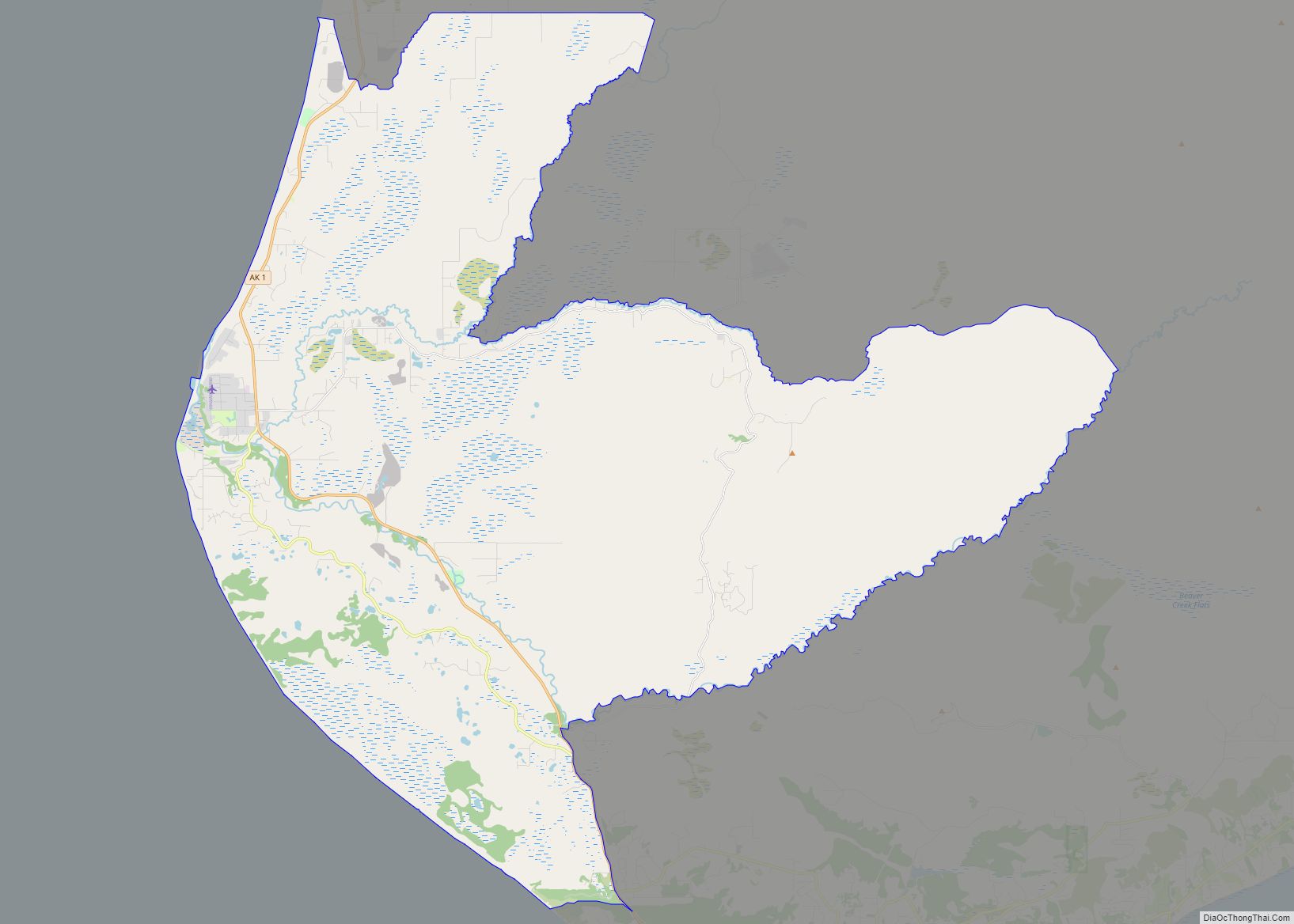
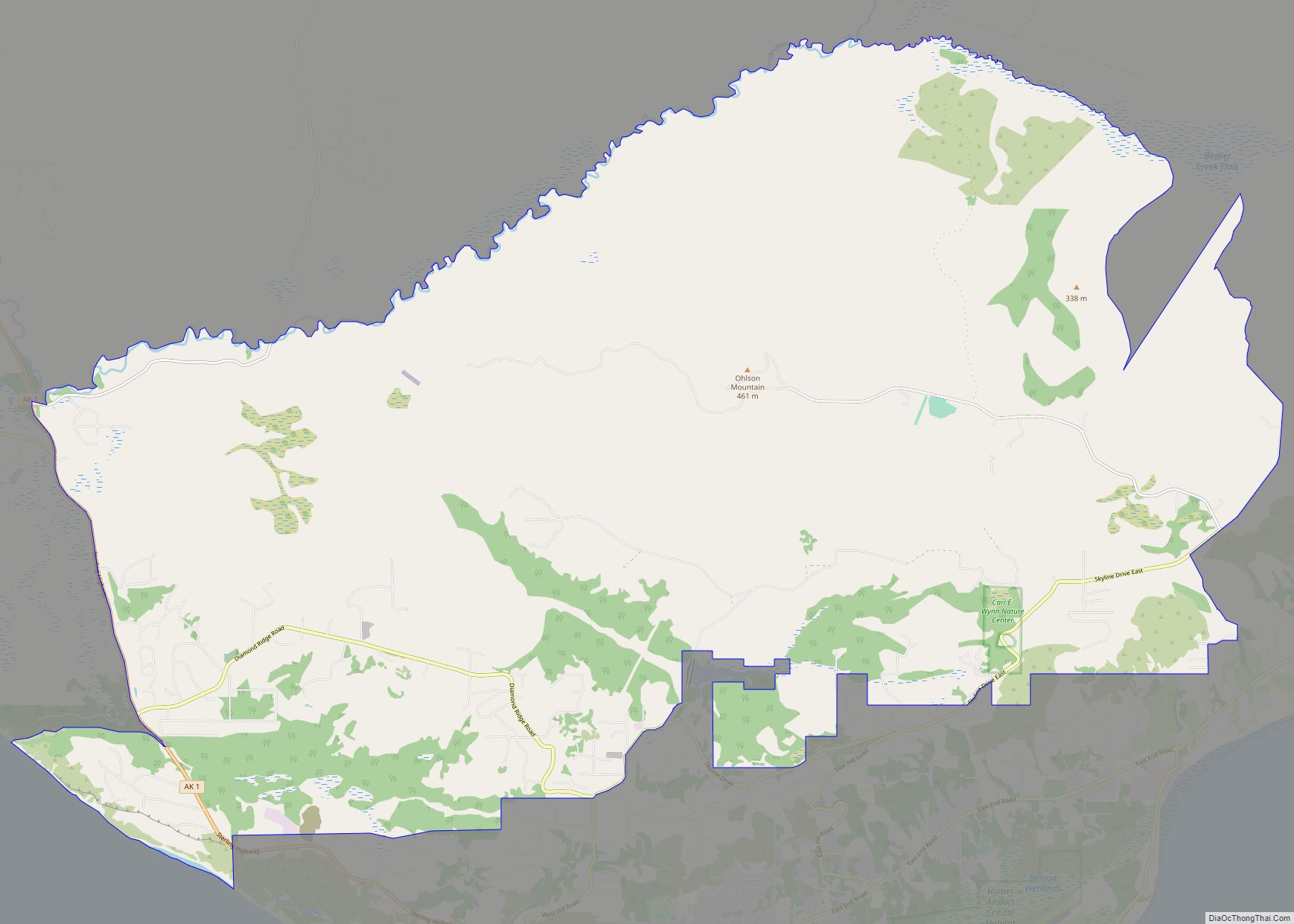
Homer Road Map
Homer city Satellite Map
Geography
Homer is located at 59°38’35” North, 151°31’33” West (59.643059, −151.525900). The only road into Homer is the Sterling Highway.
Homer is on the shore of Kachemak Bay on the southwest side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its distinguishing feature is the Homer Spit, a narrow 4.5 mi (7.2 km) long gravel bar that extends into the bay, on which is located the Homer Harbor.
Much of the coastline, as well as the Homer Spit, sank dramatically during the Good Friday earthquake in March 1964. After the earthquake, very little vegetation was able to survive on the Homer Spit.
The town has a total area of 25.5 square miles (66 km), of which 15 square miles (39 km) are land and 10.5 square miles (27 km) are covered by water.
Climate
As with much of South-central Alaska, Homer has a moderate subarctic mediterranean climate (Köppen Dsc), which causes its weather to be moderate compared to interior Alaska. Winters are snowy and long, but not particularly cold, considering the latitude, with the average January high only slightly below freezing. The annual snowfall averages 50 inches (127 cm) per season, falling primarily from November through March, with some accumulation in October and April but rarely in May. Homer receives only about 25 inches of rainfall annually due to the influence of the Chugach Mountains to the southeast, which shelter it from the Gulf of Alaska. Seven days have a minimum 0 °F (−18 °C) or below annually, and Homer falls in USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 6a. The coldest day of the year averaged 10 °F (−12 °C) in the 1991 to 2020 normals, while the warmest night average was at 55 °F (13 °C). The coldest daytime maximum on record is −8 °F (−22 °C) on January 28, 1989, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is 60 °F (16 °C) on August 9, 1971 and August 23, 1963. Summers are cool due to the marine influence, with 75 °F (24 °C) maxima or minima remaining at or above 55 °F (13 °C) being extremely rare. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −24 °F (−31 °C) on January 28–29, 1989, up to 81 °F (27 °C) on July 10, 1993. The coldest has been January 2012 with a mean temperature of 9.0 °F (−12.8 °C), while the warmest month was July 2019 at 58.6 °F (14.8 °C); the annual mean temperature has ranged from 32.9 °F (0.5 °C) in 1956 to 43.7 °F (6.5 °C) in 2014.
See or edit raw graph data.
- ^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the highest and lowest temperature readings during an entire month or year) calculated based on data at said location from 1991 to 2020.
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming