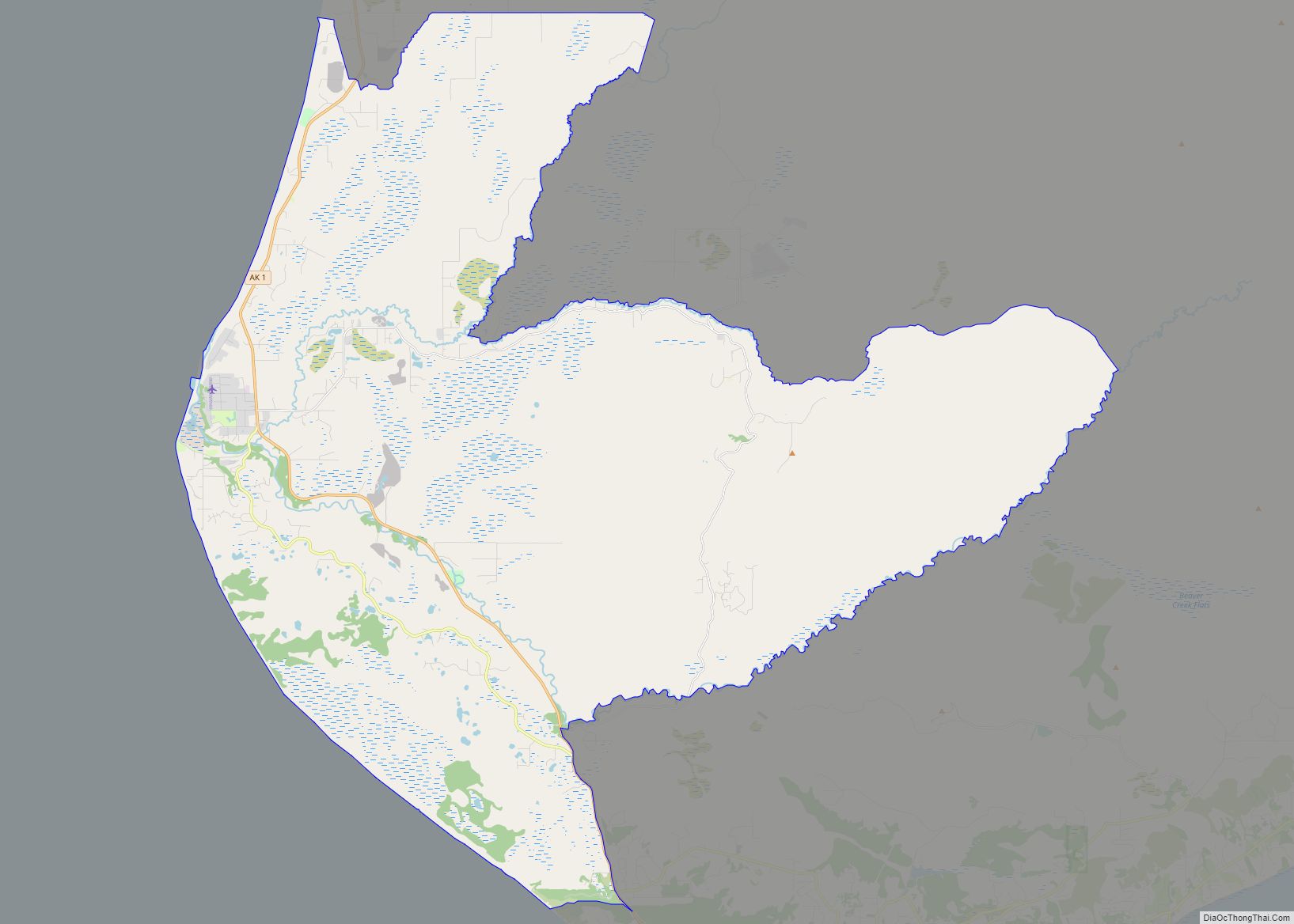
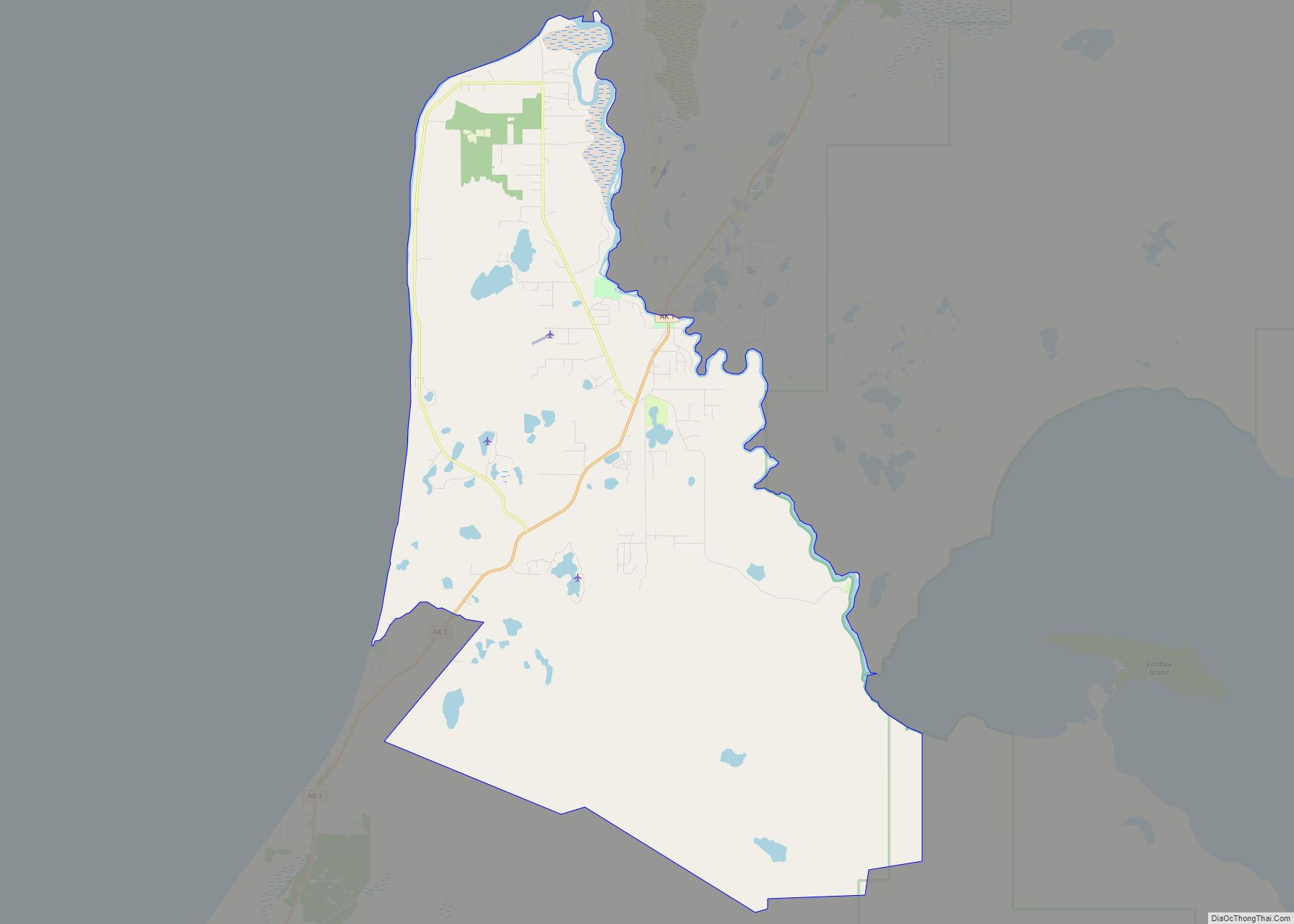
Kenai (/ˈkiːnaɪ/, KEE-ny) (Dena’ina: Shk’ituk’t; Russian: Кенай, Kenay) is a city in the Kenai Peninsula Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is one hundred and fifty-eight miles by road southwest from Anchorage. The population was 7,424 as of the 2020 census, up from 7,100 in 2010, the fifteenth-most populated city in the state.
| Name: | Kenai city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Kenai Peninsula Borough |
| Incorporated: | May 10, 1960 |
| Elevation: | 72 ft (22 m) |
| Total Area: | 35.96 sq mi (93.15 km²) |
| Land Area: | 29.14 sq mi (75.47 km²) |
| Water Area: | 6.82 sq mi (17.67 km²) |
| Total Population: | 7,424 |
| Population Density: | 254.77/sq mi (98.37/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99611, 99635 |
| Area code: | 907 |
| FIPS code: | 0238420 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1413299 |
| Website: | www.kenai.city |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
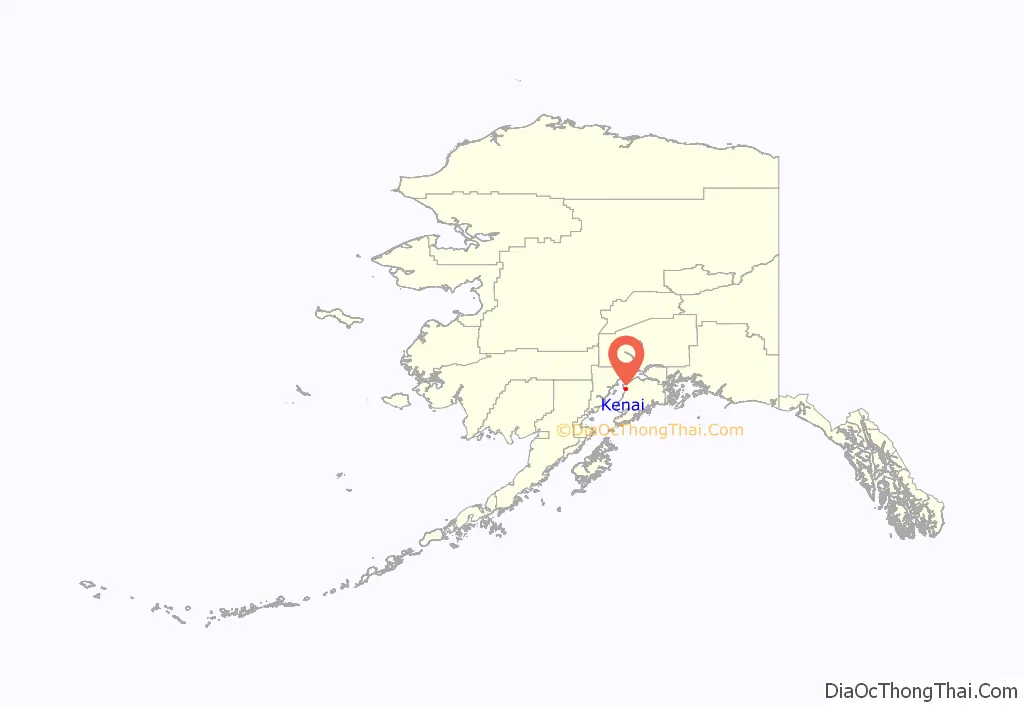
Kenai location map. Where is Kenai city?
History
The city of Kenai is named after the local Dena’ina word ‘ken’ or ‘kena’, which means ‘flat, meadow, open area with few trees; base, low ridge’, according to the Dena’ina Topical Dictionary by James Kari, Ph.D., published in 2007. This describes the area along the mouth and portion of the Kenai River near the City of Kenai. Archaeological evidence suggests that the area was first occupied by the Kachemak people from 1000 B.C., until they were displaced by the Dena’ina Athabaskan people around 1000 A.D. Before the arrival of the Russians, Kenai was a Dena’ina village called Shk’ituk’t, meaning “where we slide down.” When Russian fur traders first arrived in 1741, about 1,000 Dena’ina lived in the village. The traders called the people “Kenaitze”, which is a Russian term for “people of the flats”, or “Kenai people”. This name was later adopted when they were incorporated as the Kenaitze Alaskan Natives in the early 1970s.
Fur trade
In 1786, Pytor Zaykov built Nikolaevskaia krepost (Fort Nicholas) for the Lebedev-Lastochkin Company on the site of modern Kenai, being the first European settlement on the Alaskan mainland. Hostilities surfaced between the natives and settlers in 1797, culminating in an incident in which the Dena’ina attacked Fort St. Nicholas, later dubbed the battle of Kenai. Over one hundred deaths occurred from all involved parties. Later, in 1838, the introduction of smallpox killed one half of the Dena’ina population.
United States
In 1869, after the Alaska Purchase, the United States Army established a post called Fort Kenay. It was soon abandoned.
In 1895–96, the Holy Assumption of the Virgin Mary Russian Orthodox Church was built in the village. It is still in use today.
The establishment of shipping companies in the early 1900s broadened Kenai into a port city. Canning companies were established and helped fuel the commercial fishing boom that was the primary activity through the 1920s.
In 1940, homesteads were opened in the area. The first dirt road from Anchorage was constructed in 1951; pavement would not arrive until 1956 with the construction of the Kenai Spur Highway.
A military base, Wildwood Army Station (later Wildwood Air Force Station), was established in 1953, and served as a major communications post. Wildwood was conveyed in 1974 to the Kenai Native Association in partial settlement of Alaska Native land claims. The facility was leased and later purchased by the State of Alaska and presently serves as the Wildwood Correctional Complex.
Statehood
In 1965, offshore oil discoveries in Cook Inlet caused a period of rapid growth. They were a part of a series of oil deposits located during the middle of the 20th century. In 1957, oil was discovered at Swanson River, 20 miles (32 km) northeast of Kenai. This was the first major oil discovery in Alaska.
In 1992 and 2011, Kenai was named one of the All-America Cities.
In 2008, the Kenai River was designated as a Category 5, or “impaired,” water body by the State of Alaska in accordance with the federal Clean Water Act. The Kenai River Working Group (KRWG) was formed to address the issue of water pollution. By 2010, the status of the river was changed to a Category 2, or “water that attains its designated uses.”
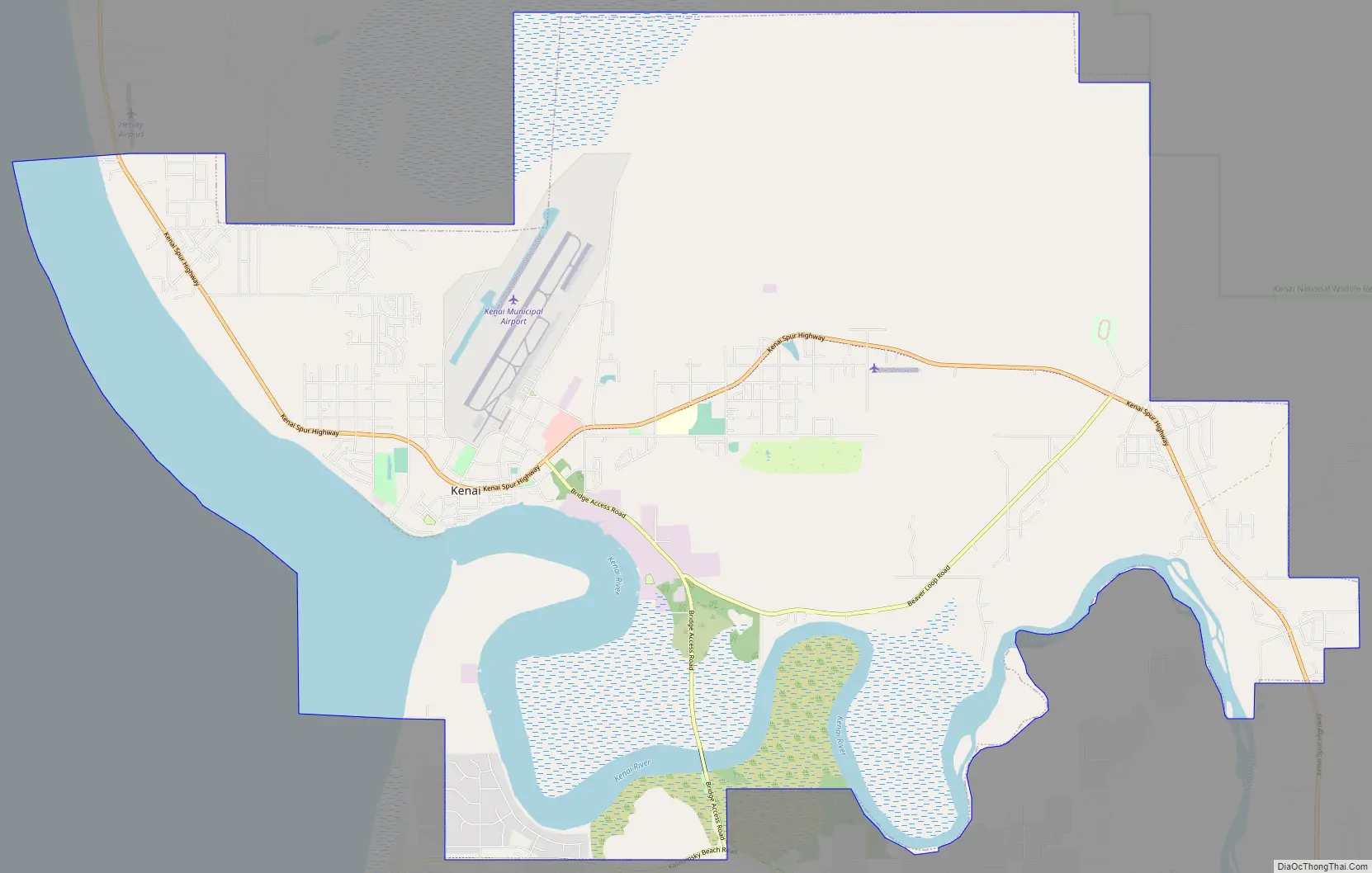
Kenai Road Map
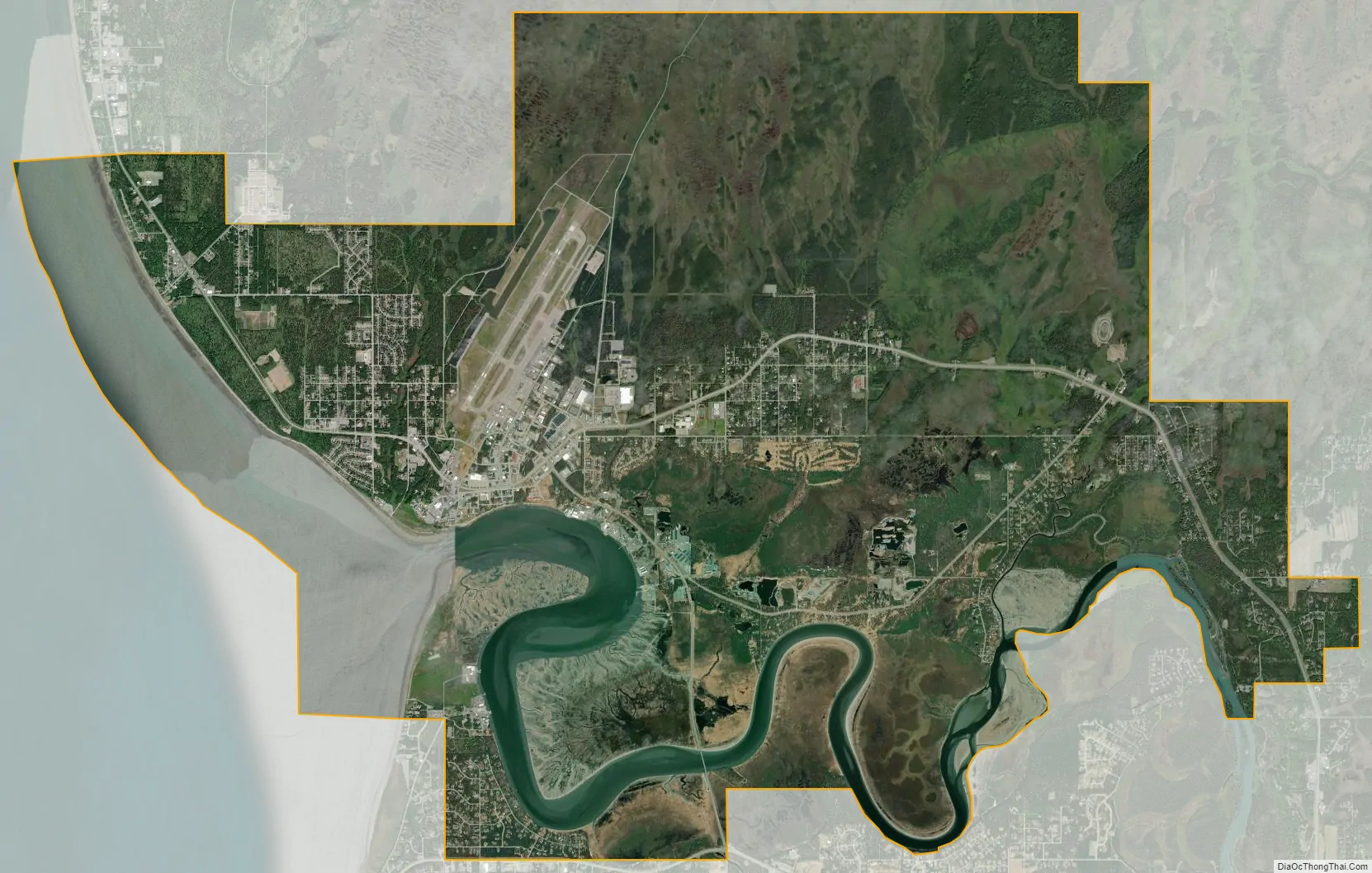
Kenai city Satellite Map
Geography
Kenai is located at 60°33′31″N 151°13′47″W / 60.55861°N 151.22972°W / 60.55861; -151.22972 (60.558738, −151.229616), on the west side of the Kenai Peninsula near the outlet of the Kenai River to the Cook Inlet of the Pacific Ocean. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 35.5 square miles (92 km), of which, 29.9 square miles (77 km) of it is land and 5.6 square miles (15 km) of it (15.85%) is water.
Climate
As with much of Southcentral Alaska, Kenai has a moderate dry-summer subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification: Dsc) due to the cool summers. Winters are snowy, long but not particularly cold, especially considering the latitude, with January featuring a daily average temperature of 15.8 °F (−9.0 °C). Snow averages 63.6 inches (162 cm) per season, falling primarily from October through March, with some accumulation in April, and rarely in May or September. There are 37 nights of sub-0 °F (−18 °C) lows annually, and the area lies in USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 4, indicating an average annual minimum in the −20 to −30 °F (−29 to −34 °C) range. Summers are cool due to the marine influence, with 75 °F (24 °C)+ highs or 55 °F (13 °C)+ lows being extremely rare. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −48 °F (−44 °C) on February 4, 1947 up to 89 °F (32 °C) on July 4, 2019.
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming