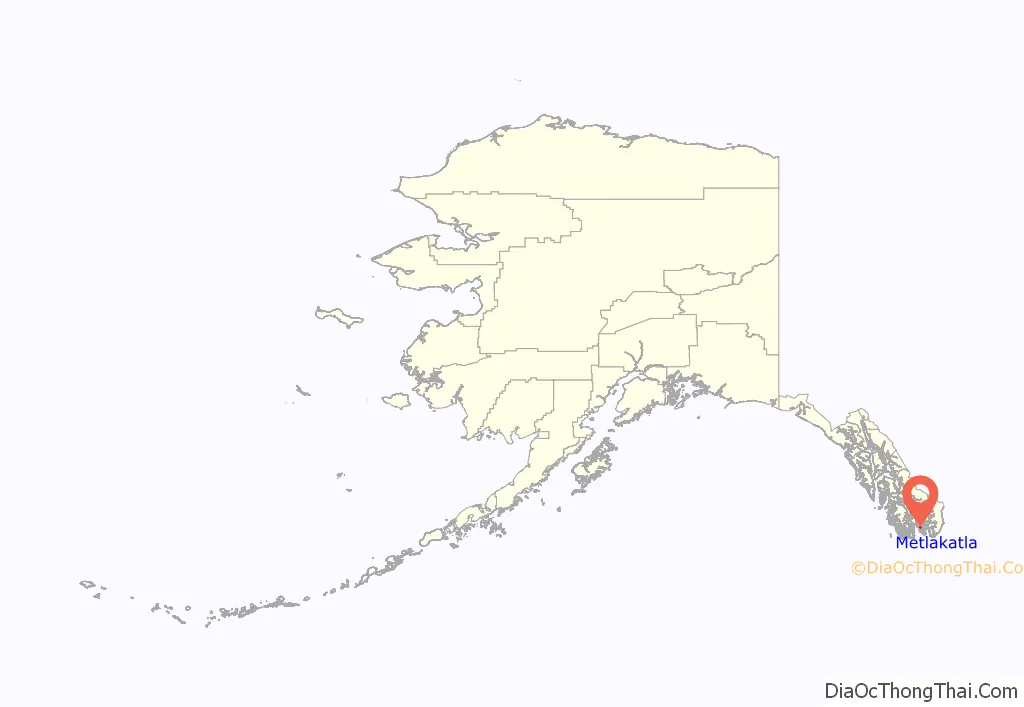
Metlakatla (/ˌmɛtləˈkætlə/; Tsimshian: Maxłakxaała or Wil uks t’aa mediik; Lingít: Tàakw.àani) is a census-designated place (CDP) on Annette Island in Prince of Wales-Hyder Census Area, Alaska, United States. At the 2010 census the population was 1,405; this had grown to 1,454 by the 2020 census.
Since the late 19th century, it has been the major settlement of the Metlakatla Indian Community of the federally recognized Annette Island Reserve, the only remaining reserve in Alaska. The Metlakatla voted to opt out of the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of the 1970s and retained rights to their land and waters. Membership in the community is primarily by lineage; it consists primarily of Tsimshian people and also includes those from other Alaskan Native tribes who wish to join the Metlakatla Indian Community as a bona fide member. Bona fide membership is granted upon approval of the Metlakatla Tribal Council and Executives.
| Name: | Metlakatla CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Alaska |
| County: | Prince of Wales-Hyder Census Area |
| Elevation: | 3 ft (1 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.33 sq mi (6.02 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.31 sq mi (5.97 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.02 sq mi (0.05 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,454 |
| Population Density: | 630.53/sq mi (243.49/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99926 |
| Area code: | 907 |
| FIPS code: | 0248870 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1423661 |
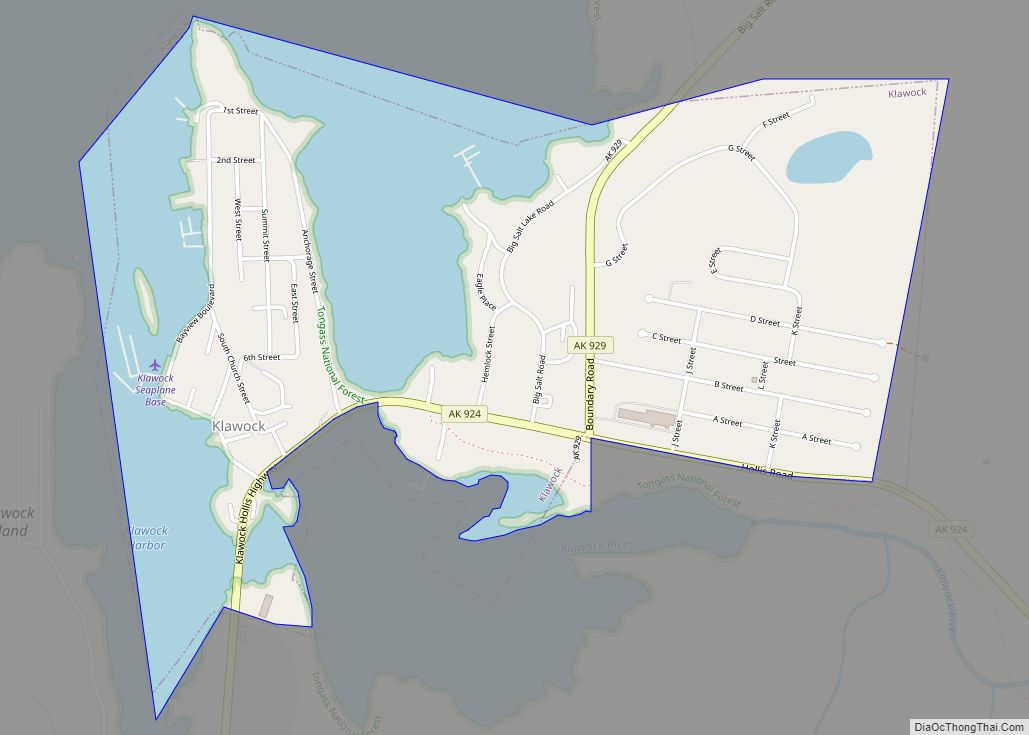
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Metlakatla location map. Where is Metlakatla CDP?
History
Metlakatla comes from Maxłakxaała, a Tsimshian word meaning “saltwater passage.” Metlakatla was named after another village of the same name (“Old Metlakatla”) in British Columbia, which is on Metlakatla Pass, near Prince Rupert. In a more ancient time, it was a Tlingit hunting ground known as Taquan. The Tsimshian were granted permission to own the land by Chief Johnson of the Tlingit tribe.
In 1886, William Duncan, an English tannery employee and lay member of the Church Missionary Society, had a doctrinal dispute with the Church authorities in Metlakatla, B.C. He and a devoted group of Tsimshian followers decided to leave Metlakatla. Duncan went to Washington, D.C., in the United States and asked the U.S. government to give his group land in Alaska. The U.S. under President Cleveland gave them Annette Island after a Tsimshian search committee in seagoing canoes discovered its calm bay, accessible beaches, nearby waterfall, and abundant fish.
In 1887, the group arrived on the island and built a settlement in the Port Chester area. They laid out the town in a European-style grid pattern. It contained a church, a school, a cannery, and a sawmill. They named the town New Metlakatla, after the town they had left behind, but later dropped the “New.” In 1888, William Duncan returned to Washington and lobbied the U.S. Congress for an Indian reserve on Annette Island. Although the reservation system had not been used in Alaska, Congress granted his request in 1891. Duncan remained at Metlakatla until his death in 1918.
During World War II, the United States made a treaty with the Metlakatla Indian Community to permit construction and operation of a military airbase on Annette Island. In exchange, the US promised to build a road connecting the ocean-side city to Alaska’s Inside Passage (in order to allow year-round ferry service to Ketchikan). The airfield on Annette Island was garrisoned by Canadians during the war. This airfield became “the first Canadian force ever based in U.S. territory to directly assist in American defense.”
After the war, the property was adapted as a United States Coast Guard search and rescue base. This airfield served the area commercially until the 1970s, when the new Ketchikan Airport was built at Gravina Island in the Inside Passage.
Annette Islands Reserve, including surrounding islands, today is the only Indian reservation in Alaska. In the 1970s, the Metlakatla did not accept the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act and thus kept the reservation and maintained sovereign immunity. “Annette Islands Reserve consists of 132,000 acres of land and water base. Metlakatla Indian Community has exclusive commercial and subsistence fishing rights to the islands’ waterways extending from 3,000 feet at mean low tide.”
Travelers into Metlakatla usually reach it via the Alaska Marine Highway ferry. They can also travel to Ketchikan on Revillagigedo Island and cross the Revillagigedo Channel to Annette Island by boat or seaplane.
More than 50 years after the end of WWII, in 1997 the US Federal Government began construction of the cross-island road promised to Metlakatla under its wartime M.O.A. treaty. From 1997 to 2007, a joint task force under the overall command of Alaska Command, and led by the Missouri Army National Guard, worked at constructing a 15-mile road from one side of Annette Island to the other. Members of the Active and Reserve components of the Army, Navy, United States Air Force, and the Marines deployed to the island on 2- to 3-week rotations to build the road.
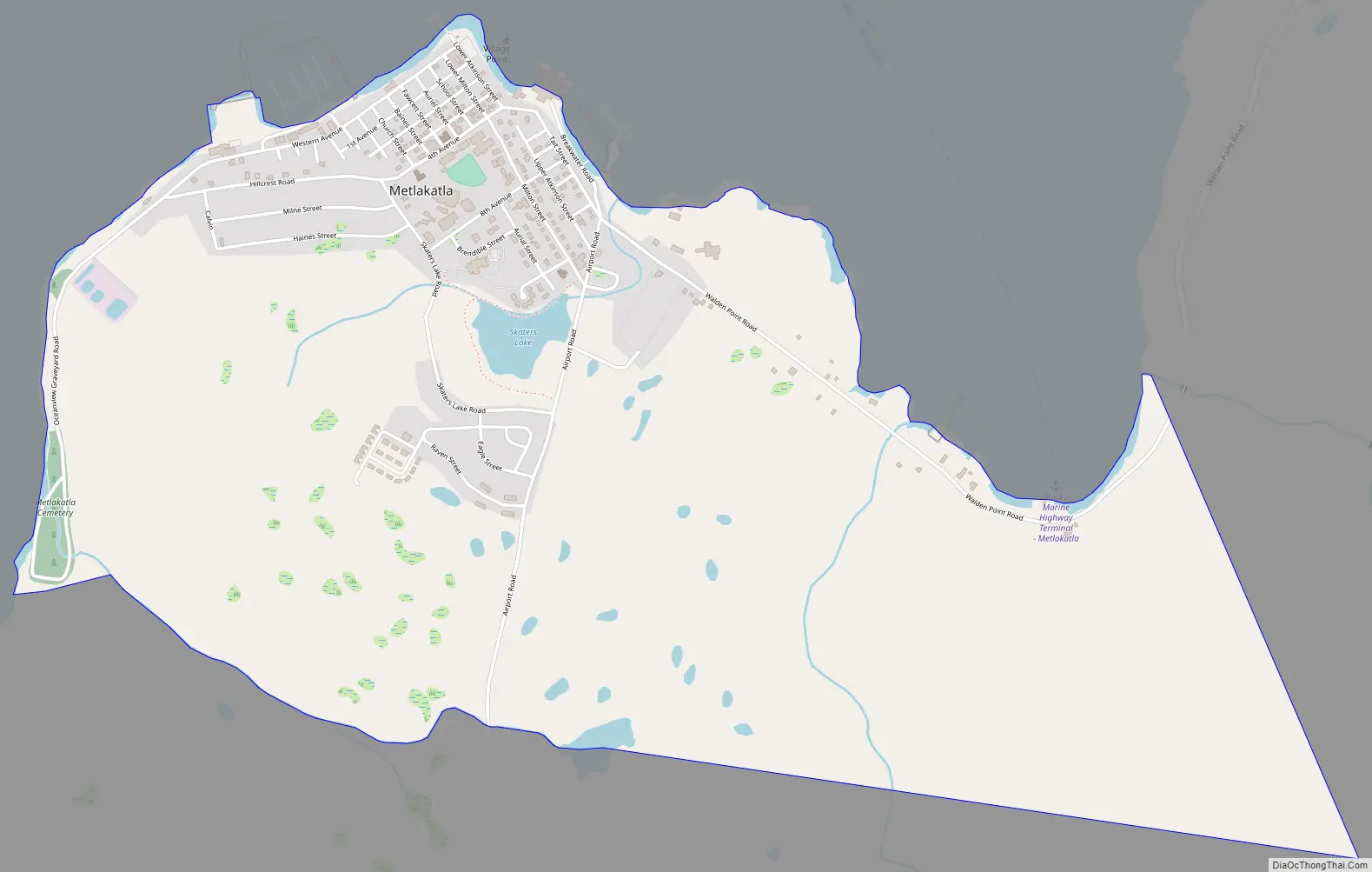
Metlakatla Road Map
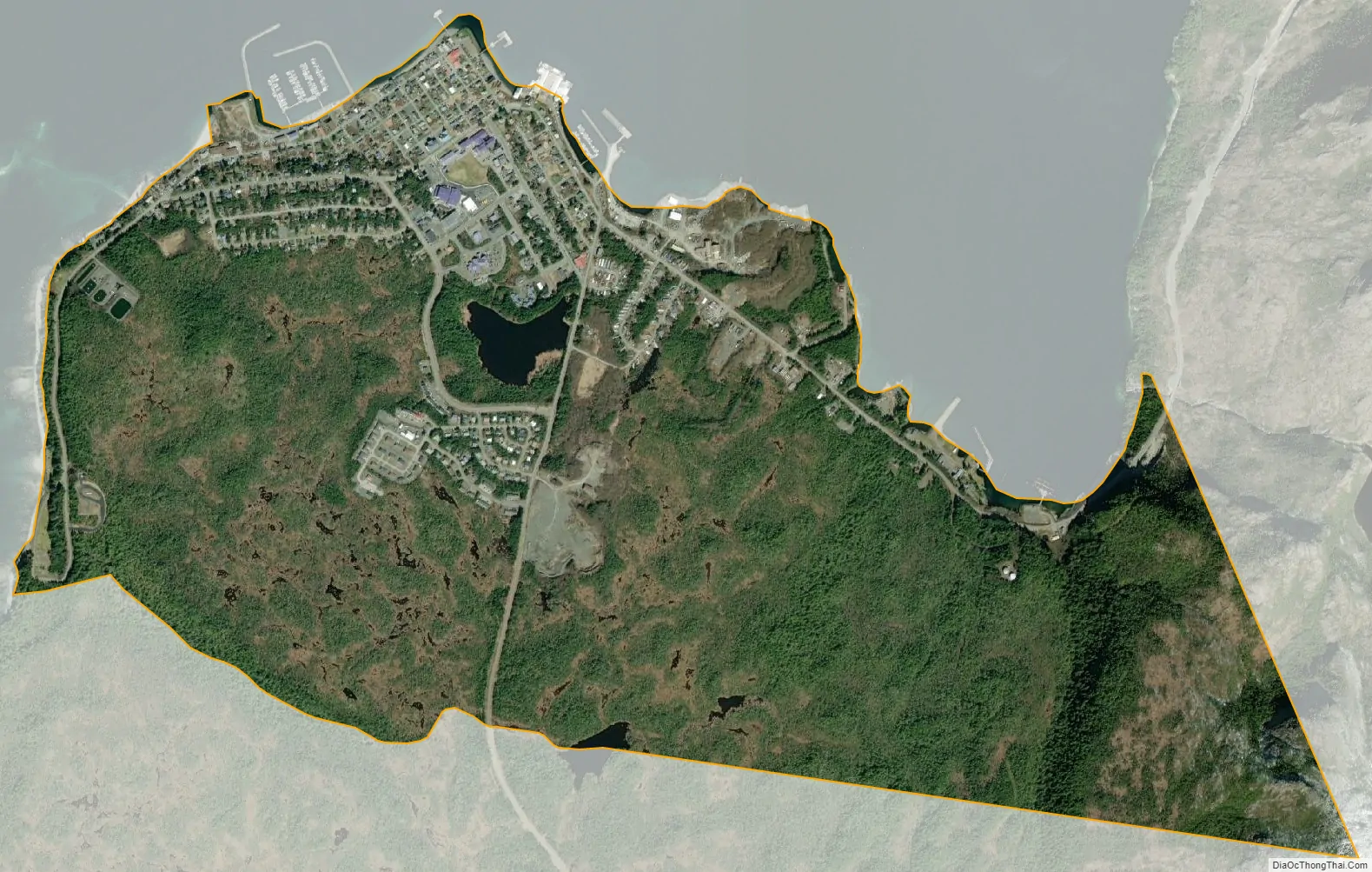
Metlakatla city Satellite Map
Geography
Metlakatla is located at 55°7′37″N 131°34′35″W / 55.12694°N 131.57639°W / 55.12694; -131.57639 (55.126916, −131.576393). It is within the Port Chester Bay, on Annette Island, about 25 km (16 mi) south of Ketchikan.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 2.3 square miles (6.0 km), of which, 2.3 square miles (6.0 km) of it is land and 0.04 square miles (0.10 km) of it (0.85%) is water.
Metlakatla has a Marine west coast climate (Köppen Cfb), with windy and wet weather year-round, cool winters, and mild summers, and straddles the border between USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 7 and 8. Due to its southerly and maritime location, with an annual mean temperature of 47.7 °F (8.7 °C), the town is one of the warmest locations statewide. Most days during the winter see precipitation fall, and the seasonal total snowfall of 34.8 inches (88 cm) occurs mostly from November to March, with some accumulation during April; warm spells raise the high to 50 °F (10 °C) for several days each month. During summer, there is an average of 23 days with 70 °F (21 °C)+ highs, and rain still falls on around half of the days. Precipitation averages more than 101 inches (2.57 m) annually, with June and July being the driest months and October and November the wettest. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −4 °F (−20 °C) on January 30, 1947 up to 93 °F (34 °C) on June 19, 2004, with the temperature having fallen below 0 °F (−18 °C) only on a handful of occasions. In addition, the Annette Island Airport holds the Alaska state monthly record high temperatures for April (82 °F or 28 °C on April 29, 1976) and November (67 °F or 19 °C on November 1, 1970).
See also
Map of Alaska State and its subdivision:- Aleutians East
- Aleutians West
- Anchorage
- Bethel
- Bristol Bay
- Denali
- Dillingham
- Fairbanks North Star
- Haines
- Juneau
- Kenai Peninsula
- Ketchikan Gateway
- Kodiak Island
- Lake and Peninsula
- Matanuska-Susitna
- Nome
- North Slope
- Northwest Arctic
- Prince of Wales-Outer Ketchi
- Sitka
- Skagway-Yakutat-Angoon
- Southeast Fairbanks
- Valdez-Cordova
- Wade Hampton
- Wrangell-Petersburg
- Yukon-Koyukuk
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming