Waltham (/ˈwɔːlθæm/ WAWL-tham) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, and was an early center for the labor movement as well as a major contributor to the American Industrial Revolution. The original home of the Boston Manufacturing Company, the city was a prototype for 19th century industrial city planning, spawning what became known as the Waltham-Lowell system of labor and production. The city is now a center for research and higher education, home to Brandeis University and Bentley University as well as industrial powerhouse Raytheon Technologies. The population was 65,218 at the census in 2020.
Waltham has been called “watch city” because of its association with the watch industry. Waltham Watch Company opened its factory in Waltham in 1854 and was the first company to make watches on an assembly line. It won the gold medal in 1876 at the Philadelphia Centennial Exposition. The company produced over 35 million watches, clocks and instruments before it closed in 1957.
| Name: | Waltham city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Massachusetts |
| County: | Middlesex County |
| Elevation: | 50 ft (15 m) |
| Total Area: | 13.76 sq mi (35.64 km²) |
| Land Area: | 12.74 sq mi (33.01 km²) |
| Water Area: | 1.02 sq mi (2.63 km²) |
| Total Population: | 65,218 |
| Population Density: | 5,117.95/sq mi (1,975.99/km²) |
| Area code: | 339/781 |
| FIPS code: | 2572600 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0612400 |
| Website: | www.city.waltham.ma.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Waltham location map. Where is Waltham city?
History
Waltham was first settled in 1634 as part of Watertown and was officially incorporated as a separate town in 1738. Waltham had no recognizable town center until the 1830s, when the nearby Boston Manufacturing Company gave the town the land that now serves as its central square.
In the early 19th century, Francis Cabot Lowell and his friends and colleagues established in Waltham the Boston Manufacturing Company—the first integrated textile mill in the United States, with the goal of eliminating the problems of co-ordination, quality control, and shipping inherent in the subcontracting based textile industry. The Waltham–Lowell system of production derives its name from the city and the founder of the mill.
The city is home to a number of large estates, including Gore Place, a mansion built in 1806 for former Massachusetts governor Christopher Gore, the Robert Treat Paine Estate, a residence designed by architect Henry Hobson Richardson and landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted for philanthropist Robert Treat Paine, Jr. (1810–1905), and the Lyman Estate, a 400-acre (1.6 km) estate built in 1793 by Boston merchant Theodore Lyman.
In 1857, the Waltham Model 1857 watch was produced by the American Watch Company in the city of Waltham, Massachusetts. In the late 19th and early 20th century, Waltham was home to the brass era automobile manufacturer Metz, where the first production motorcycle in the U.S. was built.
Another first in Waltham industrial history involves the method to mass-produce the magnetron tube, invented by Percy Spencer at Raytheon. During World War II, the magnetron tube technology was applied to radar. Later, magnetron tubes were used as components in microwave ovens.
Waltham was also the home of the Walter E. Fernald State School, the western hemisphere’s oldest publicly funded institution serving people with developmental disabilities. The storied and controversial history of the institution has long been covered by local and, at times, national media.
Timeline
- 1703 – Grove Hill Cemetery established.
- 1738 – Town of Waltham incorporated from Watertown, Massachusetts.
- 1755 – Part of Cambridge annexed to Waltham.
- 1793 – The Vale (residence) built.
- 1810 – Waltham Cotton and Wool Factory Company formed.
- 1813 – Boston Manufacturing Company in business.
- 1820
- First Congregational Church founded.
- Manufacturers’ Library active.
- Waltham Bleachery built.
- 1827 – Rumford Institute organized.
- 1833 – The Hive newspaper begins publication.
- 1835 – Waltham Bank established.
- 1837 – Methodist Episcopal Church organized.
- 1849
- Part of Newton annexed to Waltham.
- Christ Episcopal Church built.
- 1851 – Tornado.
- 1852 – Baptist Church organized.
- 1853 – Waltham Gas Light Company incorporated.
- 1854 – American Horologe Company relocates to Waltham.
- 1856 – Waltham Sentinel newspaper begins publication.
- 1857
- Waltham and Watertown Railroad constructed.
- Mount Feake Cemetery established.
- Waltham Agricultural Library Association formed.
- 1859 – Town of Belmont separates from Waltham.
- 1863 – Waltham Free Press begins publication.
- 1865 – Public Library founded.
- 1866 – Emmet Literary Association formed.
- 1870
- Waltham Horological School established.
- Waltham Foundry Co. established.
- 1876
- Waltham Weekly Record begins publication.
- Davis & Farnum Manufacturing Company in business.
- 1879 – Leland Home for aged women established.
- 1880 – Music Hall built.
- 1881 – Emery Wheel Company in business.
- 1882 – Parmenter Crayon Company chartered.
- 1884
- City of Waltham incorporated.
- Harrington Block built.
- 1885
- Board of Trade organized.
- Waltham Hospital founded.
- Waltham Training School for Nurses established.
- 1886 – Robert Treat Paine Estate built.
- 1888 – Sesquicentennial.
- 1890
- Population: 18,707.
- Massachusetts School for the Feeble-Minded relocates to Waltham.
- 1891 – O’Hara Waltham Dial Company organized.
- 1893
- Waltham Evening News begins publication.
- Waltham Manufacturing Company established.
- Beaver Brook Reservation and Charles River Reservation established.
- 1894
- Linden Street Bridge constructed.
- Waltham Bicycle Park opens.
- 1902 – Metz Company in business.
- 1908 – Company F State Armory built.
- 1910 – Population: 27,834.
- 1915 – Waltham Historical Society incorporated.
- 1924 – Waltham News Tribune newspaper in publication.
- 1928 – Middlesex College of Medicine and Surgery relocates to Waltham.
- 1933 – First Parish Church rebuilt.
- 1935 – Gore Place Society founded.
- 1936 – Hovey Players (theatre group) founded.
- 1938 – County Courthouse built.
- 1941 – Waltham Garden Club founded.
- 1948 – Brandeis University established.
- 1961 – Rose Art Museum founded at Brandeis University.
- 1968
- Bentley University relocates to Waltham.
- WBRS on air.
- 1970 – Population: 61,582.
- 1971
- Waltham Museum established.
- Robert Drinan becomes Massachusetts’s 3rd congressional district representative.
- 1975 – Aerosmith musical group rents Wherehouse.
- 1976 – Waltham Mills Artists Association open studios begins (approximate date)
- 1980 – Charles River Museum of Industry established.
- 1982 – Parexel International Corporation headquartered in Waltham.
- 1985 – Waltham Philharmonic Orchestra formed.
- 1987 – Joseph P. Kennedy II becomes Massachusetts’s 8th congressional district representative.
- 1988 – Global Petroleum Corporation headquartered in Waltham (approximate date).
- 1995 – Steinway Musical Instruments, Inc. headquartered in Waltham.
- 1996
- Lionbridge Technologies Inc. headquartered in Waltham.
- City website online.
- 1999 – Waltham Land Trust incorporated.
- 2003 – Raytheon Company and Roving Software Inc. headquartered in Waltham.
- 2004
- Jeannette A. McCarthy becomes mayor.
- Brandeis University’s Schuster Institute for Investigative Journalism nonprofit established.
- 2006 – Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. headquartered in Waltham.
- 2007
- PerkinElmer, Inc. headquartered in Waltham.
- Waltham Symphony Orchestra formed.
- 2010 – Population: 60,632.
- 2011
- A triple homicide occurs on September 11.
- Watch City Steampunk Festival begins.
- 2013 – Katherine Clark becomes Massachusetts’s 5th congressional district representative.
Pronunciation
The name of the city is pronounced with the primary stress on the first syllable and a full vowel in the second syllable, /ˈwɔːlθæm/ WAWL-tham, though the name of the Waltham watch was pronounced with a reduced schwa in the second syllable: /ˈwɔːlθəm/. As most would pronounce in the British way, “Walthum”, when people came to work in the mills from Nova Scotia, the pronunciation evolved. The “local” version became a phonetic sounding to accommodate French speakers who could not pronounce in the British way. In some areas, the city is referred to as “The Waltham”.
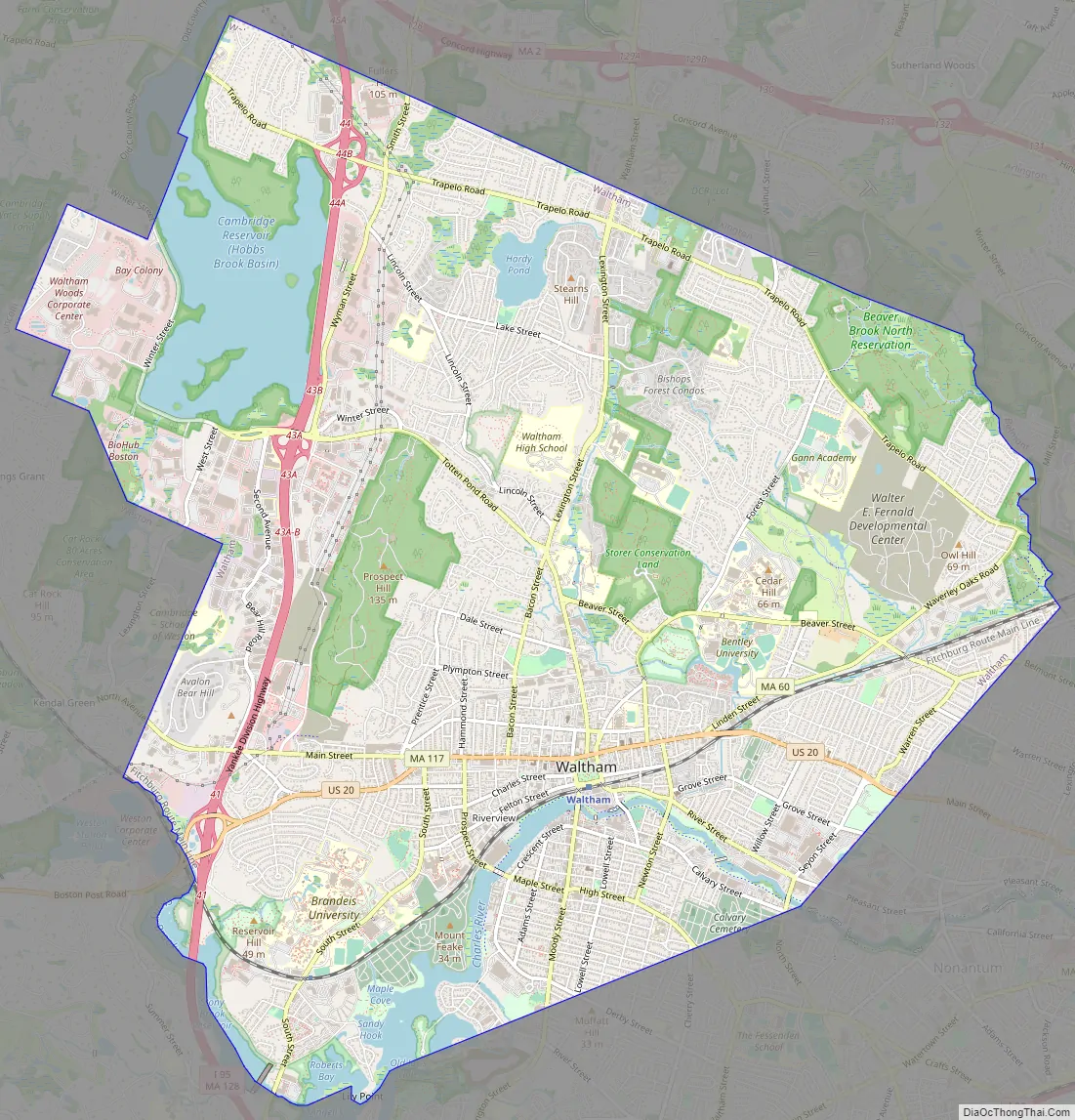
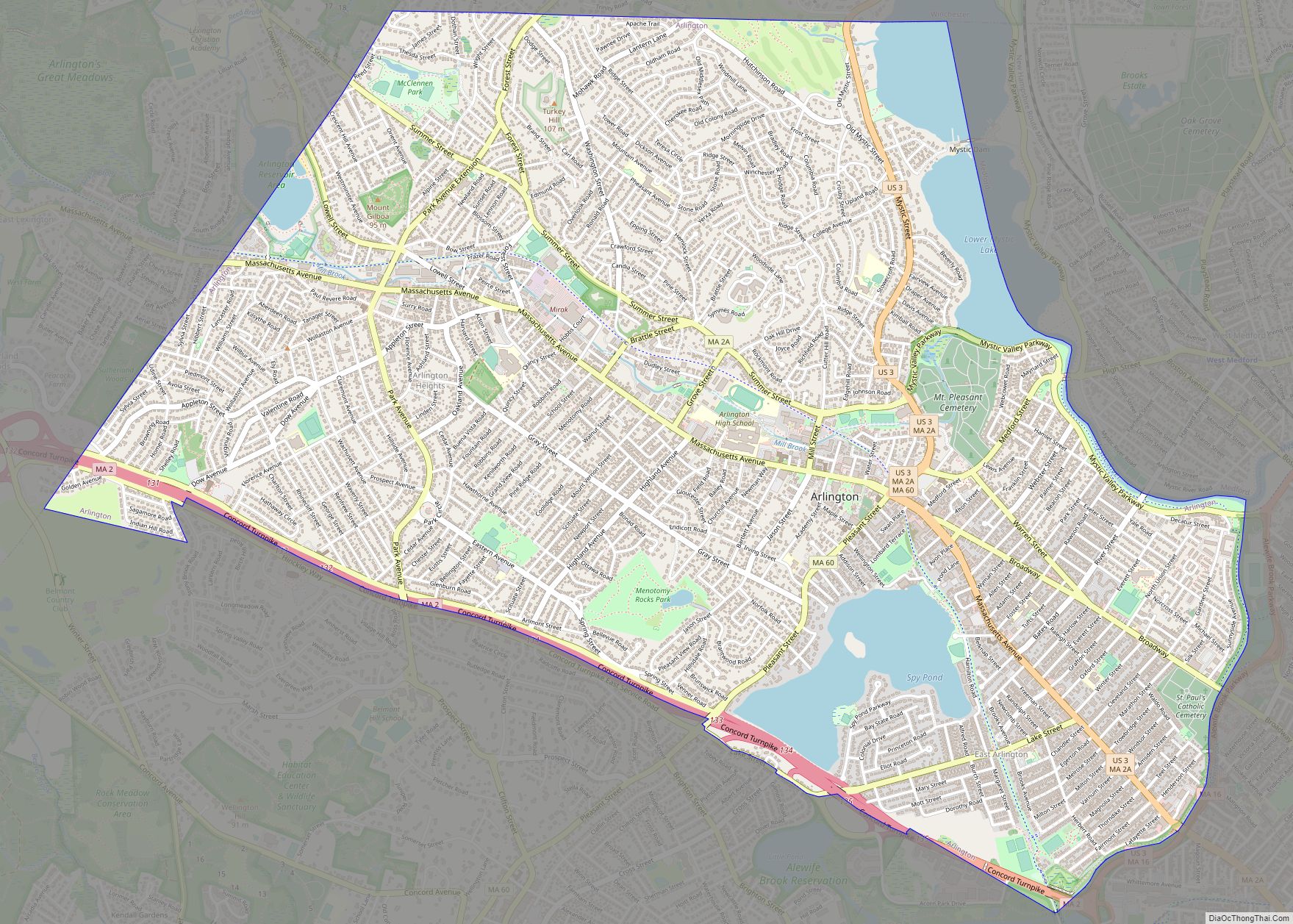
Waltham Road Map
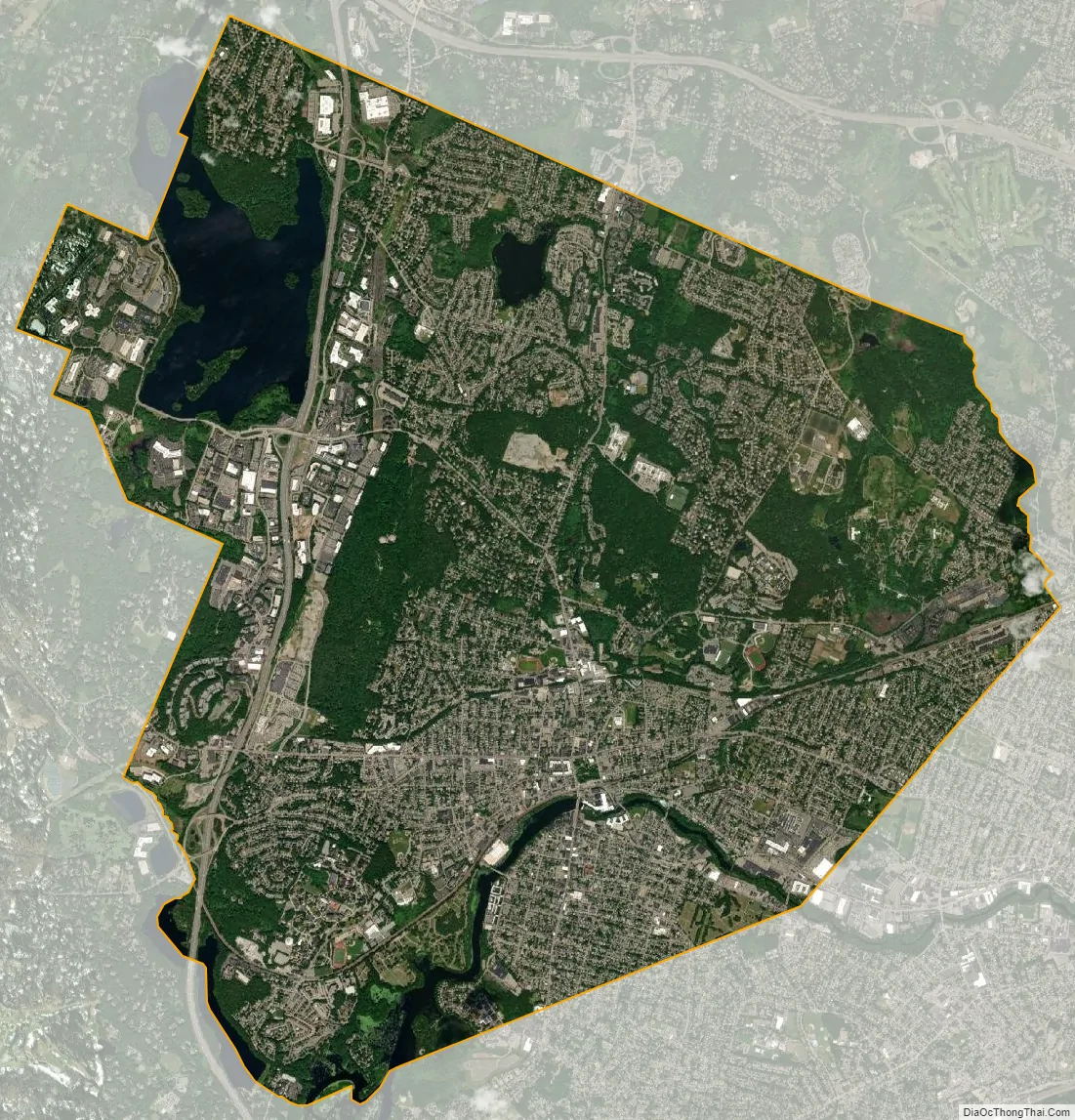
Waltham city Satellite Map
Geography
Waltham is located at 42°22′50″N 71°14′6″W / 42.38056°N 71.23500°W / 42.38056; -71.23500 (42.380596, −71.235005), about 11 miles (18 km) north-west of downtown Boston, Massachusetts, and approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) northwest of Boston’s Brighton neighborhood. The heart of the city is Waltham Common, which is home to the City Hall and various memorial statues. The Common is on Main Street, which is home to several churches, the Waltham Public Library and Post Office.
The city stretches along the Charles River and contains several dams. The dams were used to power textile mills and other endeavors in the early years of the industrial activity.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 13.6 square miles (35 km), of which 12.7 square miles (33 km) is land and 0.9 square miles (2.3 km) (6.69%) is water.
Neighborhoods
Waltham has several neighborhoods or villages, including:
- Angleside
- Banks Square
- The Bleachery (named after the former Waltham Bleachery and Dye Works)
- Cedarwood
- The Chemistry (named after the former Newton Chemical Company)
- Ellison Park
- Gardencrest
- Headyland
- The Highlands
- The Island (formerly Morse Meadow Island)
- Kendal Green (mostly in Weston)
- Kendall Park
- Lakeview
- The Lanes
- Northeast
- The North Side
- Piety Corner
- Prospectville (defunct in 1894, now under Cambridge Reservoir)
- Rangeley Acres
- Ravenswood
- Roberts
- Rock Alley
- The South Side
- Warrendale
- West End
- Wildwood Acres
Adjacent towns
It is bordered to the west by Weston and Lincoln, to the south by Newton, to the east by Belmont and Watertown, and to the north by Lexington.
See also
Map of Massachusetts State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming